-
AuthorSearch Results
-
January 24, 2023 at 11:34 am #6457
In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
“Look, Pretty Girl! That must be the lost traveler walking up those steps!”
Zara followed the mysterious man in red robes up the steps. She lost sight of him and wondered which way he’d gone in the many side alleys. She wandered up a few of them but they all came to a dead end in a courtyard with closed doors. Eventually she saw him disappearing into a manhole that looked like a labyrinth.

Zara followed him, and stepped onto the labyrinth manhole that the man in the red robes had disappeared into.
“That must be another portal,” Zara said to the parrot. “I wonder where we’ll end up now.”
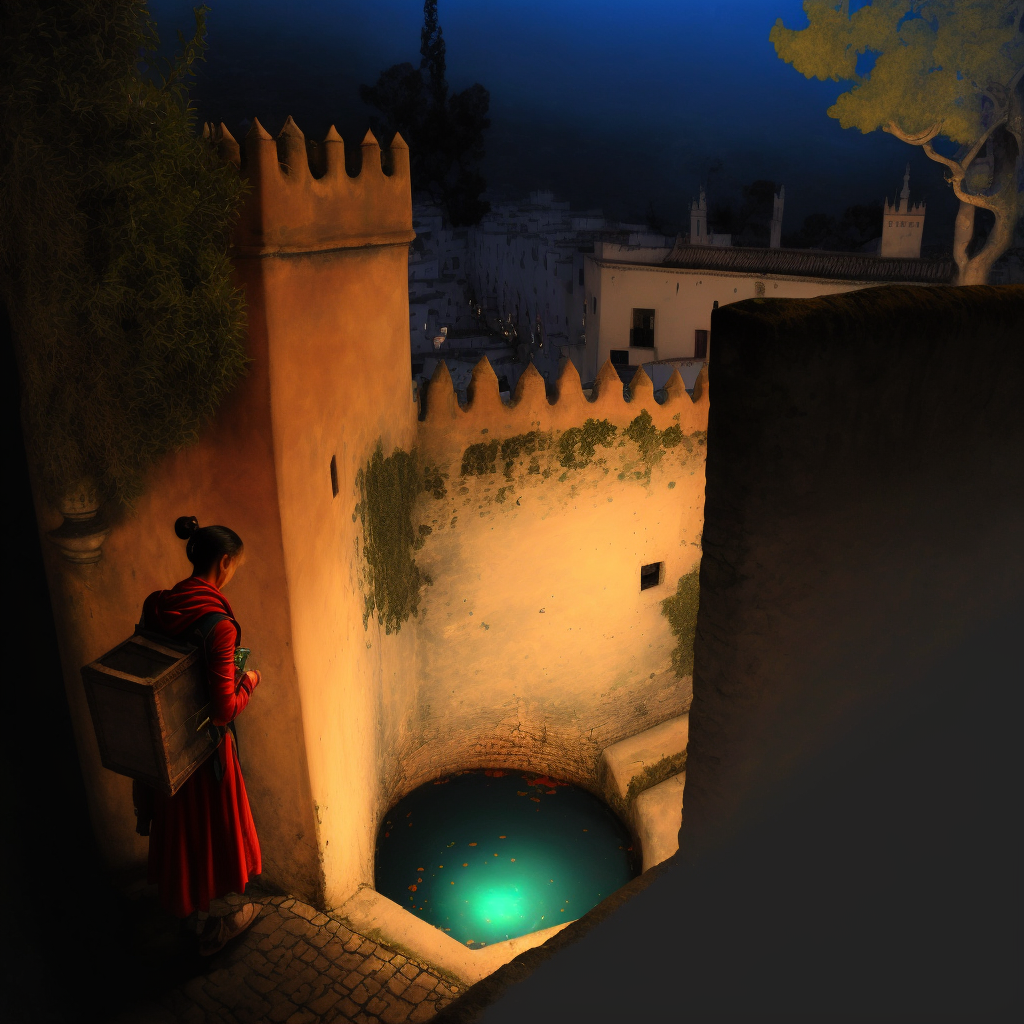
The labyrinth manhole led Zara to another portal, this time a round hole in the wall. She knew she should follow the man, who must be the lost traveler, but she couldn’t resist exploring the starlit night scene first.

She found herself in a castle, its sand coloured walls glowing in the moonlight. There was another round green pool inside the castle. Should she jump into the pool, or go back and follow the man in red through the hole in the wall? Zara walked around the castle first, exploring the many courtyards and stairs and the enchanting views from the parapets. She noticed that there were several green pools and wondered if they each led to different places.
 December 6, 2022 at 2:17 pm #6350
December 6, 2022 at 2:17 pm #6350In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Transportation
Isaac Stokes 1804-1877
Isaac was born in Churchill, Oxfordshire in 1804, and was the youngest brother of my 4X great grandfather Thomas Stokes. The Stokes family were stone masons for generations in Oxfordshire and Gloucestershire, and Isaac’s occupation was a mason’s labourer in 1834 when he was sentenced at the Lent Assizes in Oxford to fourteen years transportation for stealing tools.
Churchill where the Stokes stonemasons came from: on 31 July 1684 a fire destroyed 20 houses and many other buildings, and killed four people. The village was rebuilt higher up the hill, with stone houses instead of the old timber-framed and thatched cottages. The fire was apparently caused by a baker who, to avoid chimney tax, had knocked through the wall from her oven to her neighbour’s chimney.
Isaac stole a pick axe, the value of 2 shillings and the property of Thomas Joyner of Churchill; a kibbeaux and a trowel value 3 shillings the property of Thomas Symms; a hammer and axe value 5 shillings, property of John Keen of Sarsden.
(The word kibbeaux seems to only exists in relation to Isaac Stokes sentence and whoever was the first to write it was perhaps being creative with the spelling of a kibbo, a miners or a metal bucket. This spelling is repeated in the criminal reports and the newspaper articles about Isaac, but nowhere else).
In March 1834 the Removal of Convicts was announced in the Oxford University and City Herald: Isaac Stokes and several other prisoners were removed from the Oxford county gaol to the Justitia hulk at Woolwich “persuant to their sentences of transportation at our Lent Assizes”.
via digitalpanopticon:
Hulks were decommissioned (and often unseaworthy) ships that were moored in rivers and estuaries and refitted to become floating prisons. The outbreak of war in America in 1775 meant that it was no longer possible to transport British convicts there. Transportation as a form of punishment had started in the late seventeenth century, and following the Transportation Act of 1718, some 44,000 British convicts were sent to the American colonies. The end of this punishment presented a major problem for the authorities in London, since in the decade before 1775, two-thirds of convicts at the Old Bailey received a sentence of transportation – on average 283 convicts a year. As a result, London’s prisons quickly filled to overflowing with convicted prisoners who were sentenced to transportation but had no place to go.
To increase London’s prison capacity, in 1776 Parliament passed the “Hulks Act” (16 Geo III, c.43). Although overseen by local justices of the peace, the hulks were to be directly managed and maintained by private contractors. The first contract to run a hulk was awarded to Duncan Campbell, a former transportation contractor. In August 1776, the Justicia, a former transportation ship moored in the River Thames, became the first prison hulk. This ship soon became full and Campbell quickly introduced a number of other hulks in London; by 1778 the fleet of hulks on the Thames held 510 prisoners.
Demand was so great that new hulks were introduced across the country. There were hulks located at Deptford, Chatham, Woolwich, Gosport, Plymouth, Portsmouth, Sheerness and Cork.The Justitia via rmg collections:
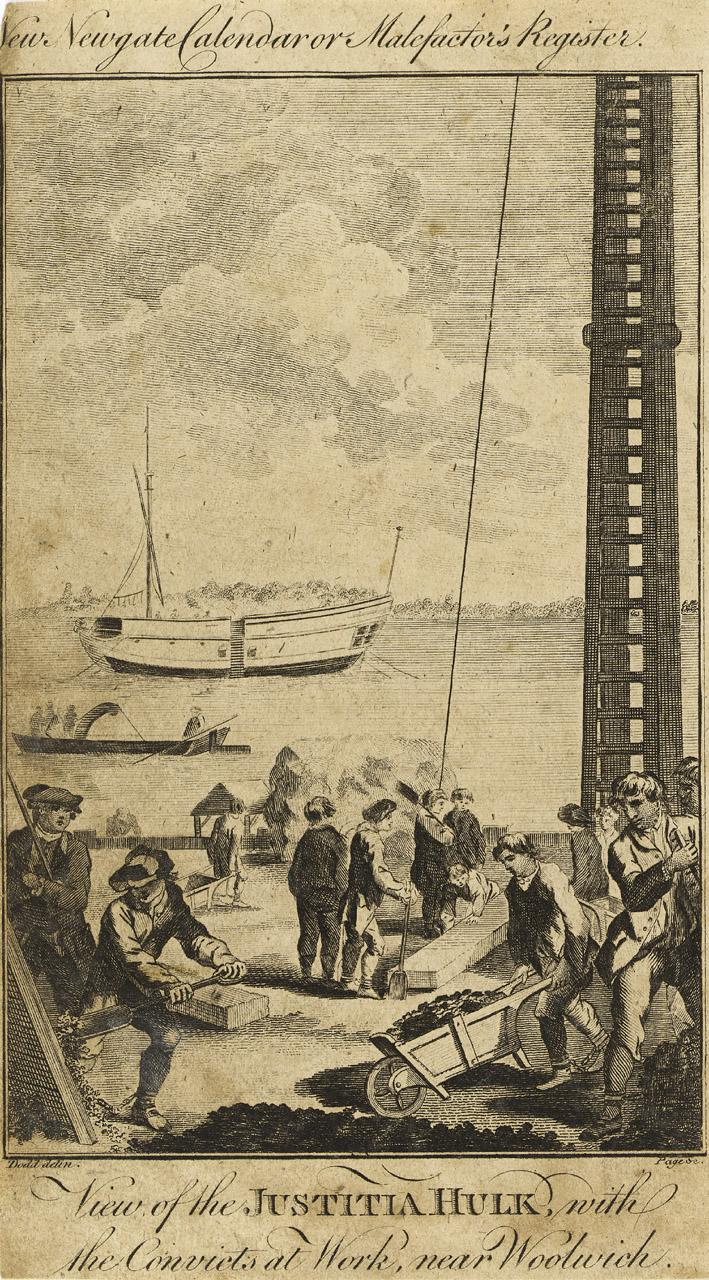

Convicts perform hard labour at the Woolwich Warren. The hulk on the river is the ‘Justitia’. Prisoners were kept on board such ships for months awaiting deportation to Australia. The ‘Justitia’ was a 260 ton prison hulk that had been originally moored in the Thames when the American War of Independence put a stop to the transportation of criminals to the former colonies. The ‘Justitia’ belonged to the shipowner Duncan Campbell, who was the Government contractor who organized the prison-hulk system at that time. Campbell was subsequently involved in the shipping of convicts to the penal colony at Botany Bay (in fact Port Jackson, later Sydney, just to the north) in New South Wales, the ‘first fleet’ going out in 1788.
While searching for records for Isaac Stokes I discovered that another Isaac Stokes was transported to New South Wales in 1835 as well. The other one was a butcher born in 1809, sentenced in London for seven years, and he sailed on the Mary Ann. Our Isaac Stokes sailed on the Lady Nugent, arriving in NSW in April 1835, having set sail from England in December 1834.
Lady Nugent was built at Bombay in 1813. She made four voyages under contract to the British East India Company (EIC). She then made two voyages transporting convicts to Australia, one to New South Wales and one to Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania). (via Wikipedia)
via freesettlerorfelon website:
On 20 November 1834, 100 male convicts were transferred to the Lady Nugent from the Justitia Hulk and 60 from the Ganymede Hulk at Woolwich, all in apparent good health. The Lady Nugent departed Sheerness on 4 December 1834.
SURGEON OLIVER SPROULE
Oliver Sproule kept a Medical Journal from 7 November 1834 to 27 April 1835. He recorded in his journal the weather conditions they experienced in the first two weeks:
‘In the course of the first week or ten days at sea, there were eight or nine on the sick list with catarrhal affections and one with dropsy which I attribute to the cold and wet we experienced during that period beating down channel. Indeed the foremost berths in the prison at this time were so wet from leaking in that part of the ship, that I was obliged to issue dry beds and bedding to a great many of the prisoners to preserve their health, but after crossing the Bay of Biscay the weather became fine and we got the damp beds and blankets dried, the leaks partially stopped and the prison well aired and ventilated which, I am happy to say soon manifested a favourable change in the health and appearance of the men.
Besides the cases given in the journal I had a great many others to treat, some of them similar to those mentioned but the greater part consisted of boils, scalds, and contusions which would not only be too tedious to enter but I fear would be irksome to the reader. There were four births on board during the passage which did well, therefore I did not consider it necessary to give a detailed account of them in my journal the more especially as they were all favourable cases.
Regularity and cleanliness in the prison, free ventilation and as far as possible dry decks turning all the prisoners up in fine weather as we were lucky enough to have two musicians amongst the convicts, dancing was tolerated every afternoon, strict attention to personal cleanliness and also to the cooking of their victuals with regular hours for their meals, were the only prophylactic means used on this occasion, which I found to answer my expectations to the utmost extent in as much as there was not a single case of contagious or infectious nature during the whole passage with the exception of a few cases of psora which soon yielded to the usual treatment. A few cases of scurvy however appeared on board at rather an early period which I can attribute to nothing else but the wet and hardships the prisoners endured during the first three or four weeks of the passage. I was prompt in my treatment of these cases and they got well, but before we arrived at Sydney I had about thirty others to treat.’
The Lady Nugent arrived in Port Jackson on 9 April 1835 with 284 male prisoners. Two men had died at sea. The prisoners were landed on 27th April 1835 and marched to Hyde Park Barracks prior to being assigned. Ten were under the age of 14 years.
The Lady Nugent:
Isaac’s distinguishing marks are noted on various criminal registers and record books:
“Height in feet & inches: 5 4; Complexion: Ruddy; Hair: Light brown; Eyes: Hazel; Marks or Scars: Yes [including] DEVIL on lower left arm, TSIS back of left hand, WS lower right arm, MHDW back of right hand.”
Another includes more detail about Isaac’s tattoos:
“Two slight scars right side of mouth, 2 moles above right breast, figure of the devil and DEVIL and raised mole, lower left arm; anchor, seven dots half moon, TSIS and cross, back of left hand; a mallet, door post, A, mans bust, sun, WS, lower right arm; woman, MHDW and shut knife, back of right hand.”

From How tattoos became fashionable in Victorian England (2019 article in TheConversation by Robert Shoemaker and Zoe Alkar):
“Historical tattooing was not restricted to sailors, soldiers and convicts, but was a growing and accepted phenomenon in Victorian England. Tattoos provide an important window into the lives of those who typically left no written records of their own. As a form of “history from below”, they give us a fleeting but intriguing understanding of the identities and emotions of ordinary people in the past.
As a practice for which typically the only record is the body itself, few systematic records survive before the advent of photography. One exception to this is the written descriptions of tattoos (and even the occasional sketch) that were kept of institutionalised people forced to submit to the recording of information about their bodies as a means of identifying them. This particularly applies to three groups – criminal convicts, soldiers and sailors. Of these, the convict records are the most voluminous and systematic.
Such records were first kept in large numbers for those who were transported to Australia from 1788 (since Australia was then an open prison) as the authorities needed some means of keeping track of them.”On the 1837 census Isaac was working for the government at Illiwarra, New South Wales. This record states that he arrived on the Lady Nugent in 1835. There are three other indent records for an Isaac Stokes in the following years, but the transcriptions don’t provide enough information to determine which Isaac Stokes it was. In April 1837 there was an abscondment, and an arrest/apprehension in May of that year, and in 1843 there was a record of convict indulgences.
From the Australian government website regarding “convict indulgences”:
“By the mid-1830s only six per cent of convicts were locked up. The vast majority worked for the government or free settlers and, with good behaviour, could earn a ticket of leave, conditional pardon or and even an absolute pardon. While under such orders convicts could earn their own living.”
In 1856 in Camden, NSW, Isaac Stokes married Catherine Daly. With no further information on this record it would be impossible to know for sure if this was the right Isaac Stokes. This couple had six children, all in the Camden area, but none of the records provided enough information. No occupation or place or date of birth recorded for Isaac Stokes.
I wrote to the National Library of Australia about the marriage record, and their reply was a surprise! Issac and Catherine were married on 30 September 1856, at the house of the Rev. Charles William Rigg, a Methodist minister, and it was recorded that Isaac was born in Edinburgh in 1821, to parents James Stokes and Sarah Ellis! The age at the time of the marriage doesn’t match Isaac’s age at death in 1877, and clearly the place of birth and parents didn’t match either. Only his fathers occupation of stone mason was correct. I wrote back to the helpful people at the library and they replied that the register was in a very poor condition and that only two and a half entries had survived at all, and that Isaac and Catherines marriage was recorded over two pages.
I searched for an Isaac Stokes born in 1821 in Edinburgh on the Scotland government website (and on all the other genealogy records sites) and didn’t find it. In fact Stokes was a very uncommon name in Scotland at the time. I also searched Australian immigration and other records for another Isaac Stokes born in Scotland or born in 1821, and found nothing. I was unable to find a single record to corroborate this mysterious other Isaac Stokes.
As the age at death in 1877 was correct, I assume that either Isaac was lying, or that some mistake was made either on the register at the home of the Methodist minster, or a subsequent mistranscription or muddle on the remnants of the surviving register. Therefore I remain convinced that the Camden stonemason Isaac Stokes was indeed our Isaac from Oxfordshire.
I found a history society newsletter article that mentioned Isaac Stokes, stone mason, had built the Glenmore church, near Camden, in 1859.
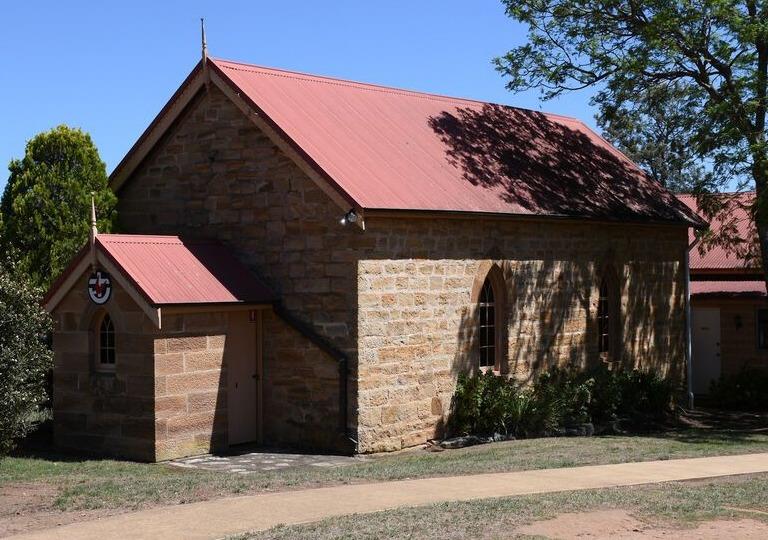

From the Wollondilly museum April 2020 newsletter:

From the Camden History website:
“The stone set over the porch of Glenmore Church gives the date of 1860. The church was begun in 1859 on land given by Joseph Moore. James Rogers of Picton was given the contract to build and local builder, Mr. Stokes, carried out the work. Elizabeth Moore, wife of Edward, laid the foundation stone. The first service was held on 19th March 1860. The cemetery alongside the church contains the headstones and memorials of the areas early pioneers.”
Isaac died on the 3rd September 1877. The inquest report puts his place of death as Bagdelly, near to Camden, and another death register has put Cambelltown, also very close to Camden. His age was recorded as 71 and the inquest report states his cause of death was “rupture of one of the large pulmonary vessels of the lung”. His wife Catherine died in childbirth in 1870 at the age of 43.
Isaac and Catherine’s children:
William Stokes 1857-1928
Catherine Stokes 1859-1846
Sarah Josephine Stokes 1861-1931
Ellen Stokes 1863-1932
Rosanna Stokes 1865-1919
Louisa Stokes 1868-1844.
It’s possible that Catherine Daly was a transported convict from Ireland.
Some time later I unexpectedly received a follow up email from The Oaks Heritage Centre in Australia.
“The Gaudry papers which we have in our archive record him (Isaac Stokes) as having built: the church, the school and the teachers residence. Isaac is recorded in the General return of convicts: 1837 and in Grevilles Post Office directory 1872 as a mason in Glenmore.”
 November 13, 2022 at 10:29 pm #6345
November 13, 2022 at 10:29 pm #6345In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Crime and Punishment in Tetbury
I noticed that there were quite a number of Brownings of Tetbury in the newspaper archives involved in criminal activities while doing a routine newspaper search to supplement the information in the usual ancestry records. I expanded the tree to include cousins, and offsping of cousins, in order to work out who was who and how, if at all, these individuals related to our Browning family.
I was expecting to find some of our Brownings involved in the Swing Riots in Tetbury in 1830, but did not. Most of our Brownings (including cousins) were stone masons. Most of the rioters in 1830 were agricultural labourers.
The Browning crimes are varied, and by todays standards, not for the most part terribly serious ~ you would be unlikely to receive a sentence of hard labour for being found in an outhouse with the intent to commit an unlawful act nowadays, or for being drunk.
The central character in this chapter is Isaac Browning (my 4x great grandfather), who did not appear in any criminal registers, but the following individuals can be identified in the family structure through their relationship to him.
RICHARD LOCK BROWNING born in 1853 was Isaac’s grandson, his son George’s son. Richard was a mason. In 1879 he and Henry Browning of the same age were sentenced to one month hard labour for stealing two pigeons in Tetbury. Henry Browning was Isaac’s nephews son.
In 1883 Richard Browning, mason of Tetbury, was charged with obtaining food and lodging under false pretences, but was found not guilty and acquitted.
In 1884 Richard Browning, mason of Tetbury, was sentenced to one month hard labour for game trespass.Richard had been fined a number of times in Tetbury:

Richard Lock Browning was five feet eight inches tall, dark hair, grey eyes, an oval face and a dark complexion. He had two cuts on the back of his head (in February 1879) and a scar on his right eyebrow.
HENRY BROWNING, who was stealing pigeons with Richard Lock Browning in 1879, (Isaac’s brother Williams grandson, son of George Browning and his wife Charity) was charged with being drunk in 1882 and ordered to pay a fine of one shilling and costs of fourteen shillings, or seven days hard labour.
Henry was found guilty of gaming in the highway at Tetbury in 1872 and was sentenced to seven days hard labour. In 1882 Henry (who was also a mason) was charged with assault but discharged.
Henry was five feet five inches tall, brown hair and brown eyes, a long visage and a fresh complexion.
Henry emigrated with his daughter to Canada in 1913, and died in Vancouver in 1919.THOMAS BUCKINGHAM 1808-1846 (Isaacs daughter Janes husband) was charged with stealing a black gelding in Tetbury in 1838. No true bill. (A “no true bill” means the jury did not find probable cause to continue a case.)
Thomas did however neglect to pay his taxes in 1832:

LEWIN BUCKINGHAM (grandson of Isaac, his daughter Jane’s son) was found guilty in 1846 stealing two fowls in Tetbury when he was sixteen years old.
In 1846 he was sentence to one month hard labour (or pay ten shillings fine and ten shillings costs) for loitering with the intent to trespass in search of conies.
A year later in 1847, he and three other young men were sentenced to four months hard labour for larceny.
Lewin was five feet three inches tall, with brown hair and brown eyes, long visage, sallow complexion, and had a scar on his left arm.JOHN BUCKINGHAM born circa 1832, a Tetbury labourer (Isaac’s grandson, Lewin’s brother) was sentenced to six weeks hard labour for larceny in 1855 for stealing a duck in Cirencester. The notes on the register mention that he had been employed by Mr LOCK, Angel Inn. (John’s grandmother was Mary Lock so this is likely a relative).
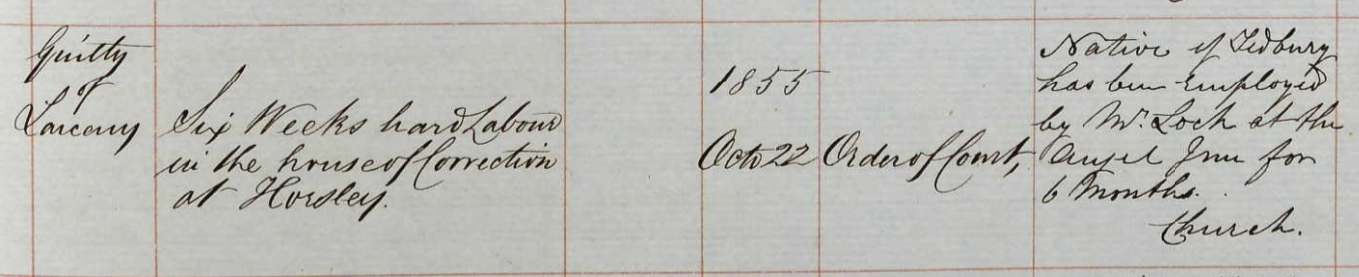
The previous year in 1854 John was sentenced to one month or a one pound fine for assaulting and beating W. Wood.
John was five feet eight and three quarter inches tall, light brown hair and grey eyes, an oval visage and a fresh complexion. He had a scar on his left arm and inside his right knee.JOSEPH PERRET was born circa 1831 and he was a Tetbury labourer. (He was Isaac’s granddaughter Charlotte Buckingham’s husband)
In 1855 he assaulted William Wood and was sentenced to one month or a two pound ten shilling fine. Was it the same W Wood that his wifes cousin John assaulted the year before?
In 1869 Joseph was sentenced to one month hard labour for feloniously receiving a cupboard known to be stolen.JAMES BUCKINGAM born circa 1822 in Tetbury was a shoemaker. (Isaac’s nephew, his sister Hannah’s son)
In 1854 the Tetbury shoemaker was sentenced to four months hard labour for stealing 30 lbs of lead off someones house.
In 1856 the Tetbury shoemaker received two months hard labour or pay £2 fine and 12 s costs for being found in pursuit of game.
In 1868 he was sentenced to two months hard labour for stealing a gander. A unspecified previous conviction is noted.
1871 the Tetbury shoemaker was found in an outhouse for an unlawful purpose and received ten days hard labour. The register notes that his sister is Mrs Cook, the Green, Tetbury. (James sister Prudence married Thomas Cook)
James sister Charlotte married a shoemaker and moved to UTAH.
James was five feet eight inches tall, dark hair and blue eyes, a long visage and a florid complexion. He had a scar on his forehead and a mole on the right side of his neck and abdomen, and a scar on the right knee.October 23, 2022 at 6:57 am #6340In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Wheelwrights of Broadway
Thomas Stokes 1816-1885
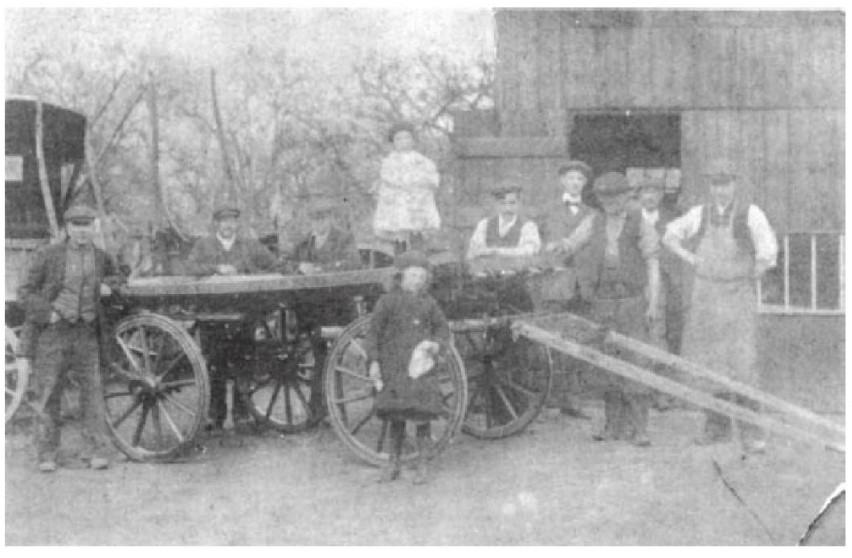
Frederick Stokes 1845-1917

Stokes Wheelwrights. Fred on left of wheel, Thomas his father on right.
Thomas Stokes
Thomas Stokes was born in Bicester, Oxfordshire in 1816. He married Eliza Browning (born in 1814 in Tetbury, Gloucestershire) in Gloucester in 1840 Q3. Their first son William was baptised in Chipping Hill, Witham, Essex, on 3 Oct 1841. This seems a little unusual, and I can’t find Thomas and Eliza on the 1841 census. However both the 1851 and 1861 census state that William was indeed born in Essex.
In 1851 Thomas and Eliza were living in Bledington, Gloucestershire, and Thomas was a journeyman carpenter.
Note that a journeyman does not mean someone who moved around a lot. A journeyman was a tradesman who had served his trade apprenticeship and mastered his craft, not bound to serve a master, but originally hired by the day. The name derives from the French for day – jour.
Also on the 1851 census: their daughter Susan, born in Churchill Oxfordshire in 1844; son Frederick born in Bledington Gloucestershire in 1846; daughter Louisa born in Foxcote Oxfordshire in 1849; and 2 month old daughter Harriet born in Bledington in 1851.
On the 1861 census Thomas and Eliza were living in Evesham, Worcestershire, and daughter Susan was no longer living at home, but William, Fred, Louisa and Harriet were, as well as daughter Emily born in Churchill Oxfordshire in 1856. Thomas was a wheelwright.
On the 1871 census Thomas and Eliza were still living in Evesham, and Thomas was a wheelwright employing three apprentices. Son Fred, also a wheelwright, and his wife Ann Rebecca live with them.
Mr Stokes, wheelwright, was found guilty of reprehensible conduct in concealing the fact that small-pox existed in his house, according to a mention in The Oxfordshire Weekly News on Wednesday 19 February 1873:

From Paul Weaver’s ancestry website:
“It was Thomas Stokes who built the first “Famous Vale of Evesham Light Gardening Dray for a Half-Legged Horse to Trot” (the quotation is from his account book), the forerunner of many that became so familiar a sight in the towns and villages from the 1860s onwards. He built many more for the use of the Vale gardeners.
Thomas also had long-standing business dealings with the people of the circus and fairgrounds, and had a contract to effect necessary repairs and renewals to their waggons whenever they visited the district. He built living waggons for many of the show people’s families as well as shooting galleries and other equipment peculiar to the trade of his wandering customers, and among the names figuring in his books are some still familiar today, such as Wilsons and Chipperfields.
He is also credited with inventing the wooden “Mushroom” which was used by housewives for many years to darn socks. He built and repaired all kinds of vehicles for the gentry as well as for the circus and fairground travellers.
Later he lived with his wife at Merstow Green, Evesham, in a house adjoining the Almonry.”
An excerpt from the book Evesham Inns and Signs by T.J.S. Baylis:

The Old Red Horse, Evesham:
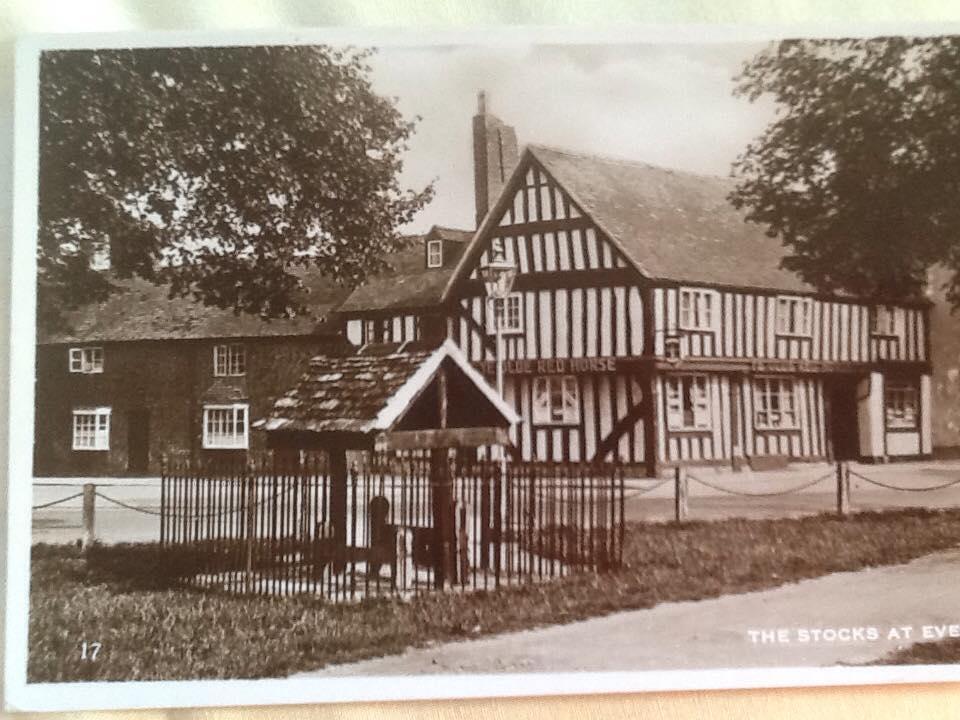

Thomas died in 1885 aged 68 of paralysis, bronchitis and debility. His wife Eliza a year later in 1886.
Frederick Stokes
In Worcester in 1870 Fred married Ann Rebecca Day, who was born in Evesham in 1845.
Ann Rebecca Day:
In 1871 Fred was still living with his parents in Evesham, with his wife Ann Rebecca as well as their three month old daughter Annie Elizabeth. Fred and Ann (referred to as Rebecca) moved to La Quinta on Main Street, Broadway.
Rebecca Stokes in the doorway of La Quinta on Main Street Broadway, with her grandchildren Ralph and Dolly Edwards:
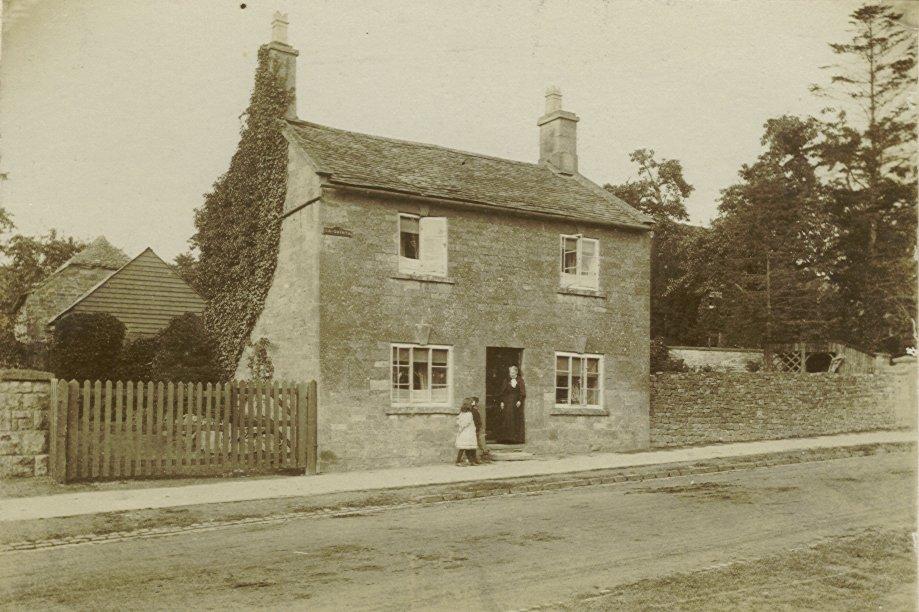

Fred was a wheelwright employing one man on the 1881 census. In 1891 they were still in Broadway, Fred’s occupation was wheelwright and coach painter, as well as his fifteen year old son Frederick.
In the Evesham Journal on Saturday 10 December 1892 it was reported that “Two cases of scarlet fever, the children of Mr. Stokes, wheelwright, Broadway, were certified by Mr. C. W. Morris to be isolated.”
Still in Broadway in 1901 and Fred’s son Albert was also a wheelwright. By 1911 Fred and Rebecca had only one son living at home in Broadway, Reginald, who was a coach painter. Fred was still a wheelwright aged 65.
Fred’s signature on the 1911 census:

Rebecca died in 1912 and Fred in 1917.
Fred Stokes:

In the book Evesham to Bredon From Old Photographs By Fred Archer:
 February 5, 2022 at 1:59 pm #6272
February 5, 2022 at 1:59 pm #6272In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
The Housley Letters
The Carringtons
Carrington Farm, Smalley:
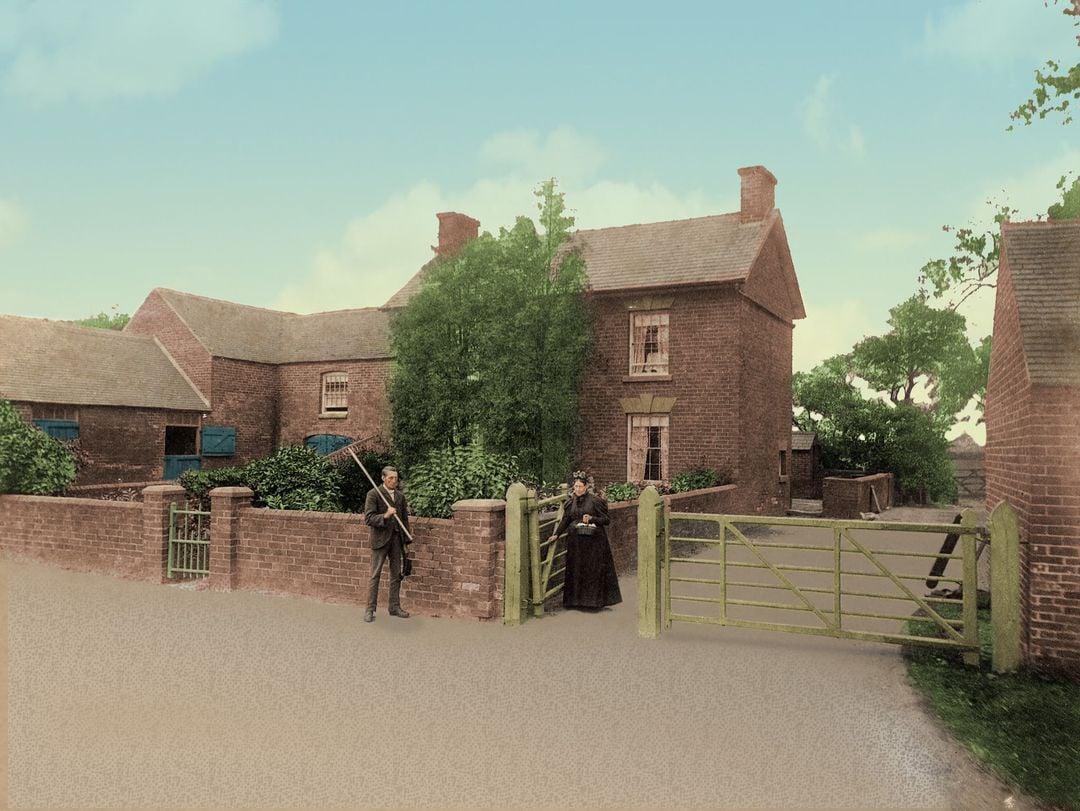

Ellen Carrington was born in 1795. Her father William Carrington 1755-1833 was from Smalley. Her mother Mary Malkin 1765-1838 was from Ellastone, in Staffordshire. Ellastone is on the Derbyshire border and very close to Ashboure, where Ellen married William Housley.
From Barbara Housley’s Narrative on the Letters:
Ellen’s family was evidently rather prominant in Smalley. Two Carringtons (John and William) served on the Parish Council in 1794. Parish records are full of Carrington marriages and christenings.
The letters refer to a variety of “uncles” who were probably Ellen’s brothers, but could be her uncles. These include:
RICHARD
Probably the youngest Uncle, and certainly the most significant, is Richard. He was a trustee for some of the property which needed to be settled following Ellen’s death. Anne wrote in 1854 that Uncle Richard “has got a new house built” and his daughters are “fine dashing young ladies–the belles of Smalley.” Then she added, “Aunt looks as old as my mother.”
Richard was born somewhere between 1808 and 1812. Since Richard was a contemporary of the older Housley children, “Aunt,” who was three years younger, should not look so old!
Richard Carrington and Harriet Faulkner were married in Repton in 1833. A daughter Elizabeth was baptised March 24, 1834. In July 1872, Joseph wrote: “Elizabeth is married too and a large family and is living in Uncle Thomas’s house for he is dead.” Elizabeth married Ayres (Eyres) Clayton of Lascoe. His occupation was listed as joiner and shopkeeper. They were married before 1864 since Elizabeth Clayton witnessed her sister’s marriage. Their children in April 1871 were Selina (1863), Agnes Maria (1866) and Elizabeth Ann (1868). A fourth daughter, Alice Augusta, was born in 1872 or 1873, probably by July 1872 to fit Joseph’s description “large family”! A son Charles Richard was born in 1880.
An Elizabeth Ann Clayton married John Arthur Woodhouse on May 12, 1913. He was a carpenter. His father was a miner. Elizabeth Ann’s father, Ayres, was also a carpenter. John Arthur’s age was given as 25. Elizabeth Ann’s age was given as 33 or 38. However, if she was born in 1868, her age would be 45. Possibly this is another case of a child being named for a deceased sibling. If she were 38 and born in 1875, she would fill the gap between Alice Augusta and Charles Richard.
Selina Clayton, who would have been 18, is not listed in the household in 1881. She died on June 11, 1914 at age 51. Agnes Maria Clayton died at the age of 25 and was buried March 31, 1891. Charles Richard died at the age of 5 and was buried on February 4, 1886. A Charles James Clayton, 18 months, was buried June 8, 1889 in Heanor.
Richard Carrington’s second daughter, Selina, born in 1837, married Walker Martin (b.1835) on February 11, 1864 and they were living at Kidsley Park Farm in 1872, according to a letter from Joseph, and, according to the census, were still there in 1881. This 100 acre farm was formerly the home of Daniel Smith and his daughter Elizabeth Davy Barber. Selina and Walker had at least five children: Elizabeth Ann (1865), Harriet Georgianna (1866/7), Alice Marian (September 6, 1868), Philip Richard (1870), and Walker (1873). In December 1972, Joseph mentioned the death of Philip Walker, a farmer of Prospect Farm, Shipley. This was probably Walker Martin’s grandfather, since Walker was born in Shipley. The stock was to be sold the following Monday, but his daughter (Walker’s mother?) died the next day. Walker’s father was named Thomas. An Annie Georgianna Martin age 13 of Shipley died in April of 1859.
Selina Martin died on October 29, 1906 but her estate was not settled until November 14, 1910. Her gross estate was worth L223.56. Her son Walker and her daughter Harriet Georgiana were her trustees and executers. Walker was to get Selina’s half of Richard’s farm. Harriet Georgiana and Alice Marian were to be allowed to live with him. Philip Richard received L25. Elizabeth Ann was already married to someone named Smith.
Richard and Harriet may also have had a son George. In 1851 a Harriet Carrington and her three year old son George were living with her step-father John Benniston in Heanor. John may have been recently widowed and needed her help. Or, the Carrington home may have been inadequate since Anne reported a new one was built by 1854. Selina’s second daughter’s name testifies to the presence of a “George” in the family! Could the death of this son account for the haggard appearance Anne described when she wrote: “Aunt looks as old as my mother?”
Harriet was buried May 19, 1866. She was 55 when she died.In 1881, Georgianna then 14, was living with her grandfather and his niece, Zilpah Cooper, age 38–who lived with Richard on his 63 acre farm as early as 1871. A Zilpah, daughter of William and Elizabeth, was christened October 1843. Her brother, William Walter, was christened in 1846 and married Anna Maria Saint in 1873. There are four Selina Coopers–one had a son William Thomas Bartrun Cooper christened in 1864; another had a son William Cooper christened in 1873.
Our Zilpah was born in Bretley 1843. She died at age 49 and was buried on September 24, 1892. In her will, which was witnessed by Selina Martin, Zilpah’s sister, Frances Elizabeth Cleave, wife of Horatio Cleave of Leicester is mentioned. James Eley and Francis Darwin Huish (Richard’s soliciter) were executers.
Richard died June 10, 1892, and was buried on June 13. He was 85. As might be expected, Richard’s will was complicated. Harriet Georgiana Martin and Zilpah Cooper were to share his farm. If neither wanted to live there it was to go to Georgiana’s cousin Selina Clayton. However, Zilpah died soon after Richard. Originally, he left his piano, parlor and best bedroom furniture to his daughter Elizabeth Clayton. Then he revoked everything but the piano. He arranged for the payment of £150 which he owed. Later he added a codicil explaining that the debt was paid but he had borrowed £200 from someone else to do it!
Richard left a good deal of property including: The house and garden in Smalley occupied by Eyres Clayton with four messuages and gardens adjoining and large garden below and three messuages at the south end of the row with the frame work knitters shop and garden adjoining; a dwelling house used as a public house with a close of land; a small cottage and garden and four cottages and shop and gardens.
THOMAS
In August 1854, Anne wrote “Uncle Thomas is about as usual.” A Thomas Carrington married a Priscilla Walker in 1810.
Their children were baptised in August 1830 at the same time as the Housley children who at that time ranged in age from 3 to 17. The oldest of Thomas and Priscilla’s children, Henry, was probably at least 17 as he was married by 1836. Their youngest son, William Thomas, born 1830, may have been Mary Ellen Weston’s beau. However, the only Richard whose christening is recorded (1820), was the son of Thomas and Lucy. In 1872 Joseph reported that Richard’s daughter Elizabeth was married and living in Uncle Thomas’s house. In 1851, Alfred Smith lived in house 25, Foulks lived in 26, Thomas and Priscilla lived in 27, Bennetts lived in 28, Allard lived in 29 and Day lived in 30. Thomas and Priscilla do not appear in 1861. In 1871 Elizabeth Ann and Ayres Clayton lived in House 54. None of the families listed as neighbors in 1851 remained. However, Joseph Carrington, who lived in house 19 in 1851, lived in house 51 in 1871.
JOHN
In August 1854, Anne wrote: “Uncle John is with Will and Frank has been home in a comfortable place in Cotmanhay.” Although John and William are two of the most popular Carrington names, only two John’s have sons named William. John and Rachel Buxton Carrington had a son William christened in 1788. At the time of the letters this John would have been over 100 years old. Their son John and his wife Ann had a son William who was born in 1805. However, this William age 46 was living with his widowed mother in 1851. A Robert Carrington and his wife Ann had a son John born 1n 1805. He would be the right age to be a brother to Francis Carrington discussed below. This John was living with his widowed mother in 1851 and was unmarried. There are no known Williams in this family grouping. A William Carrington of undiscovered parentage was born in 1821. It is also possible that the Will in question was Anne’s brother Will Housley.
–Two Francis Carringtons appear in the 1841 census both of them aged 35. One is living with Richard and Harriet Carrington. The other is living next door to Samuel and Ellen Carrington Kerry (the trustee for “father’s will”!). The next name in this sequence is John Carrington age 15 who does not seem to live with anyone! but may be part of the Kerry household.
FRANK (see above)
While Anne did not preface her mention of the name Frank with an “Uncle,” Joseph referred to Uncle Frank and James Carrington in the same sentence. A James Carrington was born in 1814 and had a wife Sarah. He worked as a framework knitter. James may have been a son of William and Anne Carrington. He lived near Richard according to the 1861 census. Other children of William and Anne are Hannah (1811), William (1815), John (1816), and Ann (1818). An Ann Carrington married a Frank Buxton in 1819. This might be “Uncle Frank.”
An Ellen Carrington was born to John and Rachel Carrington in 1785. On October 25, 1809, a Samuel Kerry married an Ellen Carrington. However this Samuel Kerry is not the trustee involved in settling Ellen’s estate. John Carrington died July 1815.
William and Mary Carrington:
 December 15, 2021 at 9:34 am #6236
December 15, 2021 at 9:34 am #6236In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
The Liverpool Fires
Catherine Housley had two older sisters, Elizabeth 1845-1883 and Mary Anne 1846-1935. Both Elizabeth and Mary Anne grew up in the Belper workhouse after their mother died, and their father was jailed for failing to maintain his three children. Mary Anne married Samuel Gilman and they had a grocers shop in Buxton. Elizabeth married in Liverpool in 1873.
What was she doing in Liverpool? How did she meet William George Stafford?
According to the census, Elizabeth Housley was in Belper workhouse in 1851. In 1861, aged 16, she was a servant in the household of Peter Lyon, a baker in Derby St Peters. We noticed that the Lyon’s were friends of the family and were mentioned in the letters to George in Pennsylvania.
No record of Elizabeth can be found on the 1871 census, but in 1872 the birth and death was registered of Elizabeth and William’s child, Elizabeth Jane Stafford. The parents are registered as William and Elizabeth Stafford, although they were not yet married. William’s occupation is a “refiner”.
In April, 1873, a Fatal Fire is reported in the Liverpool Mercury. Fearful Termination of a Saturday Night Debauch. Seven Persons Burnt To Death. Interesting to note in the article that “the middle room being let off to a coloured man named William Stafford and his wife”.

We had noted on the census that William Stafford place of birth was “Africa, British subject” but it had not occurred to us that he was “coloured”. A register of birth has not yet been found for William and it is not known where in Africa he was born.

Elizabeth and William survived the fire on Gay Street, and were still living on Gay Street in October 1873 when they got married.
William’s occupation on the marriage register is sugar refiner, and his father is Peter Stafford, farmer. Elizabeth’s father is Samuel Housley, plumber. It does not say Samuel Housley deceased, so perhaps we can assume that Samuel is still alive in 1873.
Eliza Florence Stafford, their second daughter, was born in 1876.
William’s occupation on the 1881 census is “fireman”, in his case, a fire stoker at the sugar refinery, an unpleasant and dangerous job for which they were paid slightly more. William, Elizabeth and Eliza were living in Byrom Terrace.
Byrom Terrace, Liverpool, in 1933
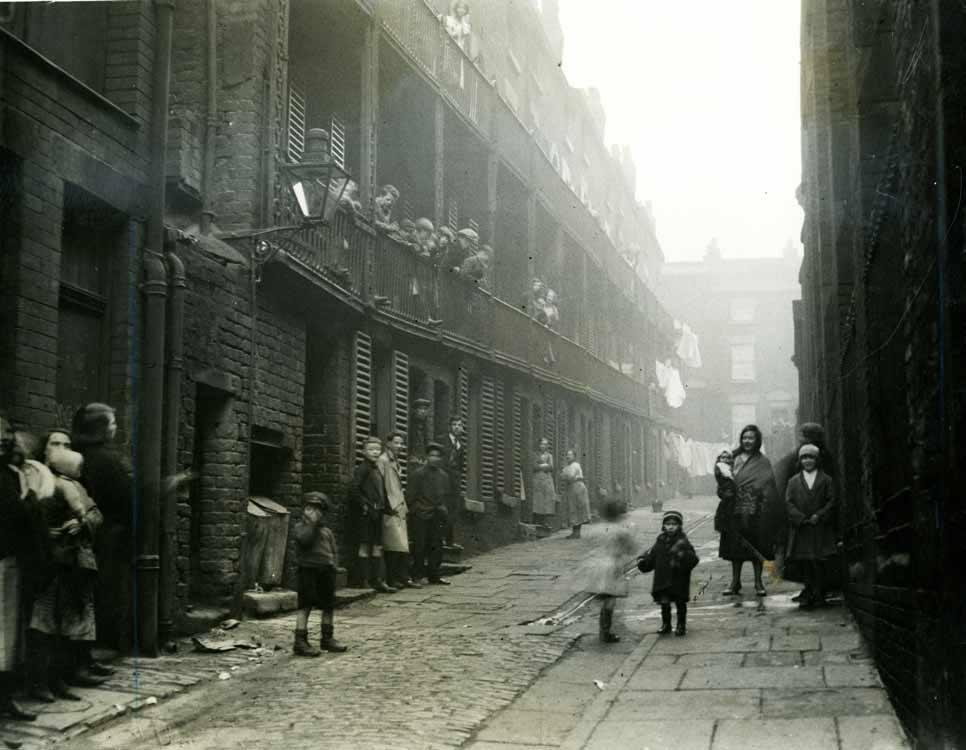

Elizabeth died of heart problems in 1883, when Eliza was six years old, and in 1891 her father died, scalded to death in a tragic accident at the sugar refinery.

Eliza, aged 15, was living as an inmate at the Walton on the Hill Institution in 1891. It’s not clear when she was admitted to the workhouse, perhaps after her mother died in 1883.
In 1901 Eliza Florence Stafford is a 24 year old live in laundrymaid, according to the census, living in West Derby (a part of Liverpool, and not actually in Derby). On the 1911 census there is a Florence Stafford listed as an unnmarried laundress, with a daughter called Florence. In 1901 census she was a laundrymaid in West Derby, Liverpool, and the daughter Florence Stafford was born in 1904 West Derby. It’s likely that this is Eliza Florence, but nothing further has been found so far.
The questions remaining are the location of William’s birth, the name of his mother and his family background, what happened to Eliza and her daughter after 1911, and how did Elizabeth meet William in the first place.
William Stafford was a seaman prior to working in the sugar refinery, and he appears on several ship’s crew lists. Nothing so far has indicated where he might have been born, or where his father came from.
Some months after finding the newspaper article about the fire on Gay Street, I saw an unusual request for information on the Liverpool genealogy group. Someone asked if anyone knew of a fire in Liverpool in the 1870’s. She had watched a programme about children recalling past lives, in this case a memory of a fire. The child recalled pushing her sister into a burning straw mattress by accident, as she attempted to save her from a falling beam. I watched the episode in question hoping for more information to confirm if this was the same fire, but details were scant and it’s impossible to say for sure.
December 13, 2021 at 11:07 am #6221In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
Mary Ann Gilman Purdy
1880-1950

Mary Ann was my grandfather George Marshall’s mother. She died in 1950, seven years before I was born. She has been referred to more often than not, since her death, as Mary Ann Gilman Purdy, rather than Mary Marshall. She was from Buxton, so we believed, as was her husband William Marshall. There are family photos of the Gilmans, grocers in Buxton, and we knew that Mary Ann was brought up by them. My grandfather, her son, said that she thought very highly of the Gilman’s, and added the Gilman name to her birth name of Purdy.
The 1891 census in Buxton:
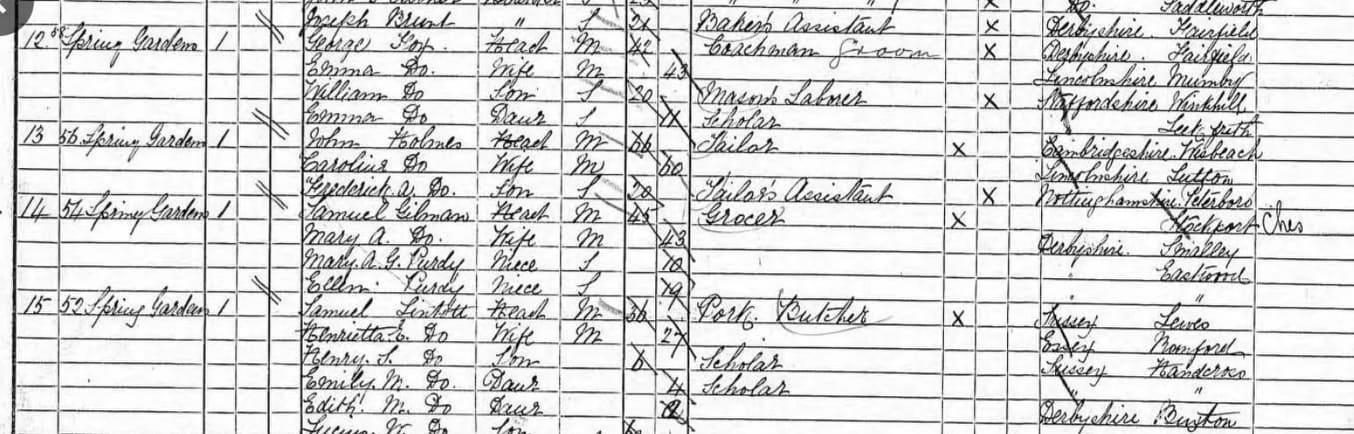
(Mary Ann’s aunt, Mrs Gilman, was also called Mary Anne, but spelled with an E.)
Samuel Gilman 1846-1909, and Mary Anne (Housley) Gilman 1846-1935, in Buxton:
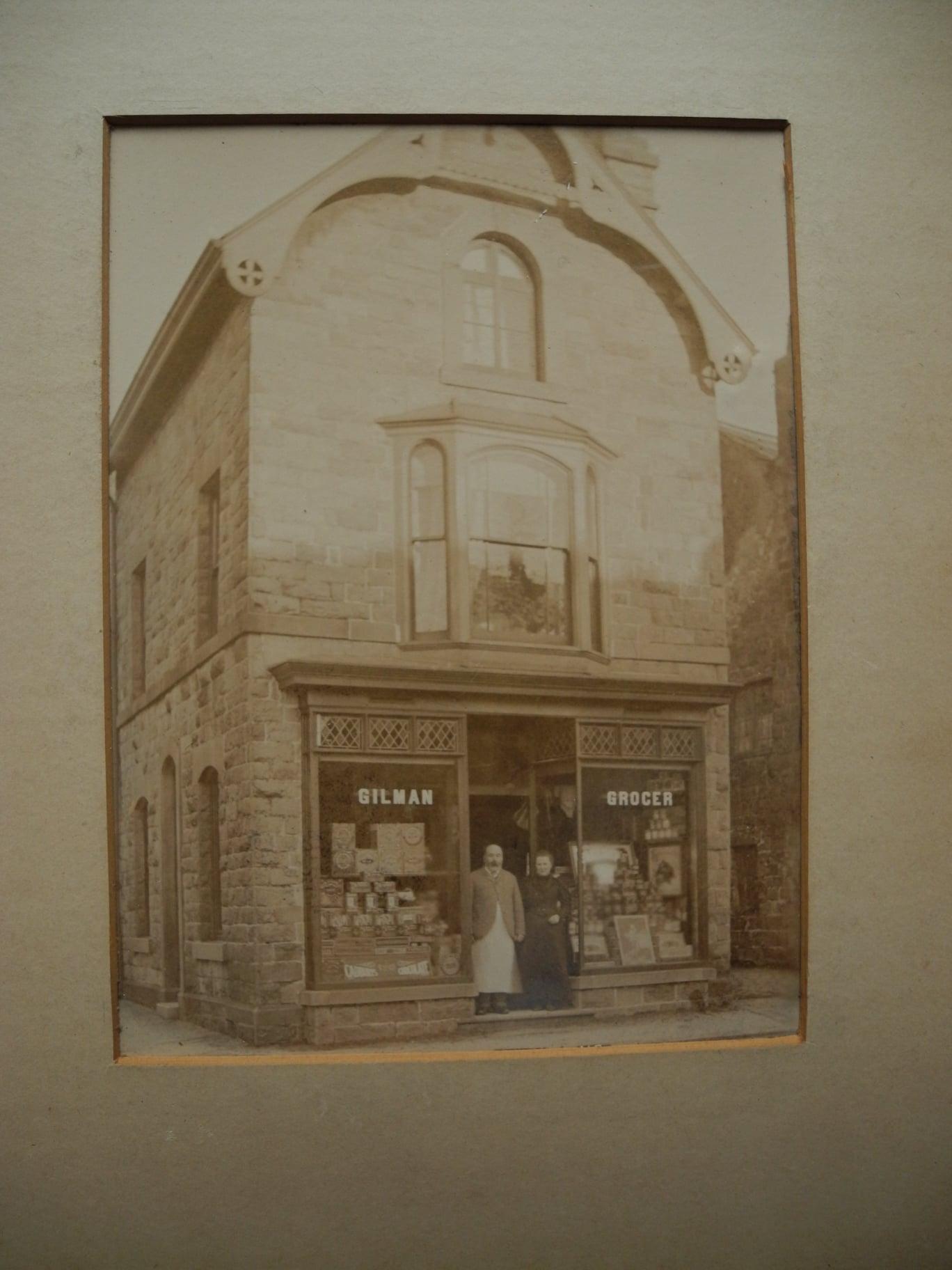


What we didn’t know was why Mary Ann (and her sister Ellen/Nellie, we later found) grew up with the Gilman’s. But Mary Ann wasn’t born in Buxton, Derbyshire, she was born in Eastwood, Nottinghamshire. When the search moved to Nottingham, we found the Purdy’s.
George Purdy 1848-1935, Mary Ann’s father:
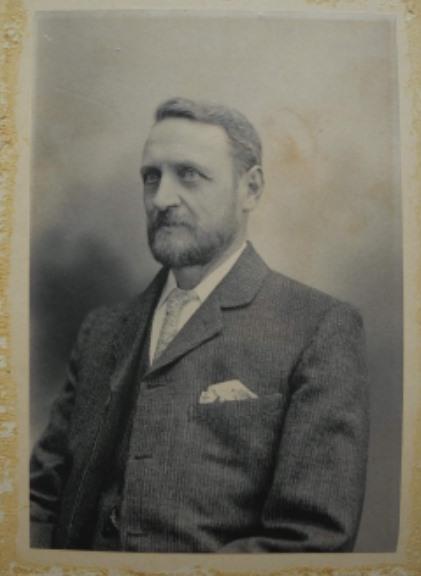

Mary Ann’s parents were George Purdy of Eastwood, and Catherine Housley of Smalley.
Catherine Housley 1849-1884, Mary Ann’s mother:
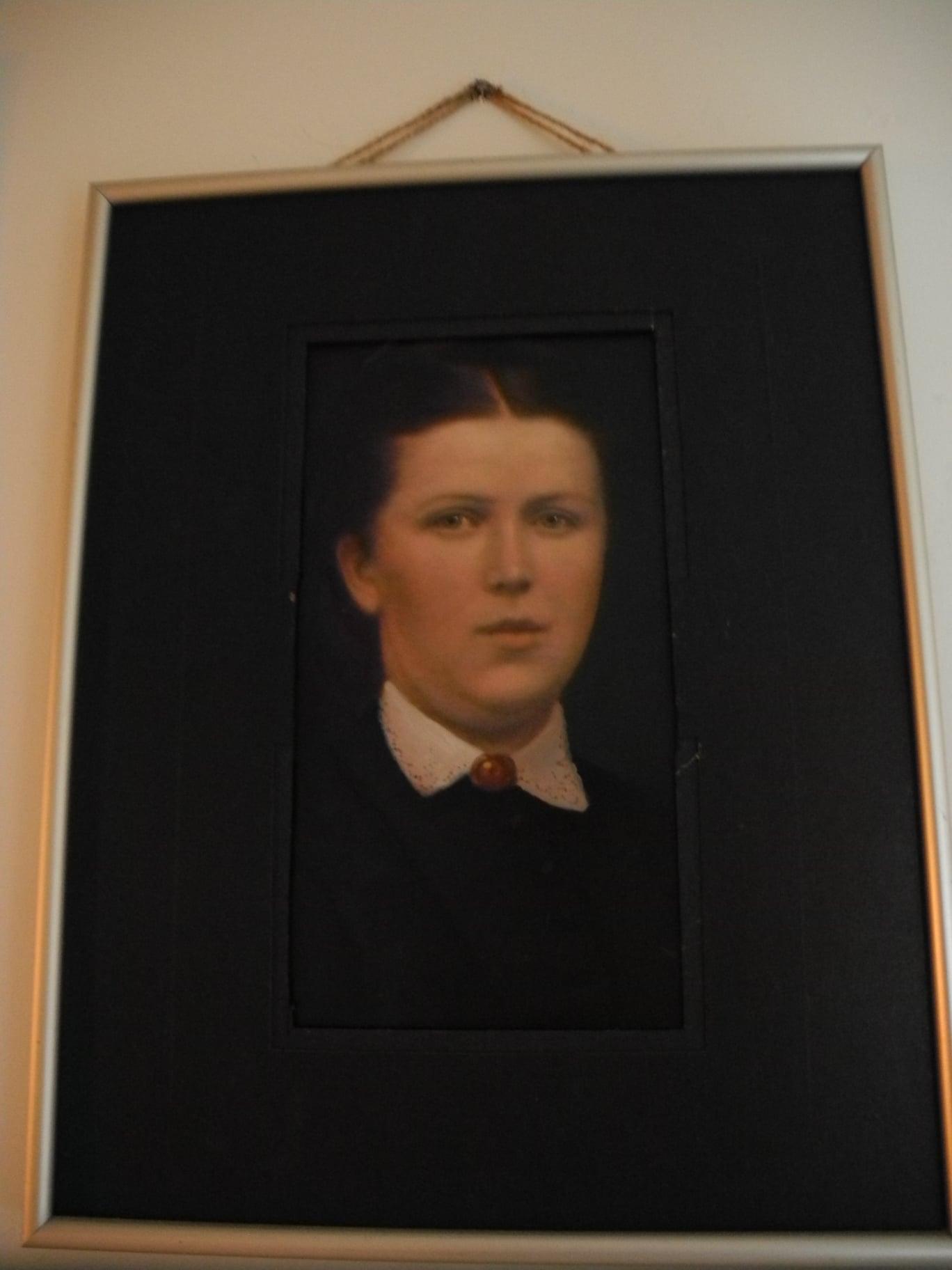

Mary Ann was four years old when her mother died. She had three sisters and one brother. George Purdy remarried and kept the two older daughters, and the young son with him. The two younger daughters, Mary Ann and Nellie, went to live with Catherine’s sister, also called Mary Anne, and her husband Samuel Gilman. They had no children of their own. One of the older daughters who stayed with their father was Kate , whose son George Gilman Rushby, went to Africa. But that is another chapter.
George was the son of Francis Purdy and his second wife Jane Eaton. Francis had some twenty children, and is believed in Eastwood to be the reason why there are so many Purdy’s.
The woman who was a mother to Mary Ann and who she thought very highly of, her mothers sister, spent her childhood in the Belper Workhouse. She and her older sister Elizabeth were admitted in June, 1850, the reason: father in prison. Their mother had died the previous year. Mary Anne Housley, Catherine’s sister, married Samuel Gilman, and looked after her dead sisters children.
Mary Ann Gilman Purdy Marshalls recipes written on the back of the Gilmans Grocers paper:
 February 10, 2013 at 11:21 am #2990
February 10, 2013 at 11:21 am #2990In reply to: The Surge Team’s Coils
Looking at the city illuminated by endless fireworks, Madame Li was almost glad to be back in Shanghai for the Chinese New Year. The vibrations, explosions and sparkling lights sent shivers of pleasure down her spine, reminding her of childhood excitement and of times before her awareness of such things as surges.
She wasn’t back for leisure however. A new snow surge had followed the air pollution surge. This was most unnerving, and she’d heard from Anita Charmpatti, her counterpart in India that a fog of pollution had hit New Dalhi as well.At the Long Poon Headquarters, against all expectations, a certain Lord Lemon had taken over the head of operations, flanked with two even older museum-worth pieces of antiquities (names Hyphen and Dash). All that had left Cornella utterly disappointed after her last past weeks of brilliant interim. Truth be told, without her scrupulous continuation in the footsteps of Steam, the Surge Team could have been no more. She’d managed to rally back Skye after her taking unnoticed leave of absence in Wales that could well have been an attempt at an early retirement. She also had talked back (and not without a fight) Pearl and Mari Fe in line of duty, and after the looting of the artefact chamber, the collection of rotes gathered after the past weeks contained surges made it look as if they were all back to business.
That Lord Lemon was an old bastard from the early ages of the Team. Usually, in that risky business, you weren’t expected to grow very old, much less to be able to retire. That one having been able to do both surely meant one thing. He wasn’t here to fool around with,… even though he looked capable of little less than managing his early bouts of Alzeihmer’s.
November 4, 2008 at 9:14 pm #1194In reply to: Circle of Eights, Stories
“Barry the White Bear is the last person having seen Arky the missing Aardvark “ Mlle Mongoose reported back to the team of worried animals.
“And did he say anything more?” Angela Goose asked, interrupting busy-looking Mlle Mongoose in mid-sentence.
“Well, if you’d let the Director speak, perhaps we could hear what she knows” said Freaky the Ferret.
“Don’t be zo mean to Angelipooh” Jobby the Hippo said compassionately “You know poor Angie is zo buzzy with Baba Yolanda coming over”
“Who?” asked Weirdy the Weasel distractedly
“Baba Yolanda the Loon !” answered Angela with a hint of exasperation “You’re not paying attention my dear? I told you ages ago she’d be coming this week to the Zoo to spend her winter here… I figure it’s getting too difficult for her in the wild given her age.”
“Well, I hope it’ll be better this time; last time she came, she left you in a pretty bad shape, it took us months to get you back on your feet. It should be time for her to get over that old ugly-duckling complex…”“Ahem”, managed to say Mlle Mongoose who was however following the discussion with great interest
She continued “As far as Arky is concerned, perhaps you should go see him yourselves. You’ll probably get more from Barry White than I did; He’s bearing the management a grudge since we decided to raise the temperature of his room because everybody around was catching colds after colds.”“Oh, great… my time of hitting the spotlight has finally come, and I’m stuck with dear ol’ Baba Yolanda” sighed Angela Goose.
-
AuthorSearch Results
Search Results for '846'
Viewing 9 results - 1 through 9 (of 9 total)
-
Search Results
Viewing 9 results - 1 through 9 (of 9 total)