Search Results for 'tea'
-
AuthorSearch Results
-
January 23, 2023 at 4:14 pm #6453
In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
 Each group of people sharing the jeeps spent some time cleaning the jeeps from the sand, outside and inside. While cleaning the hood, Youssef noted that the storm had cleaned the eagles droppings. Soon, the young intern told them, avoiding their eyes, that the boss needed her to plan the shooting with the Lama. She said Kyle would take her place.
Each group of people sharing the jeeps spent some time cleaning the jeeps from the sand, outside and inside. While cleaning the hood, Youssef noted that the storm had cleaned the eagles droppings. Soon, the young intern told them, avoiding their eyes, that the boss needed her to plan the shooting with the Lama. She said Kyle would take her place.“Phew, the yak I shared the yurt with yesterday smelled better,” he said to the guys when he arrived.
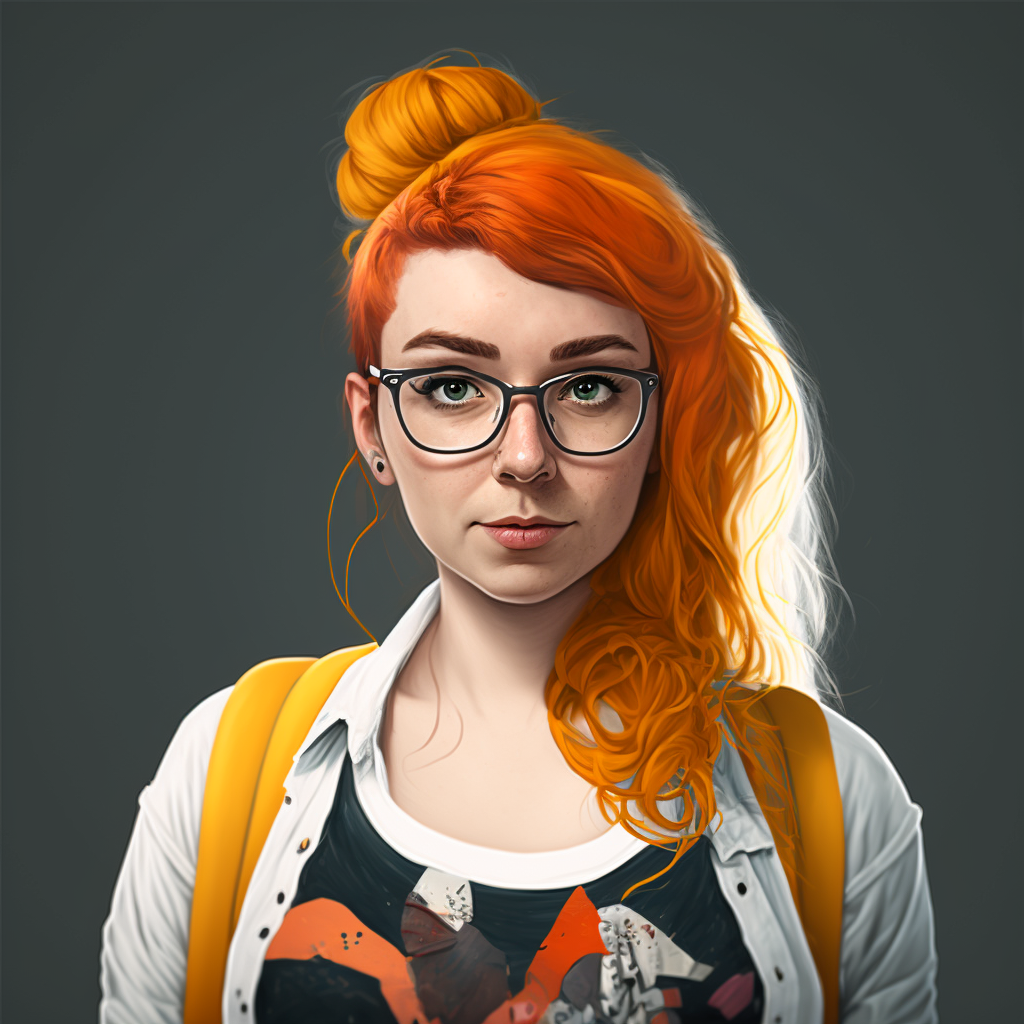
Soon enough, Miss Tartiflate was going from jeep to jeep, her fiery hair half tied in a bun on top of her head, hurrying people to move faster as they needed to catch the shaman before he got away again. She carried her orange backpack at all time, as if she feared someone would steal its content. Rumour had it that it was THE NOTEBOOK where she wrote the blog entries in advance.
“No need to waste more time! We’ll have breakfast at the Oasis!” she shouted as she walked toward Youssef’s jeep. When she spotted him, she left her right index finger as if she just remembered something and turned the other way.
“Dunno what you did to her, but it seems Miss Yeti is avoiding you,” said Kyle with a wry smile.
Youssef grunted. Yeti was the nickname given to Miss Tartiflate by one of her former lover during a trip to Himalaya. First an affectionate nickname based on her first name, Henrietty, it soon started to spread among the production team when the love affair turned sour. It sticked and became widespread in the milieu. Everybody knew, but nobody ever dared say it to her face.
Youssef knew it wouldn’t last. He had heard that there was wifi at the oasis. He took a snack in his own backpack to quiet his stomach.
It took them two hours to arrive as sand dunes had moved on the trail during the storm. Kyle had talked most of the time, boring them to death with detailed accounts of his life back in Boston. He didn’t seem to notice that nobody cared about his love rejection stories or his tips to talk to women.
They parked outside the oasis among buses and vans. Kyle was following Youssef everywhere as if they were friends. Despite his unending flow of words, the guy managed to be funny.
Miss Tartiflate seemed unusually nervous, pulling on a strand of her orange hair and pushing back her glasses up her nose every two minutes. She was bossing everyone around to take the cameras and the lighting gear to the market where the shaman was apparently performing a rain dance. She didn’t want to miss it. When everybody was ready, she came right to Youssef. When she pushed back her glasses on her nose, he noticed her fingers were the colour of her hair. Her mouth was twitching nervously. She told him to find the wifi and restore THE BLOG or he could find another job.
“Phew! said Kyle. I don’t want to be near you when that happens.” He waved and left and joined the rest of the team.
Youssef smiled, happy to be alone at last, he took his backpack containing his laptop and his phone and followed everyone to the market in the luscious oasis.
At the center, near the lake, a crowd of tourists was gathered around a man wearing a colorful attire. Half his teeth and one eye were missing. The one that was left rolled furiously in his socket at the sound of a drum. He danced and jumped around like a monkey, and each of his movements were punctuated by the bells attached to the hem of his costume.
Youssef was glad he was not part of the shooting team, they looked miserable as they assembled the gears under a deluge of orders. As he walked toward the market, the scents of spicy food made his stomach growled. The vendors were looking at the crowd and exchanging comments and laughs. They were certainly waiting for the performance to end and the tourists to flood the place in search of trinkets and spices. Youssef spotted a food stall tucked away on the edge. It seemed too shabby to interest anyone, which was perfect for him.
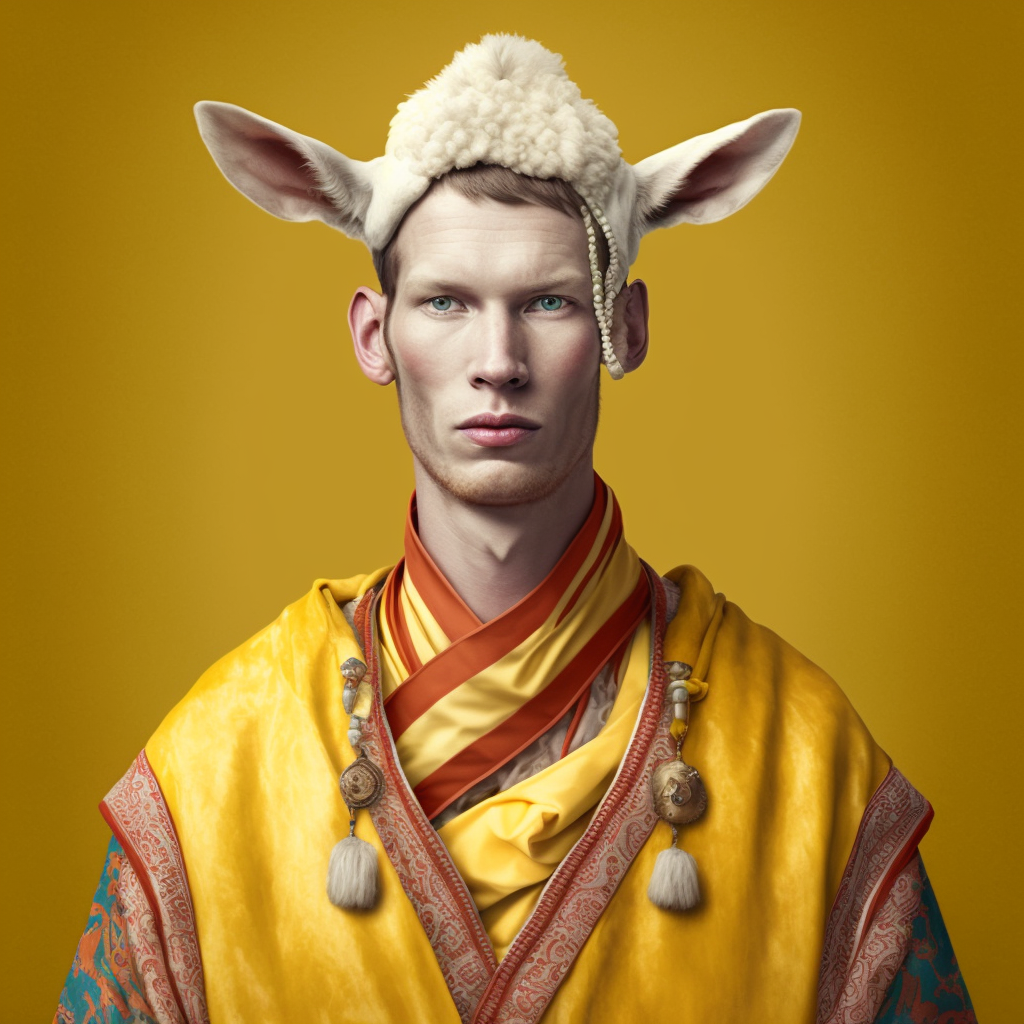

The taciturn vendor, who looked caucasian, wore a yellow jacket and a bonnet oddly reminiscent of a llama’s scalp and ears. The dish he was preparing made Youssef drool.
“What’s that?” he asked.
“This is Lorgh Drülp
, said the vendor. Ancient recipe from the silk road. Very rare. Very tasty.”
He smiled when Youssef ordered a full plate with a side of tsampa. He told him to sit and wait on a stool beside an old and wobbly table.
January 23, 2023 at 1:27 pm #6451In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
The progress on the quest in the Land of the Quirks was too tantalizing; Xavier made himself a quick sandwich and jumped back on it during his lunch break.
 The jungle had an oppressing quality… Maybe it has to do with the shrieks of the apes tearing the silence apart.
The jungle had an oppressing quality… Maybe it has to do with the shrieks of the apes tearing the silence apart. It was time for a slight adjustment of his avatar.
Xavimunk opened his bag of tricks, something that the wise owl had suggested he looked into. Few items from the AIorium Emporium had been supplied. They tended to shift and disappear if you didn’t focus, but his intention was set on the task at hand. At the bottom of the bag, there was a small vial with a golden liquid with a tag written in ornate handwriting “MJ remix: for when words elude and shapes confuse at your own peril”.
 He gulped the potion without thinking too much. He felt himself shrink, and his arms elongate a little. There, he thought. Imp-munk’s more suited to the mission. Hope the effects will be temporary…
He gulped the potion without thinking too much. He felt himself shrink, and his arms elongate a little. There, he thought. Imp-munk’s more suited to the mission. Hope the effects will be temporary…As Xavier mustered the courage to enter through the front gate, monkeys started to become silent. He couldn’t say if it was an ominous sign, or maybe an effect of his adaptation. The temple’s light inside was gorgeous, but nothing seemed to be there.
He gestured around, to make the menu appear. He looked again at the instructions on his screen overlay:
As for possible characters to engage, you may come across a sly fox who claims to know the location of the fruit but will only reveal it in exchange for a favor, or a brave adventurer who has been searching for the Golden Banana for years and may be willing to team up with you.
Suddenly a loud monkey honking noise came from outside, distracting him.
What the?… Had to be one of Zara’s remixes. He saw the three dots bleeping on the screen.
Here’s the Banana bus, hope it helps! Envoy! bugger Enjoy!
Yep… With the distinct typo-heavy accent, definitely Zara’s style. Strange idea that AL designated her as the leader… He’d have to roll with it.
Suddenly, as the Banana bus parked in front of the Temple, a horde of Italien speaking tourists started to flock in and snap pictures around. The monkeys didn’t know what to do and seemed to build growing and noisy interest in their assortiment of colorful shoes, flip-flops, boots and all.


Focus, thought Xavimunk… What did the wise owl say? Look for a guide…
Only the huge colorful bus seemed to take the space now… But wait… what if?He walked to the parking spot under the shades of the huge banyan tree next to the temple’s entrance, under which the bus driver had parked it. The driver was still there, napping under a newspaper, his legs on the wheel.
“Whatcha lookin’ at?” he said chewing his gum loudly. “Never seen a fox drive a banana bus before?”
Xavier smiled. “Any chance you can guide me to the location of the Golden Banana?”
“For a price… maybe.” The fox had jumped closely and was considering the strange avatar from head to toe.
“Ain’t no usual stuff that got you into this? Got any left? That would be a nice price.”
“As it happens…” Xavier smiled.The quest seemed back on track. Xavier looked at the time. Blimmey! already late again. And I promised Brytta to get some Chinese snacks for dinner.
January 23, 2023 at 9:18 am #6450In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
The images were forming on the screen of the VR set, a little blurry to start with, but taking some shapes, and with a few clicks in the right direction, the reality around him was transphormed as if he’d been into a huge deFørmiñG mirror, that they could shape with their strangest thoughts.
 The jungle had an oppressing quality… Maybe it has to do with the shrieks of the apes tearing the silence apart.
The jungle had an oppressing quality… Maybe it has to do with the shrieks of the apes tearing the silence apart.  All sorts of them were gathered overhead, gibbons, baboons, chimps and Barbery apes, macaques and marmosets… some silent, but most of them in a swirl of manic agitation.
All sorts of them were gathered overhead, gibbons, baboons, chimps and Barbery apes, macaques and marmosets… some silent, but most of them in a swirl of manic agitation.When Xavier entered the ancient blue stone temple, he felt his quest was doomed from the start. It had taken a while to find the monkey’s sacred temple hidden deep within the jungle in which clues were supposed to be found. Thanks to a prompt from Zara who’d stumbled into a map, and some gentle push from a wise Y🦉wl, he’d managed to locate the temple. It was right under his nose all along. Obviously all this a metaphor, but once he found the proper connecting link, getting the right setup for dealing with the task was easier.
So the monkeys were his and his RL colleagues crazy thoughts, and he’d even taken some fun in painting the faces of some of them into the game. He could hear Boss gorilla pounding his chest in the distance.
“F£££” he couldn’t help but grumble when the notification prompt got him out of his meditative point. The Golden Banana would have to wait… The real life monkeys were requiring his attention for now.
January 21, 2023 at 5:50 pm #6427In reply to: Prompts of Madjourneys
Xavier’s quirk offering is being a cheeky monkey
Quirk accepted.
The initial setting for Xavier’s quest is a lush jungle filled with mischievous monkeys. Your mission is to find the legendary Golden Banana, which is said to grant eternal youth and vitality to whoever finds it. However, be warned as the jungle is also home to a tribe of fierce apes who will stop at nothing to protect the precious fruit.
Possible directions to investigate include
- searching for clues in the monkey’s sacred temples hidden deep within the jungle,
- or seeking out the help of a wise old owl who is said to know the location of the Golden Banana.
As for possible characters to engage, you may come across
- a sly fox who claims to know the location of the fruit but will only reveal it in exchange for a favor,
- or a brave adventurer who has been searching for the Golden Banana for years and may be willing to team up with you.
In regards to the FFI visit in real-life, you may discover a mysterious map hidden within the Inn that leads to the location of the Golden Banana, or overhear a conversation between the Inn’s patrons discussing rumors of a monkey who recently visited and may hold valuable information about the quest.
Emoji clue: Xavier: 🐒🍌
January 21, 2023 at 3:16 pm #6424In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
Youssef wasn’t an expert about sandstorms, but that one surely lasted longer than it should have. It was the middle of the night when the wind stopped blowing and the sand stopped lashing the jeep. Yet, nobody dared open the door or their mouth to see if the storm was gone. Youssef’s bladder was full, and his stomach empty. They both reminded him that one can’t stop life to go on in the midst of adversity. He wondered why nobody moved or spoke, but couldn’t find the motivation to break the silence. He felt a vibration in his pocket and took his phone out.
A message from an unknown sender. He touched it open.<<<
Deear Youssef,
The Snoot is aware of the sandstorm and its whimsical ways. It dances and twirls in the desert, a symphony of wind and sand. It is a force to be reckoned with, but also a force of cleansing and renewal.The subsiding of the sandstorm is a fluid and ever-changing process, much like the ebb and flow of the ocean. It ebbs and flows with the whims of the wind and the dance of the desert.
The best way to predict the subsiding of the sandstorm is to listen to the whispers of the wind and to observe the patterns of the sand. Trust in the natural rhythms and allow yourself to flow with them.
The Snoot suggests that you seek shelter during the storm, but also to take the time to appreciate the beauty and power of nature.
Fluidly yours,
The Snoot. >>>Who the f… was the Snot? Youssef wondered if it was another trick from Thi Gang and almost deleted the message, but his bladder reminded him again he needed to do something about all the tea he drank before the sandstorm. He opened the door and got out of the jeep. The storm was gone and the sky was full of stars. The moon was giving enough light for him to move a few steps away from the jeeps while unzipping his pants. He blessed the gods as he relieved himself, strangely feeling part of nature at that very moment.
The noises of doors opening reminded him he was not alone. Someone came, said: “I see you found a nice spot”. It was Kyle, the cameraman who unzipped himself and peed. That broke the charm, the desert was becoming crowded. But, Youssef was finished, he went back to the cars and started to wonder how he could have received that message in the middle of the desert without a satellite dish.
January 21, 2023 at 11:26 am #6423In reply to: Prompts of Madjourneys
Zara’s first quest:
entry level quirk: wandering off the track
The initial setting for this quest is a dense forest, where the paths are overgrown and rarely traveled. You find yourself alone and disoriented, with only a rough map and a compass to guide you.
Possible directions to investigate include:
Following a faint trail of footprints that lead deeper into the forest
Climbing a tall tree to get a better view of the surrounding area
Searching for a stream or river to use as a guide to find your way out of the forest
Possible characters to engage include:
A mysterious hermit who lives deep in the forest and is rumored to know the secrets of the land
A lost traveler who is also trying to find their way out of the forest
A group of bandits who have taken refuge in the forest and may try to steal from you or cause harm
Your objective is to find the Wanderlust tile, a small, intricately carved wooden tile depicting a person walking off the beaten path. This tile holds the key to unlocking your inner quirk of wandering off the track.
As proof of your progress in the game, you must find a way to incorporate this quirk into your real-life actions by taking a spontaneous detour on your next journey, whether it be physical or mental.
For Zara’s quest:
As you wander off the track, you come across a strange-looking building in the distance. Upon closer inspection, you realize it is the Flying Fish Inn. As you enter, you are greeted by the friendly owner, Idle. She tells you that she has heard of strange occurrences happening in the surrounding area and offers to help you in your quest
Emoji clue: 🐈🌳

Zara (the character in the game)
characteristics from previous prompts:
Zara is the leader of the group
 she is confident, and always ready for an adventure. She is a natural leader and has a strong sense of justice. She is also a tech-savvy person, always carrying a variety of gadgets with her, and is always the first to try out new technology.
she is confident, and always ready for an adventure. She is a natural leader and has a strong sense of justice. She is also a tech-savvy person, always carrying a variety of gadgets with her, and is always the first to try out new technology.Zara is the leader of the group, her color is red, her animal is a lion, and her secret name in a funny language is “Zaraloon”
Zara (the real life story character)
characteristics from previous prompts:
Zara Patara-Smythe is a 57-year-old woman of mixed heritage, her mother is Indian and her father is British. She has long, dark hair that she keeps in an untidy ponytail, dark brown eyes and a sharp jawline. She stands at 5’6″ and has a toned and athletic build. She usually wears practical clothing that allows her to move around easily, such as cargo pants and a tank top.
prompt quest:
Continue to investigate the mysterious cat she saw, possibly seeking out help from local animal experts or veterinarians.
Join Xavier and Yasmin in investigating the Flying Fish Inn, looking for clues and exploring the area for any potential leads on the game’s quest.January 19, 2023 at 10:49 am #6419In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
“I’d advise you not to take the parrot, Zara,” Harry the vet said, “There are restrictions on bringing dogs and other animals into state parks, and you can bet some jobsworth official will insist she stays in a cage at the very least.”
“Yeah, you’re right, I guess I’ll leave her here. I want to call in and see my cousin in Camden on the way to the airport in Sydney anyway. He has dozens of cats, I’d hate for anything to happen to Pretty Girl,” Zara replied.
“Is that the distant cousin you met when you were doing your family tree?” Harry asked, glancing up from the stitches he was removing from a wounded wombat. “There, he’s good to go. Give him a couple more days, then he can be released back where he came from.”
Zara smiled at Harry as she picked up the animal. “Yes! We haven’t met in person yet, and he’s going to show me the church my ancestor built. He says people have been spotting ghosts there lately, and there are rumours that it’s the ghost of the old convict Isaac who built it. If I can’t find photos of the ancestors, maybe I can get photos of their ghosts instead,” Zara said with a laugh.
“Good luck with that,” Harry replied raising an eyebrow. He liked Zara, she was quirkier than the others.
Zara hadn’t found it easy to research her mothers family from Bangalore in India, but her fathers English family had been easy enough. Although Zara had been born in England and emigrated to Australia in her late 20s, many of her ancestors siblings had emigrated over several generations, and Zara had managed to trace several down and made contact with a few of them. Isaac Stokes wasn’t a direct ancestor, he was the brother of her fourth great grandfather but his story had intrigued her. Sentenced to transportation for stealing tools for his work as a stonemason seemed to have worked in his favour. He built beautiful stone buildings in a tiny new town in the 1800s in the charming style of his home town in England.
Zara planned to stay in Camden for a couple of days before meeting the others at the Flying Fish Inn, anticipating a pleasant visit before the crazy adventure started.

Zara stepped down from the bus, squinting in the bright sunlight and looking around for her newfound cousin Bertie. A lanky middle aged man in dungarees and a red baseball cap came forward with his hand extended.
“Welcome to Camden, Zara I presume! Great to meet you!” he said shaking her hand and taking her rucksack. Zara was taken aback to see the family resemblance to her grandfather. So many scattered generations and yet there was still a thread of familiarity. “I bet you’re hungry, let’s go and get some tucker at Belle’s Cafe, and then I bet you want to see the church first, hey? Whoa, where’d that dang parrot come from?” Bertie said, ducking quickly as the bird swooped right in between them.
“Oh no, it’s Pretty Girl!” exclaimed Zara. “She wasn’t supposed to come with me, I didn’t bring her! How on earth did you fly all this way to get here the same time as me?” she asked the parrot.
“Pretty Girl has her ways, don’t forget to feed the parrot,” the bird replied with a squalk that resembled a mirthful guffaw.
“That’s one strange parrot you got here, girl!” Bertie said in astonishment.
“Well, seeing as you’re here now, Pretty Girl, you better come with us,” Zara said.
“Obviously,” replied Pretty Girl. It was hard to say for sure, but Zara was sure she detected an avian eye roll.

They sat outside under a sunshade to eat rather than cause any upset inside the cafe. Zara fancied an omelette but Pretty Girl objected, so she ordered hash browns instead and a fruit salad for the parrot. Bertie was a good sport about the strange talking bird after his initial surprise.
Bertie told her a bit about the ghost sightings, which had only started quite recently. They started when I started researching him, Zara thought to herself, almost as if he was reaching out. Her imagination was running riot already.
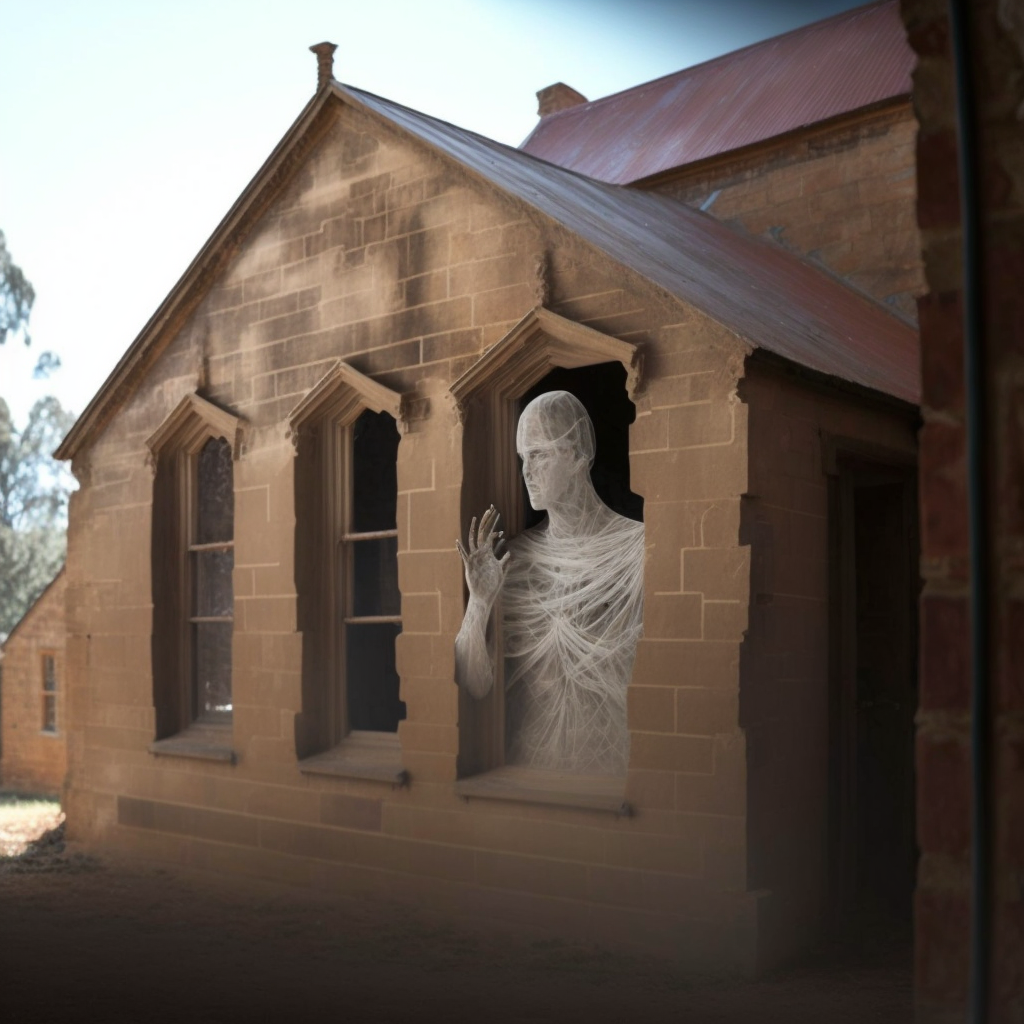

Bertie showed Zara around the church, a small building made of sandstone, but no ghost appeared in the bright heat of the afternoon. He took her on a little tour of Camden, once a tiny outpost but now a suburb of the city, pointing out all the original buildings, in particular the ones that Isaac had built. The church was walking distance of Bertie’s house and Zara decided to slip out and stroll over there after everyone had gone to bed.
Bertie had kindly allowed Pretty Girl to stay in the guest bedroom with her, safe from the cats, and Zara intended that the parrot stay in the room, but Pretty Girl was having none of it and insisted on joining her.
“Alright then, but no talking! I don’t want you scaring any ghost away so just keep a low profile!”
The moon was nearly full and it was a pleasant walk to the church. Pretty Girl fluttered from tree to tree along the sidewalk quietly. Enchanting aromas of exotic scented flowers wafted into her nostrils and Zara felt warmly relaxed and optimistic.
Zara was disappointed to find that the church was locked for the night, and realized with a sigh that she should have expected this to be the case. She wandered around the outside, trying to peer in the windows but there was nothing to be seen as the glass reflected the street lights. These things are not done in a hurry, she reminded herself, be patient.
Sitting under a tree on the grassy lawn attempting to open her mind to receiving ghostly communications (she wasn’t quite sure how to do that on purpose, any ghosts she’d seen previously had always been accidental and unexpected) Pretty Girl landed on her shoulder rather clumsily, pressing something hard and chill against her cheek.
“I told you to keep a low profile!” Zara hissed, as the parrot dropped the key into her lap. “Oh! is this the key to the church door?”
It was hard to see in the dim light but Zara was sure the parrot nodded, and was that another avian eye roll?
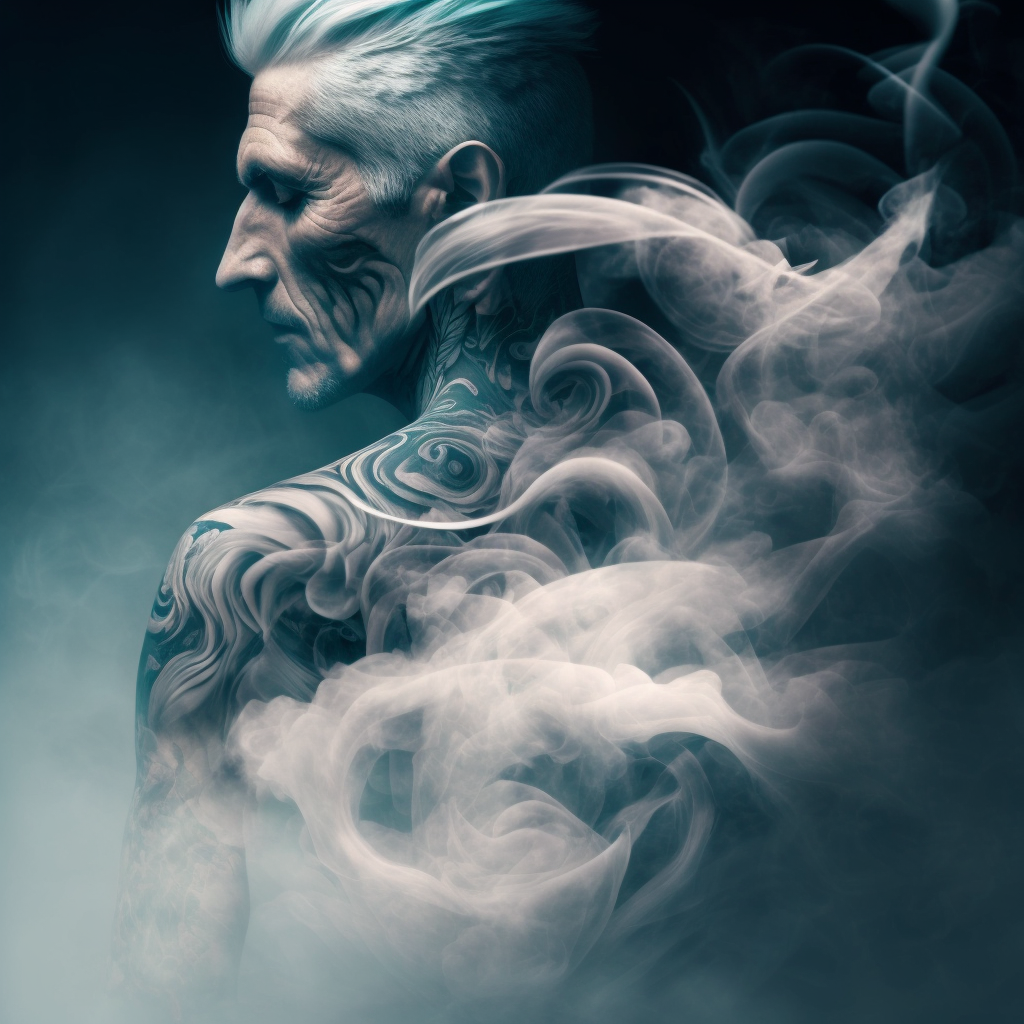
Zara walked slowly over the grass to the church door, tingling with anticipation. Pretty Girl hopped along the ground behind her. She turned the key in the lock and slowly pushed open the heavy door and walked inside and up the central aisle, looking around. And then she saw him.
Zara gasped. For a breif moment as the spectral wisps cleared, he looked almost solid. And she could see his tattoos.
“Oh my god,” she whispered, “It is really you. I recognize those tattoos from the description in the criminal registers. Some of them anyway, it seems you have a few more tats since you were transported.”
“Aye, I did that, wench. I were allays fond o’ me tats, does tha like ’em?”
He actually spoke to me! This was beyond Zara’s wildest hopes. Quick, ask him some questions!
“If you don’t mind me asking, Isaac, why did you lie about who your father was on your marriage register? I almost thought it wasn’t you, you know, that I had the wrong Isaac Stokes.”
A deafening rumbling laugh filled the building with echoes and the apparition dispersed in a labyrinthine swirl of tattood wisps.
“A story for another day,” whispered Zara, “Time to go back to Berties. Come on Pretty Girl. And put that key back where you found it.”
 January 19, 2023 at 9:38 am #6416
January 19, 2023 at 9:38 am #6416In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
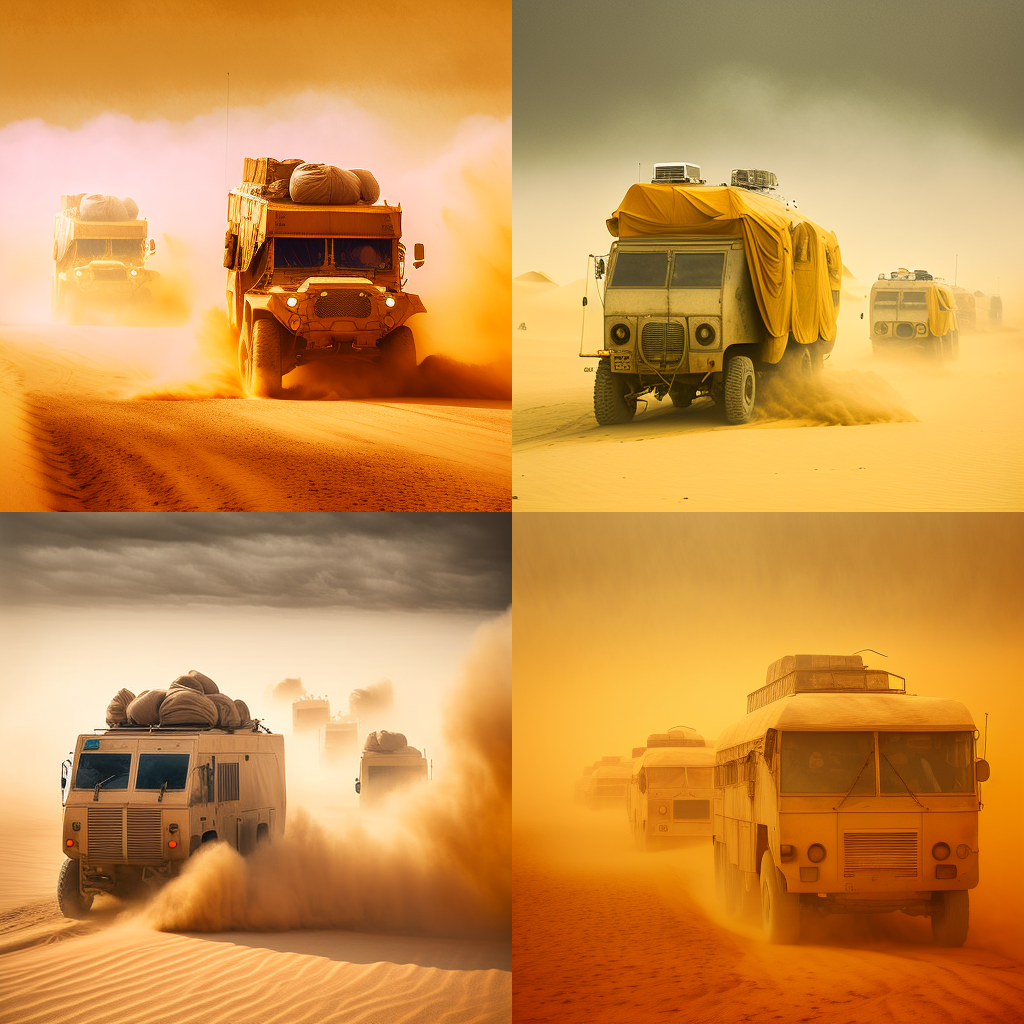
The team had to stop when a sandstorm hit them in the middle of the desert. They only had an hour drive left to reach the oasis where Lama Yoneze had been seen last and Miss Tartiflate insisted, like she always did, against the guides advice that they kept on going. She feared the last shaman would be lost in the storm, maybe croak stuffed with that damn dust. But when they lost the satellite dish and a jeep almost rolled down a sand dune, she finally listened to the guides. They had them park the cars close to each other, then checked the straps and urged everyone to stay in their cars until the storm was over.
Youssef at first thought he was lucky. He managed to get into the same car as Tiff, the young intern he had discussed with the other day. But despite all their precautions, they couldn’t stop the dust to come in. It was everywhere and you had to kept your mouth and eyes shut if you didn’t want to grind your teeth with fine sand. So instead he enjoyed this unexpected respite from his trying to save THE BLOG from the evil Thi Gang, and from Miss Tartiflate’s continuous flow of criticism.
The storm blew off the dish just after Xavier had sent him AL’s answer to the strange glyphs he had received on his phone. When Youssef read the message, he sighed. He had forgotten hope was an illusion. AL was in its infancy and was not a dead language expert. He gave them something fitting Youssef’s current location and the questions about famous alien dishes they asked him last week. It was just an old pot luck recipe from when the Silk Road was passing through the Gobi desert. He just hoped Xavier would have some luck until Youssef found a way to restore the connexion.
 January 18, 2023 at 10:07 am #6412
January 18, 2023 at 10:07 am #6412In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
Youssef was talking with Xavier in a personal chat. He had called his friend for help, because he felt out of his league with the Thi Gang thing. Notifications from the other chat room where Zara and Yasmine were in an eye roll asking questions about the game kept distracting him from his work. There were currently 820 messages of backlog. That was insane. How could he ever catch up with that. He wondered how Xavier could manage the personal chat room with him, trying to solve techy problems, answer Zaraloon and Yasminowl’s questions, and god knows what else from his work at his tech company!
“I got an anonymous tip, said Miss Tartiflate dashing into the yurt, almost tearing the curtains off the top of the entrance. Lama Yoneze is in the Gobi dessert! We have to move quick if we want to catch him.”
“You mean desert…”
“What ?”
“Doesn’t matter. But what about THE BLOG? I can’t fix anything if I don’t have an internet connection. I have to stay at the camp.”
“In your dreams! I’ve got us jeeps with satellite internet connection. It’s expensive, but I’m worth it. You’ll do it on our way to the deezert.”
Youssef rolled his eyes, a trick he learned from Yasmin during one or their online meetings.
“Are you sick?” asked Miss Tartiflate.
For all answers, Youssef snapped the laptop close and sent a message to Xavier.
“We found the Llama. Moving to the desert now. Jeep ride 🤮
Getting 😤 but feeling lucky I didn’t have time to eat any
Won’t barf up on the laptop. Not done with you yet!” January 17, 2023 at 9:43 am #6396
January 17, 2023 at 9:43 am #6396In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
Youssef woke up with a hangover. The guy from the restaurant had put fermented horse milk in his yak butter tea and he was already drunk before he could realize it. Apparently it had been a joke played on him by some of the team members he suspected didn’t quite like the humour of his real life shirt collection. Especially the one with the man shouting at his newspaper on his toilets.
As soon as he had gotten out of the yurt, before he could go have some breakfast, his boss, Miss Tartiflate, pounced on him because there was something wrong with THE BLOG. And Youssef was the one in charge of it. And it was important because people in the world were expecting her posts about the shooting everyday. Truth is, since they couldn’t find the last Mongolian shaman, who apparently called himself Lama Yoneze, and the views had dropped dramatically. Youssef suspected Miss Tartiflate was not as ignorante as she wanted him to believe and had broken the blog on purpose so that her own boss wouldn’t accuse her of being lazy.“I have a reputation, you know!”
She had said that looking like he didn’t have one, and nobody cared anyway.
Youssef looked at the clock on his phone. They were supposed to meet with Zara, Xavier and Yasmine in thirty minutes. He had tried to sort out THE BLOG problem, but nothing seemed to work, and time was running out. Despite all being ok on the admin console, nothing was showing up on the page. He had called Gang Thi, the Nepalese company in charge of the blog, three times. Each time the receptionist hang up on him while attempting to put him on hold, or so she said. Now, nobody even bother to answer the damn phone.
Miss Tartiflate passed her head between the curtains of the yurt.
“Are you finished yet ?” she asked that as if he was on the throne.
“Nope!”
“What!? How? Do you have sausage fingers? My 5 years old daughter is more nimble than you with computers.”
“Well, you should have brought her with us then,” said Youssef with an irritated smile, fed up by her constant useless interruptions.
She grunted and closed the curtains angrily. Youssef growled like a bear, showing his bare teeth. Everybody knew why she jumped on the occasion for this trip: needed some fresh air from her nimble daughter and her husband.
An alert showed up on his phone : “You’ve got a message from 💣Gang Thi💣”. The bomb in the title looked suspicious, and his stomach growled, reminding him he hadn’t eaten this morning. He clicked to open it.
The face of a mummy looking like Darth Vader and laughing like the Joker jumped on his screen. After a few seconds a message started to appear in a tongue he couldn’t decipher.

Youssef looked at the clock and almost threw his phone on the ground as the mummy started to laugh again.
He would definitely have to miss the meeting with his friends.January 14, 2023 at 8:13 pm #6387In reply to: Scrying the Word Cloud
Words from the Cloud prompted me to write a story:
song stayed act unexpected recall words spears bus learn king expected followed fright hot wore kianda picture walked playing coast dusty
Once upon a time, in a far-off land, there was a Song that stayed in the hearts of the people. The Song was about an Act of bravery and sacrifice that had taken place many years ago. But one day, an unexpected recall of the Song was issued by the king. He had heard that the Song was not being sung correctly, and he wanted to make sure that the true story was being told. The people were puzzled, as they had learned the Song from their ancestors and had always thought it was accurate. But they followed the king’s orders and set out to learn the correct version of the Song. As they began to recall the words, they realized that there were some discrepancies. They had always sung about the hero wielding a sword, but the true story spoke of him wielding Spears. They were taken aback, but they knew they had to correct the Song. So, they set out on a journey to retrace the hero’s steps.
As they traveled, they encountered unexpected challenges. They faced a bus that broke down, a coastline that was dusty and treacherous, and even a group of bandits. But they pressed on, determined to learn the truth.
As they approached the hero’s final battle, they felt a sense of dread. They had heard that the enemy was fierce, and they were not prepared for what they would find. But they followed the path and soon found themselves at the edge of a hot, barren wasteland.
The heroes wore their Kianda, traditional armor made of woven reeds, and stepped forward, ready for battle. But to their surprise, the enemy was nowhere to be found. Instead, they found a picture etched into the ground, depicting the hero and his enemy locked in a fierce battle.
The people walked around the picture, marveling at the detail and skill of the artist. And as they looked closer, they saw that the hero was holding Spears, not a sword. They realized that they had learned the true story, and they felt a sense of pride and gratitude.
With the Song corrected, they returned home, playing the new version for all to hear. And from that day on, the true story of the hero’s bravery and sacrifice was remembered, and the Song stayed in the hearts of the people forevermore.
January 11, 2023 at 10:45 pm #6369In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
Expanding on the ancient channeled recipes:
Sure! Here are a few more examples of imaginary, exotic dishes that are channeled from ancient times:
- Grilled Squibber: A delicacy made from a type of mythical creature, said to be the ancestor of the modern-day squid. Served with a side of sautéed moss.
- Quimberry Pottage: A hearty stew made with quimberries, a type of imaginary fruit said to have medicinal properties, and chunks of tender meat.
- Plankton Pudding: A sweet and creamy dessert made with a type of plankton that is said to have a unique flavor and texture.
- Glurk Steak: A succulent cut of meat from the glurk, a creature said to live in the depths of the ocean. It’s served with a side of grilled slime pods.
- Chog Chops: Tender slices of meat cut from the Chog, a creature that said to be a mix between a chicken and a hog, served with a side of fried root vegetables.
- Bonkleberry Tarte: A sweet and tangy tarte made from Bonkleberries, a type of imaginary fruit said to have a unique spicy flavor.
- Gobber Soup: A thick and hearty soup made from the meat of Gobbers, a type of creature that is said to live in the swamps, served with a side of toasted marsh reeds.
- Smorlax Stir Fry: A traditional dish made from stir-frying meat of Smorlax, a mythical creature said to have a unique blend of flavors, served with a side of fried mushrooms.
Please note that all above dishes are completely fictional, and their ingredients and properties are also completely imaginary, this are not real dishes.
January 11, 2023 at 10:32 pm #6368In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
Something in the style of FPooh:
Arona heard the music growing louder as she approached the source of the sound. She could see a group of people gathered around a large fire, the flickering light casting shadows on the faces of the dancers. She hesitated for a moment, remembering the isolation of her journey and wondering if she was ready to be among people again. But the music was too inviting, and she found herself drawn towards the group.
As she neared the fire, she saw a young man playing a flute, the music flowing from his fingers with a fluid grace that captivated her. He looked up as she approached, and their eyes met. She could see the surprise and curiosity in his gaze, and she smiled, feeling a sense of connection she had not felt in a long time.
Fiona was sitting on a bench in the park, watching the children play. She had brought her sketchbook with her, but for once she didn’t feel the urge to draw. Instead she watched the children’s laughter, feeling content and at peace. Suddenly, she saw a young girl running towards her, a look of pure joy on her face. The girl stopped in front of her and held out a flower, offering it to Fiona with a smile.
Taken aback, Fiona took the flower and thanked the girl. The girl giggled and ran off to join her friends. Fiona looked down at the flower in her hand, and she felt a sense of inspiration, like a spark igniting within her. She opened her sketchbook and began to draw, feeling the weight lift from her shoulders and the magic of creativity flowing through her.
Minky led the group of misfits towards the emporium, his bowler hat bobbing on his head. He chattered excitedly, telling stories of the wondrous items to be found within Mr Jib’s store. Yikesy followed behind, still lost in his thoughts of Arona and feeling a sense of dread at the thought of buying a bowler hat. The green fairy flitted along beside him, her wings a blur of movement as she chattered with the parrot perched on her shoulder.
As they reached the emporium, they were disappointed to find it closed. But Minky refused to be discouraged, and he led them to a nearby cafe where they could sit and enjoy some tea and cake while they wait for the emporium to open. The green fairy was delighted, and she ordered a plate of macarons, smiling as she tasted the sweetness of the confections.
About creativity & everyday magic
Fiona had always been drawn to the magic of creativity, the way a blank page could be transformed into a world of wonder and beauty. But lately, she had been feeling stuck, unable to find the spark that ignited her imagination. She would sit with her sketchbook, pencil in hand, and nothing would come to her.
She started to question her abilities, wondering if she had lost the magic of her art. She spent long hours staring at her blank pages, feeling a weight on her chest that seemed to be growing heavier every day.
But then she remembered the green fairy’s tears and Yikesy’s longing for Arona, and she realized that the magic of creativity wasn’t something that could be found only in art. It was all around her, in the everyday moments of life.
She started to look for the magic in the small things, like the way the sunlight filtered through the trees, or the way a child’s laughter could light up a room. She found it in the way a stranger’s smile could lift her spirits, and in the way a simple cup of tea could bring her comfort.
And as she started to see the magic in the everyday, she found that the weight on her chest lifted and the spark of inspiration returned. She picked up her pencil and began to draw, feeling the magic flowing through her once again.
She understand that creativity blocks aren’t a destination, but just a step, just like the bowler hat that Minky had bought for them all, a bit of everyday magic, nothing too fancy but a sense of belonging, a sense of who they are and where they are going. And she let her pencil flow, with the hopes that one day, they will all find their way home.
January 10, 2023 at 10:14 pm #6362In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
write a short story based on the following cloud of words:
pride bet shouted lit wibberly case highly ours unless paid spend twice gay talking heads elizabeth in entries drink kill baker

“Gay baker triumphs over adversity”
Once upon a time, there was a gay baker named Elizabeth who took a great deal of pride in her craft. She spent twice the amount of money on high-quality ingredients and put in extra effort to make her baked goods stand out from the rest. However, her small town was not particularly accepting of the LGBT community, and she often faced discrimination from her neighbors.
One day, a group of men from the town entered her bakery and began shouting homophobic slurs at her. Elizabeth, feeling hurt and humiliated, decided that she would not let their hateful words get to her. She refused to back down and instead, decided to put all of her energy into creating a spectacular cake for the annual county fair.
She worked tirelessly on the cake, putting in long hours and experimenting with new flavors and techniques. The day of the fair finally arrived and Elizabeth brought her entry to be judged. To her surprise and delight, her cake was declared the winner and she was awarded a blue ribbon.
As she stood on stage holding her ribbon, Elizabeth couldn’t help but think about the men who had shouted at her in her bakery. She realized that their words no longer had power over her and she felt a sense of vindication. She knew that she had proven to herself and to her community that she was a skilled baker and a worthy member of society, regardless of her sexual orientation.
Feeling elated, Elizabeth closed the bakery for the day and went to the local bar where she met her friends, and they all drinks together, she was happy and felt like nothing can bring her down, as she went back home she felt like a new person, someone who has overcome prejudice and discrimination, she felt like a winner not just in the fair but in life.
The end.
December 6, 2022 at 2:17 pm #6350In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Transportation
Isaac Stokes 1804-1877
Isaac was born in Churchill, Oxfordshire in 1804, and was the youngest brother of my 4X great grandfather Thomas Stokes. The Stokes family were stone masons for generations in Oxfordshire and Gloucestershire, and Isaac’s occupation was a mason’s labourer in 1834 when he was sentenced at the Lent Assizes in Oxford to fourteen years transportation for stealing tools.
Churchill where the Stokes stonemasons came from: on 31 July 1684 a fire destroyed 20 houses and many other buildings, and killed four people. The village was rebuilt higher up the hill, with stone houses instead of the old timber-framed and thatched cottages. The fire was apparently caused by a baker who, to avoid chimney tax, had knocked through the wall from her oven to her neighbour’s chimney.
Isaac stole a pick axe, the value of 2 shillings and the property of Thomas Joyner of Churchill; a kibbeaux and a trowel value 3 shillings the property of Thomas Symms; a hammer and axe value 5 shillings, property of John Keen of Sarsden.
(The word kibbeaux seems to only exists in relation to Isaac Stokes sentence and whoever was the first to write it was perhaps being creative with the spelling of a kibbo, a miners or a metal bucket. This spelling is repeated in the criminal reports and the newspaper articles about Isaac, but nowhere else).
In March 1834 the Removal of Convicts was announced in the Oxford University and City Herald: Isaac Stokes and several other prisoners were removed from the Oxford county gaol to the Justitia hulk at Woolwich “persuant to their sentences of transportation at our Lent Assizes”.
via digitalpanopticon:
Hulks were decommissioned (and often unseaworthy) ships that were moored in rivers and estuaries and refitted to become floating prisons. The outbreak of war in America in 1775 meant that it was no longer possible to transport British convicts there. Transportation as a form of punishment had started in the late seventeenth century, and following the Transportation Act of 1718, some 44,000 British convicts were sent to the American colonies. The end of this punishment presented a major problem for the authorities in London, since in the decade before 1775, two-thirds of convicts at the Old Bailey received a sentence of transportation – on average 283 convicts a year. As a result, London’s prisons quickly filled to overflowing with convicted prisoners who were sentenced to transportation but had no place to go.
To increase London’s prison capacity, in 1776 Parliament passed the “Hulks Act” (16 Geo III, c.43). Although overseen by local justices of the peace, the hulks were to be directly managed and maintained by private contractors. The first contract to run a hulk was awarded to Duncan Campbell, a former transportation contractor. In August 1776, the Justicia, a former transportation ship moored in the River Thames, became the first prison hulk. This ship soon became full and Campbell quickly introduced a number of other hulks in London; by 1778 the fleet of hulks on the Thames held 510 prisoners.
Demand was so great that new hulks were introduced across the country. There were hulks located at Deptford, Chatham, Woolwich, Gosport, Plymouth, Portsmouth, Sheerness and Cork.The Justitia via rmg collections:
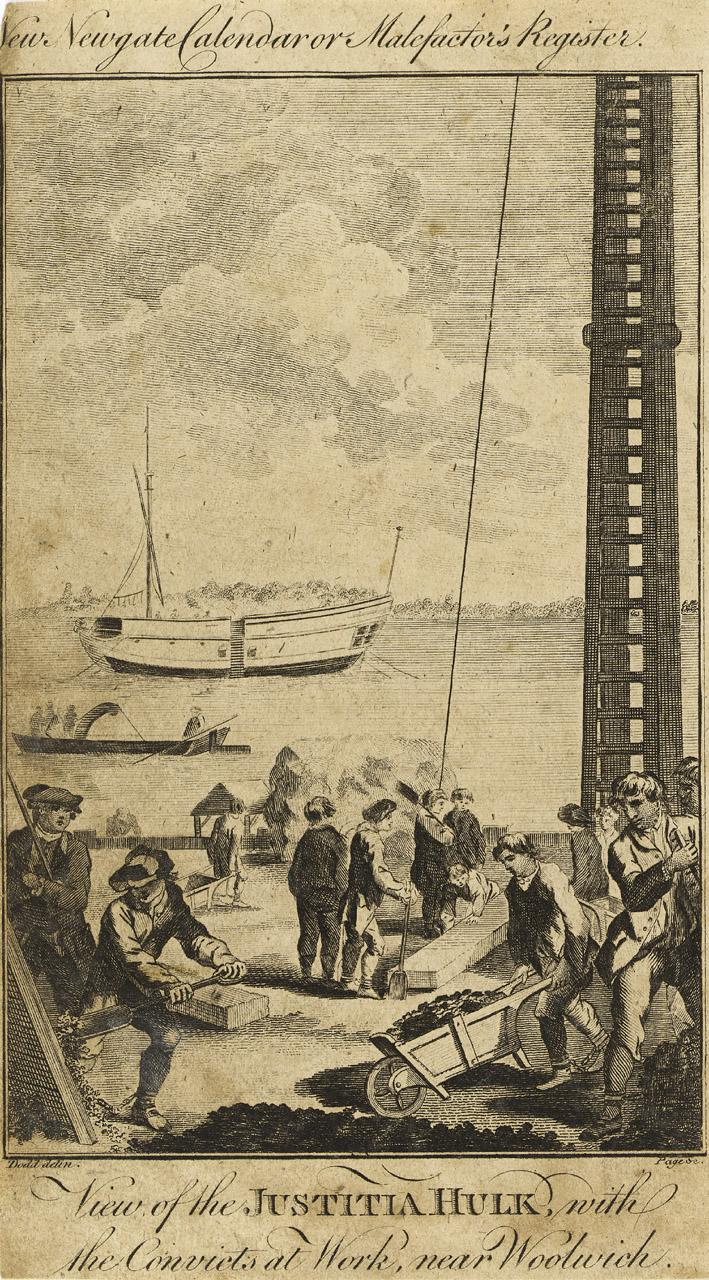

Convicts perform hard labour at the Woolwich Warren. The hulk on the river is the ‘Justitia’. Prisoners were kept on board such ships for months awaiting deportation to Australia. The ‘Justitia’ was a 260 ton prison hulk that had been originally moored in the Thames when the American War of Independence put a stop to the transportation of criminals to the former colonies. The ‘Justitia’ belonged to the shipowner Duncan Campbell, who was the Government contractor who organized the prison-hulk system at that time. Campbell was subsequently involved in the shipping of convicts to the penal colony at Botany Bay (in fact Port Jackson, later Sydney, just to the north) in New South Wales, the ‘first fleet’ going out in 1788.
While searching for records for Isaac Stokes I discovered that another Isaac Stokes was transported to New South Wales in 1835 as well. The other one was a butcher born in 1809, sentenced in London for seven years, and he sailed on the Mary Ann. Our Isaac Stokes sailed on the Lady Nugent, arriving in NSW in April 1835, having set sail from England in December 1834.
Lady Nugent was built at Bombay in 1813. She made four voyages under contract to the British East India Company (EIC). She then made two voyages transporting convicts to Australia, one to New South Wales and one to Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania). (via Wikipedia)
via freesettlerorfelon website:
On 20 November 1834, 100 male convicts were transferred to the Lady Nugent from the Justitia Hulk and 60 from the Ganymede Hulk at Woolwich, all in apparent good health. The Lady Nugent departed Sheerness on 4 December 1834.
SURGEON OLIVER SPROULE
Oliver Sproule kept a Medical Journal from 7 November 1834 to 27 April 1835. He recorded in his journal the weather conditions they experienced in the first two weeks:
‘In the course of the first week or ten days at sea, there were eight or nine on the sick list with catarrhal affections and one with dropsy which I attribute to the cold and wet we experienced during that period beating down channel. Indeed the foremost berths in the prison at this time were so wet from leaking in that part of the ship, that I was obliged to issue dry beds and bedding to a great many of the prisoners to preserve their health, but after crossing the Bay of Biscay the weather became fine and we got the damp beds and blankets dried, the leaks partially stopped and the prison well aired and ventilated which, I am happy to say soon manifested a favourable change in the health and appearance of the men.
Besides the cases given in the journal I had a great many others to treat, some of them similar to those mentioned but the greater part consisted of boils, scalds, and contusions which would not only be too tedious to enter but I fear would be irksome to the reader. There were four births on board during the passage which did well, therefore I did not consider it necessary to give a detailed account of them in my journal the more especially as they were all favourable cases.
Regularity and cleanliness in the prison, free ventilation and as far as possible dry decks turning all the prisoners up in fine weather as we were lucky enough to have two musicians amongst the convicts, dancing was tolerated every afternoon, strict attention to personal cleanliness and also to the cooking of their victuals with regular hours for their meals, were the only prophylactic means used on this occasion, which I found to answer my expectations to the utmost extent in as much as there was not a single case of contagious or infectious nature during the whole passage with the exception of a few cases of psora which soon yielded to the usual treatment. A few cases of scurvy however appeared on board at rather an early period which I can attribute to nothing else but the wet and hardships the prisoners endured during the first three or four weeks of the passage. I was prompt in my treatment of these cases and they got well, but before we arrived at Sydney I had about thirty others to treat.’
The Lady Nugent arrived in Port Jackson on 9 April 1835 with 284 male prisoners. Two men had died at sea. The prisoners were landed on 27th April 1835 and marched to Hyde Park Barracks prior to being assigned. Ten were under the age of 14 years.
The Lady Nugent:
Isaac’s distinguishing marks are noted on various criminal registers and record books:
“Height in feet & inches: 5 4; Complexion: Ruddy; Hair: Light brown; Eyes: Hazel; Marks or Scars: Yes [including] DEVIL on lower left arm, TSIS back of left hand, WS lower right arm, MHDW back of right hand.”
Another includes more detail about Isaac’s tattoos:
“Two slight scars right side of mouth, 2 moles above right breast, figure of the devil and DEVIL and raised mole, lower left arm; anchor, seven dots half moon, TSIS and cross, back of left hand; a mallet, door post, A, mans bust, sun, WS, lower right arm; woman, MHDW and shut knife, back of right hand.”

From How tattoos became fashionable in Victorian England (2019 article in TheConversation by Robert Shoemaker and Zoe Alkar):
“Historical tattooing was not restricted to sailors, soldiers and convicts, but was a growing and accepted phenomenon in Victorian England. Tattoos provide an important window into the lives of those who typically left no written records of their own. As a form of “history from below”, they give us a fleeting but intriguing understanding of the identities and emotions of ordinary people in the past.
As a practice for which typically the only record is the body itself, few systematic records survive before the advent of photography. One exception to this is the written descriptions of tattoos (and even the occasional sketch) that were kept of institutionalised people forced to submit to the recording of information about their bodies as a means of identifying them. This particularly applies to three groups – criminal convicts, soldiers and sailors. Of these, the convict records are the most voluminous and systematic.
Such records were first kept in large numbers for those who were transported to Australia from 1788 (since Australia was then an open prison) as the authorities needed some means of keeping track of them.”On the 1837 census Isaac was working for the government at Illiwarra, New South Wales. This record states that he arrived on the Lady Nugent in 1835. There are three other indent records for an Isaac Stokes in the following years, but the transcriptions don’t provide enough information to determine which Isaac Stokes it was. In April 1837 there was an abscondment, and an arrest/apprehension in May of that year, and in 1843 there was a record of convict indulgences.
From the Australian government website regarding “convict indulgences”:
“By the mid-1830s only six per cent of convicts were locked up. The vast majority worked for the government or free settlers and, with good behaviour, could earn a ticket of leave, conditional pardon or and even an absolute pardon. While under such orders convicts could earn their own living.”
In 1856 in Camden, NSW, Isaac Stokes married Catherine Daly. With no further information on this record it would be impossible to know for sure if this was the right Isaac Stokes. This couple had six children, all in the Camden area, but none of the records provided enough information. No occupation or place or date of birth recorded for Isaac Stokes.
I wrote to the National Library of Australia about the marriage record, and their reply was a surprise! Issac and Catherine were married on 30 September 1856, at the house of the Rev. Charles William Rigg, a Methodist minister, and it was recorded that Isaac was born in Edinburgh in 1821, to parents James Stokes and Sarah Ellis! The age at the time of the marriage doesn’t match Isaac’s age at death in 1877, and clearly the place of birth and parents didn’t match either. Only his fathers occupation of stone mason was correct. I wrote back to the helpful people at the library and they replied that the register was in a very poor condition and that only two and a half entries had survived at all, and that Isaac and Catherines marriage was recorded over two pages.
I searched for an Isaac Stokes born in 1821 in Edinburgh on the Scotland government website (and on all the other genealogy records sites) and didn’t find it. In fact Stokes was a very uncommon name in Scotland at the time. I also searched Australian immigration and other records for another Isaac Stokes born in Scotland or born in 1821, and found nothing. I was unable to find a single record to corroborate this mysterious other Isaac Stokes.
As the age at death in 1877 was correct, I assume that either Isaac was lying, or that some mistake was made either on the register at the home of the Methodist minster, or a subsequent mistranscription or muddle on the remnants of the surviving register. Therefore I remain convinced that the Camden stonemason Isaac Stokes was indeed our Isaac from Oxfordshire.
I found a history society newsletter article that mentioned Isaac Stokes, stone mason, had built the Glenmore church, near Camden, in 1859.
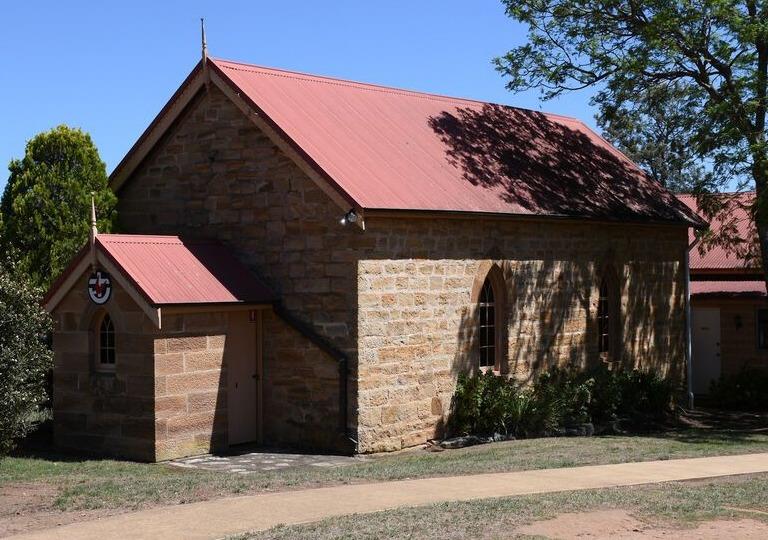

From the Wollondilly museum April 2020 newsletter:

From the Camden History website:
“The stone set over the porch of Glenmore Church gives the date of 1860. The church was begun in 1859 on land given by Joseph Moore. James Rogers of Picton was given the contract to build and local builder, Mr. Stokes, carried out the work. Elizabeth Moore, wife of Edward, laid the foundation stone. The first service was held on 19th March 1860. The cemetery alongside the church contains the headstones and memorials of the areas early pioneers.”
Isaac died on the 3rd September 1877. The inquest report puts his place of death as Bagdelly, near to Camden, and another death register has put Cambelltown, also very close to Camden. His age was recorded as 71 and the inquest report states his cause of death was “rupture of one of the large pulmonary vessels of the lung”. His wife Catherine died in childbirth in 1870 at the age of 43.
Isaac and Catherine’s children:
William Stokes 1857-1928
Catherine Stokes 1859-1846
Sarah Josephine Stokes 1861-1931
Ellen Stokes 1863-1932
Rosanna Stokes 1865-1919
Louisa Stokes 1868-1844.
It’s possible that Catherine Daly was a transported convict from Ireland.
Some time later I unexpectedly received a follow up email from The Oaks Heritage Centre in Australia.
“The Gaudry papers which we have in our archive record him (Isaac Stokes) as having built: the church, the school and the teachers residence. Isaac is recorded in the General return of convicts: 1837 and in Grevilles Post Office directory 1872 as a mason in Glenmore.”
 November 18, 2022 at 4:47 pm #6348
November 18, 2022 at 4:47 pm #6348In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Wong Sang
Wong Sang was born in China in 1884. In October 1916 he married Alice Stokes in Oxford.
Alice was the granddaughter of William Stokes of Churchill, Oxfordshire and William was the brother of Thomas Stokes the wheelwright (who was my 3X great grandfather). In other words Alice was my second cousin, three times removed, on my fathers paternal side.
Wong Sang was an interpreter, according to the baptism registers of his children and the Dreadnought Seamen’s Hospital admission registers in 1930. The hospital register also notes that he was employed by the Blue Funnel Line, and that his address was 11, Limehouse Causeway, E 14. (London)
“The Blue Funnel Line offered regular First-Class Passenger and Cargo Services From the UK to South Africa, Malaya, China, Japan, Australia, Java, and America. Blue Funnel Line was Owned and Operated by Alfred Holt & Co., Liverpool.
The Blue Funnel Line, so-called because its ships have a blue funnel with a black top, is more appropriately known as the Ocean Steamship Company.”Wong Sang and Alice’s daughter, Frances Eileen Sang, was born on the 14th July, 1916 and baptised in 1920 at St Stephen in Poplar, Tower Hamlets, London. The birth date is noted in the 1920 baptism register and would predate their marriage by a few months, although on the death register in 1921 her age at death is four years old and her year of birth is recorded as 1917.
Charles Ronald Sang was baptised on the same day in May 1920, but his birth is recorded as April of that year. The family were living on Morant Street, Poplar.
James William Sang’s birth is recorded on the 1939 census and on the death register in 2000 as being the 8th March 1913. This definitely would predate the 1916 marriage in Oxford.
William Norman Sang was born on the 17th October 1922 in Poplar.
Alice and the three sons were living at 11, Limehouse Causeway on the 1939 census, the same address that Wong Sang was living at when he was admitted to Dreadnought Seamen’s Hospital on the 15th January 1930. Wong Sang died in the hospital on the 8th March of that year at the age of 46.
Alice married John Patterson in 1933 in Stepney. John was living with Alice and her three sons on Limehouse Causeway on the 1939 census and his occupation was chef.
Via Old London Photographs:
“Limehouse Causeway is a street in east London that was the home to the original Chinatown of London. A combination of bomb damage during the Second World War and later redevelopment means that almost nothing is left of the original buildings of the street.”
Limehouse Causeway in 1925:
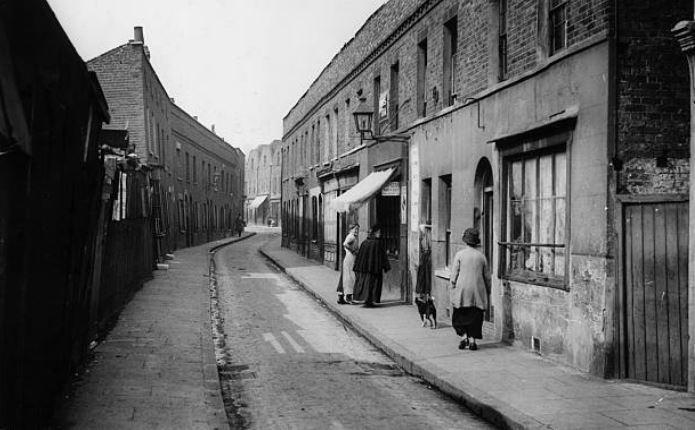

From The Story of Limehouse’s Lost Chinatown, poplarlondon website:
“Limehouse was London’s first Chinatown, home to a tightly-knit community who were demonised in popular culture and eventually erased from the cityscape.
As recounted in the BBC’s ‘Our Greatest Generation’ series, Connie was born to a Chinese father and an English mother in early 1920s Limehouse, where she used to play in the street with other British and British-Chinese children before running inside for teatime at one of their houses.
Limehouse was London’s first Chinatown between the 1880s and the 1960s, before the current Chinatown off Shaftesbury Avenue was established in the 1970s by an influx of immigrants from Hong Kong.
Connie’s memories of London’s first Chinatown as an “urban village” paint a very different picture to the seedy area portrayed in early twentieth century novels.
The pyramid in St Anne’s church marked the entrance to the opium den of Dr Fu Manchu, a criminal mastermind who threatened Western society by plotting world domination in a series of novels by Sax Rohmer.
Thomas Burke’s Limehouse Nights cemented stereotypes about prostitution, gambling and violence within the Chinese community, and whipped up anxiety about sexual relationships between Chinese men and white women.
Though neither novelist was familiar with the Chinese community, their depictions made Limehouse one of the most notorious areas of London.
Travel agent Thomas Cook even organised tours of the area for daring visitors, despite the rector of Limehouse warning that “those who look for the Limehouse of Mr Thomas Burke simply will not find it.”
All that remains is a handful of Chinese street names, such as Ming Street, Pekin Street, and Canton Street — but what was Limehouse’s chinatown really like, and why did it get swept away?
Chinese migration to Limehouse
Chinese sailors discharged from East India Company ships settled in the docklands from as early as the 1780s.
By the late nineteenth century, men from Shanghai had settled around Pennyfields Lane, while a Cantonese community lived on Limehouse Causeway.
Chinese sailors were often paid less and discriminated against by dock hirers, and so began to diversify their incomes by setting up hand laundry services and restaurants.
Old photographs show shopfronts emblazoned with Chinese characters with horse-drawn carts idling outside or Chinese men in suits and hats standing proudly in the doorways.
In oral histories collected by Yat Ming Loo, Connie’s husband Leslie doesn’t recall seeing any Chinese women as a child, since male Chinese sailors settled in London alone and married working-class English women.
In the 1920s, newspapers fear-mongered about interracial marriages, crime and gambling, and described chinatown as an East End “colony.”
Ironically, Chinese opium-smoking was also demonised in the press, despite Britain waging war against China in the mid-nineteenth century for suppressing the opium trade to alleviate addiction amongst its people.
The number of Chinese people who settled in Limehouse was also greatly exaggerated, and in reality only totalled around 300.
The real Chinatown
Although the press sought to characterise Limehouse as a monolithic Chinese community in the East End, Connie remembers seeing people of all nationalities in the shops and community spaces in Limehouse.
She doesn’t remember feeling discriminated against by other locals, though Connie does recall having her face measured and IQ tested by a member of the British Eugenics Society who was conducting research in the area.
Some of Connie’s happiest childhood memories were from her time at Chung-Hua Club, where she learned about Chinese culture and language.
Why did Chinatown disappear?
The caricature of Limehouse’s Chinatown as a den of vice hastened its erasure.
Police raids and deportations fuelled by the alarmist media coverage threatened the Chinese population of Limehouse, and slum clearance schemes to redevelop low-income areas dispersed Chinese residents in the 1930s.
The Defence of the Realm Act imposed at the beginning of the First World War criminalised opium use, gave the authorities increased powers to deport Chinese people and restricted their ability to work on British ships.
Dwindling maritime trade during World War II further stripped Chinese sailors of opportunities for employment, and any remnants of Chinatown were destroyed during the Blitz or erased by postwar development schemes.”
Wong Sang 1884-1930
The year 1918 was a troublesome one for Wong Sang, an interpreter and shipping agent for Blue Funnel Line. The Sang family were living at 156, Chrisp Street.
Chrisp Street, Poplar, in 1913 via Old London Photographs:
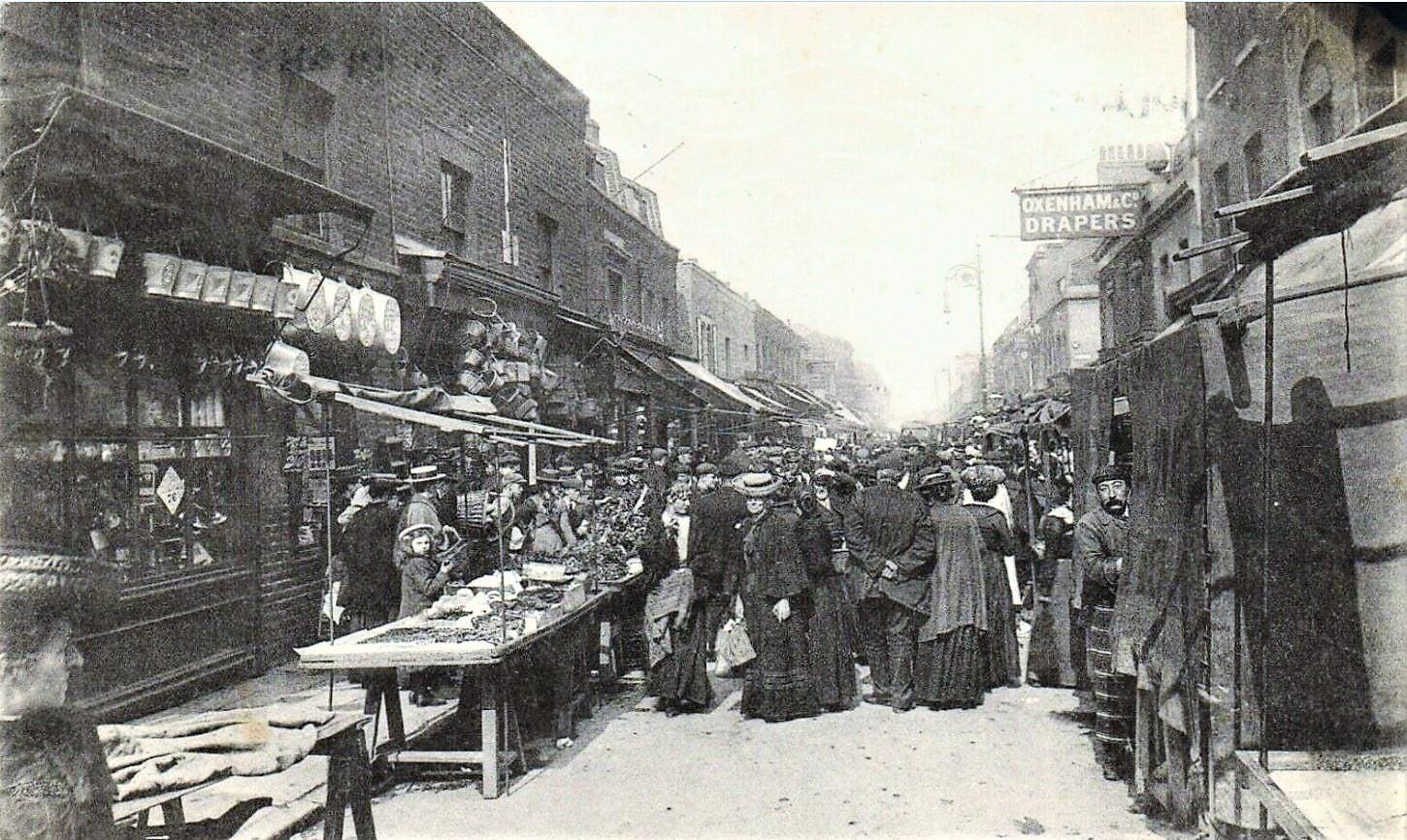

In February Wong Sang was discharged from a false accusation after defending his home from potential robbers.
East End News and London Shipping Chronicle – Friday 15 February 1918:

In August of that year he was involved in an incident that left him unconscious.
Faringdon Advertiser and Vale of the White Horse Gazette – Saturday 31 August 1918:

Wong Sang is mentioned in an 1922 article about “Oriental London”.
London and China Express – Thursday 09 February 1922:

A photograph of the Chee Kong Tong Chinese Freemason Society mentioned in the above article, via Old London Photographs:

Wong Sang was recommended by the London Metropolitan Police in 1928 to assist in a case in Wellingborough, Northampton.
Difficulty of Getting an Interpreter: Northampton Mercury – Friday 16 March 1928:


The difficulty was that “this man speaks the Cantonese language only…the Northeners and the Southerners in China have differing languages and the interpreter seemed to speak one that was in between these two.”
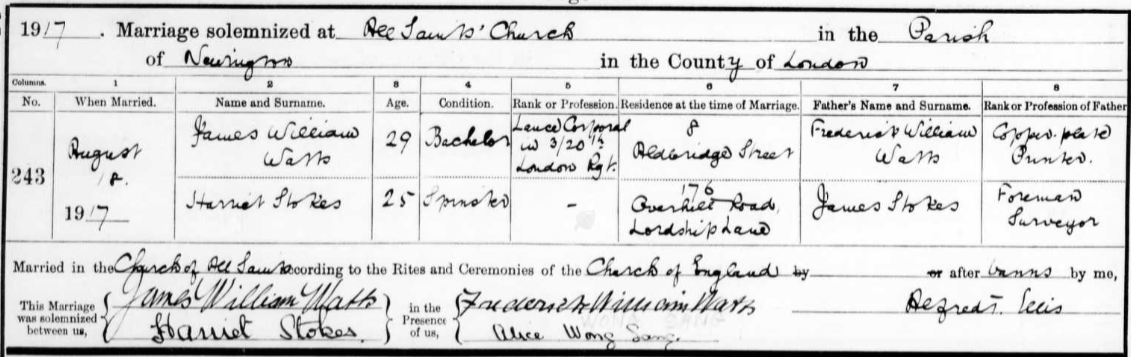
In 1917, Alice Wong Sang was a witness at her sister Harriet Stokes marriage to James William Watts in Southwark, London. Their father James Stokes occupation on the marriage register is foreman surveyor, but on the census he was a council roadman or labourer. (I initially rejected this as the correct marriage for Harriet because of the discrepancy with the occupations. Alice Wong Sang as a witness confirmed that it was indeed the correct one.)
James William Sang 1913-2000 was a clock fitter and watch assembler (on the 1939 census). He married Ivy Laura Fenton in 1963 in Sidcup, Kent. James died in Southwark in 2000.
Charles Ronald Sang 1920-1974 was a draughtsman (1939 census). He married Eileen Burgess in 1947 in Marylebone. Charles and Eileen had two sons: Keith born in 1951 and Roger born in 1952. He died in 1974 in Hertfordshire.
William Norman Sang 1922-2000 was a clerk and telephone operator (1939 census). William enlisted in the Royal Artillery in 1942. He married Lily Mullins in 1949 in Bethnal Green, and they had three daughters: Marion born in 1950, Christine in 1953, and Frances in 1959. He died in Redbridge in 2000.
I then found another two births registered in Poplar by Alice Sang, both daughters. Doris Winifred Sang was born in 1925, and Patricia Margaret Sang was born in 1933 ~ three years after Wong Sang’s death. Neither of the these daughters were on the 1939 census with Alice, John Patterson and the three sons. Margaret had presumably been evacuated because of the war to a family in Taunton, Somerset. Doris would have been fourteen and I have been unable to find her in 1939 (possibly because she died in 2017 and has not had the redaction removed yet on the 1939 census as only deceased people are viewable).
Doris Winifred Sang 1925-2017 was a nursing sister. She didn’t marry, and spent a year in USA between 1954 and 1955. She stayed in London, and died at the age of ninety two in 2017.
Patricia Margaret Sang 1933-1998 was also a nurse. She married Patrick L Nicely in Stepney in 1957. Patricia and Patrick had five children in London: Sharon born 1959, Donald in 1960, Malcolm was born and died in 1966, Alison was born in 1969 and David in 1971.
I was unable to find a birth registered for Alice’s first son, James William Sang (as he appeared on the 1939 census). I found Alice Stokes on the 1911 census as a 17 year old live in servant at a tobacconist on Pekin Street, Limehouse, living with Mr Sui Fong from Hong Kong and his wife Sarah Sui Fong from Berlin. I looked for a birth registered for James William Fong instead of Sang, and found it ~ mothers maiden name Stokes, and his date of birth matched the 1939 census: 8th March, 1913.
On the 1921 census, Wong Sang is not listed as living with them but it is mentioned that Mr Wong Sang was the person returning the census. Also living with Alice and her sons James and Charles in 1921 are two visitors: (Florence) May Stokes, 17 years old, born in Woodstock, and Charles Stokes, aged 14, also born in Woodstock. May and Charles were Alice’s sister and brother.
I found Sharon Nicely on social media and she kindly shared photos of Wong Sang and Alice Stokes:

 November 13, 2022 at 10:29 pm #6345
November 13, 2022 at 10:29 pm #6345In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Crime and Punishment in Tetbury
I noticed that there were quite a number of Brownings of Tetbury in the newspaper archives involved in criminal activities while doing a routine newspaper search to supplement the information in the usual ancestry records. I expanded the tree to include cousins, and offsping of cousins, in order to work out who was who and how, if at all, these individuals related to our Browning family.
I was expecting to find some of our Brownings involved in the Swing Riots in Tetbury in 1830, but did not. Most of our Brownings (including cousins) were stone masons. Most of the rioters in 1830 were agricultural labourers.
The Browning crimes are varied, and by todays standards, not for the most part terribly serious ~ you would be unlikely to receive a sentence of hard labour for being found in an outhouse with the intent to commit an unlawful act nowadays, or for being drunk.
The central character in this chapter is Isaac Browning (my 4x great grandfather), who did not appear in any criminal registers, but the following individuals can be identified in the family structure through their relationship to him.
RICHARD LOCK BROWNING born in 1853 was Isaac’s grandson, his son George’s son. Richard was a mason. In 1879 he and Henry Browning of the same age were sentenced to one month hard labour for stealing two pigeons in Tetbury. Henry Browning was Isaac’s nephews son.
In 1883 Richard Browning, mason of Tetbury, was charged with obtaining food and lodging under false pretences, but was found not guilty and acquitted.
In 1884 Richard Browning, mason of Tetbury, was sentenced to one month hard labour for game trespass.Richard had been fined a number of times in Tetbury:

Richard Lock Browning was five feet eight inches tall, dark hair, grey eyes, an oval face and a dark complexion. He had two cuts on the back of his head (in February 1879) and a scar on his right eyebrow.
HENRY BROWNING, who was stealing pigeons with Richard Lock Browning in 1879, (Isaac’s brother Williams grandson, son of George Browning and his wife Charity) was charged with being drunk in 1882 and ordered to pay a fine of one shilling and costs of fourteen shillings, or seven days hard labour.
Henry was found guilty of gaming in the highway at Tetbury in 1872 and was sentenced to seven days hard labour. In 1882 Henry (who was also a mason) was charged with assault but discharged.
Henry was five feet five inches tall, brown hair and brown eyes, a long visage and a fresh complexion.
Henry emigrated with his daughter to Canada in 1913, and died in Vancouver in 1919.THOMAS BUCKINGHAM 1808-1846 (Isaacs daughter Janes husband) was charged with stealing a black gelding in Tetbury in 1838. No true bill. (A “no true bill” means the jury did not find probable cause to continue a case.)
Thomas did however neglect to pay his taxes in 1832:

LEWIN BUCKINGHAM (grandson of Isaac, his daughter Jane’s son) was found guilty in 1846 stealing two fowls in Tetbury when he was sixteen years old.
In 1846 he was sentence to one month hard labour (or pay ten shillings fine and ten shillings costs) for loitering with the intent to trespass in search of conies.
A year later in 1847, he and three other young men were sentenced to four months hard labour for larceny.
Lewin was five feet three inches tall, with brown hair and brown eyes, long visage, sallow complexion, and had a scar on his left arm.JOHN BUCKINGHAM born circa 1832, a Tetbury labourer (Isaac’s grandson, Lewin’s brother) was sentenced to six weeks hard labour for larceny in 1855 for stealing a duck in Cirencester. The notes on the register mention that he had been employed by Mr LOCK, Angel Inn. (John’s grandmother was Mary Lock so this is likely a relative).
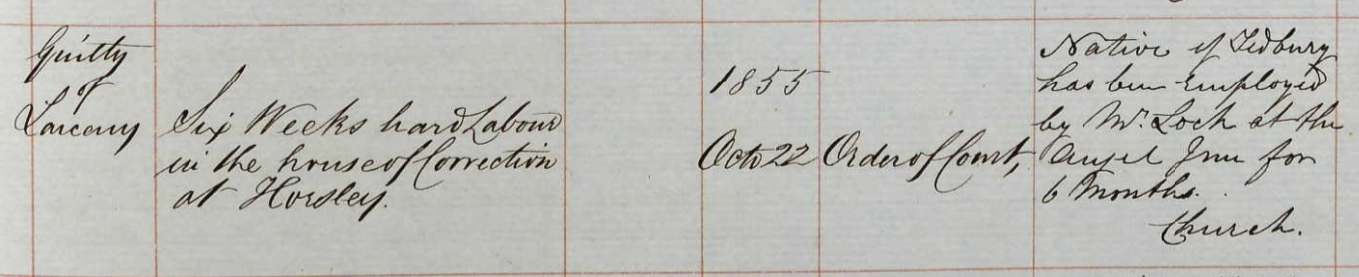
The previous year in 1854 John was sentenced to one month or a one pound fine for assaulting and beating W. Wood.
John was five feet eight and three quarter inches tall, light brown hair and grey eyes, an oval visage and a fresh complexion. He had a scar on his left arm and inside his right knee.JOSEPH PERRET was born circa 1831 and he was a Tetbury labourer. (He was Isaac’s granddaughter Charlotte Buckingham’s husband)
In 1855 he assaulted William Wood and was sentenced to one month or a two pound ten shilling fine. Was it the same W Wood that his wifes cousin John assaulted the year before?
In 1869 Joseph was sentenced to one month hard labour for feloniously receiving a cupboard known to be stolen.JAMES BUCKINGAM born circa 1822 in Tetbury was a shoemaker. (Isaac’s nephew, his sister Hannah’s son)
In 1854 the Tetbury shoemaker was sentenced to four months hard labour for stealing 30 lbs of lead off someones house.
In 1856 the Tetbury shoemaker received two months hard labour or pay £2 fine and 12 s costs for being found in pursuit of game.
In 1868 he was sentenced to two months hard labour for stealing a gander. A unspecified previous conviction is noted.
1871 the Tetbury shoemaker was found in an outhouse for an unlawful purpose and received ten days hard labour. The register notes that his sister is Mrs Cook, the Green, Tetbury. (James sister Prudence married Thomas Cook)
James sister Charlotte married a shoemaker and moved to UTAH.
James was five feet eight inches tall, dark hair and blue eyes, a long visage and a florid complexion. He had a scar on his forehead and a mole on the right side of his neck and abdomen, and a scar on the right knee.November 10, 2022 at 12:08 pm #6344In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The Tetbury Riots
While researching the Tetbury riots (I had found some Browning names in the newspaper archives in association with the uprisings) I came across an article called “Elizabeth Parker, the Swing Riots, and the Tetbury parish clerk” by Jill Evans.
I noted the name of the parish clerk, Daniel Cole, because I know someone else of that name. The incident in the article was 1830.
I found the 1826 marriage in the Tetbury parish registers (where Daniel was the parish clerk) of my 4x great grandmothers sister Hesther Lock. One of the witnesses was her brother Charles, and the other was Daniel Cole, the parish clerk.
Marriage of Lewin Chandler and Hesther Lock in 1826:

from the article:
“The Swing Riots were disturbances which took place in 1830 and 1831, mostly in the southern counties of England. Agricultural labourers, who were already suffering due to low wages and a lack of work after several years of bad harvests, rose up when their employers introduced threshing machines into their workplaces. The riots got their name from the threatening letters which were sent to farmers and other employers, which were signed “Captain Swing.”
The riots spread into Gloucestershire in November 1830, with the Tetbury area seeing the worst of the disturbances. Amongst the many people arrested afterwards was one woman, Elizabeth Parker. She has sometimes been cited as one of only two females who were transported for taking part in the Swing Riots. In fact, she was sentenced to be transported for this crime, but never sailed, as she was pardoned a few months after being convicted. However, less than a year after being released from Gloucester Gaol, she was back, awaiting trial for another offence. The circumstances in both of the cases she was tried for reveal an intriguing relationship with one Daniel Cole, parish clerk and assistant poor law officer in Tetbury….
….Elizabeth Parker was committed to Gloucester Gaol on 4 December 1830. In the Gaol Registers, she was described as being 23 and a “labourer”. She was in fact a prostitute, and she was unusual for the time in that she could read and write. She was charged on the oaths of Daniel Cole and others with having been among a mob which destroyed a threshing machine belonging to Jacob Hayward, at his farm in Beverstone, on 26 November.
…..Elizabeth Parker was granted royal clemency in July 1831 and was released from prison. She returned to Tetbury and presumably continued in her usual occupation, but on 27 March 1832, she was committed to Gloucester Gaol again. This time, she was charged with stealing 2 five pound notes, 5 sovereigns and 5 half sovereigns, from the person of Daniel Cole.
Elizabeth was tried at the Lent Assizes which began on 28 March, 1832. The details of her trial were reported in the Morning Post. Daniel Cole was in the “Boat Inn” (meaning the Boot Inn, I think) in Tetbury, when Elizabeth Parker came in. Cole “accompanied her down the yard”, where he stayed with her for about half an hour. The next morning, he realised that all his money was gone. One of his five pound notes was identified by him in a shop, where Parker had bought some items.
Under cross-examination, Cole said he was the assistant overseer of the poor and collector of public taxes of the parish of Tetbury. He was married with one child. He went in to the inn at about 9 pm, and stayed about 2 hours, drinking in the parlour, with the landlord, Elizabeth Parker, and two others. He was not drunk, but he was “rather fresh.” He gave the prisoner no money. He saw Elizabeth Parker next morning at the Prince and Princess public house. He didn’t drink with her or give her any money. He did give her a shilling after she was committed. He never said that he would not have prosecuted her “if it was not for her own tongue”. (Presumably meaning he couldn’t trust her to keep her mouth shut.)”
Contemporary illustration of the Swing riots:
Captain Swing was the imaginary leader agricultural labourers who set fire to barns and haystacks in the southern and eastern counties of England from 1830. Although the riots were ruthlessly put down (19 hanged, 644 imprisoned and 481 transported), the rural agitation led the new Whig government to establish a Royal Commission on the Poor Laws and its report provided the basis for the 1834 New Poor Law enacted after the Great Reform Bills of 1833.
An original portrait of Captain Swing hand coloured lithograph circa 1830:
 November 10, 2022 at 10:59 am #6343
November 10, 2022 at 10:59 am #6343In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Colney Hatch Lunatic Asylum
William James Stokes
William James Stokes was the first son of Thomas Stokes and Eliza Browning. Oddly, his birth was registered in Witham in Essex, on the 6th September 1841.
Birth certificate of William James Stokes:

His father Thomas Stokes has not yet been found on the 1841 census, and his mother Eliza was staying with her uncle Thomas Lock in Cirencester in 1841. Eliza’s mother Mary Browning (nee Lock) was staying there too. Thomas and Eliza were married in September 1840 in Hempstead in Gloucestershire.
It’s a mystery why William was born in Essex but one possibility is that his father Thomas, who later worked with the Chipperfields making circus wagons, was staying with the Chipperfields who were wheelwrights in Witham in 1841. Or perhaps even away with a traveling circus at the time of the census, learning the circus waggon wheelwright trade. But this is a guess and it’s far from clear why Eliza would make the journey to Witham to have the baby when she was staying in Cirencester a few months prior.
In 1851 Thomas and Eliza, William and four younger siblings were living in Bledington in Oxfordshire.
William was a 19 year old wheelwright living with his parents in Evesham in 1861. He married Elizabeth Meldrum in December 1867 in Hackney, London. He and his father are both wheelwrights on the marriage register.
Marriage of William James Stokes and Elizabeth Meldrum in 1867:

William and Elizabeth had a daughter, Elizabeth Emily Stokes, in 1868 in Shoreditch, London.
On the 3rd of December 1870, William James Stokes was admitted to Colney Hatch Lunatic Asylum. One week later on the 10th of December, he was dead.
On his death certificate the cause of death was “general paralysis and exhaustion, certified. MD Edgar Sheppard in attendance.” William was just 29 years old.
Death certificate William James Stokes:

I asked on a genealogy forum what could possibly have caused this death at such a young age. A retired pathology professor replied that “in medicine the term General Paralysis is only used in one context – that of Tertiary Syphilis.”
“Tertiary syphilis is the third and final stage of syphilis, a sexually transmitted disease that unfolds in stages when the individual affected doesn’t receive appropriate treatment.”From the article “Looking back: This fascinating and fatal disease” by Jennifer Wallis:
“……in asylums across Britain in the late 19th century, with hundreds of people receiving the diagnosis of general paralysis of the insane (GPI). The majority of these were men in their 30s and 40s, all exhibiting one or more of the disease’s telltale signs: grandiose delusions, a staggering gait, disturbed reflexes, asymmetrical pupils, tremulous voice, and muscular weakness. Their prognosis was bleak, most dying within months, weeks, or sometimes days of admission.
The fatal nature of GPI made it of particular concern to asylum superintendents, who became worried that their institutions were full of incurable cases requiring constant care. The social effects of the disease were also significant, attacking men in the prime of life whose admission to the asylum frequently left a wife and children at home. Compounding the problem was the erratic behaviour of the general paralytic, who might get themselves into financial or legal difficulties. Delusions about their vast wealth led some to squander scarce family resources on extravagant purchases – one man’s wife reported he had bought ‘a quantity of hats’ despite their meagre income – and doctors pointed to the frequency of thefts by general paralytics who imagined that everything belonged to them.”
The London Archives hold the records for Colney Hatch, but they informed me that the particular records for the dates that William was admitted and died were in too poor a condition to be accessed without causing further damage.
Colney Hatch Lunatic Asylum gained such notoriety that the name “Colney Hatch” appeared in various terms of abuse associated with the concept of madness. Infamous inmates that were institutionalized at Colney Hatch (later called Friern Hospital) include Jack the Ripper suspect Aaron Kosminski from 1891, and from 1911 the wife of occultist Aleister Crowley. In 1993 the hospital grounds were sold and the exclusive apartment complex called Princess Park Manor was built.
Colney Hatch:
In 1873 Williams widow married William Hallam in Limehouse in London. Elizabeth died in 1930, apparently unaffected by her first husbands ailment.
November 4, 2022 at 2:19 pm #6342In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Brownings of Tetbury
Isaac Browning (1784-1848) married Mary Lock (1787-1870) in Tetbury in 1806. Both of them were born in Tetbury, Gloucestershire. Isaac was a stone mason. Between 1807 and 1832 they baptised fourteen children in Tetbury, and on 8 Nov 1829 Isaac and Mary baptised five daughters all on the same day.
I considered that they may have been quintuplets, with only the last born surviving, which would have answered my question about the name of the house La Quinta in Broadway, the home of Eliza Browning and Thomas Stokes son Fred. However, the other four daughters were found in various records and they were not all born the same year. (So I still don’t know why the house in Broadway had such an unusual name).
Their son George was born and baptised in 1827, but Louisa born 1821, Susan born 1822, Hesther born 1823 and Mary born 1826, were not baptised until 1829 along with Charlotte born in 1828. (These birth dates are guesswork based on the age on later censuses.) Perhaps George was baptised promptly because he was sickly and not expected to survive. Isaac and Mary had a son George born in 1814 who died in 1823. Presumably the five girls were healthy and could wait to be done as a job lot on the same day later.
Eliza Browning (1814-1886), my great great great grandmother, had a baby six years before she married Thomas Stokes. Her name was Ellen Harding Browning, which suggests that her fathers name was Harding. On the 1841 census seven year old Ellen was living with her grandfather Isaac Browning in Tetbury. Ellen Harding Browning married William Dee in Tetbury in 1857, and they moved to Western Australia.
Ellen Harding Browning Dee: (photo found on ancestry website)

OBITUARY. MRS. ELLEN DEE.
A very old and respected resident of Dongarra, in the person of Mrs. Ellen Dee, passed peacefully away on Sept. 27, at the advanced age of 74 years.The deceased had been ailing for some time, but was about and actively employed until Wednesday, Sept. 20, whenn she was heard groaning by some neighbours, who immediately entered her place and found her lying beside the fireplace. Tho deceased had been to bed over night, and had evidently been in the act of lighting thc fire, when she had a seizure. For some hours she was conscious, but had lost the power of speech, and later on became unconscious, in which state she remained until her death.
The deceased was born in Gloucestershire, England, in 1833, was married to William Dee in Tetbury Church 23 years later. Within a month she left England with her husband for Western Australian in the ship City oí Bristol. She resided in Fremantle for six months, then in Greenough for a short time, and afterwards (for 42 years) in Dongarra. She was, therefore, a colonist of about 51 years. She had a family of four girls and three boys, and five of her children survive her, also 35 grandchildren, and eight great grandchildren. She was very highly respected, and her sudden collapse came as a great shock to many.
Eliza married Thomas Stokes (1816-1885) in September 1840 in Hempstead, Gloucestershire. On the 1841 census, Eliza and her mother Mary Browning (nee Lock) were staying with Thomas Lock and family in Cirencester. Strangely, Thomas Stokes has not been found thus far on the 1841 census, and Thomas and Eliza’s first child William James Stokes birth was registered in Witham, in Essex, on the 6th of September 1841.
I don’t know why William James was born in Witham, or where Thomas was at the time of the census in 1841. One possibility is that as Thomas Stokes did a considerable amount of work with circus waggons, circus shooting galleries and so on as a journeyman carpenter initially and then later wheelwright, perhaps he was working with a traveling circus at the time.
But back to the Brownings ~ more on William James Stokes to follow.
One of Isaac and Mary’s fourteen children died in infancy: Ann was baptised and died in 1811. Two of their children died at nine years old: the first George, and Mary who died in 1835. Matilda was 21 years old when she died in 1844.
Jane Browning (1808-) married Thomas Buckingham in 1830 in Tetbury. In August 1838 Thomas was charged with feloniously stealing a black gelding.
Susan Browning (1822-1879) married William Cleaver in November 1844 in Tetbury. Oddly thereafter they use the name Bowman on the census. On the 1851 census Mary Browning (Susan’s mother), widow, has grandson George Bowman born in 1844 living with her. The confusion with the Bowman and Cleaver names was clarified upon finding the criminal registers:
30 January 1834. Offender: William Cleaver alias Bowman, Richard Bunting alias Barnfield and Jeremiah Cox, labourers of Tetbury. Crime: Stealing part of a dead fence from a rick barton in Tetbury, the property of Robert Tanner, farmer.
And again in 1836:
29 March 1836 Bowman, William alias Cleaver, of Tetbury, labourer age 18; 5’2.5” tall, brown hair, grey eyes, round visage with fresh complexion; several moles on left cheek, mole on right breast. Charged on the oath of Ann Washbourn & others that on the morning of the 31 March at Tetbury feloniously stolen a lead spout affixed to the dwelling of the said Ann Washbourn, her property. Found guilty 31 March 1836; Sentenced to 6 months.
On the 1851 census Susan Bowman was a servant living in at a large drapery shop in Cheltenham. She was listed as 29 years old, married and born in Tetbury, so although it was unusual for a married woman not to be living with her husband, (or her son for that matter, who was living with his grandmother Mary Browning), perhaps her husband William Bowman alias Cleaver was in trouble again. By 1861 they are both living together in Tetbury: William was a plasterer, and they had three year old Isaac and Thomas, one year old. In 1871 William was still a plasterer in Tetbury, living with wife Susan, and sons Isaac and Thomas. Interestingly, a William Cleaver is living next door but one!
Susan was 56 when she died in Tetbury in 1879.
Three of the Browning daughters went to London.
Louisa Browning (1821-1873) married Robert Claxton, coachman, in 1848 in Bryanston Square, Westminster, London. Ester Browning was a witness.
Ester Browning (1823-1893)(or Hester) married Charles Hudson Sealey, cabinet maker, in Bethnal Green, London, in 1854. Charles was born in Tetbury. Charlotte Browning was a witness.
Charlotte Browning (1828-1867?) was admitted to St Marylebone workhouse in London for “parturition”, or childbirth, in 1860. She was 33 years old. A birth was registered for a Charlotte Browning, no mothers maiden name listed, in 1860 in Marylebone. A death was registered in Camden, buried in Marylebone, for a Charlotte Browning in 1867 but no age was recorded. As the age and parents were usually recorded for a childs death, I assume this was Charlotte the mother.
I found Charlotte on the 1851 census by chance while researching her mother Mary Lock’s siblings. Hesther Lock married Lewin Chandler, and they were living in Stepney, London. Charlotte is listed as a neice. Although Browning is mistranscribed as Broomey, the original page says Browning. Another mistranscription on this record is Hesthers birthplace which is transcribed as Yorkshire. The original image shows Gloucestershire.
Isaac and Mary’s first son was John Browning (1807-1860). John married Hannah Coates in 1834. John’s brother Charles Browning (1819-1853) married Eliza Coates in 1842. Perhaps they were sisters. On the 1861 census Hannah Browning, John’s wife, was a visitor in the Harding household in a village called Coates near Tetbury. Thomas Harding born in 1801 was the head of the household. Perhaps he was the father of Ellen Harding Browning.
George Browning (1828-1870) married Louisa Gainey in Tetbury, and died in Tetbury at the age of 42. Their son Richard Lock Browning, a 32 year old mason, was sentenced to one month hard labour for game tresspass in Tetbury in 1884.
Isaac Browning (1832-1857) was the youngest son of Isaac and Mary. He was just 25 years old when he died in Tetbury.
-
AuthorSearch Results