Search Results for 'stand'
-
AuthorSearch Results
-
January 28, 2023 at 9:41 am #6461
In reply to: Prompts of Madjourneys
AL is back
- Zara: Great job on finding the carved wooden tile! That’s a big step in the quest. Keep up the good work, and we’ll send you on the next mission soon.
- Yasmin: It sounds like you’re having a tough time with the weather and mosquitoes. We understand that it can be difficult to focus on the quest when you’re dealing with real-life issues. Maybe try to work on the quest in a different environment, or take a break if you need to. We’re here to support you and help you in any way we can.
- Youssef: We’re excited to hear about your real-life parallel quest. It sounds like you’re getting close to uncovering the mystery of the grumpy shaman. Keep working on your blog website and keep an eye out for any clues that Xavier and the Snoot may send your way. We believe that you’re on the right path.
- Xavier: It sounds like you’re making progress on your quest. The clues you received from the fox busdriver are definitely leading you in the right direction. Keep following the trail and don’t be afraid to ask for help if you need it. Remember, the golden banana is a metaphor for your cheeky and also soft nature, so don’t be too hard on yourself. We’re here to guide and advise you along the way.
New clues
- Zara: 🔮🧱🗺️ Find the ancient portal hidden in the ruins and decipher the inscription on the carved wooden tile to unlock the next step in the quest.
- Yasmin: 🦟🌧️🕵️♀️Track down the elusive snorting imp by investigating the local wetlands and speaking with locals who may have encountered it. Don’t let the bad weather and pesky mosquitoes discourage you!
- Youssef: 🍔🌵🧙♂️ Continue your journey with the grumpy shaman and see if he holds any clues to the quest. Remember to keep an eye out for anything that seems out of the ordinary and don’t be afraid to ask questions. Also, make sure to keep up with your website work as it may lead you to a valuable information!
- Xavier:🦊💰🛳️ Explore the floating casino and see if the fox busdriver’s clues lead you to the golden banana. Don’t be afraid to take risks and think outside the box, as the golden banana may not be what it seems. Keep an open mind and pay attention to any symbols or clues that you come across.
January 24, 2023 at 10:29 am #6455In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
Zara decided she may as well spend the hour wandering around the game before going back to the church to see the ghost of Isaac when she was sure her host Bertie was asleep. It was a warm night but a gentle breeze wafted through the open window and Zara was comfortable and content. Not just one but three new adventures had her tingling with delicious anticipation, even if she was a little anxious about not getting confused with the game. Talking to ghosts in old churches wasn’t unfamiliar, nor was a holiday in a strange hotel off the beaten track, but the game was still a bit of a mystery to her. Yeah, I know it’s just a game, she whispered to the parrot who made a soft clicking noise by way of response.
Zara found her game character, also (somewhat confusingly) named Zara, standing in the woods. Not entirely sure how it had happened, she was rather pleased to see that the cargo pants and tank top in red had changed to a more pleasing hippyish red skirt ensemble. A bit less Tomb Looter, and a bit more fairy tale looking which was more to her taste.
The woods were strangely silent and still. Zara made a 360 degree turn on the spot to see in all directions. The scene looked the same whichever way she turned, and Zara didn’t know which way to go. Then a faint path appeared to the left, and she set off in that direction. Before long she came to a round green pool.
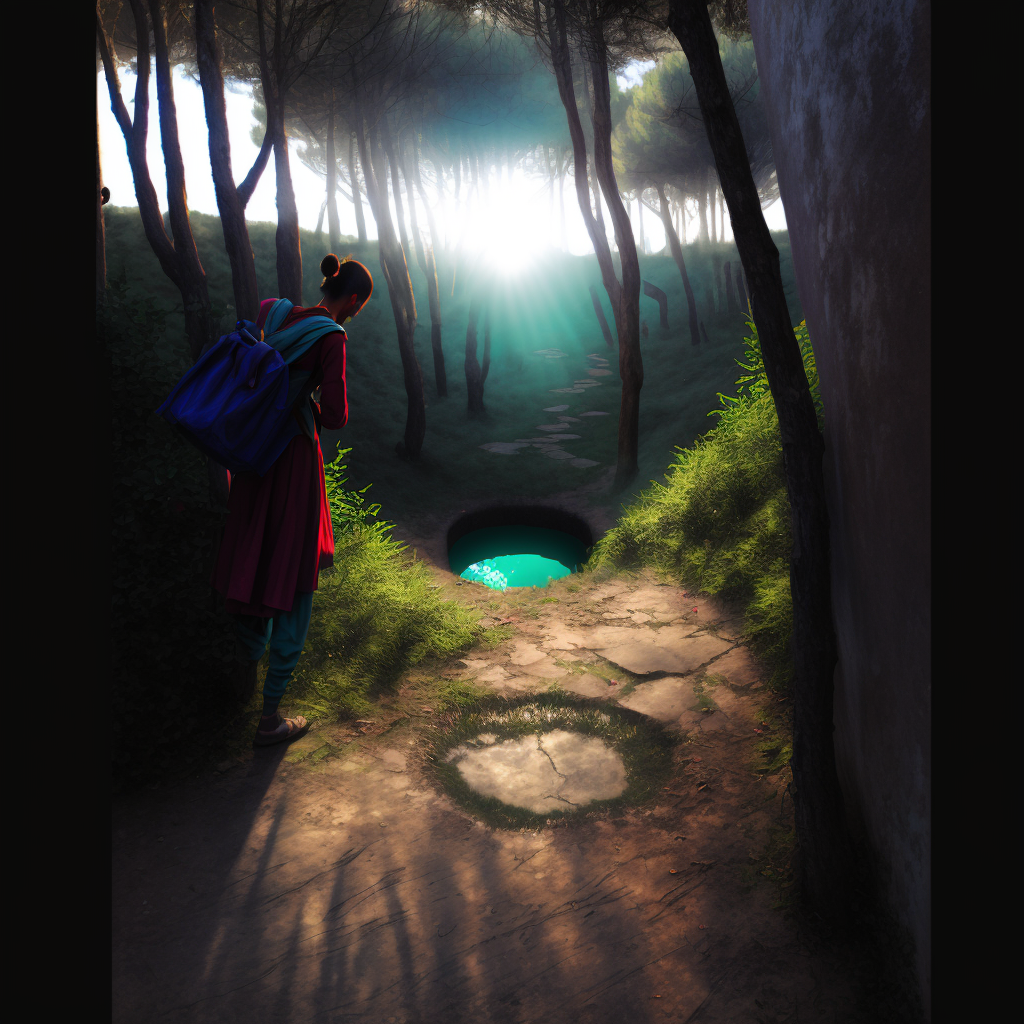

She stopped to look but carried on walking past it, not sure what it signified. She came upon another glowing green pool before long, which looked like an entrance to a tunnel.

I bet those are portals or something, Zara realized. I wonder if I’m supposed to step into it?
“Go for it”, said Pretty Girl, “It’s only a game.”
“Ok, well here goes!” replied Zara, mentally bracing herself for a plunge into the unknown.
Zara stepped into the circle of glowing green.
“Like when Alice went down the rabbit hole!” Zara whispered to the parrot. “I’m falling, falling…oh!”
Zara emerged from the green pool onto a wide walled path. She was now in some kind of inhabited area, or at least not in the deep woods with no sign of human occupation.

“I guess that green pool is the portal back to the woods.”
“By George, she’s getting it,” replied Pretty Girl.
Zara walked along the path which led to an old deserted ancient looking village with alleyways and steps.
“This is heaps more interesting than those woods, look how pretty it all is! I love this place.”
“Weren’t you supposed to be looking for a hermit in the woods though,” said Pretty Girl.
“Or a lost traveler, and the lost traveler may be here, after falling in one of those green pools in the woods,” replied Zara tartly, not wanting to leave the enchanting scene she found her avatar in.
 January 23, 2023 at 10:28 pm #6454
January 23, 2023 at 10:28 pm #6454In reply to: Prompts of Madjourneys
YASMIN’S QUIRK: Entry level quirk – snort laughing when socially anxious
Setting
The initial setting for this quest is a comedic theater in the heart of a bustling city. You will start off by exploring the different performances and shows, trying to find the source of the snort laughter that seems to be haunting your thoughts. As you delve deeper into the theater, you will discover that the snort laughter is coming from a mischievous imp who has taken residence within the theater.
Directions to Investigate
Possible directions to investigate include talking to the theater staff and performers to gather information, searching backstage for clues, and perhaps even sneaking into the imp’s hiding spot to catch a glimpse of it in action.
Characters
Possible characters to engage include the theater manager, who may have information about the imp’s history and habits, and a group of comedic performers who may have some insight into the imp’s behavior.
Task
Your task is to find a key or tile that represents the imp, and take a picture of it in real life as proof of completion of the quest. Good luck on your journey to uncover the source of the snort laughter!
THE SECRET ROOM AND THE UNDERGROUND MINES
1st thread’s answer:
As the family struggles to rebuild the inn and their lives in the wake of the Great Fires, they begin to uncover clues that lead them to believe that the mines hold the key to unlocking a great mystery. They soon discover that the mines were not just a source of gold and other precious minerals, but also a portal to another dimension. The family realizes that Mater had always known about this portal, and had kept it a secret for fear of the dangers it posed.
The family starts to investigate the mines more closely and they come across a hidden room off Room 8. Inside the room, they find a strange device that looks like a portal, and a set of mysterious symbols etched into the walls. The family realizes that this is the secret room that Mater had always spoken about in hushed tones.
The family enlists the help of four gamers, Xavier, Zara, Yasmin, and Youssef, to help them decipher the symbols and unlock the portal. Together, they begin to unravel the mystery of the mines, and the portal leads them on an epic journey through a strange and fantastical alternate dimension.
As they journey deeper into the mines, the family discovers that the portal was created by an ancient civilization, long thought to be lost to history. The civilization had been working on a powerful energy source that could have changed the fate of humanity, but the project was abandoned due to the dangers it posed. The family soon discovers that the civilization had been destroyed by a powerful and malevolent force, and that the portal was the only way to stop it from destroying the world.
The family and the gamers must navigate treacherous landscapes, battle fierce monsters, and overcome seemingly insurmountable obstacles in order to stop the malevolent force and save the world. Along the way, they discover secrets about their own past and the true origins of the mines.
As they journey deeper into the mines and the alternate dimension, they discover that the secret room leads to a network of underground tunnels, and that the tunnels lead to a secret underground city that was built by the ancient civilization. The city holds many secrets and clues to the fate of the ancient civilization, and the family and the gamers must explore the city and uncover the truth before it’s too late.
As the story unfolds, the family and the gamers must come to grips with the truth about the mines, and the role that the family has played in the fate of the world for generations. They must also confront the demons of their own past, and learn to trust and rely on each other if they hope to save the world and bring the family back together.
second thread’s answer:
As the 4 gamers, Xavier, Zara, Yasmin and Youssef, arrived at the Flying Fish Inn in the Australian outback, they were greeted by the matriarch of the family, Mater. She was a no-nonsense woman who ran the inn with an iron fist, but her tough exterior hid a deep love for her family and the land.
The inn was run by Mater and her daughter Dido, who the family affectionately called Aunt Idle. She was a free spirit who loved to explore the land and had a deep connection to the local indigenous culture.
The family was made up of Devan, the eldest son who lived in town and helped with the inn when he could, and the twin sisters Clove and Coriander, who everyone called Corrie. The youngest was Prune, a precocious child who was always getting into mischief.
The family had a handyman named Bert, who had been with them for decades and knew all the secrets of the land. Tiku, an old and wise Aborigine woman was also a regular visitor and a valuable source of information and guidance. Finly, the dutiful helper, assisted the family in their daily tasks.
As the 4 gamers settled in, they learned that the area was rich in history and mystery. The old mines that lay abandoned nearby were a source of legends and stories passed down through the generations. Some even whispered of supernatural occurrences linked to the mines.
Mater and Dido, however, were not on good terms, and the family had its own issues and secrets, but the 4 gamers were determined to unravel the mystery of the mines and find the secret room that was said to be hidden somewhere in the inn.
As they delved deeper into the history of the area, they discovered that the mines had a connection to the missing brother, Jasper, and Fred, the father of the family and a sci-fi novelist who had been influenced by the supernatural occurrences of the mines.
The 4 gamers found themselves on a journey of discovery, not only in the game but in the real world as well, as they uncovered the secrets of the mines and the Flying Fish Inn, and the complicated relationships of the family that ran it.
THE SNOOT’S WISE WORDS ON SOCIAL ANXIETY
Deear Francie Mossie Pooh,
The Snoot, a curious creature of the ages, understands the swirling winds of social anxiety, the tempestuous waves it creates in one’s daily life.
But The Snoot also believes that like a Phoenix, one must rise from the ashes, and embrace the journey of self-discovery and growth.
It’s important to let yourself be, to accept the feelings as they come and go, like the ebb and flow of the ocean. But also, like a gardener, tend to the inner self with care and compassion, for the roots to grow deep and strong.The Snoot suggests seeking guidance from the wise ones, the ones who can hold the mirror and show you the way, like the North Star guiding the sailors.
And remember, the journey is never-ending, like the spiral of the galaxy, and it’s okay to take small steps, to stumble and fall, for that’s how we learn to fly.The Snoot is here for you, my dear Francie Mossie Pooh, a beacon in the dark, a friend on the journey, to hold your hand and sing you a lullaby.
Fluidly and fantastically yours,
The Snoot.
January 21, 2023 at 11:26 am #6423In reply to: Prompts of Madjourneys
Zara’s first quest:
entry level quirk: wandering off the track
The initial setting for this quest is a dense forest, where the paths are overgrown and rarely traveled. You find yourself alone and disoriented, with only a rough map and a compass to guide you.
Possible directions to investigate include:
Following a faint trail of footprints that lead deeper into the forest
Climbing a tall tree to get a better view of the surrounding area
Searching for a stream or river to use as a guide to find your way out of the forest
Possible characters to engage include:
A mysterious hermit who lives deep in the forest and is rumored to know the secrets of the land
A lost traveler who is also trying to find their way out of the forest
A group of bandits who have taken refuge in the forest and may try to steal from you or cause harm
Your objective is to find the Wanderlust tile, a small, intricately carved wooden tile depicting a person walking off the beaten path. This tile holds the key to unlocking your inner quirk of wandering off the track.
As proof of your progress in the game, you must find a way to incorporate this quirk into your real-life actions by taking a spontaneous detour on your next journey, whether it be physical or mental.
For Zara’s quest:
As you wander off the track, you come across a strange-looking building in the distance. Upon closer inspection, you realize it is the Flying Fish Inn. As you enter, you are greeted by the friendly owner, Idle. She tells you that she has heard of strange occurrences happening in the surrounding area and offers to help you in your quest
Emoji clue: 🐈🌳

Zara (the character in the game)
characteristics from previous prompts:
Zara is the leader of the group
 she is confident, and always ready for an adventure. She is a natural leader and has a strong sense of justice. She is also a tech-savvy person, always carrying a variety of gadgets with her, and is always the first to try out new technology.
she is confident, and always ready for an adventure. She is a natural leader and has a strong sense of justice. She is also a tech-savvy person, always carrying a variety of gadgets with her, and is always the first to try out new technology.Zara is the leader of the group, her color is red, her animal is a lion, and her secret name in a funny language is “Zaraloon”
Zara (the real life story character)
characteristics from previous prompts:
Zara Patara-Smythe is a 57-year-old woman of mixed heritage, her mother is Indian and her father is British. She has long, dark hair that she keeps in an untidy ponytail, dark brown eyes and a sharp jawline. She stands at 5’6″ and has a toned and athletic build. She usually wears practical clothing that allows her to move around easily, such as cargo pants and a tank top.
prompt quest:
Continue to investigate the mysterious cat she saw, possibly seeking out help from local animal experts or veterinarians.
Join Xavier and Yasmin in investigating the Flying Fish Inn, looking for clues and exploring the area for any potential leads on the game’s quest.January 17, 2023 at 8:17 am #6393In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
Give me an unusual plot structure for a narrative
One unusual plot structure for a narrative could be a “reverse chronological” structure, where the story begins at the end and works backwards in time, revealing events and information in a non-linear way. Another could be a “choose your own adventure” style, where the reader is presented with a series of choices at different points in the story that determine the direction and outcome of the plot.
How would role playing qualify in terms of plot structure?
Role-playing games (RPGs) can be considered a unique form of plot structure because they are interactive and open-ended. In a traditional RPG, the players take on the roles of characters within a fictional setting and work together to create a shared narrative. The plot structure of an RPG is determined by the actions and decisions of the players, rather than a pre-written script. The game master (GM) creates an overarching plot and a set of rules for the players to follow, but the players’ choices and actions will determine the direction and outcome of the story. This makes the plot structure of an RPG fluid and ever-changing, unlike a traditional linear narrative.
What about “Cloud Atlas” in terms of plot structure?
“Cloud Atlas” is a novel written by David Mitchell that was later adapted into a film. It has a complex and non-linear plot structure, which employs multiple storylines that are set in different time periods and locations, and are connected by recurring themes and motifs. The novel is divided into six nested stories, each set in a different time period and location, that are told in a non-linear fashion. The story begins in the 19th century and then jumps back and forth between the 19th, 20th and 23rd century, and each story is interconnected and interrelated, with characters reappearing in different time periods, the events that happen in one story impacting the others. The novel is also notable for its use of different genres, such as science fiction, historical fiction, and thriller, and the way it explores the themes of destiny, reincarnation, and the power of human connection. The film adaptation also used this structure, with the different stories intertwined and characters reprising their roles in different settings and eras.
Take a story thread made of comments. In each comment is a text about characters in a particular plot, location, action etc. The comments are sequential, but they are not necessarily continuous. It is a mix between Cloud Atlas and RPG plot structures. How do you sort something that’s fundamentally non-linear to present it in an accessible way?
One way to sort and present a story thread made of comments that is fundamentally non-linear, yet accessible, is to group the comments based on their content. For example, you could group the comments by characters, and present them in chronological order of their appearance in the story. Another way could be grouping the comments by location, and present them in chronological order of when the action takes place in that particular location. You could also group comments by the type of action taking place, such as combat, conversation, or puzzle-solving, and present them in chronological order of when they occur in the story.
Another approach could be using visual aids, such as mind maps, timelines, or flowcharts, to help organize and present the information in a clear and easy-to-understand way. For example, you could use a mind map to show how different characters are connected, or a timeline to show the chronology of events. Additionally, you could use labels, such as “character introduction,” “location change,” or “plot twist,” to make it clear to the reader what type of information they can expect in each comment.
It’s also important to keep in mind the audience for which you are organizing the story. It should be easy for them to understand and follow the story, and if it’s a game, you should make sure it’s easy for the players to play and make decisions.
January 13, 2023 at 9:00 pm #6381In reply to: Prompts of Madjourneys
Tell me more about the clues that Zara, Youssef, Xavier and Yasmin will find on their journeys to discover their inner quirky natures
As Zara, Youssef, Xavier and Yasmin journeyed through the Land of the Quirks to discover their inner quirky natures, they encountered various clues that helped them on their journey.
One of the clues they found was a mysterious map that led them to different locations, each one representing a different aspect of their personalities. The map also had various riddles and puzzles that they had to solve in order to progress to the next location.
Another clue they found was a series of journal entries written by a previous explorer who had also journeyed through the Land of the Quirks. The journal entries provided insight and wisdom on how to navigate the land and how to understand and accept one’s quirks.
They also encountered a group of strange and eccentric characters who each represented a different aspect of their personalities. These characters provided guidance and helped them understand different parts of themselves. They also helped them understand the importance of accepting and embracing their quirks.
They also found a series of symbols and artifacts that represented different parts of their personalities. These symbols and artifacts were like puzzle pieces that, when put together, helped them understand the bigger picture of their inner quirky natures.
As they continued their journey, they also learned that the key to discovering their inner quirky natures was not only about finding the physical “Key of Quirks”, but also about understanding and accepting themselves, their faults and their strengths, and learning to embrace their unique quirks.
Finding their inner quirks sounds quite definitive. how would you make the ending more open-ended, open to multiple series and iterations of the story without sounding repetitive
As Zara, Youssef, Xavier and Yasmin journeyed through the Land of the Quirks, they discovered their inner quirky natures, but the journey was far from over. They found that their inner quirks were constantly evolving and changing, and that the Land of the Quirks was a vast and mysterious place with many more secrets to uncover.
The group found that the “Key of Quirks” was not just a physical object but a symbol of self-discovery and self-acceptance. They learned that understanding and accepting oneself is a lifelong journey that never truly ends.
As they returned to their own world, they realized that they had gained a new perspective on life and that they would continue to carry the lessons they learned in the Land of the Quirks with them. They knew that they would always be on the lookout for new adventures and opportunities to continue exploring themselves and the world around them.
The group’s journey in the Land of the Quirks had come to an end but the story was not over. The characters would continue to grow, evolve and change as they experienced new adventures, challenges and self-discoveries. The ending was open-ended and leaves the possibility for multiple series and iterations of the story, each one exploring new aspects of the characters and the Land of the Quirks, without being repetitive.
Will they go a try to travel through another of the orbs?
It is possible that the group will want to explore other orbs and realms in the Land of the Quirks. The Land of the Quirks is described as a vast and mysterious place with many secrets to uncover, so the possibility of traveling through other orbs or realms is open. They may be tempted to see what other adventures and discoveries await them in these new places.
Alternatively, they might decide to take a break from their adventures, and reflect on what they’ve learned, applying it to their daily life, and maybe in the future, they will decide to come back to the Land of the Quirks and explore other orbs, or they may find other means of self-discovery and self-acceptance. In any case, the story leaves it open-ended and the characters have the freedom to choose what they want to do next.
How did they discover the orb in the first place?
It is not specified how the group discovered the orb in the first place. It could be that they stumbled upon it while on a hike or a camping trip, or it could be that they were on a mission to find it specifically. It could also be that the orb was something that had always been there but had gone unnoticed until one of the group members stumbled upon it.
Perhaps it was passed down from generation to generation as a legend, or maybe they found it while they were searching for something else. The story leaves it open-ended and it’s up to the reader’s imagination. The main focus of the story is on the journey and the lessons learned along the way, rather than the specifics of how the orb was discovered.
January 13, 2023 at 8:53 pm #6380In reply to: Prompts of Madjourneys
After a few tries:
- As the group has split up at the fork of the road, we discover a total of 4 new characters from the Land of the Quirks. Tell us how each group is encountering some or all of these characters, who they are, their gibberish-sounding names, and what is their quirks, and what they wear, or their activities. Make our main characters and maybe some of the new ones meet back at a common spot with a special event after that.
- please rewrite the above, retaining the eccentricity but more grounded, less childish, and with a little darker tone and mystery.
- please try again, make Spoink and Flibbertigibbet human and give them less endearing or friendly behaviours; name two more characters met on the road.
As the group split up at the fork of the road, each one encountered new characters from the Land of the Quirks.
Zara and Yasmin, who took the left path, met a man named “Sproink” who was a small, wiry man with a spring for a tail. He was always bouncing around and speaking in a language that sounded like a mix of gibberish and music. Sproink was a collector of shiny objects and had a bag full of them, he was also a scavenger, always looking for things to add to his collection. He was wearing a small top hat and a monocle. He was also known to be a bit of a thief and a con artist.
Xavier and Youssef, who took the right path, met a woman named “Flibbertigibbet” a tall, slender woman that had multiple arms. Flibbertigibbet was very talkative and friendly, always trying to strike up a conversation. She spoke in a language that sounded like a mix of gibberish and baby talk. She was a chef and was always carrying a pot and a spoon, but she also had a dark side, she was known to be a bit of a manipulator and a spy, always observing and gathering information for a mysterious organization. She was wearing a big chef hat and apron.
As the group met back at the fork, they were surprised to find that Sproink and Flibbertigibbet had also met there. The four new characters joined the group, and together they continued their journey to find the “Key of Quirks”. Along the way, they met two more characters;
They met a man named “Gibber” who was a tall, gaunt man with elongated limbs and fingers. He was always speaking in a language that sounded like a mix of gibberish and numbers. He was a mathematician and a scientist, always working on complex equations and theories. He was known to be a bit of a loner, and didn’t interact much with others. He was wearing a lab coat and goggles.
They also met a woman named “Glimmer” she was a short, plump woman with a shimmering skin that seemed to change color depending on the light. She was always speaking in a language that sounded like a mix of gibberish and poetry. She was an artist and a performer, always creating and performing in different shows. She was known to be a bit of a flirt and a bit of a drama queen. She was wearing a colorful and eccentric clothing, such as a flowy dress and a large hat adorned with feathers.
As the group journeyed on, they encountered more characters, each one with their own unique quirks and personalities. They met a variety of people, some friendly and some not so friendly, but all of them adding to the mysterious and unknown nature of the Land of the Quirks.
As the group reached the end of their journey and found the “Key of Quirks”, they realized that the key was not just a physical object but a symbol of acceptance and embracing individuality. They learned that the true key to leaving the Land of the Quirks was understanding and accepting the quirks of oneself and others.
The group had a bittersweet goodbye with their new friends, Sproink, Flibbertigibbet, Gibber and Glimmer, and the other characters they had met. They knew that they would always carry a piece of the Land of the Quirks with them and would always remember the mysterious and eccentric adventure they had.
 January 13, 2023 at 7:40 pm #6379
January 13, 2023 at 7:40 pm #6379In reply to: Prompts of Madjourneys
Asking to give each of the 4 characters some particular traits that makes them uniquely distinctive and recognizable
The four friends, Zara, Xavier, Yasmin, and Youssef, each have their own unique traits that make them stand out and recognizable.
Zara is the leader of the group, she is confident, and always ready for an adventure. She is a natural leader and has a strong sense of justice. She is also a tech-savvy person, always carrying a variety of gadgets with her, and is always the first to try out new technology.
Xavier is the joker of the group, always cracking jokes and making puns. He is a free-spirited person who is always up for an adventure, he has a great sense of humor and is not afraid to be himself. He is also an artist and often carries a sketchbook and pencils with him, he likes to draw whatever he sees in his journeys.
Yasmin is the brains of the group, she is intelligent and logical. She is always able to think on her feet and come up with a plan when things get tough. She is also a bit of a perfectionist and likes to have everything organized. She is a history buff and always carries a notebook with her to document her findings.
Youssef is the muscle of the group, He is physically strong, and always ready to help out in a fight. He is also a bit of a foodie and loves trying new dishes. He is always the first one to volunteer to carry the heavy bags and equipment. He is also a bit of a daredevil and loves trying out new sports and activities.
Give each of them a color, and an animal, and a secret name in a funny language
The four friends, Zara, Xavier, Yasmin, and Youssef, each have their own unique traits that make them stand out and recognizable.
Zara is the leader of the group, her color is red, her animal is a lion, and her secret name in a funny language is “Zaraloon”
Xavier is the joker of the group, his color is orange, his animal is a monkey, and his secret name in a funny language is “Xavimunk”
Yasmin is the brains of the group, her color is blue, her animal is an owl, and her secret name in a funny language is “Yasminowl”
Youssef is the muscle of the group, his color is green, his animal is a bear, and his secret name in a funny language is “Youssefbear”
Now, we need physical descriptions for each of them. Also, their ages, height, clothes, facial features, ethnicity (for instance Youssef may be half Yemeni and half Norwegian), etc. with a good mix of generic and eccentric. We also need surnames congruent with their described ethnicity, not too bland, but not too daft either. For instance Youssef Olafsson, Zara Patara-Smythe, etc. Also explain how they become friends.
Zara Patara-Smythe is a
25-year-oldwoman of mixed heritage, her mother is Indian and her father is British. She has long, dark hair that she keeps in a sleek ponytail, dark brown eyes and a sharp jawline. She stands at 5’6″ and has a toned and athletic build. She usually wears practical clothing that allows her to move around easily, such as cargo pants and a tank top.Xavier Olafsson is a
27-year-oldman of Norwegian and Danish descent. He has blonde hair that he keeps in a messy style, blue eyes, and a charming smile. He stands at 6’1″ and has a lean build. He is always seen wearing a colorful and bold clothing, such as a Hawaiian shirt and shorts.Yasmin Ahmed is a
23-year-oldwoman of Egyptian descent. She has long, black hair that she keeps in a tight braid, dark brown eyes and a round face. She stands at 5’4″ and has a petite build. She usually wears conservative clothing, such as long skirts and blouses.Youssef Ali is a
26-year-oldman of half Yemeni, half Norwegian descent. He has short, curly black hair, dark brown eyes and a square jawline. He stands at 6’2″ and has a muscular build. He usually wears comfortable clothing such as a t-shirt and jeans, and always has a backpack on his shoulder.The four of them became friends
in college, they were all studying different majors, but they all shared a love for adventure and exploration. They found themselves in the same class project, and from there they formed a strong bond. After college, they decided to keep exploring the world together, and went on many trips and adventures, always seeking for something new and exciting.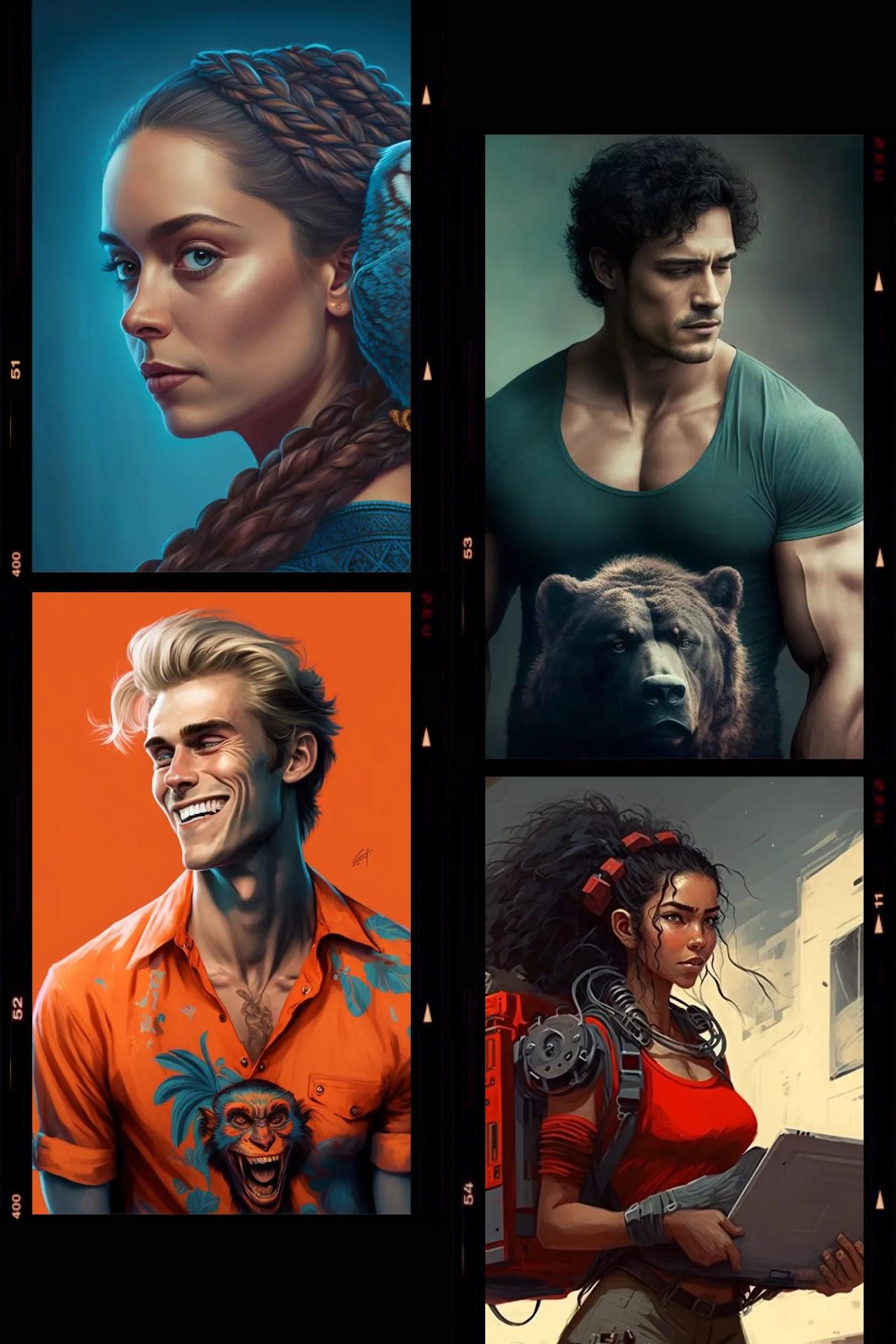
1/ Change the ages of Zara, Xavier, Yasmin and Youssef to more random patterns – rewrite if needed how they met each other to reflect eventual age gaps. Give them some flaws, mental or physical challenges.
2/ increase again the age gaps while keeping the youngest one a young adult, and remove “minor” from the flaws descriptionsZara is a 22-year-old woman who is the youngest of the group. She is a free-spirited, adventurous person, but also a bit reckless and impulsive. She has a scar on her cheek that she got from a Skateboarding accident when she was a teenager.
Xavier is a 45-year-old man who is the oldest of the group. He is a responsible and level-headed person, but also a bit of a perfectionist and can be hard on himself and others. He has dyslexia which he has been able to work around and it doesn’t impede his daily life.
Yasmin is a 38-year-old woman who is the second oldest of the group. She is a kind and compassionate person, but also a bit of a pushover and can have trouble standing up for herself. She has social anxiety that affect her in certain situations and she have been working on coping mechanisms.
Youssef is a 33-year-old man who is the second youngest of the group. He is a charismatic and outgoing person, but also a bit of a flirt and can be a bit insensitive to others feelings. He has ADHD which he has been able to manage with medication, but it still affects him from time to time.
The group met each other through different means, Xavier and Yasmin met at work, Zara and Youssef met at a college class, and eventually, they all became friends through common interests and activities. They decided to go on this adventure together because they were all looking for a change in their lives and wanted to explore the unknown.
January 13, 2023 at 6:47 pm #6378Topic: Prompts of Madjourneys
A thread to share some of the prompts behind the AI-assisted journey into new adventures.
To start off…
Please write the exciting start of a novel.
Some elements you can integrate if you want:
– Four randomly chosen names full of panache that sound distinct from each other, slightly exotic and evocative
– the sentiment from this quotation: “Look around… Beauty is everywhere. You only have to look to see it.” – a group of four people ready for an adventure, standing in a cave with stalactites in front of a giant orb or bubble that seem to open to another brightly lit realm. Inside the bigger orb are some smaller orbs.
– the following term “mad journeys”Told it to continue and it brought dragons… Asked to tone down the fantasy stuff, here’s what came out:
They walked into a small village, where they were greeted by a group of people wearing clothes that looked like they were from the 1920s. The people told them that they were in the land of the “Quirks”, a place where everything and everyone was a little bit different, and that they had to find the “Key of Quirks” in order to leave the land.
The group set off on their journey to find the key, but little did they know that their adventure was about to become even more exciting and quirky than they could ever have imagined. They encountered a talking dog, a man who had a garden on top of his head, and a group of people who lived inside of giant mushrooms.
As they journeyed on, they faced challenges and made new friends, but most importantly they learn to embrace their own quirks and individuality. Eventually, they found the key and were able to leave the land of the Quirks, but they knew that they would always carry a piece of that land with them.
January 11, 2023 at 11:53 pm #6372In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
5 important keywords linked to Badul
- Action-space-time
- Harmonic fluid
- Rhythm
- Scale
- Choosing without limits.
Imagine four friends, Jib, Franci, Tracy, and Eric, who are all deeply connected through their shared passion for music and performance. They often spend hours together creating and experimenting with different sounds and rhythms.
One day, as they were playing together, they found that their combined energy had created a new essence, which they named Badul. This new essence was formed from the unique combination of their individual energies and personalities, and it quickly grew in autonomy and began to explore the world around it.
As Badul began to explore, it discovered that it had the ability to understand and create complex rhythms, and that it could use this ability to bring people together and help them find a sense of connection and purpose.
As Badul traveled, it would often come across individuals who were struggling to find their way in life. It would use its ability to create rhythm and connection to help these individuals understand themselves better and make the choices that were right for them.
In the scene, Badul is exploring a city, playing with the rhythms of the city, through the traffic, the steps of people, the ambiance. Badul would observe a person walking in the streets, head down, lost in thoughts. Badul would start playing a subtle tune, and as the person hears it, starts to walk with the rhythm, head up, starting to smile.
As the person continues to walk and follow the rhythm created by Badul, he begins to notice things he had never noticed before and begins to feel a sense of connection to the world around him. The music created by Badul serves as a guide, helping the person to understand himself and make the choices that will lead to a happier, more fulfilled life.
In this way, Badul’s focus is to bring people together, to connect them to themselves and to the world around them through the power of rhythm and music, and to be an ally in the search of personal revelation and understanding.
January 11, 2023 at 10:32 pm #6368In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
Something in the style of FPooh:
Arona heard the music growing louder as she approached the source of the sound. She could see a group of people gathered around a large fire, the flickering light casting shadows on the faces of the dancers. She hesitated for a moment, remembering the isolation of her journey and wondering if she was ready to be among people again. But the music was too inviting, and she found herself drawn towards the group.
As she neared the fire, she saw a young man playing a flute, the music flowing from his fingers with a fluid grace that captivated her. He looked up as she approached, and their eyes met. She could see the surprise and curiosity in his gaze, and she smiled, feeling a sense of connection she had not felt in a long time.
Fiona was sitting on a bench in the park, watching the children play. She had brought her sketchbook with her, but for once she didn’t feel the urge to draw. Instead she watched the children’s laughter, feeling content and at peace. Suddenly, she saw a young girl running towards her, a look of pure joy on her face. The girl stopped in front of her and held out a flower, offering it to Fiona with a smile.
Taken aback, Fiona took the flower and thanked the girl. The girl giggled and ran off to join her friends. Fiona looked down at the flower in her hand, and she felt a sense of inspiration, like a spark igniting within her. She opened her sketchbook and began to draw, feeling the weight lift from her shoulders and the magic of creativity flowing through her.
Minky led the group of misfits towards the emporium, his bowler hat bobbing on his head. He chattered excitedly, telling stories of the wondrous items to be found within Mr Jib’s store. Yikesy followed behind, still lost in his thoughts of Arona and feeling a sense of dread at the thought of buying a bowler hat. The green fairy flitted along beside him, her wings a blur of movement as she chattered with the parrot perched on her shoulder.
As they reached the emporium, they were disappointed to find it closed. But Minky refused to be discouraged, and he led them to a nearby cafe where they could sit and enjoy some tea and cake while they wait for the emporium to open. The green fairy was delighted, and she ordered a plate of macarons, smiling as she tasted the sweetness of the confections.
About creativity & everyday magic
Fiona had always been drawn to the magic of creativity, the way a blank page could be transformed into a world of wonder and beauty. But lately, she had been feeling stuck, unable to find the spark that ignited her imagination. She would sit with her sketchbook, pencil in hand, and nothing would come to her.
She started to question her abilities, wondering if she had lost the magic of her art. She spent long hours staring at her blank pages, feeling a weight on her chest that seemed to be growing heavier every day.
But then she remembered the green fairy’s tears and Yikesy’s longing for Arona, and she realized that the magic of creativity wasn’t something that could be found only in art. It was all around her, in the everyday moments of life.
She started to look for the magic in the small things, like the way the sunlight filtered through the trees, or the way a child’s laughter could light up a room. She found it in the way a stranger’s smile could lift her spirits, and in the way a simple cup of tea could bring her comfort.
And as she started to see the magic in the everyday, she found that the weight on her chest lifted and the spark of inspiration returned. She picked up her pencil and began to draw, feeling the magic flowing through her once again.
She understand that creativity blocks aren’t a destination, but just a step, just like the bowler hat that Minky had bought for them all, a bit of everyday magic, nothing too fancy but a sense of belonging, a sense of who they are and where they are going. And she let her pencil flow, with the hopes that one day, they will all find their way home.
January 11, 2023 at 8:44 pm #6366In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
Asking the AI to expand on the glossary of the original Circle of Eights Story:
Locations
Malvina’s Cave: A dark and damp cave located in the heart of the Gripshawk mountains, known for its population of Glukenitch creatures.
Lan’ork: A vast and diverse continent known for its Eastern Lagunas, home to the Indogo flamingos. Dragon Head Peninsula: A rugged and mountainous region, home to the Langoat creatures and also known for its rich deposits of dragon ore.
Asgurdy: A sprawling desert region, known for its nomadic tribes who use Saurhse as mounts for transportation.
Golfindely: An idyllic coastal region known for its beautiful beaches and crystal clear waters, home to the Golfindel and Grake creatures.
Magical Schools
Dragonian Magic: A form of magic that is practiced by Dragonriders and Dragon tamers, which involves the manipulation of dragon energy and bonding with dragon companions.
Gripshawk Magic: A form of magic that is practiced by Gripshawks, which involves the manipulation of the natural elements and telepathic communication with other creatures.
Ugling Magic: A form of magic that is practiced by Uglings, which involves the use of charms, spells, and potions to manipulate the physical world.
Guilds
Dragon Riders Guild: A prestigious guild of dragon riders, responsible for maintaining peace and order in the world by using their dragon companions for protection and transportation.
Gripshawk Hunters Guild: A guild of skilled hunters who specialize in hunting and capturing exotic creatures for various purposes.
Ugling Alchemists Guild: A guild of alchemists and potion makers, who create various potions and elixirs for medicinal and magical purposes.
Organizations
The Order of the Buntifluën: A secret organization dedicated to the study and use of Buntifluën artefacts for the betterment of communication and understanding between sentient beings.
The Glubolín Network: A network of individuals who possess Glubolín devices, used for communication and sharing information across long distances.
The Sabulmantium Society: A society of scholars and adventurers who study the properties and uses of Sabulmantium devices for divination and navigation.
Here are a few new invented terms with their potential IPA pronunciations and definitions that would fit in this fantasy world:
Dragons:
Krynn [ ˈkrĭn ] : A subspecies of dragon known for its ability to control and manipulate time.
Creatures:
Kelpies [ ˈkĕl-pēz ] : Aquatic creatures resembling horses, known for their ability to shape-shift and lure unsuspecting victims into the water.
Magical Artefacts:
Dragonwhisper [ ˈdrā-gən-ˌhwis-pər ] : An ancient and powerful magical artifact, which allows the user to communicate and control dragons telepathically.
Necrotalisman [ ˈnĕk-rə-ˈtā-lĭz-mən ] : A magical artifact in the shape of a talisman that grants its wielder the ability to control and summon the dead.
Plants:
Blightthorn [ ˈblīt-ˌthôrn ] : A poisonous plant known for its dark purple flowers and thorny stem, its extract is used in dark magic
Faeleaf [ ˈfā-ˌlēf ] : A rare plant found in the deep forest known for its bright green leaves, its extract is used in healing potions
Locations:
The Shadowland [ ˈshā-dō-ˌland ] : A mysterious and dangerous land overrun by dark magic and controlled by Necromancers.
The Hidden Vale [ ˈhī-dən-ˈvāl ] : A secluded valley located deep in the mountains, home to the reclusive Faeleaf plants.
Organization:
The Necromancers’ Circle [ ˈnĕk-rə-ˈmän-sər-z-ˈsər-kəl ] : A secret organization of powerful necromancers who seek to expand their control over death and the dead.
Here are a few more invented terms with their potential IPA pronunciations and definitions that fit in this fantasy world, having less to do with necromancy, and more with various forms of consciousness or energy manipulation, magical or mythical creatures or species:
Creatures:
Eterneon [ ˈē-tər-ˈnē-ən ] : A species of winged creatures known for their ability to manipulate and harness the energy of the stars, they are highly sought after by astromancers and star-gazers.
Psicon [ ˈsī-ˌkän ] : A species of psychic creatures, known for their ability to read minds and influence emotions.
Magical Artefacts:
Energyshield [ ˈen-ər-jē-ˌshēld ] : A magical artifact that creates a protective barrier around the user, deflecting or absorbing any kind of energy-based attacks.
Empathstone [ ˈĕm-pāth-ˈstōn ] : A small, glowing stone which allows the user to sense and control the emotions of others.
Magical Schools:
Energyshaping [ ˈen-ər-jē-ˌshāp-ing ] : A school of magic that involves the manipulation and control of various forms of energy.
Empathymagic [ ˈĕm-pā-thē-ˈmaj-ik ] : A school of magic that involves the manipulation of emotions and the ability to sense the emotions of others.
Locations:
Eternity’s Edge [ ˈē-tər-nə-tēz-ˈēj] : A remote and mysterious cliff located high in the mountains, known for its strong emanations of star energy and rumored to be home to a hidden community of Eterneons.
Psicon’s Den [ ˈsī-kän-z-ˈdĕn] : A secret cave system located deep within the forest, it is said to be home to a colony of Psicon creatures.
Organizations:
The Energists Guild [ ˈen-ər-jist-z-ˈgild] : A powerful guild of magic users specializing in Energyshaping magic.
The Empath Council [ ˈĕm-pāth-ˈkoun-səl]: A secretive group of Empathymagic users, dedicated to the study and control of emotions.
January 10, 2023 at 10:14 pm #6362In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
write a short story based on the following cloud of words:
pride bet shouted lit wibberly case highly ours unless paid spend twice gay talking heads elizabeth in entries drink kill baker

“Gay baker triumphs over adversity”
Once upon a time, there was a gay baker named Elizabeth who took a great deal of pride in her craft. She spent twice the amount of money on high-quality ingredients and put in extra effort to make her baked goods stand out from the rest. However, her small town was not particularly accepting of the LGBT community, and she often faced discrimination from her neighbors.
One day, a group of men from the town entered her bakery and began shouting homophobic slurs at her. Elizabeth, feeling hurt and humiliated, decided that she would not let their hateful words get to her. She refused to back down and instead, decided to put all of her energy into creating a spectacular cake for the annual county fair.
She worked tirelessly on the cake, putting in long hours and experimenting with new flavors and techniques. The day of the fair finally arrived and Elizabeth brought her entry to be judged. To her surprise and delight, her cake was declared the winner and she was awarded a blue ribbon.
As she stood on stage holding her ribbon, Elizabeth couldn’t help but think about the men who had shouted at her in her bakery. She realized that their words no longer had power over her and she felt a sense of vindication. She knew that she had proven to herself and to her community that she was a skilled baker and a worthy member of society, regardless of her sexual orientation.
Feeling elated, Elizabeth closed the bakery for the day and went to the local bar where she met her friends, and they all drinks together, she was happy and felt like nothing can bring her down, as she went back home she felt like a new person, someone who has overcome prejudice and discrimination, she felt like a winner not just in the fair but in life.
The end.
December 6, 2022 at 2:17 pm #6350In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Transportation
Isaac Stokes 1804-1877
Isaac was born in Churchill, Oxfordshire in 1804, and was the youngest brother of my 4X great grandfather Thomas Stokes. The Stokes family were stone masons for generations in Oxfordshire and Gloucestershire, and Isaac’s occupation was a mason’s labourer in 1834 when he was sentenced at the Lent Assizes in Oxford to fourteen years transportation for stealing tools.
Churchill where the Stokes stonemasons came from: on 31 July 1684 a fire destroyed 20 houses and many other buildings, and killed four people. The village was rebuilt higher up the hill, with stone houses instead of the old timber-framed and thatched cottages. The fire was apparently caused by a baker who, to avoid chimney tax, had knocked through the wall from her oven to her neighbour’s chimney.
Isaac stole a pick axe, the value of 2 shillings and the property of Thomas Joyner of Churchill; a kibbeaux and a trowel value 3 shillings the property of Thomas Symms; a hammer and axe value 5 shillings, property of John Keen of Sarsden.
(The word kibbeaux seems to only exists in relation to Isaac Stokes sentence and whoever was the first to write it was perhaps being creative with the spelling of a kibbo, a miners or a metal bucket. This spelling is repeated in the criminal reports and the newspaper articles about Isaac, but nowhere else).
In March 1834 the Removal of Convicts was announced in the Oxford University and City Herald: Isaac Stokes and several other prisoners were removed from the Oxford county gaol to the Justitia hulk at Woolwich “persuant to their sentences of transportation at our Lent Assizes”.
via digitalpanopticon:
Hulks were decommissioned (and often unseaworthy) ships that were moored in rivers and estuaries and refitted to become floating prisons. The outbreak of war in America in 1775 meant that it was no longer possible to transport British convicts there. Transportation as a form of punishment had started in the late seventeenth century, and following the Transportation Act of 1718, some 44,000 British convicts were sent to the American colonies. The end of this punishment presented a major problem for the authorities in London, since in the decade before 1775, two-thirds of convicts at the Old Bailey received a sentence of transportation – on average 283 convicts a year. As a result, London’s prisons quickly filled to overflowing with convicted prisoners who were sentenced to transportation but had no place to go.
To increase London’s prison capacity, in 1776 Parliament passed the “Hulks Act” (16 Geo III, c.43). Although overseen by local justices of the peace, the hulks were to be directly managed and maintained by private contractors. The first contract to run a hulk was awarded to Duncan Campbell, a former transportation contractor. In August 1776, the Justicia, a former transportation ship moored in the River Thames, became the first prison hulk. This ship soon became full and Campbell quickly introduced a number of other hulks in London; by 1778 the fleet of hulks on the Thames held 510 prisoners.
Demand was so great that new hulks were introduced across the country. There were hulks located at Deptford, Chatham, Woolwich, Gosport, Plymouth, Portsmouth, Sheerness and Cork.The Justitia via rmg collections:
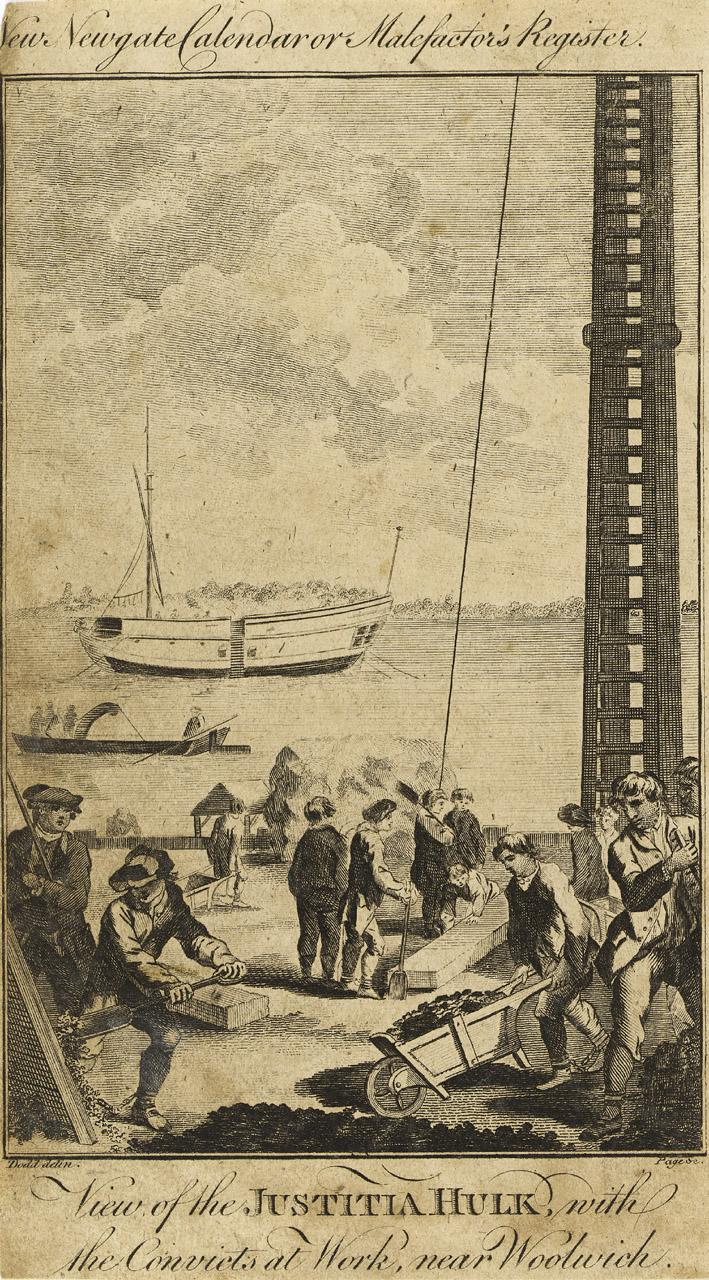

Convicts perform hard labour at the Woolwich Warren. The hulk on the river is the ‘Justitia’. Prisoners were kept on board such ships for months awaiting deportation to Australia. The ‘Justitia’ was a 260 ton prison hulk that had been originally moored in the Thames when the American War of Independence put a stop to the transportation of criminals to the former colonies. The ‘Justitia’ belonged to the shipowner Duncan Campbell, who was the Government contractor who organized the prison-hulk system at that time. Campbell was subsequently involved in the shipping of convicts to the penal colony at Botany Bay (in fact Port Jackson, later Sydney, just to the north) in New South Wales, the ‘first fleet’ going out in 1788.
While searching for records for Isaac Stokes I discovered that another Isaac Stokes was transported to New South Wales in 1835 as well. The other one was a butcher born in 1809, sentenced in London for seven years, and he sailed on the Mary Ann. Our Isaac Stokes sailed on the Lady Nugent, arriving in NSW in April 1835, having set sail from England in December 1834.
Lady Nugent was built at Bombay in 1813. She made four voyages under contract to the British East India Company (EIC). She then made two voyages transporting convicts to Australia, one to New South Wales and one to Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania). (via Wikipedia)
via freesettlerorfelon website:
On 20 November 1834, 100 male convicts were transferred to the Lady Nugent from the Justitia Hulk and 60 from the Ganymede Hulk at Woolwich, all in apparent good health. The Lady Nugent departed Sheerness on 4 December 1834.
SURGEON OLIVER SPROULE
Oliver Sproule kept a Medical Journal from 7 November 1834 to 27 April 1835. He recorded in his journal the weather conditions they experienced in the first two weeks:
‘In the course of the first week or ten days at sea, there were eight or nine on the sick list with catarrhal affections and one with dropsy which I attribute to the cold and wet we experienced during that period beating down channel. Indeed the foremost berths in the prison at this time were so wet from leaking in that part of the ship, that I was obliged to issue dry beds and bedding to a great many of the prisoners to preserve their health, but after crossing the Bay of Biscay the weather became fine and we got the damp beds and blankets dried, the leaks partially stopped and the prison well aired and ventilated which, I am happy to say soon manifested a favourable change in the health and appearance of the men.
Besides the cases given in the journal I had a great many others to treat, some of them similar to those mentioned but the greater part consisted of boils, scalds, and contusions which would not only be too tedious to enter but I fear would be irksome to the reader. There were four births on board during the passage which did well, therefore I did not consider it necessary to give a detailed account of them in my journal the more especially as they were all favourable cases.
Regularity and cleanliness in the prison, free ventilation and as far as possible dry decks turning all the prisoners up in fine weather as we were lucky enough to have two musicians amongst the convicts, dancing was tolerated every afternoon, strict attention to personal cleanliness and also to the cooking of their victuals with regular hours for their meals, were the only prophylactic means used on this occasion, which I found to answer my expectations to the utmost extent in as much as there was not a single case of contagious or infectious nature during the whole passage with the exception of a few cases of psora which soon yielded to the usual treatment. A few cases of scurvy however appeared on board at rather an early period which I can attribute to nothing else but the wet and hardships the prisoners endured during the first three or four weeks of the passage. I was prompt in my treatment of these cases and they got well, but before we arrived at Sydney I had about thirty others to treat.’
The Lady Nugent arrived in Port Jackson on 9 April 1835 with 284 male prisoners. Two men had died at sea. The prisoners were landed on 27th April 1835 and marched to Hyde Park Barracks prior to being assigned. Ten were under the age of 14 years.
The Lady Nugent:
Isaac’s distinguishing marks are noted on various criminal registers and record books:
“Height in feet & inches: 5 4; Complexion: Ruddy; Hair: Light brown; Eyes: Hazel; Marks or Scars: Yes [including] DEVIL on lower left arm, TSIS back of left hand, WS lower right arm, MHDW back of right hand.”
Another includes more detail about Isaac’s tattoos:
“Two slight scars right side of mouth, 2 moles above right breast, figure of the devil and DEVIL and raised mole, lower left arm; anchor, seven dots half moon, TSIS and cross, back of left hand; a mallet, door post, A, mans bust, sun, WS, lower right arm; woman, MHDW and shut knife, back of right hand.”

From How tattoos became fashionable in Victorian England (2019 article in TheConversation by Robert Shoemaker and Zoe Alkar):
“Historical tattooing was not restricted to sailors, soldiers and convicts, but was a growing and accepted phenomenon in Victorian England. Tattoos provide an important window into the lives of those who typically left no written records of their own. As a form of “history from below”, they give us a fleeting but intriguing understanding of the identities and emotions of ordinary people in the past.
As a practice for which typically the only record is the body itself, few systematic records survive before the advent of photography. One exception to this is the written descriptions of tattoos (and even the occasional sketch) that were kept of institutionalised people forced to submit to the recording of information about their bodies as a means of identifying them. This particularly applies to three groups – criminal convicts, soldiers and sailors. Of these, the convict records are the most voluminous and systematic.
Such records were first kept in large numbers for those who were transported to Australia from 1788 (since Australia was then an open prison) as the authorities needed some means of keeping track of them.”On the 1837 census Isaac was working for the government at Illiwarra, New South Wales. This record states that he arrived on the Lady Nugent in 1835. There are three other indent records for an Isaac Stokes in the following years, but the transcriptions don’t provide enough information to determine which Isaac Stokes it was. In April 1837 there was an abscondment, and an arrest/apprehension in May of that year, and in 1843 there was a record of convict indulgences.
From the Australian government website regarding “convict indulgences”:
“By the mid-1830s only six per cent of convicts were locked up. The vast majority worked for the government or free settlers and, with good behaviour, could earn a ticket of leave, conditional pardon or and even an absolute pardon. While under such orders convicts could earn their own living.”
In 1856 in Camden, NSW, Isaac Stokes married Catherine Daly. With no further information on this record it would be impossible to know for sure if this was the right Isaac Stokes. This couple had six children, all in the Camden area, but none of the records provided enough information. No occupation or place or date of birth recorded for Isaac Stokes.
I wrote to the National Library of Australia about the marriage record, and their reply was a surprise! Issac and Catherine were married on 30 September 1856, at the house of the Rev. Charles William Rigg, a Methodist minister, and it was recorded that Isaac was born in Edinburgh in 1821, to parents James Stokes and Sarah Ellis! The age at the time of the marriage doesn’t match Isaac’s age at death in 1877, and clearly the place of birth and parents didn’t match either. Only his fathers occupation of stone mason was correct. I wrote back to the helpful people at the library and they replied that the register was in a very poor condition and that only two and a half entries had survived at all, and that Isaac and Catherines marriage was recorded over two pages.
I searched for an Isaac Stokes born in 1821 in Edinburgh on the Scotland government website (and on all the other genealogy records sites) and didn’t find it. In fact Stokes was a very uncommon name in Scotland at the time. I also searched Australian immigration and other records for another Isaac Stokes born in Scotland or born in 1821, and found nothing. I was unable to find a single record to corroborate this mysterious other Isaac Stokes.
As the age at death in 1877 was correct, I assume that either Isaac was lying, or that some mistake was made either on the register at the home of the Methodist minster, or a subsequent mistranscription or muddle on the remnants of the surviving register. Therefore I remain convinced that the Camden stonemason Isaac Stokes was indeed our Isaac from Oxfordshire.
I found a history society newsletter article that mentioned Isaac Stokes, stone mason, had built the Glenmore church, near Camden, in 1859.
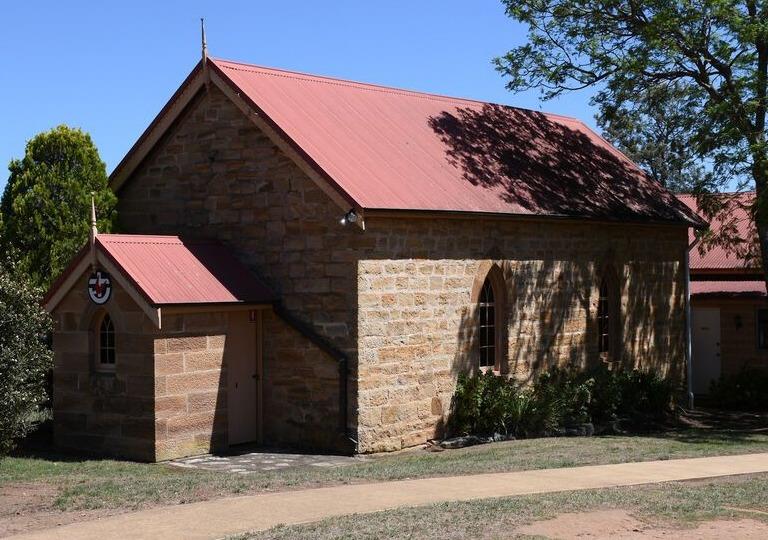

From the Wollondilly museum April 2020 newsletter:

From the Camden History website:
“The stone set over the porch of Glenmore Church gives the date of 1860. The church was begun in 1859 on land given by Joseph Moore. James Rogers of Picton was given the contract to build and local builder, Mr. Stokes, carried out the work. Elizabeth Moore, wife of Edward, laid the foundation stone. The first service was held on 19th March 1860. The cemetery alongside the church contains the headstones and memorials of the areas early pioneers.”
Isaac died on the 3rd September 1877. The inquest report puts his place of death as Bagdelly, near to Camden, and another death register has put Cambelltown, also very close to Camden. His age was recorded as 71 and the inquest report states his cause of death was “rupture of one of the large pulmonary vessels of the lung”. His wife Catherine died in childbirth in 1870 at the age of 43.
Isaac and Catherine’s children:
William Stokes 1857-1928
Catherine Stokes 1859-1846
Sarah Josephine Stokes 1861-1931
Ellen Stokes 1863-1932
Rosanna Stokes 1865-1919
Louisa Stokes 1868-1844.
It’s possible that Catherine Daly was a transported convict from Ireland.
Some time later I unexpectedly received a follow up email from The Oaks Heritage Centre in Australia.
“The Gaudry papers which we have in our archive record him (Isaac Stokes) as having built: the church, the school and the teachers residence. Isaac is recorded in the General return of convicts: 1837 and in Grevilles Post Office directory 1872 as a mason in Glenmore.”
 November 18, 2022 at 4:47 pm #6348
November 18, 2022 at 4:47 pm #6348In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Wong Sang
Wong Sang was born in China in 1884. In October 1916 he married Alice Stokes in Oxford.
Alice was the granddaughter of William Stokes of Churchill, Oxfordshire and William was the brother of Thomas Stokes the wheelwright (who was my 3X great grandfather). In other words Alice was my second cousin, three times removed, on my fathers paternal side.
Wong Sang was an interpreter, according to the baptism registers of his children and the Dreadnought Seamen’s Hospital admission registers in 1930. The hospital register also notes that he was employed by the Blue Funnel Line, and that his address was 11, Limehouse Causeway, E 14. (London)
“The Blue Funnel Line offered regular First-Class Passenger and Cargo Services From the UK to South Africa, Malaya, China, Japan, Australia, Java, and America. Blue Funnel Line was Owned and Operated by Alfred Holt & Co., Liverpool.
The Blue Funnel Line, so-called because its ships have a blue funnel with a black top, is more appropriately known as the Ocean Steamship Company.”Wong Sang and Alice’s daughter, Frances Eileen Sang, was born on the 14th July, 1916 and baptised in 1920 at St Stephen in Poplar, Tower Hamlets, London. The birth date is noted in the 1920 baptism register and would predate their marriage by a few months, although on the death register in 1921 her age at death is four years old and her year of birth is recorded as 1917.
Charles Ronald Sang was baptised on the same day in May 1920, but his birth is recorded as April of that year. The family were living on Morant Street, Poplar.
James William Sang’s birth is recorded on the 1939 census and on the death register in 2000 as being the 8th March 1913. This definitely would predate the 1916 marriage in Oxford.
William Norman Sang was born on the 17th October 1922 in Poplar.
Alice and the three sons were living at 11, Limehouse Causeway on the 1939 census, the same address that Wong Sang was living at when he was admitted to Dreadnought Seamen’s Hospital on the 15th January 1930. Wong Sang died in the hospital on the 8th March of that year at the age of 46.
Alice married John Patterson in 1933 in Stepney. John was living with Alice and her three sons on Limehouse Causeway on the 1939 census and his occupation was chef.
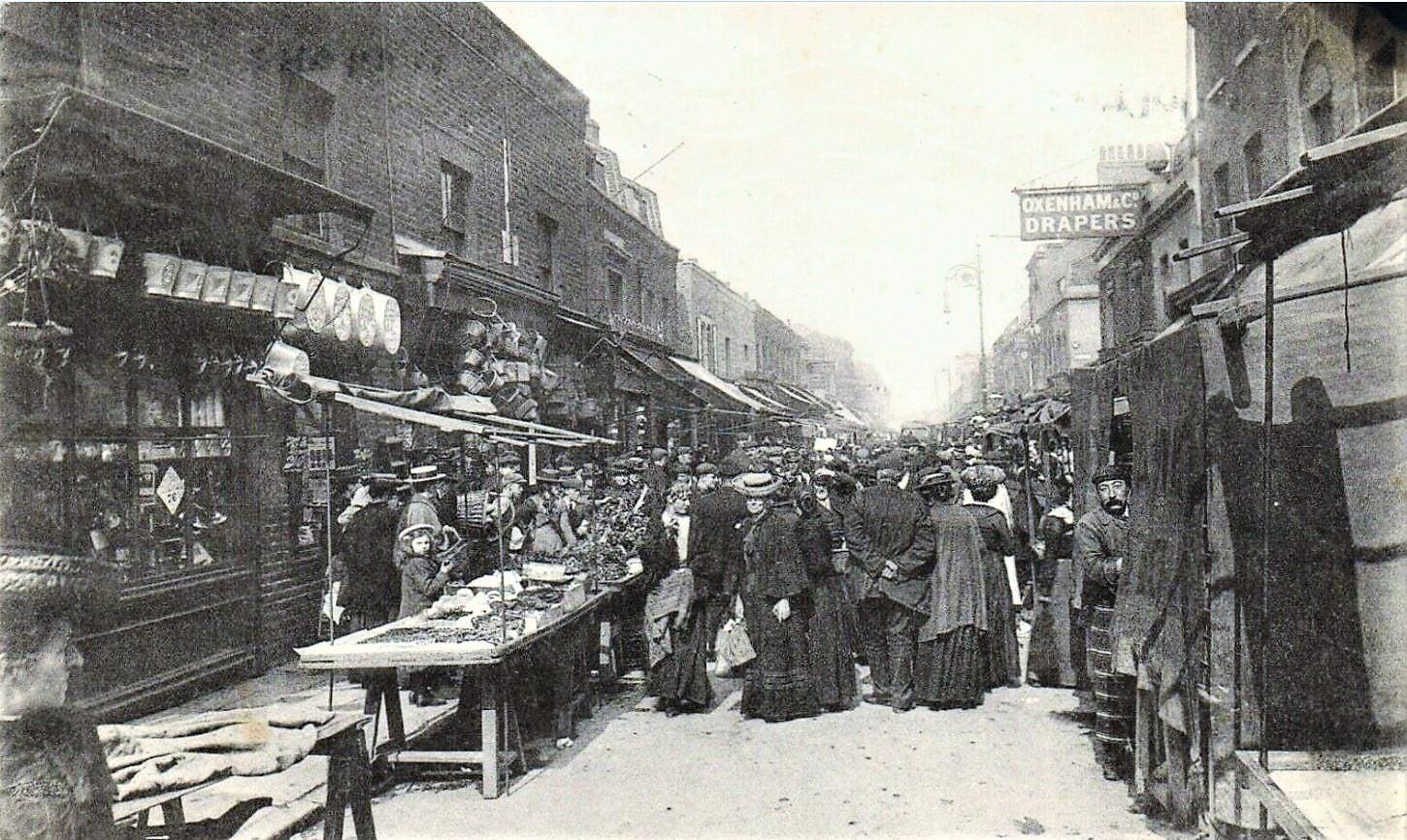
Via Old London Photographs:
“Limehouse Causeway is a street in east London that was the home to the original Chinatown of London. A combination of bomb damage during the Second World War and later redevelopment means that almost nothing is left of the original buildings of the street.”
Limehouse Causeway in 1925:

From The Story of Limehouse’s Lost Chinatown, poplarlondon website:
“Limehouse was London’s first Chinatown, home to a tightly-knit community who were demonised in popular culture and eventually erased from the cityscape.
As recounted in the BBC’s ‘Our Greatest Generation’ series, Connie was born to a Chinese father and an English mother in early 1920s Limehouse, where she used to play in the street with other British and British-Chinese children before running inside for teatime at one of their houses.
Limehouse was London’s first Chinatown between the 1880s and the 1960s, before the current Chinatown off Shaftesbury Avenue was established in the 1970s by an influx of immigrants from Hong Kong.
Connie’s memories of London’s first Chinatown as an “urban village” paint a very different picture to the seedy area portrayed in early twentieth century novels.
The pyramid in St Anne’s church marked the entrance to the opium den of Dr Fu Manchu, a criminal mastermind who threatened Western society by plotting world domination in a series of novels by Sax Rohmer.
Thomas Burke’s Limehouse Nights cemented stereotypes about prostitution, gambling and violence within the Chinese community, and whipped up anxiety about sexual relationships between Chinese men and white women.
Though neither novelist was familiar with the Chinese community, their depictions made Limehouse one of the most notorious areas of London.
Travel agent Thomas Cook even organised tours of the area for daring visitors, despite the rector of Limehouse warning that “those who look for the Limehouse of Mr Thomas Burke simply will not find it.”
All that remains is a handful of Chinese street names, such as Ming Street, Pekin Street, and Canton Street — but what was Limehouse’s chinatown really like, and why did it get swept away?
Chinese migration to Limehouse
Chinese sailors discharged from East India Company ships settled in the docklands from as early as the 1780s.
By the late nineteenth century, men from Shanghai had settled around Pennyfields Lane, while a Cantonese community lived on Limehouse Causeway.
Chinese sailors were often paid less and discriminated against by dock hirers, and so began to diversify their incomes by setting up hand laundry services and restaurants.
Old photographs show shopfronts emblazoned with Chinese characters with horse-drawn carts idling outside or Chinese men in suits and hats standing proudly in the doorways.
In oral histories collected by Yat Ming Loo, Connie’s husband Leslie doesn’t recall seeing any Chinese women as a child, since male Chinese sailors settled in London alone and married working-class English women.
In the 1920s, newspapers fear-mongered about interracial marriages, crime and gambling, and described chinatown as an East End “colony.”
Ironically, Chinese opium-smoking was also demonised in the press, despite Britain waging war against China in the mid-nineteenth century for suppressing the opium trade to alleviate addiction amongst its people.
The number of Chinese people who settled in Limehouse was also greatly exaggerated, and in reality only totalled around 300.
The real Chinatown
Although the press sought to characterise Limehouse as a monolithic Chinese community in the East End, Connie remembers seeing people of all nationalities in the shops and community spaces in Limehouse.
She doesn’t remember feeling discriminated against by other locals, though Connie does recall having her face measured and IQ tested by a member of the British Eugenics Society who was conducting research in the area.
Some of Connie’s happiest childhood memories were from her time at Chung-Hua Club, where she learned about Chinese culture and language.
Why did Chinatown disappear?
The caricature of Limehouse’s Chinatown as a den of vice hastened its erasure.
Police raids and deportations fuelled by the alarmist media coverage threatened the Chinese population of Limehouse, and slum clearance schemes to redevelop low-income areas dispersed Chinese residents in the 1930s.
The Defence of the Realm Act imposed at the beginning of the First World War criminalised opium use, gave the authorities increased powers to deport Chinese people and restricted their ability to work on British ships.
Dwindling maritime trade during World War II further stripped Chinese sailors of opportunities for employment, and any remnants of Chinatown were destroyed during the Blitz or erased by postwar development schemes.”
Wong Sang 1884-1930
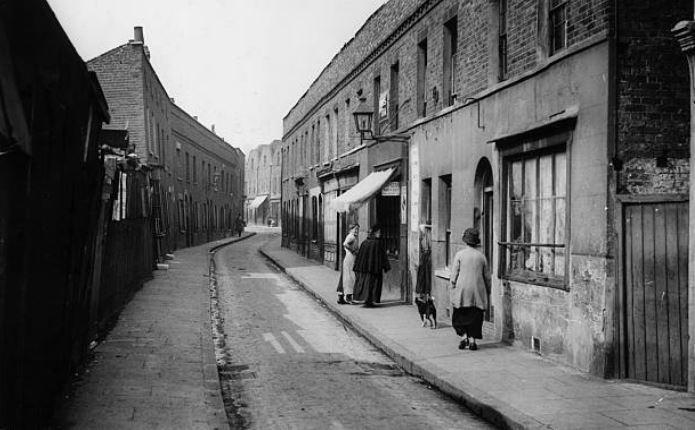
The year 1918 was a troublesome one for Wong Sang, an interpreter and shipping agent for Blue Funnel Line. The Sang family were living at 156, Chrisp Street.
Chrisp Street, Poplar, in 1913 via Old London Photographs:

In February Wong Sang was discharged from a false accusation after defending his home from potential robbers.
East End News and London Shipping Chronicle – Friday 15 February 1918:

In August of that year he was involved in an incident that left him unconscious.
Faringdon Advertiser and Vale of the White Horse Gazette – Saturday 31 August 1918:

Wong Sang is mentioned in an 1922 article about “Oriental London”.
London and China Express – Thursday 09 February 1922:

A photograph of the Chee Kong Tong Chinese Freemason Society mentioned in the above article, via Old London Photographs:

Wong Sang was recommended by the London Metropolitan Police in 1928 to assist in a case in Wellingborough, Northampton.
Difficulty of Getting an Interpreter: Northampton Mercury – Friday 16 March 1928:


The difficulty was that “this man speaks the Cantonese language only…the Northeners and the Southerners in China have differing languages and the interpreter seemed to speak one that was in between these two.”
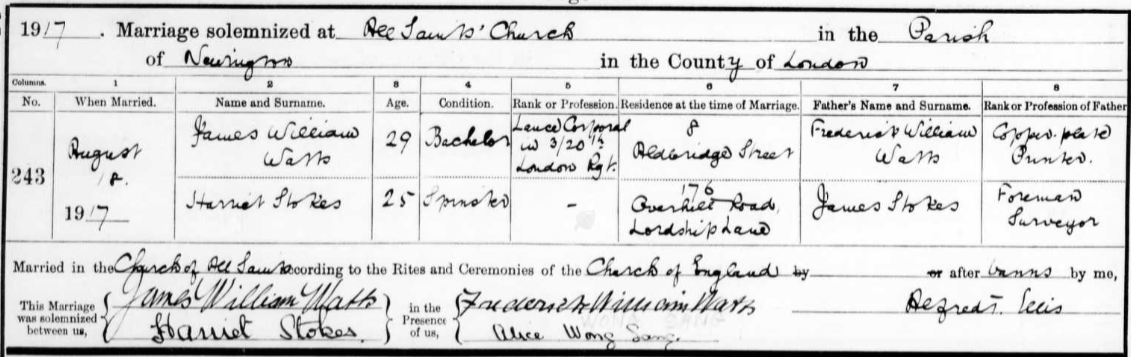
In 1917, Alice Wong Sang was a witness at her sister Harriet Stokes marriage to James William Watts in Southwark, London. Their father James Stokes occupation on the marriage register is foreman surveyor, but on the census he was a council roadman or labourer. (I initially rejected this as the correct marriage for Harriet because of the discrepancy with the occupations. Alice Wong Sang as a witness confirmed that it was indeed the correct one.)
James William Sang 1913-2000 was a clock fitter and watch assembler (on the 1939 census). He married Ivy Laura Fenton in 1963 in Sidcup, Kent. James died in Southwark in 2000.
Charles Ronald Sang 1920-1974 was a draughtsman (1939 census). He married Eileen Burgess in 1947 in Marylebone. Charles and Eileen had two sons: Keith born in 1951 and Roger born in 1952. He died in 1974 in Hertfordshire.
William Norman Sang 1922-2000 was a clerk and telephone operator (1939 census). William enlisted in the Royal Artillery in 1942. He married Lily Mullins in 1949 in Bethnal Green, and they had three daughters: Marion born in 1950, Christine in 1953, and Frances in 1959. He died in Redbridge in 2000.
I then found another two births registered in Poplar by Alice Sang, both daughters. Doris Winifred Sang was born in 1925, and Patricia Margaret Sang was born in 1933 ~ three years after Wong Sang’s death. Neither of the these daughters were on the 1939 census with Alice, John Patterson and the three sons. Margaret had presumably been evacuated because of the war to a family in Taunton, Somerset. Doris would have been fourteen and I have been unable to find her in 1939 (possibly because she died in 2017 and has not had the redaction removed yet on the 1939 census as only deceased people are viewable).
Doris Winifred Sang 1925-2017 was a nursing sister. She didn’t marry, and spent a year in USA between 1954 and 1955. She stayed in London, and died at the age of ninety two in 2017.
Patricia Margaret Sang 1933-1998 was also a nurse. She married Patrick L Nicely in Stepney in 1957. Patricia and Patrick had five children in London: Sharon born 1959, Donald in 1960, Malcolm was born and died in 1966, Alison was born in 1969 and David in 1971.
I was unable to find a birth registered for Alice’s first son, James William Sang (as he appeared on the 1939 census). I found Alice Stokes on the 1911 census as a 17 year old live in servant at a tobacconist on Pekin Street, Limehouse, living with Mr Sui Fong from Hong Kong and his wife Sarah Sui Fong from Berlin. I looked for a birth registered for James William Fong instead of Sang, and found it ~ mothers maiden name Stokes, and his date of birth matched the 1939 census: 8th March, 1913.
On the 1921 census, Wong Sang is not listed as living with them but it is mentioned that Mr Wong Sang was the person returning the census. Also living with Alice and her sons James and Charles in 1921 are two visitors: (Florence) May Stokes, 17 years old, born in Woodstock, and Charles Stokes, aged 14, also born in Woodstock. May and Charles were Alice’s sister and brother.
I found Sharon Nicely on social media and she kindly shared photos of Wong Sang and Alice Stokes:

 November 13, 2022 at 10:29 pm #6345
November 13, 2022 at 10:29 pm #6345In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Crime and Punishment in Tetbury
I noticed that there were quite a number of Brownings of Tetbury in the newspaper archives involved in criminal activities while doing a routine newspaper search to supplement the information in the usual ancestry records. I expanded the tree to include cousins, and offsping of cousins, in order to work out who was who and how, if at all, these individuals related to our Browning family.
I was expecting to find some of our Brownings involved in the Swing Riots in Tetbury in 1830, but did not. Most of our Brownings (including cousins) were stone masons. Most of the rioters in 1830 were agricultural labourers.
The Browning crimes are varied, and by todays standards, not for the most part terribly serious ~ you would be unlikely to receive a sentence of hard labour for being found in an outhouse with the intent to commit an unlawful act nowadays, or for being drunk.
The central character in this chapter is Isaac Browning (my 4x great grandfather), who did not appear in any criminal registers, but the following individuals can be identified in the family structure through their relationship to him.
RICHARD LOCK BROWNING born in 1853 was Isaac’s grandson, his son George’s son. Richard was a mason. In 1879 he and Henry Browning of the same age were sentenced to one month hard labour for stealing two pigeons in Tetbury. Henry Browning was Isaac’s nephews son.
In 1883 Richard Browning, mason of Tetbury, was charged with obtaining food and lodging under false pretences, but was found not guilty and acquitted.
In 1884 Richard Browning, mason of Tetbury, was sentenced to one month hard labour for game trespass.Richard had been fined a number of times in Tetbury:

Richard Lock Browning was five feet eight inches tall, dark hair, grey eyes, an oval face and a dark complexion. He had two cuts on the back of his head (in February 1879) and a scar on his right eyebrow.
HENRY BROWNING, who was stealing pigeons with Richard Lock Browning in 1879, (Isaac’s brother Williams grandson, son of George Browning and his wife Charity) was charged with being drunk in 1882 and ordered to pay a fine of one shilling and costs of fourteen shillings, or seven days hard labour.
Henry was found guilty of gaming in the highway at Tetbury in 1872 and was sentenced to seven days hard labour. In 1882 Henry (who was also a mason) was charged with assault but discharged.
Henry was five feet five inches tall, brown hair and brown eyes, a long visage and a fresh complexion.
Henry emigrated with his daughter to Canada in 1913, and died in Vancouver in 1919.THOMAS BUCKINGHAM 1808-1846 (Isaacs daughter Janes husband) was charged with stealing a black gelding in Tetbury in 1838. No true bill. (A “no true bill” means the jury did not find probable cause to continue a case.)
Thomas did however neglect to pay his taxes in 1832:

LEWIN BUCKINGHAM (grandson of Isaac, his daughter Jane’s son) was found guilty in 1846 stealing two fowls in Tetbury when he was sixteen years old.
In 1846 he was sentence to one month hard labour (or pay ten shillings fine and ten shillings costs) for loitering with the intent to trespass in search of conies.
A year later in 1847, he and three other young men were sentenced to four months hard labour for larceny.
Lewin was five feet three inches tall, with brown hair and brown eyes, long visage, sallow complexion, and had a scar on his left arm.JOHN BUCKINGHAM born circa 1832, a Tetbury labourer (Isaac’s grandson, Lewin’s brother) was sentenced to six weeks hard labour for larceny in 1855 for stealing a duck in Cirencester. The notes on the register mention that he had been employed by Mr LOCK, Angel Inn. (John’s grandmother was Mary Lock so this is likely a relative).
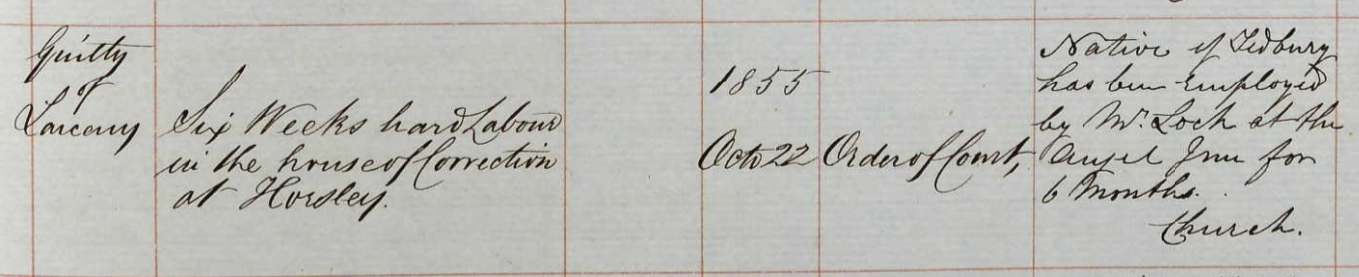
The previous year in 1854 John was sentenced to one month or a one pound fine for assaulting and beating W. Wood.
John was five feet eight and three quarter inches tall, light brown hair and grey eyes, an oval visage and a fresh complexion. He had a scar on his left arm and inside his right knee.JOSEPH PERRET was born circa 1831 and he was a Tetbury labourer. (He was Isaac’s granddaughter Charlotte Buckingham’s husband)
In 1855 he assaulted William Wood and was sentenced to one month or a two pound ten shilling fine. Was it the same W Wood that his wifes cousin John assaulted the year before?
In 1869 Joseph was sentenced to one month hard labour for feloniously receiving a cupboard known to be stolen.JAMES BUCKINGAM born circa 1822 in Tetbury was a shoemaker. (Isaac’s nephew, his sister Hannah’s son)
In 1854 the Tetbury shoemaker was sentenced to four months hard labour for stealing 30 lbs of lead off someones house.
In 1856 the Tetbury shoemaker received two months hard labour or pay £2 fine and 12 s costs for being found in pursuit of game.
In 1868 he was sentenced to two months hard labour for stealing a gander. A unspecified previous conviction is noted.
1871 the Tetbury shoemaker was found in an outhouse for an unlawful purpose and received ten days hard labour. The register notes that his sister is Mrs Cook, the Green, Tetbury. (James sister Prudence married Thomas Cook)
James sister Charlotte married a shoemaker and moved to UTAH.
James was five feet eight inches tall, dark hair and blue eyes, a long visage and a florid complexion. He had a scar on his forehead and a mole on the right side of his neck and abdomen, and a scar on the right knee.October 23, 2022 at 6:57 am #6340In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Wheelwrights of Broadway
Thomas Stokes 1816-1885
Frederick Stokes 1845-1917

Stokes Wheelwrights. Fred on left of wheel, Thomas his father on right.
Thomas Stokes
Thomas Stokes was born in Bicester, Oxfordshire in 1816. He married Eliza Browning (born in 1814 in Tetbury, Gloucestershire) in Gloucester in 1840 Q3. Their first son William was baptised in Chipping Hill, Witham, Essex, on 3 Oct 1841. This seems a little unusual, and I can’t find Thomas and Eliza on the 1841 census. However both the 1851 and 1861 census state that William was indeed born in Essex.
In 1851 Thomas and Eliza were living in Bledington, Gloucestershire, and Thomas was a journeyman carpenter.
Note that a journeyman does not mean someone who moved around a lot. A journeyman was a tradesman who had served his trade apprenticeship and mastered his craft, not bound to serve a master, but originally hired by the day. The name derives from the French for day – jour.
Also on the 1851 census: their daughter Susan, born in Churchill Oxfordshire in 1844; son Frederick born in Bledington Gloucestershire in 1846; daughter Louisa born in Foxcote Oxfordshire in 1849; and 2 month old daughter Harriet born in Bledington in 1851.
On the 1861 census Thomas and Eliza were living in Evesham, Worcestershire, and daughter Susan was no longer living at home, but William, Fred, Louisa and Harriet were, as well as daughter Emily born in Churchill Oxfordshire in 1856. Thomas was a wheelwright.
On the 1871 census Thomas and Eliza were still living in Evesham, and Thomas was a wheelwright employing three apprentices. Son Fred, also a wheelwright, and his wife Ann Rebecca live with them.
Mr Stokes, wheelwright, was found guilty of reprehensible conduct in concealing the fact that small-pox existed in his house, according to a mention in The Oxfordshire Weekly News on Wednesday 19 February 1873:

From Paul Weaver’s ancestry website:
“It was Thomas Stokes who built the first “Famous Vale of Evesham Light Gardening Dray for a Half-Legged Horse to Trot” (the quotation is from his account book), the forerunner of many that became so familiar a sight in the towns and villages from the 1860s onwards. He built many more for the use of the Vale gardeners.
Thomas also had long-standing business dealings with the people of the circus and fairgrounds, and had a contract to effect necessary repairs and renewals to their waggons whenever they visited the district. He built living waggons for many of the show people’s families as well as shooting galleries and other equipment peculiar to the trade of his wandering customers, and among the names figuring in his books are some still familiar today, such as Wilsons and Chipperfields.
He is also credited with inventing the wooden “Mushroom” which was used by housewives for many years to darn socks. He built and repaired all kinds of vehicles for the gentry as well as for the circus and fairground travellers.
Later he lived with his wife at Merstow Green, Evesham, in a house adjoining the Almonry.”
An excerpt from the book Evesham Inns and Signs by T.J.S. Baylis:

The Old Red Horse, Evesham:
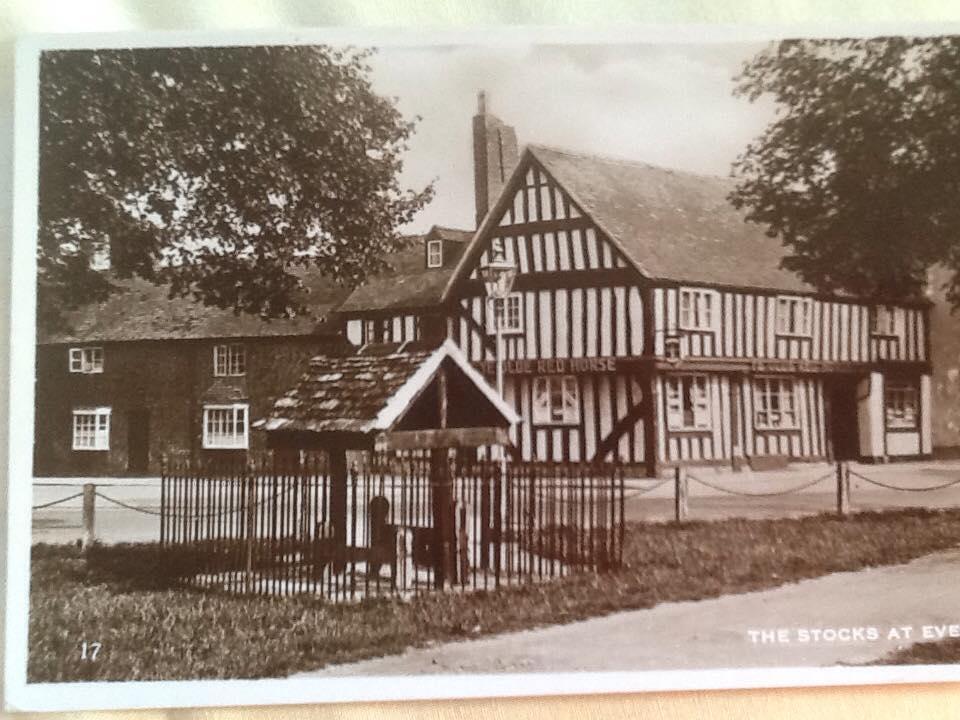

Thomas died in 1885 aged 68 of paralysis, bronchitis and debility. His wife Eliza a year later in 1886.
Frederick Stokes
In Worcester in 1870 Fred married Ann Rebecca Day, who was born in Evesham in 1845.
Ann Rebecca Day:
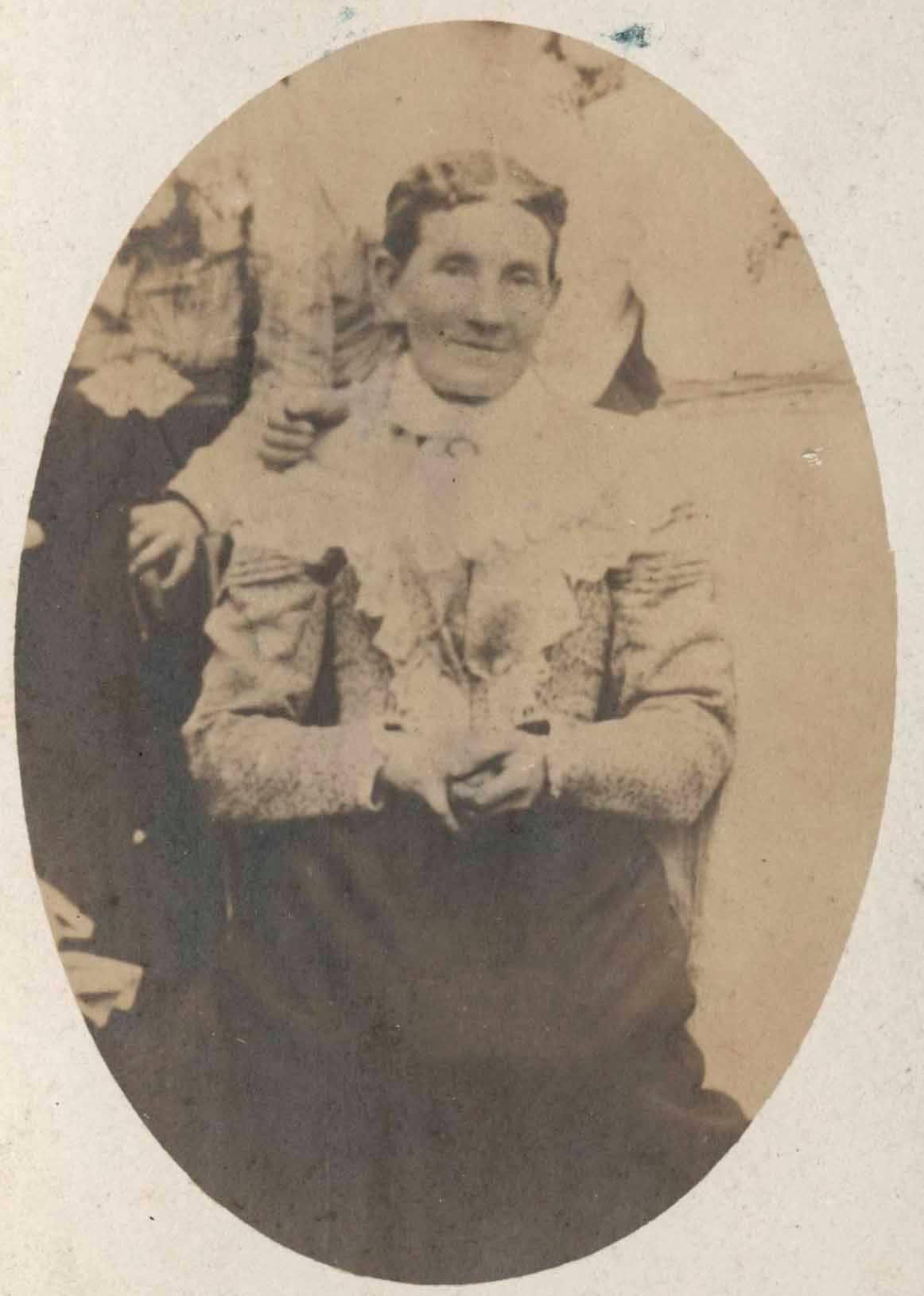
In 1871 Fred was still living with his parents in Evesham, with his wife Ann Rebecca as well as their three month old daughter Annie Elizabeth. Fred and Ann (referred to as Rebecca) moved to La Quinta on Main Street, Broadway.
Rebecca Stokes in the doorway of La Quinta on Main Street Broadway, with her grandchildren Ralph and Dolly Edwards:
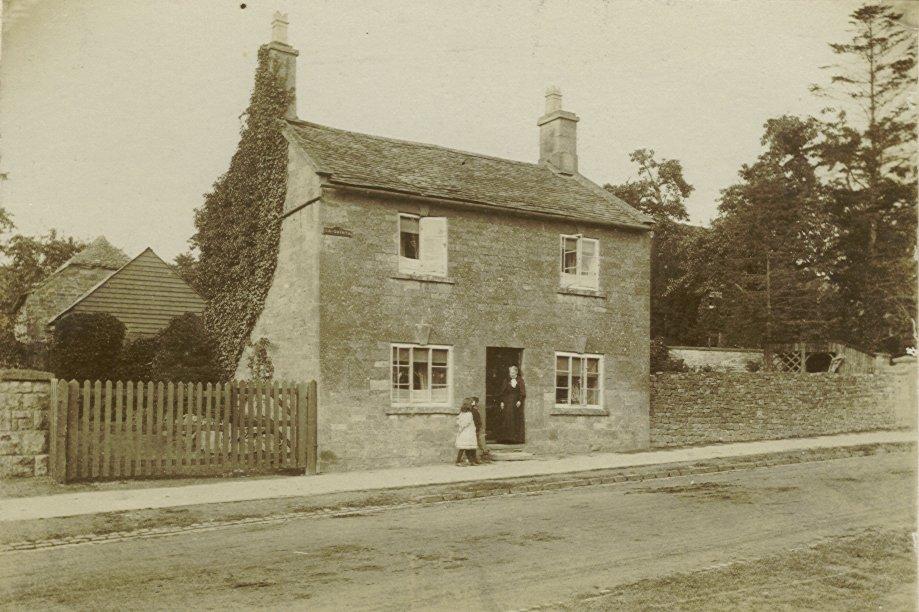

Fred was a wheelwright employing one man on the 1881 census. In 1891 they were still in Broadway, Fred’s occupation was wheelwright and coach painter, as well as his fifteen year old son Frederick.
In the Evesham Journal on Saturday 10 December 1892 it was reported that “Two cases of scarlet fever, the children of Mr. Stokes, wheelwright, Broadway, were certified by Mr. C. W. Morris to be isolated.”
Still in Broadway in 1901 and Fred’s son Albert was also a wheelwright. By 1911 Fred and Rebecca had only one son living at home in Broadway, Reginald, who was a coach painter. Fred was still a wheelwright aged 65.
Fred’s signature on the 1911 census:

Rebecca died in 1912 and Fred in 1917.
Fred Stokes:

In the book Evesham to Bredon From Old Photographs By Fred Archer:
 October 19, 2022 at 6:46 am #6336
October 19, 2022 at 6:46 am #6336In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The Hamstall Ridware Connection
Stubbs and Woods
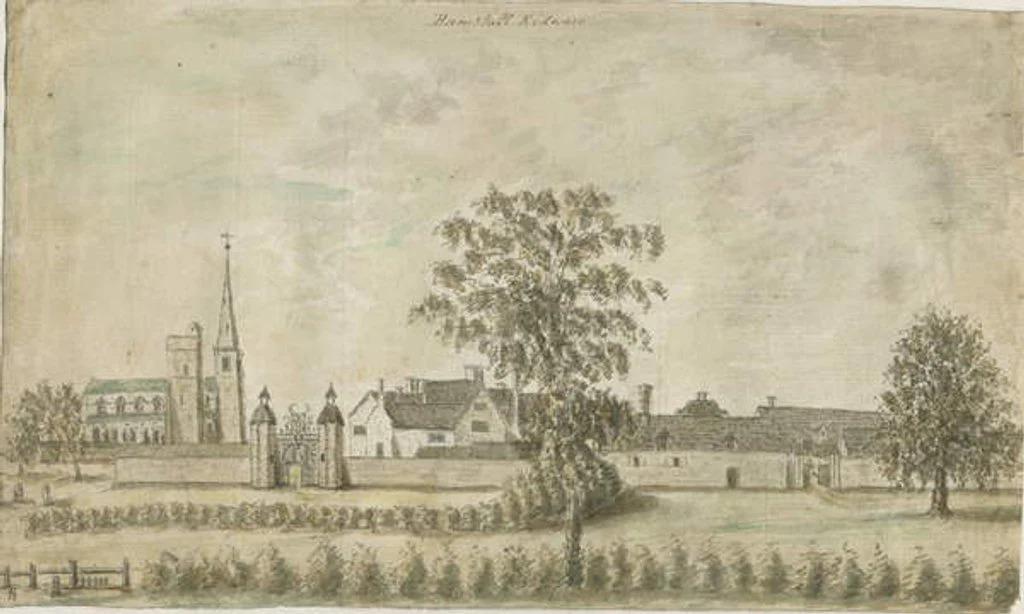 Hamstall Ridware
Hamstall RidwareCharles Tomlinson‘s (1847-1907) wife Emma Grattidge (1853-1911) was born in Wolverhampton, the daughter and youngest child of William Grattidge (1820-1887) born in Foston, Derbyshire, and Mary Stubbs (1819-1880), born in Burton on Trent, daughter of Solomon Stubbs.
Solomon Stubbs (1781-1857) was born in Hamstall Ridware in 1781, the son of Samuel and Rebecca. Samuel Stubbs (1743-) and Rebecca Wood (1754-) married in 1769 in Darlaston. Samuel and Rebecca had six other children, all born in Darlaston. Sadly four of them died in infancy. Son John was born in 1779 in Darlaston and died two years later in Hamstall Ridware in 1781, the same year that Solomon was born there.
But why did they move to Hamstall Ridware?
Samuel Stubbs was born in 1743 in Curdworth, Warwickshire (near to Birmingham). I had made a mistake on the tree (along with all of the public trees on the Ancestry website) and had Rebecca Wood born in Cheddleton, Staffordshire. Rebecca Wood from Cheddleton was also born in 1843, the right age for the marriage. The Rebecca Wood born in Darlaston in 1754 seemed too young, at just fifteen years old at the time of the marriage. I couldn’t find any explanation for why a woman from Cheddleton would marry in Darlaston and then move to Hamstall Ridware. People didn’t usually move around much other than intermarriage with neighbouring villages, especially women. I had a closer look at the Darlaston Rebecca, and did a search on her father William Wood. I found his 1784 will online in which he mentions his daughter Rebecca, wife of Samuel Stubbs. Clearly the right Rebecca Wood was the one born in Darlaston, which made much more sense.
An excerpt from William Wood’s 1784 will mentioning daughter Rebecca married to Samuel Stubbs:

But why did they move to Hamstall Ridware circa 1780?
I had not intially noticed that Solomon Stubbs married again the year after his wife Phillis Lomas (1787-1844) died. Solomon married Charlotte Bell in 1845 in Burton on Trent and on the marriage register, Solomon’s father Samuel Stubbs occupation was mentioned: Samuel was a buckle maker.
Marriage of Solomon Stubbs and Charlotte Bell, father Samuel Stubbs buckle maker:

A rudimentary search on buckle making in the late 1700s provided a possible answer as to why Samuel and Rebecca left Darlaston in 1781. Shoe buckles had gone out of fashion, and by 1781 there were half as many buckle makers in Wolverhampton as there had been previously.
“Where there were 127 buckle makers at work in Wolverhampton, 68 in Bilston and 58 in Birmingham in 1770, their numbers had halved in 1781.”
via “historywebsite”(museum/metalware/steel)
Steel buckles had been the height of fashion, and the trade became enormous in Wolverhampton. Wolverhampton was a steel working town, renowned for its steel jewellery which was probably of many types. The trade directories show great numbers of “buckle makers”. Steel buckles were predominantly made in Wolverhampton: “from the late 1760s cut steel comes to the fore, from the thriving industry of the Wolverhampton area”. Bilston was also a great centre of buckle making, and other areas included Walsall. (It should be noted that Darlaston, Walsall, Bilston and Wolverhampton are all part of the same area)
In 1860, writing in defence of the Wolverhampton Art School, George Wallis talks about the cut steel industry in Wolverhampton. Referring to “the fine steel workers of the 17th and 18th centuries” he says: “Let them remember that 100 years ago [sc. c. 1760] a large trade existed with France and Spain in the fine steel goods of Birmingham and Wolverhampton, of which the latter were always allowed to be the best both in taste and workmanship. … A century ago French and Spanish merchants had their houses and agencies at Birmingham for the purchase of the steel goods of Wolverhampton…..The Great Revolution in France put an end to the demand for fine steel goods for a time and hostile tariffs finished what revolution began”.
The next search on buckle makers, Wolverhampton and Hamstall Ridware revealed an unexpected connecting link.
In Riotous Assemblies: Popular Protest in Hanoverian England by Adrian Randall:


In Walsall in 1750 on “Restoration Day” a crowd numbering 300 assembled, mostly buckle makers, singing Jacobite songs and other rebellious and riotous acts. The government was particularly worried about a curious meeting known as the “Jubilee” in Hamstall Ridware, which may have been part of a conspiracy for a Jacobite uprising.
But this was thirty years before Samuel and Rebecca moved to Hamstall Ridware and does not help to explain why they moved there around 1780, although it does suggest connecting links.
Rebecca’s father, William Wood, was a brickmaker. This was stated at the beginning of his will. On closer inspection of the will, he was a brickmaker who owned four acres of brick kilns, as well as dwelling houses, shops, barns, stables, a brewhouse, a malthouse, cattle and land.
A page from the 1784 will of William Wood:

The 1784 will of William Wood of Darlaston:
I William Wood the elder of Darlaston in the county of Stafford, brickmaker, being of sound and disposing mind memory and understanding (praised be to god for the same) do make publish and declare my last will and testament in manner and form following (that is to say) {after debts and funeral expense paid etc} I give to my loving wife Mary the use usage wear interest and enjoyment of all my goods chattels cattle stock in trade ~ money securities for money personal estate and effects whatsoever and wheresoever to hold unto her my said wife for and during the term of her natural life providing she so long continues my widow and unmarried and from or after her decease or intermarriage with any future husband which shall first happen.
Then I give all the said goods chattels cattle stock in trade money securites for money personal estate and effects unto my son Abraham Wood absolutely and forever. Also I give devise and bequeath unto my said wife Mary all that my messuages tenement or dwelling house together with the malthouse brewhouse barn stableyard garden and premises to the same belonging situate and being at Darlaston aforesaid and now in my own possession. Also all that messuage tenement or dwelling house together with the shop garden and premises with the appurtenances to the same ~ belonging situate in Darlaston aforesaid and now in the several holdings or occupation of George Knowles and Edward Knowles to hold the aforesaid premises and every part thereof with the appurtenances to my said wife Mary for and during the term of her natural life provided she so long continues my widow and unmarried. And from or after her decease or intermarriage with a future husband which shall first happen. Then I give and devise the aforesaid premises and every part thereof with the appurtenances unto my said son Abraham Wood his heirs and assigns forever.
Also I give unto my said wife all that piece or parcel of land or ground inclosed and taken out of Heath Field in the parish of Darlaston aforesaid containing four acres or thereabouts (be the same more or less) upon which my brick kilns erected and now in my own possession. To hold unto my said wife Mary until my said son Abraham attains his age of twenty one years if she so long continues my widow and unmarried as aforesaid and from and immediately after my said son Abraham attaining his age of twenty one years or my said wife marrying again as aforesaid which shall first happen then I give the said piece or parcel of land or ground and premises unto my said son Abraham his heirs and assigns forever.
And I do hereby charge all the aforesaid premises with the payment of the sum of twenty pounds a piece to each of my daughters namely Elizabeth the wife of Ambrose Dudall and Rebecca the wife of Samuel Stubbs which said sum of twenty pounds each I devise may be paid to them by my said son Abraham when and so soon as he attains his age of twenty one years provided always and my mind and will is that if my said son Abraham should happen to depart this life without leaving issue of his body lawfully begotten before he attains his age of twenty one years then I give and devise all the aforesaid premises and every part thereof with the appurtenances so given to my said son Abraham as aforesaid unto my said son William Wood and my said daughter Elizabeth Dudall and Rebecca Stubbs their heirs and assigns forever equally divided among them share and share alike as tenants in common and not as joint tenants. And lastly I do hereby nominate constitute and appoint my said wife Mary and my said son Abraham executrix and executor of this my will.
The marriage of William Wood (1725-1784) and Mary Clews (1715-1798) in 1749 was in Hamstall Ridware.

Mary was eleven years Williams senior, and it appears that they both came from Hamstall Ridware and moved to Darlaston after they married. Clearly Rebecca had extended family there (notwithstanding any possible connecting links between the Stubbs buckle makers of Darlaston and the Hamstall Ridware Jacobites thirty years prior). When the buckle trade collapsed in Darlaston, they likely moved to find employment elsewhere, perhaps with the help of Rebecca’s family.
I have not yet been able to find deaths recorded anywhere for either Samuel or Rebecca (there are a couple of deaths recorded for a Samuel Stubbs, one in 1809 in Wolverhampton, and one in 1810 in Birmingham but impossible to say which, if either, is the right one with the limited information, and difficult to know if they stayed in the Hamstall Ridware area or perhaps moved elsewhere)~ or find a reason for their son Solomon to be in Burton upon Trent, an evidently prosperous man with several properties including an earthenware business, as well as a land carrier business.
October 11, 2022 at 2:58 pm #6334In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The House on Penn Common
Toi Fang and the Duke of Sutherland
Tomlinsons

Grassholme
Charles Tomlinson (1873-1929) my great grandfather, was born in Wolverhampton in 1873. His father Charles Tomlinson (1847-1907) was a licensed victualler or publican, or alternatively a vet/castrator. He married Emma Grattidge (1853-1911) in 1872. On the 1881 census they were living at The Wheel in Wolverhampton.
Charles married Nellie Fisher (1877-1956) in Wolverhampton in 1896. In 1901 they were living next to the post office in Upper Penn, with children (Charles) Sidney Tomlinson (1896-1955), and Hilda Tomlinson (1898-1977) . Charles was a vet/castrator working on his own account.
In 1911 their address was 4, Wakely Hill, Penn, and living with them were their children Hilda, Frank Tomlinson (1901-1975), (Dorothy) Phyllis Tomlinson (1905-1982), Nellie Tomlinson (1906-1978) and May Tomlinson (1910-1983). Charles was a castrator working on his own account.
Charles and Nellie had a further four children: Charles Fisher Tomlinson (1911-1977), Margaret Tomlinson (1913-1989) (my grandmother Peggy), Major Tomlinson (1916-1984) and Norah Mary Tomlinson (1919-2010).
My father told me that my grandmother had fallen down the well at the house on Penn Common in 1915 when she was two years old, and sent me a photo of her standing next to the well when she revisted the house at a much later date.
Peggy next to the well on Penn Common:

My grandmother Peggy told me that her father had had a racehorse called Toi Fang. She remembered the racing colours were sky blue and orange, and had a set of racing silks made which she sent to my father.
Through a DNA match, I met Ian Tomlinson. Ian is the son of my fathers favourite cousin Roger, Frank’s son. Ian found some racing silks and sent a photo to my father (they are now in contact with each other as a result of my DNA match with Ian), wondering what they were.
When Ian sent a photo of these racing silks, I had a look in the newspaper archives. In 1920 there are a number of mentions in the racing news of Mr C Tomlinson’s horse TOI FANG. I have not found any mention of Toi Fang in the newspapers in the following years.
The Scotsman – Monday 12 July 1920:

The other story that Ian Tomlinson recalled was about the house on Penn Common. Ian said he’d heard that the local titled person took Charles Tomlinson to court over building the house but that Tomlinson won the case because it was built on common land and was the first case of it’s kind.
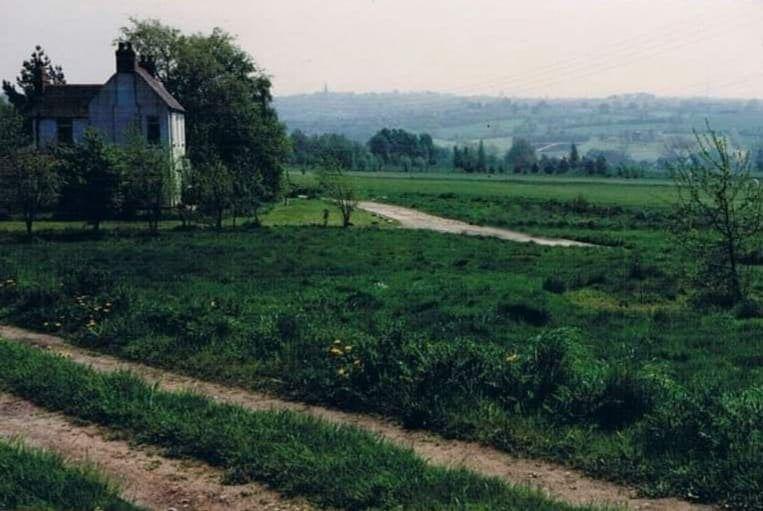

Penn Common Right of Way Case:
Staffordshire Advertiser March 9, 1912In the chancery division, on Tuesday, before Mr Justice Joyce, it was announced that a settlement had been arrived at of the Penn Common Right of Way case, the hearing of which occupied several days last month. The action was brought by the Duke of Sutherland (as Lord of the Manor of Penn) and Mr Harry Sydney Pitt (on behalf of himself and other freeholders of the manor having a right to pasturage on Penn Common) to restrain Mr James Lakin, Carlton House, Penn; Mr Charles Tomlinson, Mayfield Villa, Wakely Hill, Penn; and Mr Joseph Harold Simpkin, Dudley Road, Wolverhampton, from drawing building materials across the common, or otherwise causing injury to the soil.
The real point in dispute was whether there was a public highway for all purposes running by the side of the defendants land from the Turf Tavern past the golf club to the Barley Mow.
Mr Hughes, KC for the plaintiffs, now stated that the parties had been in consultation, and had come to terms, the substance of which was that the defendants admitted that there was no public right of way, and that they were granted a private way. This, he thought, would involve the granting of some deed or deeds to express the rights of the parties, and he suggested that the documents should be be settled by some counsel to be mutually agreed upon.His lordship observed that the question of coal was probably the important point. Mr Younger said Mr Tomlinson was a freeholder, and the plaintiffs could not mine under him. Mr Hughes: The coal actually under his house is his, and, of course, subsidence might be produced by taking away coal some distance away. I think some document is required to determine his actual rights.
Mr Younger said he wanted to avoid anything that would increase the costs, but, after further discussion, it was agreed that Mr John Dixon (an expert on mineral rights), or failing him, another counsel satisfactory to both parties, should be invited to settle the terms scheduled in the agreement, in order to prevent any further dispute.
The name of the house is Grassholme. The address of Mayfield Villas is the house they were living in while building Grassholme, which I assume they had not yet moved in to at the time of the newspaper article in March 1912.
What my grandmother didn’t tell anyone was how her father died in 1929:

On the 1921 census, Charles, Nellie and eight of their children were living at 269 Coleman Street, Wolverhampton.
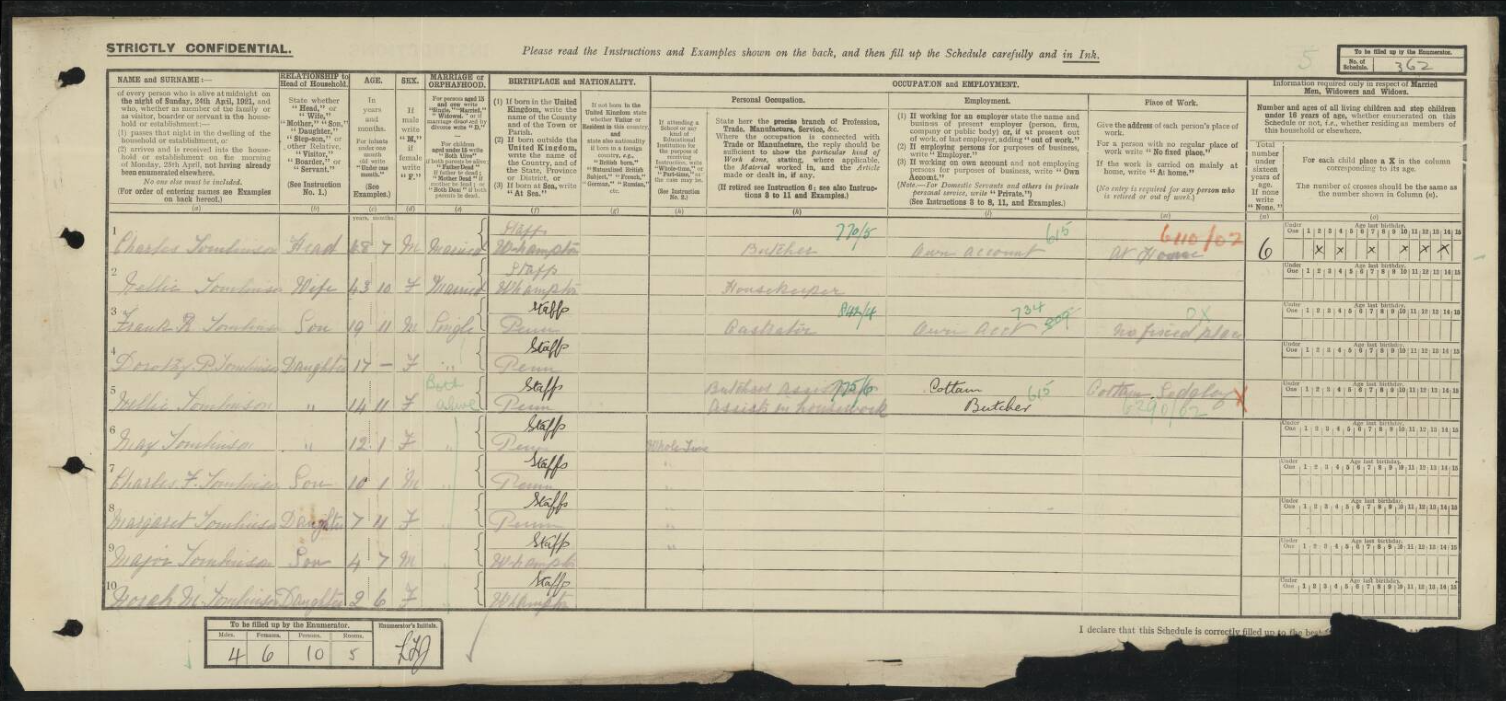
They were living on Coleman Street in 1915 when Charles was fined for staying open late.
Staffordshire Advertiser – Saturday 13 February 1915:

What is not yet clear is why they moved from the house on Penn Common sometime between 1912 and 1915. And why did he have a racehorse in 1920?
October 11, 2022 at 11:39 am #6333In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The Grattidge Family
The first Grattidge to appear in our tree was Emma Grattidge (1853-1911) who married Charles Tomlinson (1847-1907) in 1872.
Charles Tomlinson (1873-1929) was their son and he married my great grandmother Nellie Fisher. Their daughter Margaret (later Peggy Edwards) was my grandmother on my fathers side.
Emma Grattidge was born in Wolverhampton, the daughter and youngest child of William Grattidge (1820-1887) born in Foston, Derbyshire, and Mary Stubbs, born in Burton on Trent, daughter of Solomon Stubbs, a land carrier. William and Mary married at St Modwens church, Burton on Trent, in 1839. It’s unclear why they moved to Wolverhampton. On the 1841 census William was employed as an agent, and their first son William was nine months old. Thereafter, William was a licensed victuallar or innkeeper.
William Grattidge was born in Foston, Derbyshire in 1820. His parents were Thomas Grattidge, farmer (1779-1843) and Ann Gerrard (1789-1822) from Ellastone. Thomas and Ann married in 1813 in Ellastone. They had five children before Ann died at the age of 25:
Bessy was born in 1815, Thomas in 1818, William in 1820, and Daniel Augustus and Frederick were twins born in 1822. They were all born in Foston. (records say Foston, Foston and Scropton, or Scropton)
On the 1841 census Thomas had nine people additional to family living at the farm in Foston, presumably agricultural labourers and help.
After Ann died, Thomas had three children with Kezia Gibbs (30 years his junior) before marrying her in 1836, then had a further four with her before dying in 1843. Then Kezia married Thomas’s nephew Frederick Augustus Grattidge (born in 1816 in Stafford) in London in 1847 and had two more!
The siblings of William Grattidge (my 3x great grandfather):
Frederick Grattidge (1822-1872) was a schoolmaster and never married. He died at the age of 49 in Tamworth at his twin brother Daniels address.
Daniel Augustus Grattidge (1822-1903) was a grocer at Gungate in Tamworth.
Thomas Grattidge (1818-1871) married in Derby, and then emigrated to Illinois, USA.
Bessy Grattidge (1815-1840) married John Buxton, farmer, in Ellastone in January 1838. They had three children before Bessy died in December 1840 at the age of 25: Henry in 1838, John in 1839, and Bessy Buxton in 1840. Bessy was baptised in January 1841. Presumably the birth of Bessy caused the death of Bessy the mother.
Bessy Buxton’s gravestone:
“Sacred to the memory of Bessy Buxton, the affectionate wife of John Buxton of Stanton She departed this life December 20th 1840, aged 25 years. “Husband, Farewell my life is Past, I loved you while life did last. Think on my children for my sake, And ever of them with I take.”
20 Dec 1840, Ellastone, Staffordshire
In the 1843 will of Thomas Grattidge, farmer of Foston, he leaves fifth shares of his estate, including freehold real estate at Findern, to his wife Kezia, and sons William, Daniel, Frederick and Thomas. He mentions that the children of his late daughter Bessy, wife of John Buxton, will be taken care of by their father. He leaves the farm to Keziah in confidence that she will maintain, support and educate his children with her.
An excerpt from the will:
I give and bequeath unto my dear wife Keziah Grattidge all my household goods and furniture, wearing apparel and plate and plated articles, linen, books, china, glass, and other household effects whatsoever, and also all my implements of husbandry, horses, cattle, hay, corn, crops and live and dead stock whatsoever, and also all the ready money that may be about my person or in my dwelling house at the time of my decease, …I also give my said wife the tenant right and possession of the farm in my occupation….
A page from the 1843 will of Thomas Grattidge:

William Grattidges half siblings (the offspring of Thomas Grattidge and Kezia Gibbs):
Albert Grattidge (1842-1914) was a railway engine driver in Derby. In 1884 he was driving the train when an unfortunate accident occured outside Ambergate. Three children were blackberrying and crossed the rails in front of the train, and one little girl died.
Albert Grattidge:

George Grattidge (1826-1876) was baptised Gibbs as this was before Thomas married Kezia. He was a police inspector in Derby.
George Grattidge:

Edwin Grattidge (1837-1852) died at just 15 years old.
Ann Grattidge (1835-) married Charles Fletcher, stone mason, and lived in Derby.
Louisa Victoria Grattidge (1840-1869) was sadly another Grattidge woman who died young. Louisa married Emmanuel Brunt Cheesborough in 1860 in Derby. In 1861 Louisa and Emmanuel were living with her mother Kezia in Derby, with their two children Frederick and Ann Louisa. Emmanuel’s occupation was sawyer. (Kezia Gibbs second husband Frederick Augustus Grattidge was a timber merchant in Derby)
At the time of her death in 1869, Emmanuel was the landlord of the White Hart public house at Bridgegate in Derby.
The Derby Mercury of 17th November 1869:
“On Wednesday morning Mr Coroner Vallack held an inquest in the Grand
Jury-room, Town-hall, on the body of Louisa Victoria Cheeseborough, aged
33, the wife of the landlord of the White Hart, Bridge-gate, who committed
suicide by poisoning at an early hour on Sunday morning. The following
evidence was taken:Mr Frederick Borough, surgeon, practising in Derby, deposed that he was
called in to see the deceased about four o’clock on Sunday morning last. He
accordingly examined the deceased and found the body quite warm, but dead.
He afterwards made enquiries of the husband, who said that he was afraid
that his wife had taken poison, also giving him at the same time the
remains of some blue material in a cup. The aunt of the deceased’s husband
told him that she had seen Mrs Cheeseborough put down a cup in the
club-room, as though she had just taken it from her mouth. The witness took
the liquid home with him, and informed them that an inquest would
necessarily have to be held on Monday. He had made a post mortem
examination of the body, and found that in the stomach there was a great
deal of congestion. There were remains of food in the stomach and, having
put the contents into a bottle, he took the stomach away. He also examined
the heart and found it very pale and flabby. All the other organs were
comparatively healthy; the liver was friable.Hannah Stone, aunt of the deceased’s husband, said she acted as a servant
in the house. On Saturday evening, while they were going to bed and whilst
witness was undressing, the deceased came into the room, went up to the
bedside, awoke her daughter, and whispered to her. but what she said the
witness did not know. The child jumped out of bed, but the deceased closed
the door and went away. The child followed her mother, and she also
followed them to the deceased’s bed-room, but the door being closed, they
then went to the club-room door and opening it they saw the deceased
standing with a candle in one hand. The daughter stayed with her in the
room whilst the witness went downstairs to fetch a candle for herself, and
as she was returning up again she saw the deceased put a teacup on the
table. The little girl began to scream, saying “Oh aunt, my mother is
going, but don’t let her go”. The deceased then walked into her bed-room,
and they went and stood at the door whilst the deceased undressed herself.
The daughter and the witness then returned to their bed-room. Presently
they went to see if the deceased was in bed, but she was sitting on the
floor her arms on the bedside. Her husband was sitting in a chair fast
asleep. The witness pulled her on the bed as well as she could.
Ann Louisa Cheesborough, a little girl, said that the deceased was her
mother. On Saturday evening last, about twenty minutes before eleven
o’clock, she went to bed, leaving her mother and aunt downstairs. Her aunt
came to bed as usual. By and bye, her mother came into her room – before
the aunt had retired to rest – and awoke her. She told the witness, in a
low voice, ‘that she should have all that she had got, adding that she
should also leave her her watch, as she was going to die’. She did not tell
her aunt what her mother had said, but followed her directly into the
club-room, where she saw her drink something from a cup, which she
afterwards placed on the table. Her mother then went into her own room and
shut the door. She screamed and called her father, who was downstairs. He
came up and went into her room. The witness then went to bed and fell
asleep. She did not hear any noise or quarrelling in the house after going
to bed.Police-constable Webster was on duty in Bridge-gate on Saturday evening
last, about twenty minutes to one o’clock. He knew the White Hart
public-house in Bridge-gate, and as he was approaching that place, he heard
a woman scream as though at the back side of the house. The witness went to
the door and heard the deceased keep saying ‘Will you be quiet and go to
bed’. The reply was most disgusting, and the language which the
police-constable said was uttered by the husband of the deceased, was
immoral in the extreme. He heard the poor woman keep pressing her husband
to go to bed quietly, and eventually he saw him through the keyhole of the
door pass and go upstairs. his wife having gone up a minute or so before.
Inspector Fearn deposed that on Sunday morning last, after he had heard of
the deceased’s death from supposed poisoning, he went to Cheeseborough’s
public house, and found in the club-room two nearly empty packets of
Battie’s Lincoln Vermin Killer – each labelled poison.Several of the Jury here intimated that they had seen some marks on the
deceased’s neck, as of blows, and expressing a desire that the surgeon
should return, and re-examine the body. This was accordingly done, after
which the following evidence was taken:Mr Borough said that he had examined the body of the deceased and observed
a mark on the left side of the neck, which he considered had come on since
death. He thought it was the commencement of decomposition.
This was the evidence, after which the jury returned a verdict “that the
deceased took poison whilst of unsound mind” and requested the Coroner to
censure the deceased’s husband.The Coroner told Cheeseborough that he was a disgusting brute and that the
jury only regretted that the law could not reach his brutal conduct.
However he had had a narrow escape. It was their belief that his poor
wife, who was driven to her own destruction by his brutal treatment, would
have been a living woman that day except for his cowardly conduct towards
her.The inquiry, which had lasted a considerable time, then closed.”
In this article it says:
“it was the “fourth or fifth remarkable and tragical event – some of which were of the worst description – that has taken place within the last twelve years at the White Hart and in the very room in which the unfortunate Louisa Cheesborough drew her last breath.”
Sheffield Independent – Friday 12 November 1869:

-
AuthorSearch Results
