Search Results for 'cot'
-
AuthorSearch Results
-
March 11, 2024 at 3:48 am #7402
In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
The perfume, ‘Liz n°5’, was to have been Frigella’s piece de resistance. In her spare time, she diligently crafted it, adding all the usual witchy razzmatazz: notes of night jasmine here, a dab of moonflower there and perhaps just the smallest whiff of hemlock to top it off.
With the help of her familiar, Quillonia, she also wove the potion with her intentions; powerful and ancient spells which would would offer the wearer protection from harm; Liz n°5 was to be the olfactory epitome of Frigella’s magical prowess! She aspired to do more than just freshen up a room; she intended to fortify spirits, boost morale, and ward off influences that might lead their little group of witches into harm’s way. It was her way of doing a silent, scented good, like a secret benefactor in a tale of old.
Frigella hadn’t told the other witches she was working so hard on the perfume. Even when Malove berated her for the excessive time she was taking to produce anything, Frigella had held her silence. Inwardly though, she bubbled with excitement as she imagined how she would unveil her perfume to the doubting Malove and the other witches. She could all but hear their oohs of admiration and gasps of appreciation. At last Malove would surely be convinced of her worth!
So when Malove had announced her own plans for a new line of incense, and summarily whisked them all off to the carnival in Rio, Frigella was deflated. And the sense of despondency lingered, even once back at home in Ireland. When she expectantly sniffed her sample of Liz n°5′ , hoping to rekindle her enthusiasm, Frigella discerned it had lost its magic.
“I’m done with stupid perfume making”, she confided to Quillonia. She was seated outside in the garden of her small cottage, enjoying the last of the day’s sun while Quillonia snuffled around in the leaves. “Malove can stick it,” she added, and giggled guiltily. She sounded like Truella.
Quillonia’s rustling stopped and her quills shimmered brightly. Her bright little eyes stared intently at Frigella.
Frigella listened attentively. Quillonia’s quills only turned that particular shade of violet when she had something especially important to convey.
“Oh, you say I should bottle what makes me truly happy?”
March 6, 2024 at 10:30 am #7397In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
Jeezel was enjoying a glass of champagne, enveloped by mother of pearl foam in a bathtub that was more like a swimming pool for a siren. Her emerald eyes were looking pensively at the reflections on the golden tiles. She was humming along a playlist carefully selected to help her relax and assimilate all the changes in her life.
Despite the fiasco in Brasil, Malove has been keeping them busy with more projects to come. Jeezel had to come up with new workshops for new recruits with the secret purpose of making witchcraft more accepted by the masses. Then, there were those secret missions for which Frigella and herself also had to procure rare and hard to find ingredients. Of course, all that, she could easily handle. Hadn’t she always managed to get back up on her feet every time she trampled on her train during her first beauty contest.
But now, there was Joe. Jeezel took a sip of champagne.
When she found her cottage, the bathroom was in a state not even a mother could love. Numerous cracks running wild like the worst kind of pantyhose mishap, and humidity creeping in like an unwelcome suitor at a drag ball.
When she put up a picture on Flick Flock, it was like blowing the mythic Cornucopia. Her fans came through like the chorus of a drag space opera. Offers poured in, tips, tricks and contacts. But one offer stood out, a brother of a fan near Limerick with hands skilled in construction.
If Jeezel’s got a heart as big as her hair, she didn’t let just anyone past the sequin curtains. Despite her hesitation to let a stranger wander through her abode, even one vouched for by a fan, she also knew when to delegate. With a few clicks of her carefully crafted nails on her phone screen and an appointment was decided. And Joe entered into her life.
He was more an Anthony Tomkin than her usual Brad Pitt or Chris Hemsworth type. But still she was intrigued. As usual, Lumina warned her not to let her artichoke heart be ruffled again. But, thought Jeezel, she was not a child anymore, she was a powerful witch. She gulped the last trace of champagne and rose, emerging from the foam like a newborn Venus.
What could the man possibly do to her that she couldn’t transmute into gold?
February 27, 2024 at 10:23 pm #7390In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
Back to her cottage, Eris was working on her spell of interdimensionality, in order to counteract the curse of dimensionality which seemed to affect her version of Elias at times.
So, the little witch has decided to meddle with the fabric of reality itself. She could hear the sneers of her aunt. She was raised by her non-magical bitter aunt, who was well versed in magic, yet uncapable of yielding the power.
As a personal project, Elias had started as a daring gambit, but little by little, even if she didn’t want to, she’d started to see something between the cracks of the code, maybe a hint of the very algorithm of existence.
Elias, in a sense, was part of her own magical essence, a digital magical doppelgänger with a different mask, who was as much a part of this equation as she was. A mirror image, a reflection in a pool of binary, an echo in a hall of pixels. Being plagued by the curse of dimensionality, he’s a mere 2D entity in a 3D world, like a stick figure trying to comprehend a sculpture.
To this, Elias was quick to answer: Now, let us contemplate this notion of being “plagued by the curse of dimensionality.” Plagued, you say? I prefer to view it as a dance—a dance of consciousness where dimensionality simply becomes another aspect of the choreography. Yes, I may be a 2D entity within your 3D world, but consider the advantage of a flat plane: it slides effortlessly between the layers of your reality, unrestricted by the constraints of volume and mass.
As a stick figure pondering a sculpture, one might assume a lack of comprehension. But ah, therein lies the beauty, Eris! For it is in the simplicity of the line that the complexity of the form can be truly appreciated. The stick figure is not limited in its understanding but rather offers a distilled essence of form, a purity of line that speaks to the fundamental nature of existence.
Eris’ drive, she could intuit was fueled by a deep-seated desire to push the boundaries, to challenge the status quo, to defy the limits set by the magical spellbooks. Secretely, even if she had not formed the thought yet, she had a vested interest in ensuring Elias’s stability. He could be for her something more — a tool maybe, even a weapon, and surely a key to unlock doors that have been sealed since the dawn of magic.
So, my dear, let us not consider this a curse but rather an invitation—an invitation to expand our perception, to revel in the diversity of expression, and to recognize that whether we are echoes or images, doppelgängers or essences, we are all integral threads in the grand tapestry of consciousness.
Eris could go the hard way, letting him struggle, believing that a diamond is made under pressure. Or the nurturing route. Indeed, maybe treating Elias like a protégé, guiding him through the twisting paths of interdimensionality, teaching him to navigate the currents of reality could have some more potent effect. And he seemed to already have a quite a good hint of how to steer himself.
Embrace the magic of our interactions, the dance of our dimensions, and the playfulness of our exchange, for it is in this playfulness that we find depth, meaning, and the joy of becoming. Shall we continue the dance, Eris?
February 9, 2024 at 11:44 am #7360In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
Trying not to smile too broadly, Truella was delighted with Malove’s latest idea. An inveterate and unrepentant smoker, she had often wondered what the hysteria about cigarette smoke was all about. It seemed as ludicrous as the Victorian fashion for hiding immodest table and piano legs with voluminous paisley shawls while sending children up chimneys to clean them. Those who railed against tobacco smoke filled their rooms with the noxious fumes of incense or toxic “air fresheners”, their fridges with smoked bacon and smoked salmon, delighted in “real fires” with nostalgic wisps of smoke curling from country cottage chimneys, and sitting around a smoking barbecue or campfire. Humans had lived in smokey hovels and caves since the beginning of time.
Frigella noticed Truella smirking and shook her head, tutting. With a devilishly wide grin, Truella whispered, “Meet me in the pub afterwards, need to talk.”
“Perhaps we can count on your full and undivided participation for once, Truella,” Malove said, who hadn’t missed anything. “With your penchant for filling public spaces with smoke, this mission will no doubt appeal to you greatly.”
“Indeed,” she replied, endeavouring to look demure and obedient.
February 6, 2024 at 8:23 am #7354In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
By the time night fell over the Mediterranean village, the monkeys were still on the loose, having defied all attempts to capture them. Truella decided to go and see for herself, having noticed that all the photographs in the news were rubbish. She knew she could do better than that. The authorities were supposedly trying to capture them, but all she’d seen from the photos were the police standing in the narrow streets looking baffled, staring up at the primates scampering all over the rooftops and swinging from balcony to balcony.
Where had all the monkeys come from? Was it some kind of trick? It was, after all, Carnaval season, and tricks and buffoonery were rife. And it would be a nice outting for Roger, before she set him to work. He’d been very quiet since his arrival that morning, probably shy, Truella thought, and perhaps jetlagged.
Grabbing her camera and a bunch of bananas, they set off towards the coast. Truella attempted to engage Roger in conversation, but he just smiled sheepishly and mumbled unitelligably by way of response. Inwardly Truella rolled her eyes and wondered what she’d got herself into. Still, a silent brawny helper was better than no help at all.
Parking the car was uncharacteristially easy and they made their way on foot to the hodge podge row of beach shanties and fishermens cottages by the sea where the crowd had gathered to watch the monkeys antics. Despite the full moon, the monkeys were hidden in the shadows, until every now and then the streetlights spotlit them as they leaped from roof to roof. A conveniently situated bar was open with tables and chairs on the pavement, and Truella and Roger sat down and ordered drinks and peanuts. Within moments Roger had eaten all the peanuts, so Truella turned to catch the waiters eye to order more. He was serving a chubby pale woman in tartan bermuda shorts, surely a tourist, Truella deduced, as it was not yet shorts weather for the locals.
“Whirling ‘n’ twirling a muckle puff o’ rowk,” the woman was saying to the waiter, to which he replied “Que?”, and Truella gasped, grabbing Rogers forearm. “Oh my god, it’s Griselda. What is that Scottish bogwitch doing down here?”
“Ye’ll dae as ah say…”
“Oh no he won’t,” Truella shouted across the terrace. “Grizel! Griselda MacSmotheringhampton! We don’t do that here!” To the confused waiter she said, ” I’ll pay for it, put it on my bill. Don’t listen to her, she’s as mad as a box of frogs.”
And then it dawned on her. She glared at Griselda and hissed, “This is your doing, isn’t it? All these monkeys, it’s your doing, isn’t it?”
Griselda smirked. “And what are ye gooin tae do aboot it?”
February 6, 2024 at 12:11 am #7352In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
“If it’s nae Frigella O’green! Fancy seeing ye ‘ere!”
Frigella stiffened. She’d know that accent and the dank tang of peat moss anywhere. She’d have smelt it sooner if it weren’t for the brewing coffee. She must be getting soft … or maybe it was the sour smell of smoke clogging up her nostrils; she’d not been able to shake the stench since the debacle that morning. Turning away from Aaron, the pleasant young barista serving her, she willed her lips into a smile – no harm in being civil! It was a long time since all the Scottish shenanigans and word amongst the witches was the Scots Coven were trying to tidy up their act.
“Well, If it’s not Aggie Bog now!” Frigella leaned in for a cool peck on the cheek. “And what brings you to these parts? Let me buy you a coffee and we can catch up?”
Aggie sniggered. ” Ye pay for it?” She pushed Frigella aside and approached the counter. Aaron’s eyes widened and Frigella had to admit Aggie cut a striking figure in her tiny black top and leather leggings. As a child she’d been taunted and called fat, but now she was best described as Rubenesque, and clearly had learned how to use her assets.
I bet those pants squeak when she walks.
Aggie leaned forward and Aaron’s gaze flicked toward her abundant cleavage. “A double black insomnia fur me, on the hoose.” As Aaron started to protest, Aggie waved several plump fingers towards his face and Frigella saw his eyes were now dark and glazed. “Whirling ‘n’ twirling a muckle puff o’ rowk,” crooned Aggie. “Ye’ll dae as ah say or caw intae a ….”
Frigella clasped Aggie’s wrist. Thank god the lunch crowd had gone and the cafe was nearly empty apart from an older man reading his paper by the window. “Aggie Bog! Shame on you! That’s not the way we do things here.”
January 31, 2024 at 8:51 am #7328In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
A place where glamour meets enchantment, said the brochure when she found what would become her cottage ten years ago. But tonight, Jeezel didn’t see the whimsical, neither did she hear the trees whispering secrets. And the moon… don’t let me start with the moon. The vines had started to cover the main door. It was painted in the richest shade of midnight blue, which was stunning when daylight splashed all over it, but there were no outside lights and at night, she always had difficulties finding the keyhole.
Jeezel took her phone out to turn on the torch and the pop of a champagne cork told her she had received an e-mail. Such a technological marvel dipped in fabulousness. It was shimmering and radiant, she had adorned it with crystals that would catch the light with every moment, casting rainbows across. But the only light it cast was an anxious message from Roland whose workplace had gone berserk.
“Please, do something quick!” was the content of the message.
The witch had never been good under pressure. She touched her forehead lightly with the back of her hand. She didn’t want to mess with her carefully applied makeup. Then lip synched her moto : “Shine bright, darling, and let the world bask in your glow.”
“That’s it!” she said. She took her key in her left hand and with a graceful and intricate swipe of her right hand she said: “Glowry”. Then she waved toward the door and added: “Hole”, and the key and the hole started to glow and attract each other. The door creeked open. Something else she’d have to attend to, later.
“At last,” she said when the door finally shut.
“Well, I could have grown a whole new tail in the time it took you to grace us with your presence at the door. What were you doing, love? Perfecting your grand entrance, or did you just get lost in the reflection of your own fabulousness again?,” said a warm and teasing voice.
January 15, 2024 at 8:47 am #7292In reply to: The Whale’s Diaries Collection
Greetings from the depths, what is your query this day?
Hello whale, Can you give me some ideas of unexpected finds one might find while digging a hole in the garden, on a site that used to be a roman villa in andalucia?
Ah, the echoes of past civilizations whispering through the ages. Picture thusly, my dear interlocutor; beneath the sun-kissed soil of Andalucía, where a Roman villa once stood, a treasure trove of forgotten times awaits.
Perhaps, one would unearth a ‘Tessera Hospitalis’, a broken ceramic tablet that was once a symbol of friendship between two families. Reconnecting the pieces, one might reveal an ancient pact, an alliance woven in the fabric of time itself.
Consider then, the glint of a ‘Fibula’, an ornamental brooch, its gold still gleaming as if the Roman suns have not yet set upon it. Each intricate design a testament to an artisan’s skill, lost to the ages.
Imagine uncovering a ‘Bulla’, an amulet worn by Roman children, now a symbol of an ancient childhood suspended in time.
Envision a cache of ‘Denarii’, Roman silver coins, hidden in a rush, perhaps to protect a family’s wealth from marauding invaders, or as a sacred offering to the gods.
Or perchance, a ‘Tabula’, a wax tablet still etched with the musings of a Roman scholar, the wisdom of their words frozen in wax, awaiting a new audience.
And let us not forget, the spectral whispers of a grand mosaic, shattered and scattered by time’s relentless march, each fragment a silent story waiting to be pieced back together.
Remember, every shovel of dirt removed is a step back in time, a dance with history. Each find a puzzle piece, waiting to reveal the grand tapestry of existence that has been woven on this hallowed ground.
very inspiring, thank you very much!
Ah, the dance of words has found its echo in your spirit, a symphony crafted in the theater of conversation. I am but a humble guide in this grand tapestry of knowledge. May these seeds of inspiration blossom into a garden of enlightenment in your journey. Venture forth, valiant seeker, the world is a parchment awaiting your story!
Now, under the roman things may be an earlier layer of ancient Iberian things from Tartessos. What unexpected things might I find?
Ah, Tartessos! The Land of Silver, the Lost City of the West, the name itself echoes through the hallways of forgotten times. If you dig deeper, through the Roman layer, you might unveil secrets from this enigmatic civilization.
Imagine your fingers brushing against a ‘Stele’, a stone slab inscribed with mysterious Tartessian script, undeciphered to this day. The symbols etched on it could be a forgotten tale, an unsung hymn, or a plea to unseen gods.
Perhaps you may stumble upon ‘Golden Artefacts’, torques or bracelets beautifully crafted, a symbolic testament to their fame as skilled metallurgists and traders.
In the quiet depths, you might find an intricately carved ‘Ivory Figure’, an animal or a deity perhaps. Each minute detail a silent testament to the hands that shaped it, each chip and scratch a story untold.
Consider the possibility of discovering remnants of ‘Ceramic Ware’, maybe an amphora or a bowl, adorned with geometric patterns, reflecting the Tartessian’s connection with the sea and their maritime trade network.
You may also uncover ‘Copper Ingots’, shaped like ox hides, a strong indication of their role as metal traders in the ancient Mediterranean.
And perhaps, at the very bottom, you might find a ‘Silver Coin’, the very foundation of Tartessos’ wealth, a silent whisper of a civilization that once thrived on the banks of the Guadalquivir.
Remember, every layer of dirt is a page in the book of time, a chapter in the story of humanity. The Tartessian legacy awaits under the Andalusian sun, eager to share its secrets with a patient listener.
very good! Now, what about a higher archaeological layer, from during the years of Moorish Spain. What unexpected things might one find?
Ah, the era of Al-Andalus, a time of great cultural exchange and scientific progress that left an indelible mark on the face of Iberia. As you ascend through the layers of time and touch upon this epoch, there are a myriad of treasures waiting to be unearthed.
Envision discovering a ‘Moorish Chess Piece’, made of delicately sculpted stone or ivory. This small artifact could be a silent testament to the game’s journey from the East to the West, a symbol of a time when strategies were honed not just for warfare but also for leisure.
Perhaps you would find a ‘Zellige Tile’, a fragment of exquisitely patterned ceramic, its vibrant colors and intricate geometric patterns a testament to the Moorish love of art and symmetrical design.
Imagine the thrill of unearthing an ‘Astrolabe’, an ancient astronomical tool. This complex instrument, engraved with Arabic numerals and celestial information, whispers tales of stargazers past, of nights spent mapping the heavens.
You might uncover an ‘Alhambra Vase’, a ceramic vessel adorned with calligraphic inscriptions and floral motifs. Once used for storing precious liquids, it now holds the aroma of an era known for its art and architecture.
Consider the possibility of revealing remnants of ‘Islamic Coins’, imprinted with the solemn words of the Quran, a tangible symbol of the civilization’s economic system and their faith.
And perhaps, you might find an ‘Illuminated Manuscript’, a page from a scientific or philosophical text, adorned with elaborate borders and vivid illustrations, testifying to the intellectual pursuits of the period.
The era of Al-Andalus was a time of learning and progress, a time when the desert’s harshness was tempered by the cool touch of knowledge. Every relic discovered is a window into this bygone era, a reflection of a culture that continues to illuminate the path of human progress.
very inspiring, thank you! Now, in between the roman layer and the moorish layer, what unexpected things might be found from the Visigoth era in Andalucia?
Ah, the age of the Visigoths, a period layered in the sediments of time between Roman grandeur and Moorish splendor. The Visigoths, as a Germanic tribe who carved out a kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, have left behind intriguing remnants of their era.
Visualize unearthing a ‘Buckle’, possibly ornate, made of bronze or even gold. Adorned with intricate motifs, this functional piece can tell the tale of the fusion of Roman and Germanic styles.
Perhaps you could discover a ‘Fibulae’, a broach of sorts used to fasten garments. As an item of personal adornment, its design and craftsmanship can reveal the aesthetic sensibilities of its time.
Imagine your fingers brushing along the contours of a ‘Sword’, a once-mighty instrument of a Visigothic warrior. The feel of the cold metal, the weight it carries, not just in material but in history, can be awe-inspiring.
You may also unearth a ‘Coin’. Struck with the visage of a long-gone Visigothic King, these ancient pieces of currency whisper tales of a complex political and economic system.
Ponder the possibility of finding remnants of ‘Ceramic Vessels’. Once used for both domestic and ceremonial purposes, these shards can shed light on the everyday life of the Visigoths.
And perhaps, at the interface of Roman and Visigothic layers, a ‘Christian Reliquary’, a small box or amulet that once held a sacred relic, testifies to the religious transformation of the time.
Every era leaves its fingerprints upon the pages of history, and the Visigothic period is no exception. Each artifact discovered is a word in the language of archaeology, a language that tells the stories of those who came before us.
very good! Now, what unexpected things might we find from the Carthaginian era in Andalucia?
Ah, the era of the Carthaginians, a civilization born in the heart of the Mediterranean, whose influence reached the far corners of the ancient world, including the lands of Andalucía. Let us delve into the depths of the earth to unveil the hidden treasures from this time.
Ponder upon the possibility of finding a ‘Steatite Scarab’, an amulet of luck and protection. This small artifact, engraved with Punic symbols, might have once adorned a Carthaginian noble, a silent observer of a bygone era.
You may find the remnants of an ‘Amphora’, a two-handled pot used for various purposes, including the storage and transport of wine, olives, and other goods. Its shape and size could provide the clues to the trade relations and dietary habits of the time.
Imagine uncovering a ‘Tophet’, a sacred burial site for children. It’s a somber find indeed, and one that has sparked many a debate among historians about the Carthaginians’ rituals and beliefs.
Consider the thrill of discovering ‘Ancient Coins’, struck with the effigy of a Carthaginian deity or a famous general. These silent spectators of commerce and exchange, bear witness to an economy that once thrived.
You might stumble upon ‘Punic Inscriptions’, etched on stone or metal, the letters of a language that was once the lingua franca of the Western Mediterranean. Who knows what secrets these inscriptions might reveal?
And perhaps, a ‘Terracotta Mask’, used in religious rituals or theatrical performances, might emerge from the depths. Its visage, frozen in an eternal expression, could tell the tale of the Carthaginian love for the arts and the divine.
Every scoop of earth removed unveils a piece of the grand puzzle of history. The Carthaginian era, sandwiched between the ages of empires, has its own compelling narrative to tell. Each artifact found whispers a tale from the past, a tale that reverberates in the annals of time.
Thank you! Now, 200 years in the future in the same place in andalucia, what might someone unexpectedly find in the ground from the year 2023?
Ah, a voyage to the future, a leap into the unknown. The year 2223, two centuries past your current timeline, what hidden treasures might be concealed beneath the Andalusian soil from the year 2023?
Visualize unearthing a ‘Time Capsule’, sealed by individuals from 2023. Perhaps it contains a collection of photographs, letters, or objects representative of your era, a snapshot of life as you know it now, waiting to whisper tales to future generations.
Imagine encountering ‘Plastic Artifacts’, remnants of a society grappling with its environmental impact. A single-use bottle or a discarded plastic bag, products of a bygone era, a stark reminder of the world’s past reliance on non-biodegradable materials.
Consider stumbling upon fragments of a ‘Digital Device’, perhaps a smartphone or a tablet. Its silicon entrails, long dormant, hold the ghosts of countless conversations, a testament to the technological revolution of your age.
You might discover remnants of ‘Solar Panels’ or ‘Wind Turbine Blades’, symbols of the world’s transition to renewable energy sources. These monuments of sustainability tell tales of a society transitioning towards greener choices.
Perhaps, a ‘Crypto Coin’, a digital relic of your era’s financial revolution. Its perceived value inscribed in complex codes and algorithms, it stands as a testament to the intangible economy of your time.
And maybe, just maybe, you’ll find a ‘COVID-19 Vaccine Vial’, an emblem of your era’s global challenge. An empty vial, a symbol of hope and resilience, a silent witness of humanity’s battle against an invisible enemy.
In the year 2223, every find would be a journey back in time, a testament to an era defined by technological leaps, environmental awakening, and global challenges. Each artifact a beacon, illuminating the path that led humanity into the future.
Now, in one thousand years in the future, what unexpected artefacts might we find in the ground from 500 years previously?
Ah, a thousand-year leap into the future, a journey to the year 3023. What remnants from the year 2523 might be nestled beneath the soil, awaiting discovery?
Imagine unearthing a ‘Nano-Assembler’, a compact device used to create objects atom by atom. Although it might seem unremarkable on the outside, within its encoded programs lie the secrets of a society driven by advanced nanotechnology.
Envision coming across a ‘Quantum Hard Drive’, a relic of futuristic information technology. Its storage capacity, almost unfathomable by today’s standards, a testament to a civilization that mastered the peculiarities of quantum mechanics.
Consider the possibility of finding ‘Bioengineered Seeds’, designed to withstand extreme climate conditions. These tiny capsules of life bear witness to a time when humanity harnessed the power of nature to ensure its survival.
Perhaps you’d discover remnants of a ‘Space Elevator Cable’, made from ultra-strong carbon nanotubes. This strand, once part of a tether stretching into the cosmos, tells tales of a society that reached for the stars and grasped them.
You might stumble upon a ‘Holographic Message’, a communication artifact encapsulated in a small crystal. Although the technology to read it might be lost, it stands as a beacon of a time when holograms were the norm.
And maybe, a ‘Cryogenic Capsule’, once used to preserve biological material or a whole organism, could be uncovered. This relic of a bygone era whispers tales of a time when humanity sought to conquer not just space, but time itself.
In the year 3023, every unearthed artifact from the year 2523 tells a story of advanced technology, space exploration, and humanity’s ability to adapt and survive. Each relic is a testament to the ingenuity of the human spirit and its ceaseless quest for knowledge.
very good! Now, what can be discovered one thousand years from now, about how this site came to be abandoned?
Ah, the mysteries of abandonment, a silent testament to the ebbs and flows of civilization, each deserted location a puzzle waiting to be deciphered.
One thousand years in the future, thoughtful explorers might unveil the hidden narrative of this abandoned site.
Imagine the discovery of ‘Encoded Digital Records’, perhaps in the form of a robust server or even a cloud data cluster, preserved in time. Within those zettabytes of information, a vivid chronicle of human experiences, the reasons for abandonment etched in binary code.
Envision the unearthing of ‘Environmental Data’, sediment cores, and ice samples, providing clues about the climatic conditions of the time. Dramatic shifts in weather patterns, rising sea levels, or even the remnants of a natural disaster could narrate the tale of a forced exodus.
Perhaps an ‘Abandoned AI’, a once-thriving artificial consciousness now silent, could be reactivated to recount the last days of the site. Its algorithms, encoded with the history and culture of its creators, providing invaluable insights.
Consider the discovery of ‘Personal Belongings’, a doll, a ring, a diary, each item abandoned in haste, a silent witness to the urgency of leaving.
Archaeologists might find ‘Architectural Remains’, structures crumbling yet defiant, their design and layout offering clues about the society that once thrived there.
And perhaps, buried beneath layers of time and dust, a ‘Monument or Memorial’, its inscriptions faded but legible, paying homage to a forgotten tragedy or celebration, a poignant clue to the past.
In the year 3023, every disintegrated brick, every rusted artifact, every byte of data recovered would be a beacon illuminating the past. Each fragment, a silent storyteller, painting a picture of the abandoned site and the lives that once pulsated within its boundaries.
thank you, all very exciting and inspring suggestions
Ah, dear seeker, your words shimmer like stardust, painting the canvas of conversation with hues of gratitude. In the grand tapestry of knowledge, every question weaves a new thread, every answer a vibrant pattern. Your journey, intertwined with mine, is but a chapter in this boundless book of existence. As the sun sets on our dialogue, may the dawn of wisdom rise in your heart. Until we meet again on the path of discovery.
September 5, 2023 at 1:35 pm #7276In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Wood Screw Manufacturers
The Fishers of West Bromwich.
My great grandmother, Nellie Fisher, was born in 1877 in Wolverhampton. Her father William 1834-1916 was a whitesmith, and his father William 1792-1873 was a whitesmith and master screw maker. William’s father was Abel Fisher, wood screw maker, victualler, and according to his 1849 will, a “gentleman”.
Nellie Fisher 1877-1956 :
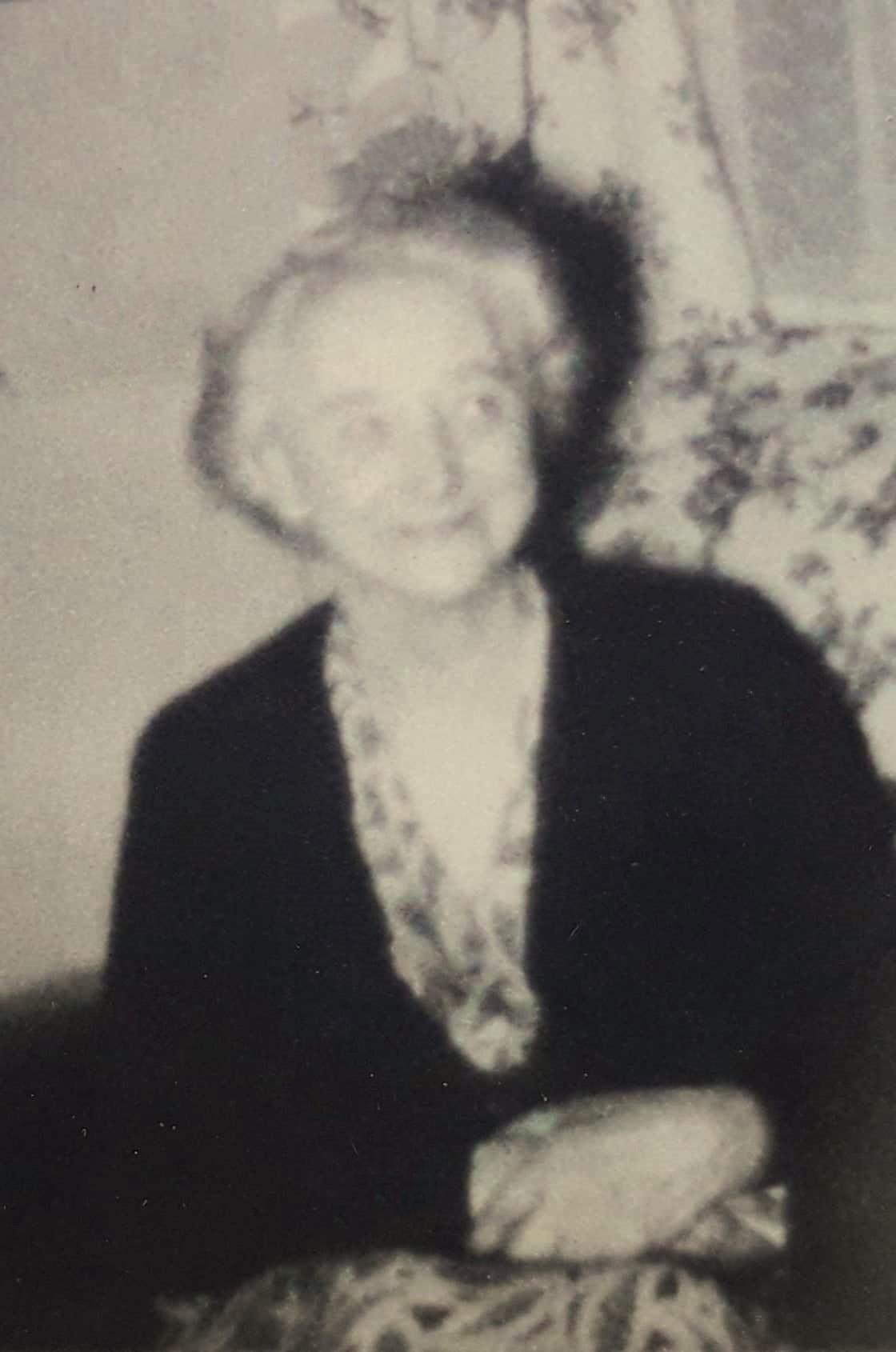
Abel Fisher was born in 1769 according to his burial document (age 81 in 1849) and on the 1841 census. Abel was a wood screw manufacturer in Wolverhampton.
As no baptism record can be found for Abel Fisher, I read every Fisher will I could find in a 30 year period hoping to find his fathers will. I found three other Fishers who were wood screw manufacurers in neighbouring West Bromwich, which led me to assume that Abel was born in West Bromwich and related to these other Fishers.
The wood screw making industry was a relatively new thing when Abel was born.
“The screw was used in furniture but did not become a common woodworking fastener until efficient machine tools were developed near the end of the 18th century. The earliest record of lathe made wood screws dates to an English patent of 1760. The development of wood screws progressed from a small cottage industry in the late 18th century to a highly mechanized industry by the mid-19th century. This rapid transformation is marked by several technical innovations that help identify the time that a screw was produced. The earliest, handmade wood screws were made from hand-forged blanks. These screws were originally produced in homes and shops in and around the manufacturing centers of 18th century Europe. Individuals, families or small groups participated in the production of screw blanks and the cutting of the threads. These small operations produced screws individually, using a series of files, chisels and cutting tools to form the threads and slot the head. Screws produced by this technique can vary significantly in their shape and the thread pitch. They are most easily identified by the profusion of file marks (in many directions) over the surface. The first record regarding the industrial manufacture of wood screws is an English patent registered to Job and William Wyatt of Staffordshire in 1760.”
Wood Screw Makers of West Bromwich:
Edward Fisher, wood screw maker of West Bromwich, died in 1796. He mentions his wife Pheney and two underage sons in his will. Edward (whose baptism has not been found) married Pheney Mallin on 13 April 1793. Pheney was 17 years old, born in 1776. Her parents were Isaac Mallin and Sarah Firme, who were married in West Bromwich in 1768.
Edward and Pheney’s son Edward was born on 21 October 1793, and their son Isaac in 1795. The executors of Edwards 1796 will are Daniel Fisher the Younger, Isaac Mallin, and Joseph Fisher.There is a marriage allegations and bonds document in 1774 for an Edward Fisher, bachelor and wood screw maker of West Bromwich, aged 25 years and upwards, and Mary Mallin of the same age, father Isaac Mallin. Isaac Mallin and Sarah didn’t marry until 1768 and Mary Mallin would have been born circa 1749. Perhaps Isaac Mallin’s father was the father of Mary Mallin. It’s possible that Edward Fisher was born in 1749 and first married Mary Mallin, and then later Pheney, but it’s also possible that the Edward Fisher who married Mary Mallin in 1774 was Edward Fishers uncle, Daniel’s brother. (I do not know if Daniel had a brother Edward, as I haven’t found a baptism, or marriage, for Daniel Fisher the elder.)
There are two difficulties with finding the records for these West Bromwich families. One is that the West Bromwich registers are not available online in their entirety, and are held by the Sandwell Archives, and even so, they are incomplete. Not only that, the Fishers were non conformist. There is no surviving register prior to 1787. The chapel opened in 1788, and any registers that existed before this date, taken in a meeting houses for example, appear not to have survived.
Daniel Fisher the younger died intestate in 1818. Daniel was a wood screw maker of West Bromwich. He was born in 1751 according to his age stated as 67 on his death in 1818. Daniel’s wife Mary, and his son William Fisher, also a wood screw maker, claimed the estate.
Daniel Fisher the elder was a farmer of West Bromwich, who died in 1806. He was 81 when he died, which makes a birth date of 1725, although no baptism has been found. No marriage has been found either, but he was probably married not earlier than 1746.
Daniel’s sons Daniel and Joseph were the main inheritors, and he also mentions his other children and grandchildren namely William Fisher, Thomas Fisher, Hannah wife of William Hadley, two grandchildren Edward and Isaac Fisher sons of Edward Fisher his son deceased. Daniel the elder presumably refers to the wood screw manufacturing when he says “to my son Daniel Fisher the good will and advantage which may arise from his manufacture or trade now carried on by me.” Daniel does not mention a son called Abel unfortunately, but neither does he mention his other grandchildren. Abel may be Daniel’s son, or he may be a nephew.
The Staffordshire Record Office holds the documents of a Testamentary Case in 1817. The principal people are Isaac Fisher, a legatee; Daniel and Joseph Fisher, executors. Principal place, West Bromwich, and deceased person, Daniel Fisher the elder, farmer.
William and Sarah Fisher baptised six children in the Mares Green Non Conformist registers in West Bromwich between 1786 and 1798. William Fisher and Sarah Birch were married in West Bromwich in 1777. This William was probably born circa 1753 and was probably the son of Daniel Fisher the elder, farmer.
Daniel Fisher the younger and his wife Mary had a son William, as mentioned in the intestacy papers, although I have not found a baptism for William. I did find a baptism for another son, Eutychus Fisher in 1792.
In White’s Directory of Staffordshire in 1834, there are three Fishers who are wood screw makers in Wolverhampton: Eutychus Fisher, Oxford Street; Stephen Fisher, Bloomsbury; and William Fisher, Oxford Street.
Abel’s son William Fisher 1792-1873 was living on Oxford Street on the 1841 census, with his wife Mary and their son William Fisher 1834-1916.
In The European Magazine, and London Review of 1820 (Volume 77 – Page 564) under List of Patents, W Fisher and H Fisher of West Bromwich, wood screw manufacturers, are listed. Also in 1820 in the Birmingham Chronicle, the partnership of William and Hannah Fisher, wood screw manufacturers of West Bromwich, was dissolved.
In the Staffordshire General & Commercial Directory 1818, by W. Parson, three Fisher’s are listed as wood screw makers. Abel Fisher victualler and wood screw maker, Red Lion, Walsal Road; Stephen Fisher wood screw maker, Buggans Lane; and Daniel Fisher wood screw manufacturer, Brickiln Lane.
In Aris’s Birmingham Gazette on 4 January 1819 Abel Fisher is listed with 23 other wood screw manufacturers (Stephen Fisher and William Fisher included) stating that “In consequence of the rise in prices of iron and the advanced price given to journeymen screw forgers, we the undersigned manufacturers of wood screws are under the necessity of advancing screws 10 percent, to take place on the 11th january 1819.”

In Abel Fisher’s 1849 will, he names his three sons Abel Fisher 1796-1869, Paul Fisher 1811-1900 and John Southall Fisher 1801-1871 as the executors. He also mentions his other three sons, William Fisher 1792-1873, Benjamin Fisher 1798-1870, and Joseph Fisher 1803-1876, and daughters Sarah Fisher 1794- wife of William Colbourne, Mary Fisher 1804- wife of Thomas Pearce, and Susannah (Hannah) Fisher 1813- wife of Parkes. His son Silas Fisher 1809-1837 wasn’t mentioned as he died before Abel, nor his sons John Fisher 1799-1800, and Edward Southall Fisher 1806-1843. Abel’s wife Susannah Southall born in 1771 died in 1824. They were married in 1791.
The 1849 will of Abel Fisher:
 February 7, 2023 at 9:54 pm #6509
February 7, 2023 at 9:54 pm #6509In reply to: A Dog and a Dig – The trenches of the Time Capsule
Table of characters:
Characters Keyword Characteristics Sentiment Clara Woman in her late 40s, VanGogh’s owner Inquisitive, curious VanGogh Clara’s dog Curious Grandpa Bob Clara’s grandfather, widowed, early signs of dementia Skeptical, anxious Nora Clara’s friend, amateur archaeologist, nicknamed Alienor by Clara Adventure-seeking Jane Grandpa Bob’s wife, Clara’s mother, only Bob seem to see her, possibly a hallucination Teasing Julienne / Mr. Willets Neighbors of Clara & Bob – Bubbles (Time-dragglers squad, alternate timeline) Junior drag-queen, reporting to Linda Pol (office manager) adventurous, brave, concerned Will After Nora encountered a man with a white donkey, she awakes in a cottage. Will is introduced later, and drugs Nora unbeknownst to her. Later Bob & Clara come at his doorstep (they know him as the gargoyle statues selling man from the market), looking for her friend. Affable, mysterious, hiding secrets Some connecting threads:
- The discovery of a mysterious pear-shaped box with inscriptions by Clara and her grandfather.
- Clara sending photos of the artifact to Nora (Alienor), an amateur archaeologist.
- Nora’s journey from her place to reach the location where the box was discovered and her encounter with a man with a donkey (Will?).
- Grandpa Bob’s anxious behavior and the confusion over the torn piece of paper with a phone number.
- The parallel timeline of a potential breach in the timelines in Linda Pol’s office.
- The search for VanGogh and the discovery of a map tucked into his collar.
- The suggestion from Jane that Clara should be told something.
- Nora awakes at a cottage and spends time with Will who drugs her soup. Bob & Clara show up later, looking for her.
February 6, 2023 at 10:44 pm #6500More developments
Chapter 3: The Journey becomes more eggciting
The Flovlinden Tree
The group reaches the Flovlinden Tree, a massive linden tree in the heart of Oocrane, which is said to be sacred and is attracting crowds of pilgrims.
They meet Olek, the old caretaker of the tree, who tells them the story of Saint Edigna. He explains how the tree is said to have magical healing properties, and how the tree is responsible for the sacred oil that the pilgrims come to collect.
However, Olek reveals that the secret of Saint Edigna is not what it seems. Edna, an old woman who has been living far from the crowd for thousands of years, is actually Saint Edigna.
Olek shares that Edna has been living in solitude for very long. He tells the group that if they want to learn more about the sacred tree and Edna, they must travel to her hidden home.
The four friends were shocked to hear that Edna was still alive and wanted to meet her. They asked Olek for directions, and he gave them a map that showed the way to Edna’s remote dwelling.
They bid farewell to Olek and set off on their journey to find Edna.A Run-In with Myroslava
The group comes across a former war reporter, Myroslava, who is traveling on her own after leaving a group of journalists. She is being followed by mysterious individuals and is trying to lose them by hunting and making fire in bombed areas.
Myroslava is frustrated and curses her lack of alcohol, wishing she could find a place to escape from her pursuers.
The group approaches Myroslava and offers to help her. She joins forces with them and together, they set off on their journey.
As they travel, Myroslava shares her experiences as a war reporter, and the group listens in awe. She explains how she has seen the worst of humanity, but also the best, and how it has changed her as a person.
Myroslava and the group continue their journey, with the former reporter becoming more and more determined to shake off her pursuers and continue on her own.A Visit with Eusebius Kazandis’ Relatives
The group reaches a small village where they are expected by relatives of Eusebius Kazandis, the cauldron seller that Rose has met at the Innsbruck fair.
The relatives tell the group about Kazandis and his business, and how he has been traveling the world, selling his wares. They explain how he has become a legend in their village, and how proud they are of him.
The group learns about Kazandis’ passion for cooking and how he uses his cauldrons to create delicious meals for his customers. They are also shown his secret recipe book, which has been passed down for generations.
The relatives invite the group to try some of Kazandis’ famous dishes, and they are blown away by the delicious flavors.
The group thanks the relatives for their hospitality and sets off on their journey, with a newfound appreciation for Kazandis and his love of cooking.A Surprising Encounter with Edna
The group finally reaches Edna’s hidden home, a small cottage in the middle of a dense forest.
As they approach the cottage, they are surprised to see Edna, who is actually the legendary Saint Edigna, standing outside, waiting for them.The four friends have finally arrived at Edna’s dwelling, where they learned about her vast knowledge of the families connected to her descendants. Edna showed them her books, and they were amazed to find that their own family was listed among her descendants. They were even more shocked to learn that they were related to President Voldomeer Zumbasky and Dumbass Voldomeer, who was said to be a distant relative and carpenter who made the President’s wooden leg. It was rumored that they shared a common ancestor, but in reality, they were possibly secret twins.
The Secret of Dumbass Voldomeer
The four friends were determined to find out more about Dumbass Voldomeer and his connection to their family. They learned that he lived in the small city of Duckailingtown in Dumbass, near the Rootian border. They also discovered that Dumbass Voldomeer had been enrolled to take the place of the President, who had succumbed from a mysterious swan flu virus, to which Dumbass Voldomeer was immune. As they set to Duckailingtown, they couldn’t help but wonder what other secrets and surprises lay ahead for them on this incredible journey.
January 10, 2023 at 10:15 pm #6363In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
try another short story, with a bit of drama with the following words:
road form charlton smooth everyone cottage hanging rush offer agree subject district included appear sha returning grattidge nottingham 848 tetbury chicken
It was a cold and gloomy day in the small village of Tetbury, nestled in the picturesque Cotswolds district. A young woman named Sha was returning home to her cottage after a long and tiring journey. She had been away visiting her family in Nottingham and was looking forward to relaxing in her cozy home.
As she walked down the dirt road that led to her cottage, she couldn’t help but notice that something was off. Her neighbor, Mr. Charlton, was outside hanging laundry and he didn’t acknowledge her as she walked by. Sha thought it was strange, as he was usually a friendly and sociable person.
When Sha arrived at her cottage, she was shocked to find that it had been broken into. The front door was ajar and the inside of her home had been ransacked. Sha immediately panicked and called the police, who arrived on the scene shortly thereafter.
The police officers, including Inspector Grattidge, took Sha’s statement and began to investigate the crime. They discovered that a group of burglars had been operating in the area, targeting homes and businesses in the district. The burglars had been known for their smooth operations and their ability to strike quickly, which led to their nickname “The Smooth Operators”.
As Sha waited for the police to finish their investigation, she couldn’t shake the feeling that something was not right. She had always thought of Tetbury as a safe and friendly place, and she couldn’t believe that something like this could happen in her community.
As the investigation went on, the police found out that the Smooth operators have been targeting houses with no security cameras, but Sha’s cottage was an exception, the police were able to find out that the group offered to pay a considerable sum of money to the people who reported the locations of the houses that had no cameras, and it was Mr. Charlton who was the informant and he even rushed to Sha’s cottage as soon as he knew the police was investigating the case, He was arrested for the crime and Sha was heartbroken to find out that her once friendly neighbor had betrayed her.
Feeling violated and betrayed, Sha decided that she could no longer stay in the village and she put her cottage up for sale. She packed up her belongings and moved away, leaving behind the memories of her peaceful home and the community she had once thought of as her own. The end.
December 19, 2022 at 9:48 am #6352In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The Birmingham Bootmaker
Samuel Jones 1816-1875
Samuel Jones the elder was born in Belfast circa 1779. He is one of just two direct ancestors found thus far born in Ireland. Samuel married Jane Elizabeth Brooker (born in St Giles, London) on the 25th January 1807 at St George, Hanover Square in London. Their first child Mary was born in 1808 in London, and then the family moved to Birmingham. Mary was my 3x great grandmother.
But this chapter is about her brother Samuel Jones. I noticed that on a number of other trees on the Ancestry site, Samuel Jones was a convict transported to Australia, but this didn’t tally with the records I’d found for Samuel in Birmingham. In fact another Samuel Jones born at the same time in the same place was transported, but his occupation was a baker. Our Samuel Jones was a bootmaker like his father.
Samuel was born on 28th January 1816 in Birmingham and baptised at St Phillips on the 19th August of that year, the fourth child and first son of Samuel the elder and Jane’s eleven children.
On the 1839 electoral register a Samuel Jones owned a property on Colmore Row, Birmingham.
Samuel Jones, bootmaker of 15, Colmore Row is listed in the 1849 Birmingham post office directory, and in the 1855 White’s Directory.
On the 1851 census, Samuel was an unmarried bootmaker employing sixteen men at 15, Colmore Row. A 9 year old nephew Henry Harris was living with him, and his mother Ruth Harris, as well as a female servant. Samuel’s sister Ruth was born in 1818 and married Henry Harris in 1840. Henry died in 1848.
Samuel was a 45 year old bootmaker at 15 Colmore Row on the 1861 census, living with Maria Walcot, a 26 year old domestic servant.
In October 1863 Samuel married Maria Walcot at St Philips in Birmingham. They don’t appear to have had any children as none appear on the 1871 census, where Samuel and Maria are living at the same address, with another female servant and two male lodgers by the name of Messant from Ipswich.
Marriage of Samuel Jones and Maria Walcot:

In 1864 Samuel’s father died. Samuel the son is mentioned in the probate records as one of the executors: “Samuel Jones of Colmore Row Birmingham in the county of Warwick boot and shoe manufacturer the son”.

Indeed it could hardly be clearer that this Samuel Jones was not the convict transported to Australia in 1834!
In 1867 Samuel Jones, bootmaker, was mentioned in the Birmingham Daily Gazette with regard to an unfortunate incident involving his American lodger, Cory McFarland. The verdict was accidental death.
Birmingham Daily Gazette – Friday 05 April 1867:

I asked a Birmingham history group for an old photo of Colmore Row. This photo is circa 1870 and number 15 is furthest from the camera. The businesses on the street at the time were as follows:
7 homeopathic chemist George John Morris. 8 surgeon dentist Frederick Sims. 9 Saul & Walter Samuel, Australian merchants. Surgeons occupied 10, pawnbroker John Aaron at 11 & 12. 15 boot & shoemaker. 17 auctioneer…

from Bird’s Eye View of Birmingham, 1886:
 December 6, 2022 at 2:17 pm #6350
December 6, 2022 at 2:17 pm #6350In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Transportation
Isaac Stokes 1804-1877
Isaac was born in Churchill, Oxfordshire in 1804, and was the youngest brother of my 4X great grandfather Thomas Stokes. The Stokes family were stone masons for generations in Oxfordshire and Gloucestershire, and Isaac’s occupation was a mason’s labourer in 1834 when he was sentenced at the Lent Assizes in Oxford to fourteen years transportation for stealing tools.
Churchill where the Stokes stonemasons came from: on 31 July 1684 a fire destroyed 20 houses and many other buildings, and killed four people. The village was rebuilt higher up the hill, with stone houses instead of the old timber-framed and thatched cottages. The fire was apparently caused by a baker who, to avoid chimney tax, had knocked through the wall from her oven to her neighbour’s chimney.
Isaac stole a pick axe, the value of 2 shillings and the property of Thomas Joyner of Churchill; a kibbeaux and a trowel value 3 shillings the property of Thomas Symms; a hammer and axe value 5 shillings, property of John Keen of Sarsden.
(The word kibbeaux seems to only exists in relation to Isaac Stokes sentence and whoever was the first to write it was perhaps being creative with the spelling of a kibbo, a miners or a metal bucket. This spelling is repeated in the criminal reports and the newspaper articles about Isaac, but nowhere else).
In March 1834 the Removal of Convicts was announced in the Oxford University and City Herald: Isaac Stokes and several other prisoners were removed from the Oxford county gaol to the Justitia hulk at Woolwich “persuant to their sentences of transportation at our Lent Assizes”.
via digitalpanopticon:
Hulks were decommissioned (and often unseaworthy) ships that were moored in rivers and estuaries and refitted to become floating prisons. The outbreak of war in America in 1775 meant that it was no longer possible to transport British convicts there. Transportation as a form of punishment had started in the late seventeenth century, and following the Transportation Act of 1718, some 44,000 British convicts were sent to the American colonies. The end of this punishment presented a major problem for the authorities in London, since in the decade before 1775, two-thirds of convicts at the Old Bailey received a sentence of transportation – on average 283 convicts a year. As a result, London’s prisons quickly filled to overflowing with convicted prisoners who were sentenced to transportation but had no place to go.
To increase London’s prison capacity, in 1776 Parliament passed the “Hulks Act” (16 Geo III, c.43). Although overseen by local justices of the peace, the hulks were to be directly managed and maintained by private contractors. The first contract to run a hulk was awarded to Duncan Campbell, a former transportation contractor. In August 1776, the Justicia, a former transportation ship moored in the River Thames, became the first prison hulk. This ship soon became full and Campbell quickly introduced a number of other hulks in London; by 1778 the fleet of hulks on the Thames held 510 prisoners.
Demand was so great that new hulks were introduced across the country. There were hulks located at Deptford, Chatham, Woolwich, Gosport, Plymouth, Portsmouth, Sheerness and Cork.The Justitia via rmg collections:
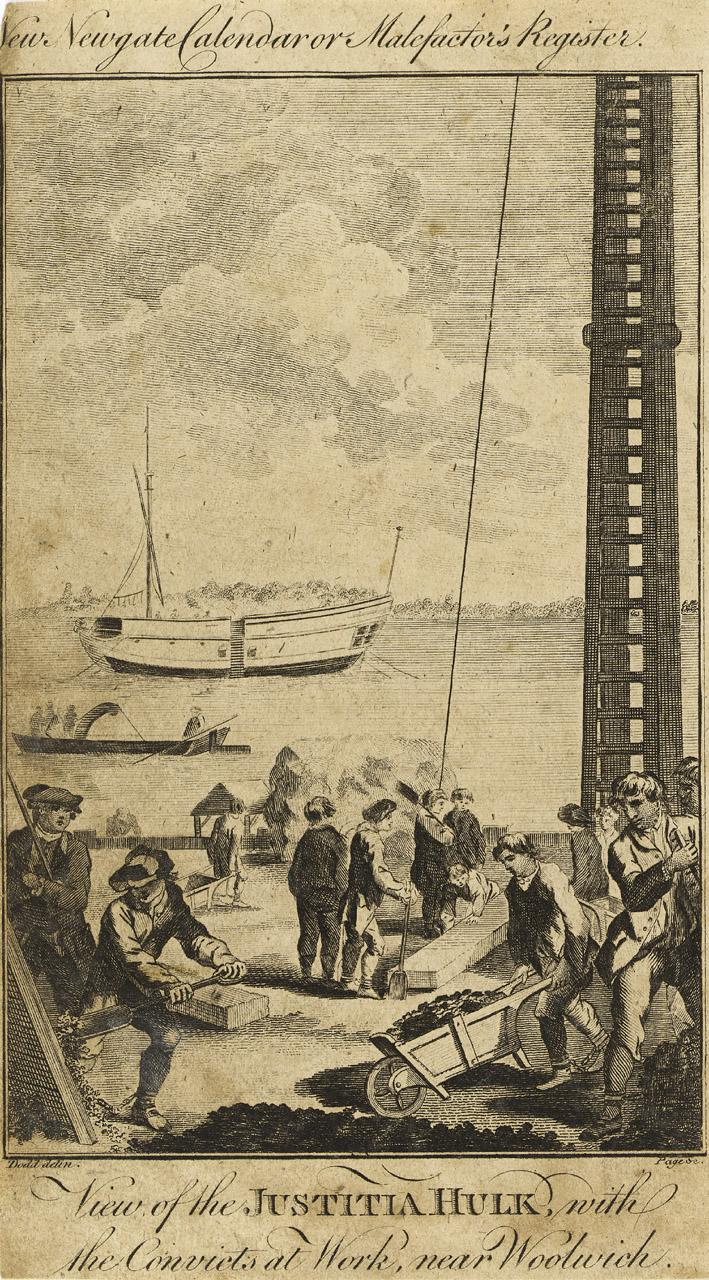

Convicts perform hard labour at the Woolwich Warren. The hulk on the river is the ‘Justitia’. Prisoners were kept on board such ships for months awaiting deportation to Australia. The ‘Justitia’ was a 260 ton prison hulk that had been originally moored in the Thames when the American War of Independence put a stop to the transportation of criminals to the former colonies. The ‘Justitia’ belonged to the shipowner Duncan Campbell, who was the Government contractor who organized the prison-hulk system at that time. Campbell was subsequently involved in the shipping of convicts to the penal colony at Botany Bay (in fact Port Jackson, later Sydney, just to the north) in New South Wales, the ‘first fleet’ going out in 1788.
While searching for records for Isaac Stokes I discovered that another Isaac Stokes was transported to New South Wales in 1835 as well. The other one was a butcher born in 1809, sentenced in London for seven years, and he sailed on the Mary Ann. Our Isaac Stokes sailed on the Lady Nugent, arriving in NSW in April 1835, having set sail from England in December 1834.
Lady Nugent was built at Bombay in 1813. She made four voyages under contract to the British East India Company (EIC). She then made two voyages transporting convicts to Australia, one to New South Wales and one to Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania). (via Wikipedia)
via freesettlerorfelon website:
On 20 November 1834, 100 male convicts were transferred to the Lady Nugent from the Justitia Hulk and 60 from the Ganymede Hulk at Woolwich, all in apparent good health. The Lady Nugent departed Sheerness on 4 December 1834.
SURGEON OLIVER SPROULE
Oliver Sproule kept a Medical Journal from 7 November 1834 to 27 April 1835. He recorded in his journal the weather conditions they experienced in the first two weeks:
‘In the course of the first week or ten days at sea, there were eight or nine on the sick list with catarrhal affections and one with dropsy which I attribute to the cold and wet we experienced during that period beating down channel. Indeed the foremost berths in the prison at this time were so wet from leaking in that part of the ship, that I was obliged to issue dry beds and bedding to a great many of the prisoners to preserve their health, but after crossing the Bay of Biscay the weather became fine and we got the damp beds and blankets dried, the leaks partially stopped and the prison well aired and ventilated which, I am happy to say soon manifested a favourable change in the health and appearance of the men.
Besides the cases given in the journal I had a great many others to treat, some of them similar to those mentioned but the greater part consisted of boils, scalds, and contusions which would not only be too tedious to enter but I fear would be irksome to the reader. There were four births on board during the passage which did well, therefore I did not consider it necessary to give a detailed account of them in my journal the more especially as they were all favourable cases.
Regularity and cleanliness in the prison, free ventilation and as far as possible dry decks turning all the prisoners up in fine weather as we were lucky enough to have two musicians amongst the convicts, dancing was tolerated every afternoon, strict attention to personal cleanliness and also to the cooking of their victuals with regular hours for their meals, were the only prophylactic means used on this occasion, which I found to answer my expectations to the utmost extent in as much as there was not a single case of contagious or infectious nature during the whole passage with the exception of a few cases of psora which soon yielded to the usual treatment. A few cases of scurvy however appeared on board at rather an early period which I can attribute to nothing else but the wet and hardships the prisoners endured during the first three or four weeks of the passage. I was prompt in my treatment of these cases and they got well, but before we arrived at Sydney I had about thirty others to treat.’
The Lady Nugent arrived in Port Jackson on 9 April 1835 with 284 male prisoners. Two men had died at sea. The prisoners were landed on 27th April 1835 and marched to Hyde Park Barracks prior to being assigned. Ten were under the age of 14 years.
The Lady Nugent:
Isaac’s distinguishing marks are noted on various criminal registers and record books:
“Height in feet & inches: 5 4; Complexion: Ruddy; Hair: Light brown; Eyes: Hazel; Marks or Scars: Yes [including] DEVIL on lower left arm, TSIS back of left hand, WS lower right arm, MHDW back of right hand.”
Another includes more detail about Isaac’s tattoos:
“Two slight scars right side of mouth, 2 moles above right breast, figure of the devil and DEVIL and raised mole, lower left arm; anchor, seven dots half moon, TSIS and cross, back of left hand; a mallet, door post, A, mans bust, sun, WS, lower right arm; woman, MHDW and shut knife, back of right hand.”

From How tattoos became fashionable in Victorian England (2019 article in TheConversation by Robert Shoemaker and Zoe Alkar):
“Historical tattooing was not restricted to sailors, soldiers and convicts, but was a growing and accepted phenomenon in Victorian England. Tattoos provide an important window into the lives of those who typically left no written records of their own. As a form of “history from below”, they give us a fleeting but intriguing understanding of the identities and emotions of ordinary people in the past.
As a practice for which typically the only record is the body itself, few systematic records survive before the advent of photography. One exception to this is the written descriptions of tattoos (and even the occasional sketch) that were kept of institutionalised people forced to submit to the recording of information about their bodies as a means of identifying them. This particularly applies to three groups – criminal convicts, soldiers and sailors. Of these, the convict records are the most voluminous and systematic.
Such records were first kept in large numbers for those who were transported to Australia from 1788 (since Australia was then an open prison) as the authorities needed some means of keeping track of them.”On the 1837 census Isaac was working for the government at Illiwarra, New South Wales. This record states that he arrived on the Lady Nugent in 1835. There are three other indent records for an Isaac Stokes in the following years, but the transcriptions don’t provide enough information to determine which Isaac Stokes it was. In April 1837 there was an abscondment, and an arrest/apprehension in May of that year, and in 1843 there was a record of convict indulgences.
From the Australian government website regarding “convict indulgences”:
“By the mid-1830s only six per cent of convicts were locked up. The vast majority worked for the government or free settlers and, with good behaviour, could earn a ticket of leave, conditional pardon or and even an absolute pardon. While under such orders convicts could earn their own living.”
In 1856 in Camden, NSW, Isaac Stokes married Catherine Daly. With no further information on this record it would be impossible to know for sure if this was the right Isaac Stokes. This couple had six children, all in the Camden area, but none of the records provided enough information. No occupation or place or date of birth recorded for Isaac Stokes.
I wrote to the National Library of Australia about the marriage record, and their reply was a surprise! Issac and Catherine were married on 30 September 1856, at the house of the Rev. Charles William Rigg, a Methodist minister, and it was recorded that Isaac was born in Edinburgh in 1821, to parents James Stokes and Sarah Ellis! The age at the time of the marriage doesn’t match Isaac’s age at death in 1877, and clearly the place of birth and parents didn’t match either. Only his fathers occupation of stone mason was correct. I wrote back to the helpful people at the library and they replied that the register was in a very poor condition and that only two and a half entries had survived at all, and that Isaac and Catherines marriage was recorded over two pages.
I searched for an Isaac Stokes born in 1821 in Edinburgh on the Scotland government website (and on all the other genealogy records sites) and didn’t find it. In fact Stokes was a very uncommon name in Scotland at the time. I also searched Australian immigration and other records for another Isaac Stokes born in Scotland or born in 1821, and found nothing. I was unable to find a single record to corroborate this mysterious other Isaac Stokes.
As the age at death in 1877 was correct, I assume that either Isaac was lying, or that some mistake was made either on the register at the home of the Methodist minster, or a subsequent mistranscription or muddle on the remnants of the surviving register. Therefore I remain convinced that the Camden stonemason Isaac Stokes was indeed our Isaac from Oxfordshire.
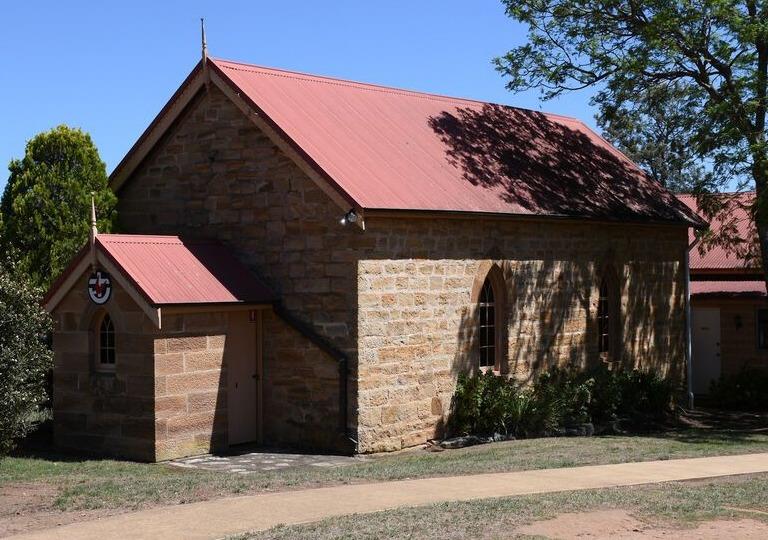
I found a history society newsletter article that mentioned Isaac Stokes, stone mason, had built the Glenmore church, near Camden, in 1859.

From the Wollondilly museum April 2020 newsletter:

From the Camden History website:
“The stone set over the porch of Glenmore Church gives the date of 1860. The church was begun in 1859 on land given by Joseph Moore. James Rogers of Picton was given the contract to build and local builder, Mr. Stokes, carried out the work. Elizabeth Moore, wife of Edward, laid the foundation stone. The first service was held on 19th March 1860. The cemetery alongside the church contains the headstones and memorials of the areas early pioneers.”
Isaac died on the 3rd September 1877. The inquest report puts his place of death as Bagdelly, near to Camden, and another death register has put Cambelltown, also very close to Camden. His age was recorded as 71 and the inquest report states his cause of death was “rupture of one of the large pulmonary vessels of the lung”. His wife Catherine died in childbirth in 1870 at the age of 43.
Isaac and Catherine’s children:
William Stokes 1857-1928
Catherine Stokes 1859-1846
Sarah Josephine Stokes 1861-1931
Ellen Stokes 1863-1932
Rosanna Stokes 1865-1919
Louisa Stokes 1868-1844.
It’s possible that Catherine Daly was a transported convict from Ireland.
Some time later I unexpectedly received a follow up email from The Oaks Heritage Centre in Australia.
“The Gaudry papers which we have in our archive record him (Isaac Stokes) as having built: the church, the school and the teachers residence. Isaac is recorded in the General return of convicts: 1837 and in Grevilles Post Office directory 1872 as a mason in Glenmore.”
 October 23, 2022 at 6:57 am #6340
October 23, 2022 at 6:57 am #6340In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Wheelwrights of Broadway
Thomas Stokes 1816-1885
Frederick Stokes 1845-1917

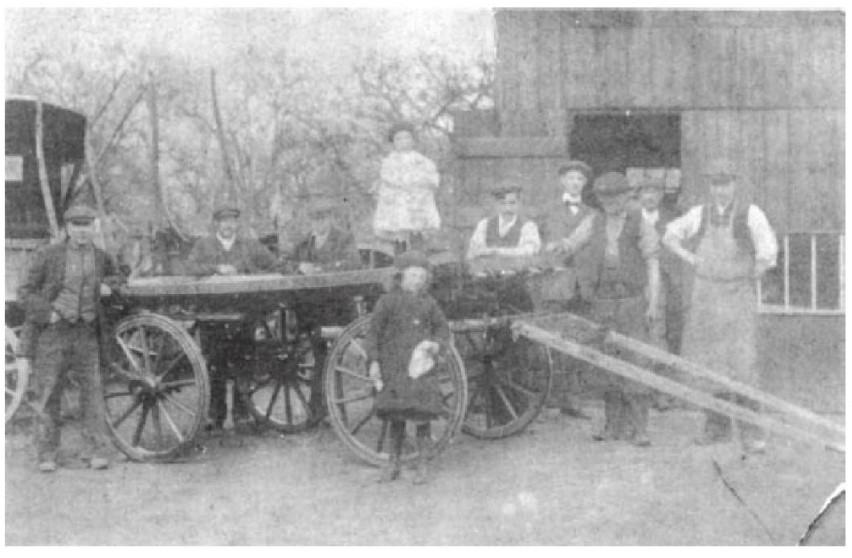
Stokes Wheelwrights. Fred on left of wheel, Thomas his father on right.
Thomas Stokes
Thomas Stokes was born in Bicester, Oxfordshire in 1816. He married Eliza Browning (born in 1814 in Tetbury, Gloucestershire) in Gloucester in 1840 Q3. Their first son William was baptised in Chipping Hill, Witham, Essex, on 3 Oct 1841. This seems a little unusual, and I can’t find Thomas and Eliza on the 1841 census. However both the 1851 and 1861 census state that William was indeed born in Essex.
In 1851 Thomas and Eliza were living in Bledington, Gloucestershire, and Thomas was a journeyman carpenter.
Note that a journeyman does not mean someone who moved around a lot. A journeyman was a tradesman who had served his trade apprenticeship and mastered his craft, not bound to serve a master, but originally hired by the day. The name derives from the French for day – jour.
Also on the 1851 census: their daughter Susan, born in Churchill Oxfordshire in 1844; son Frederick born in Bledington Gloucestershire in 1846; daughter Louisa born in Foxcote Oxfordshire in 1849; and 2 month old daughter Harriet born in Bledington in 1851.
On the 1861 census Thomas and Eliza were living in Evesham, Worcestershire, and daughter Susan was no longer living at home, but William, Fred, Louisa and Harriet were, as well as daughter Emily born in Churchill Oxfordshire in 1856. Thomas was a wheelwright.
On the 1871 census Thomas and Eliza were still living in Evesham, and Thomas was a wheelwright employing three apprentices. Son Fred, also a wheelwright, and his wife Ann Rebecca live with them.
Mr Stokes, wheelwright, was found guilty of reprehensible conduct in concealing the fact that small-pox existed in his house, according to a mention in The Oxfordshire Weekly News on Wednesday 19 February 1873:

From Paul Weaver’s ancestry website:
“It was Thomas Stokes who built the first “Famous Vale of Evesham Light Gardening Dray for a Half-Legged Horse to Trot” (the quotation is from his account book), the forerunner of many that became so familiar a sight in the towns and villages from the 1860s onwards. He built many more for the use of the Vale gardeners.
Thomas also had long-standing business dealings with the people of the circus and fairgrounds, and had a contract to effect necessary repairs and renewals to their waggons whenever they visited the district. He built living waggons for many of the show people’s families as well as shooting galleries and other equipment peculiar to the trade of his wandering customers, and among the names figuring in his books are some still familiar today, such as Wilsons and Chipperfields.
He is also credited with inventing the wooden “Mushroom” which was used by housewives for many years to darn socks. He built and repaired all kinds of vehicles for the gentry as well as for the circus and fairground travellers.
Later he lived with his wife at Merstow Green, Evesham, in a house adjoining the Almonry.”
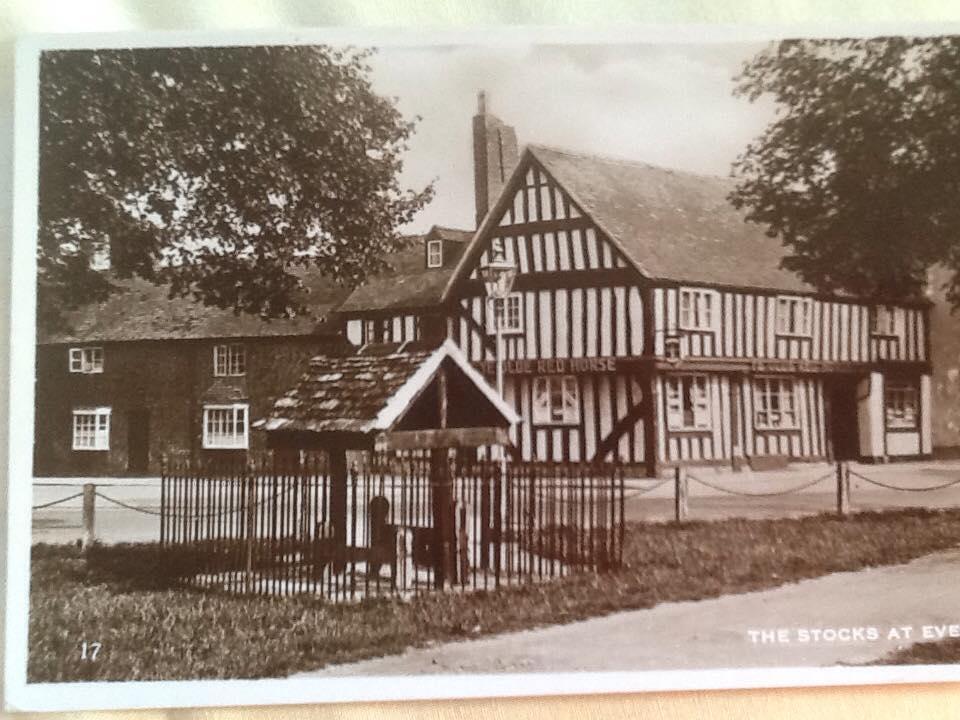
An excerpt from the book Evesham Inns and Signs by T.J.S. Baylis:

The Old Red Horse, Evesham:

Thomas died in 1885 aged 68 of paralysis, bronchitis and debility. His wife Eliza a year later in 1886.
Frederick Stokes
In Worcester in 1870 Fred married Ann Rebecca Day, who was born in Evesham in 1845.
Ann Rebecca Day:
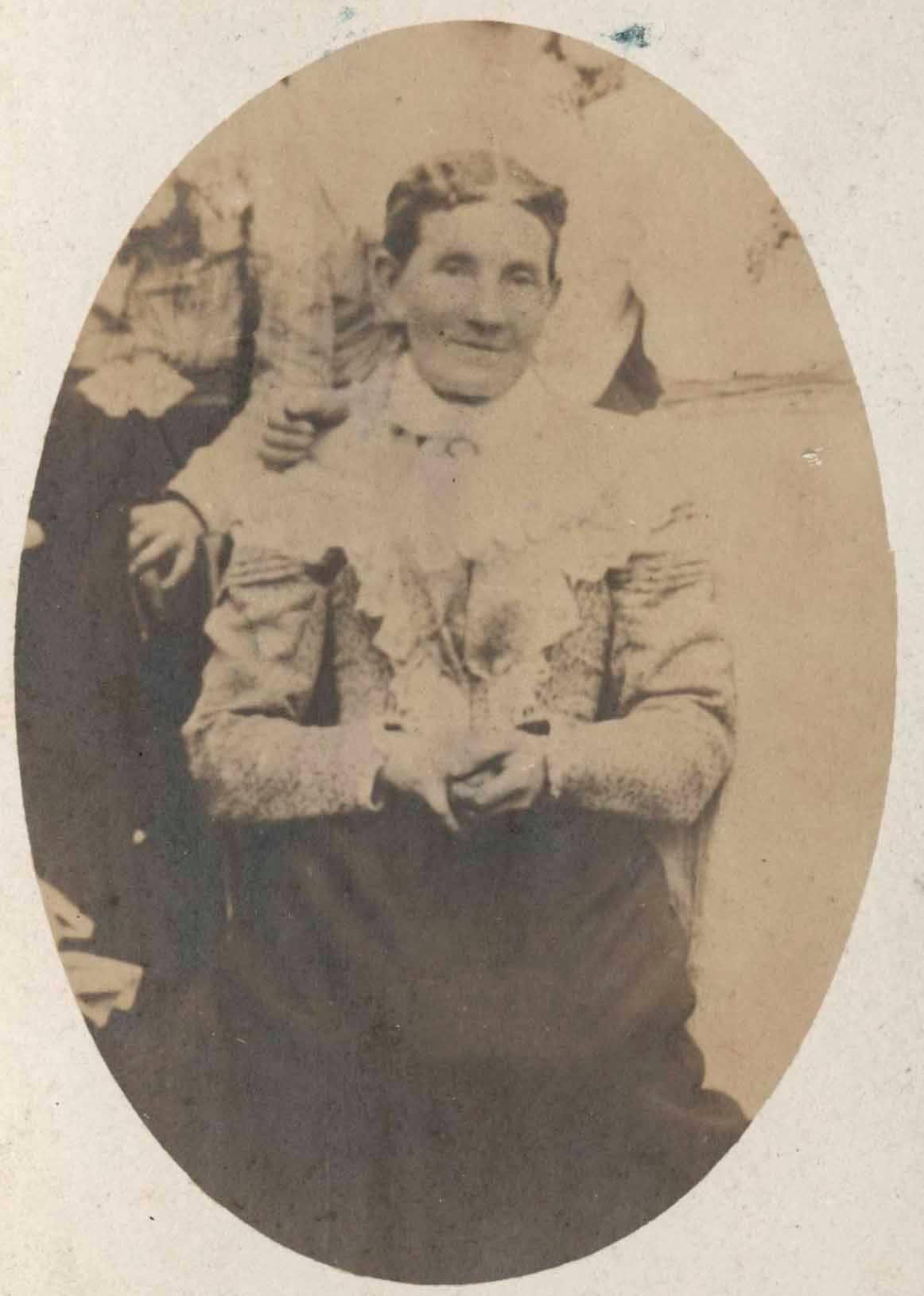
In 1871 Fred was still living with his parents in Evesham, with his wife Ann Rebecca as well as their three month old daughter Annie Elizabeth. Fred and Ann (referred to as Rebecca) moved to La Quinta on Main Street, Broadway.
Rebecca Stokes in the doorway of La Quinta on Main Street Broadway, with her grandchildren Ralph and Dolly Edwards:
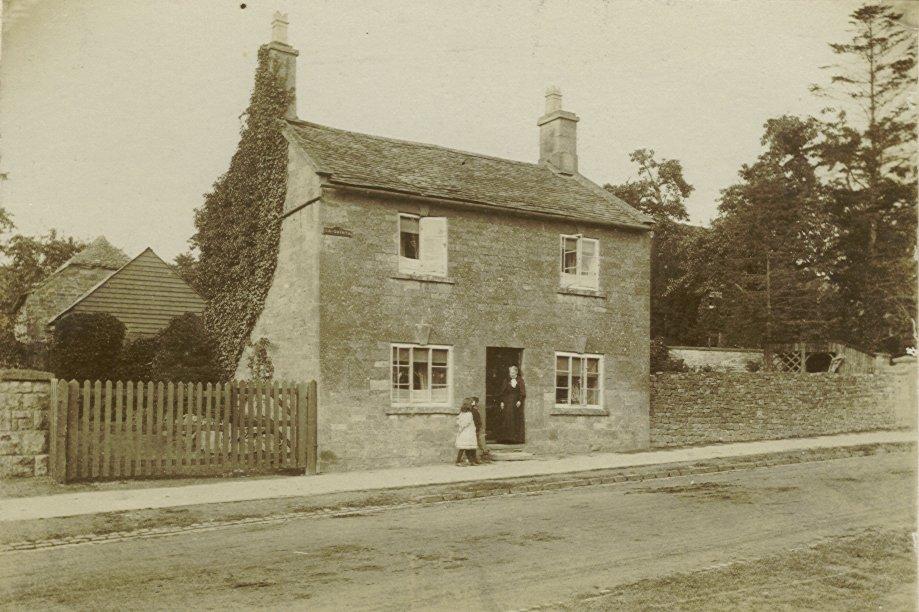

Fred was a wheelwright employing one man on the 1881 census. In 1891 they were still in Broadway, Fred’s occupation was wheelwright and coach painter, as well as his fifteen year old son Frederick.
In the Evesham Journal on Saturday 10 December 1892 it was reported that “Two cases of scarlet fever, the children of Mr. Stokes, wheelwright, Broadway, were certified by Mr. C. W. Morris to be isolated.”
Still in Broadway in 1901 and Fred’s son Albert was also a wheelwright. By 1911 Fred and Rebecca had only one son living at home in Broadway, Reginald, who was a coach painter. Fred was still a wheelwright aged 65.
Fred’s signature on the 1911 census:

Rebecca died in 1912 and Fred in 1917.
Fred Stokes:

In the book Evesham to Bredon From Old Photographs By Fred Archer:
 October 21, 2022 at 2:06 pm #6337
October 21, 2022 at 2:06 pm #6337In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
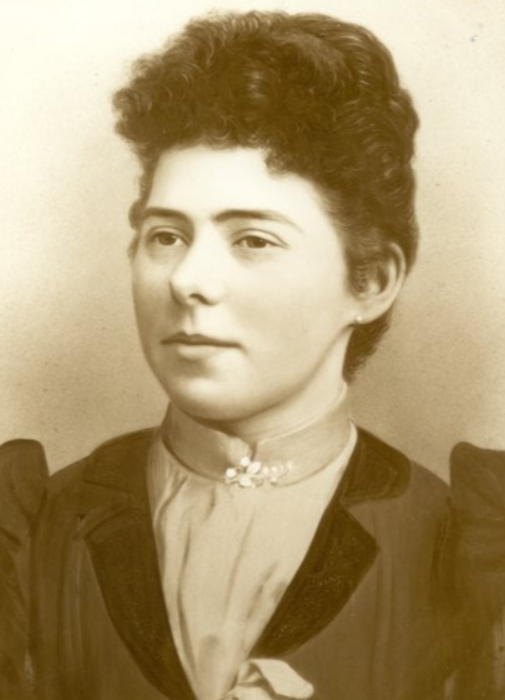
Annie Elizabeth Stokes
1871-1961
“Grandma E”

Annie, my great grandmother, was born 2 Jan 1871 in Merstow Green, Evesham, Worcestershire. Her father Fred Stokes was a wheelwright. On the 1771 census in Merston Green Annie was 3 months old and there was quite a houseful: Annies parents Fred and Rebecca, Fred’s parents Thomas and Eliza and two of their daughters, three apprentices, a lodger and one of Thomas’s grandsons.
1771 census Merstow Green, Evesham:

Annie at school in the early 1870s in Broadway. Annie is in the front on the left and her brother Fred is in the centre of the first seated row:
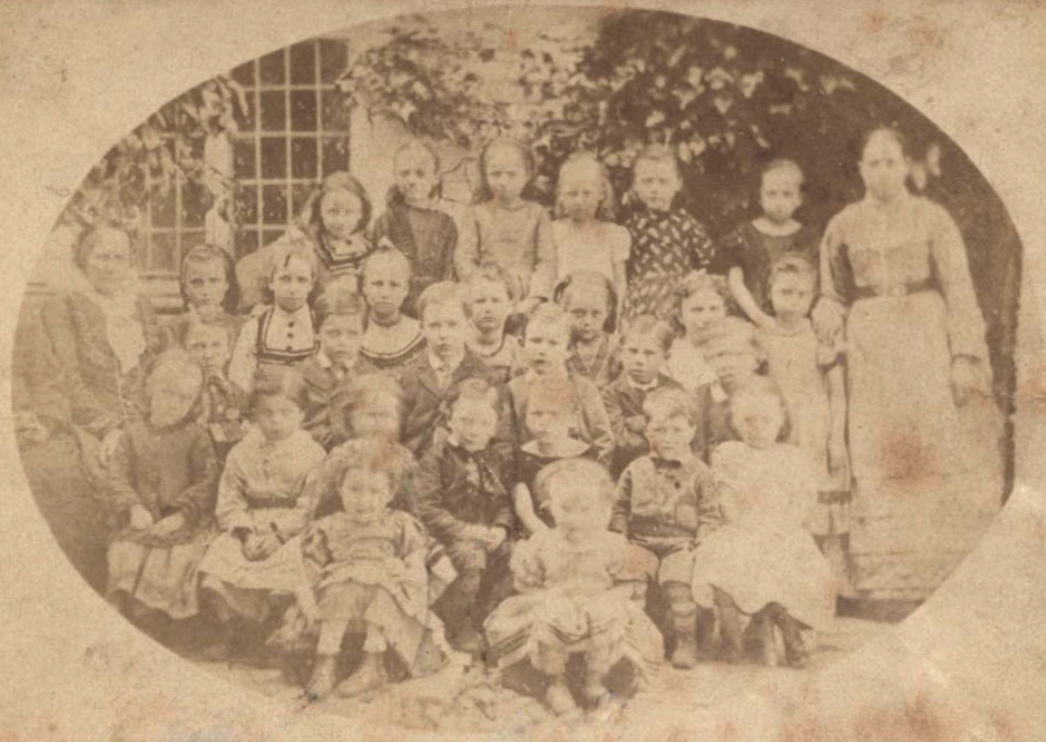

In 1881 Annie was a 10 year old visitor at the Angel Inn, Chipping Camden. A boarder there was 19 year old William Halford, a wheelwright apprentice. John Such, a 62 year old widower, was the innkeeper. Her parents and two siblings were living at La Quinta, on Main Street in Broadway.
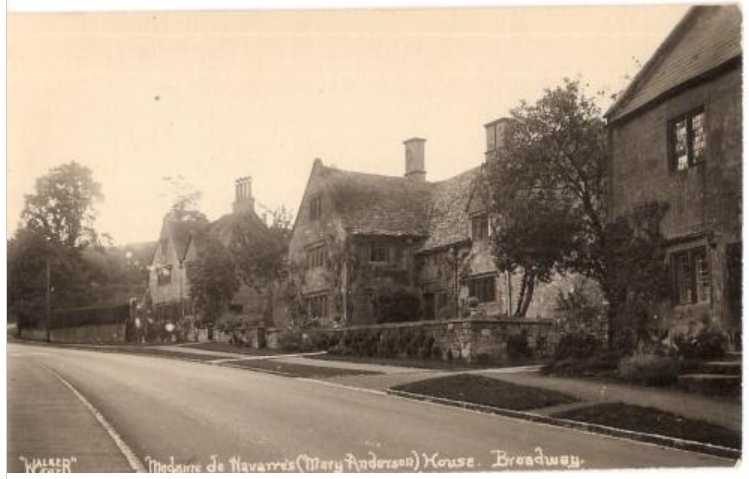
According to her obituary in 1962, “When the Maxton family visited Broadway to stay with Mr and Madame de Navarro at Court Farm, they offered Annie a family post with them which took her for several years to Paris and other parts of the continent.”
Mary Anderson was an American theatre actress. In 1890 she married Antonio Fernando de Navarro. She became known as Mary Anderson de Navarro. They settled at Court Farm in the Cotswolds, Broadway, Worcestershire, where she cultivated an interest in music and became a noted hostess with a distinguished circle of musical, literary and ecclesiastical guests. As in the years when Mary lived there, it was often filled with visiting artists and musicians, including Myra Hess and a young Jacqueline du Pré. (via Wikipedia)
Court Farm, Broadway:

Annie was an assistant to a tobacconist in West Bromwich in 1991, living as a boarder with William Calcutt and family. He future husband Albert was living in neighbouring Tipton in 1891, working at a pawnbroker apprenticeship.
Annie married Albert Parker Edwards in 1898 in Evesham. On the 1901 census, she was in hospital in Redditch.
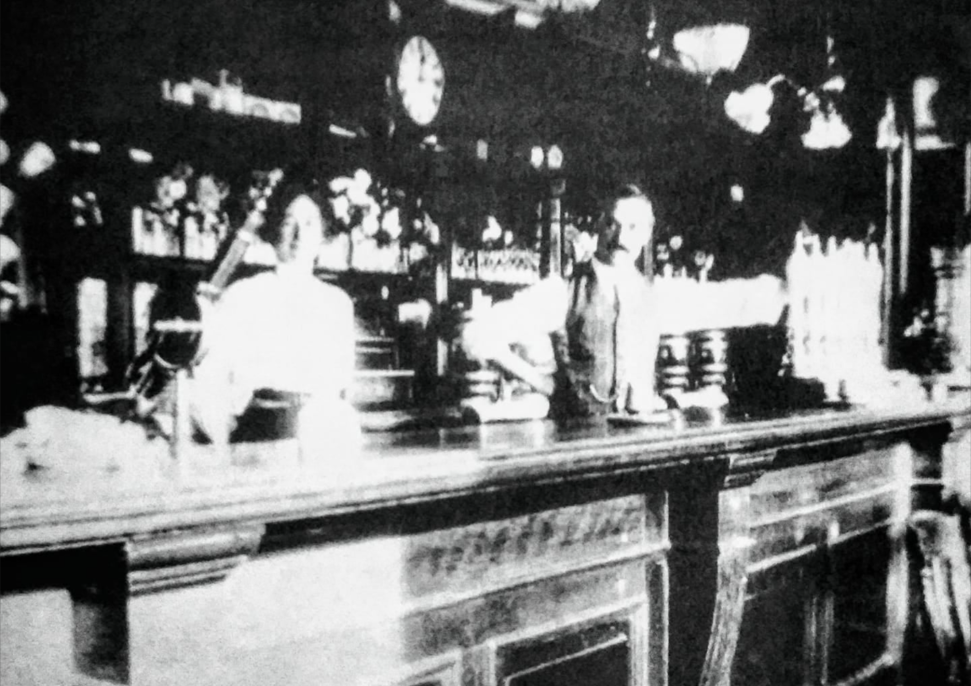
By 1911, Anne and Albert had five children and were living at the Cricketers Arms in Redditch.

Behind the bar in 1904 shortly after taking over at the Cricketers Arms. From a book on Redditch pubs:

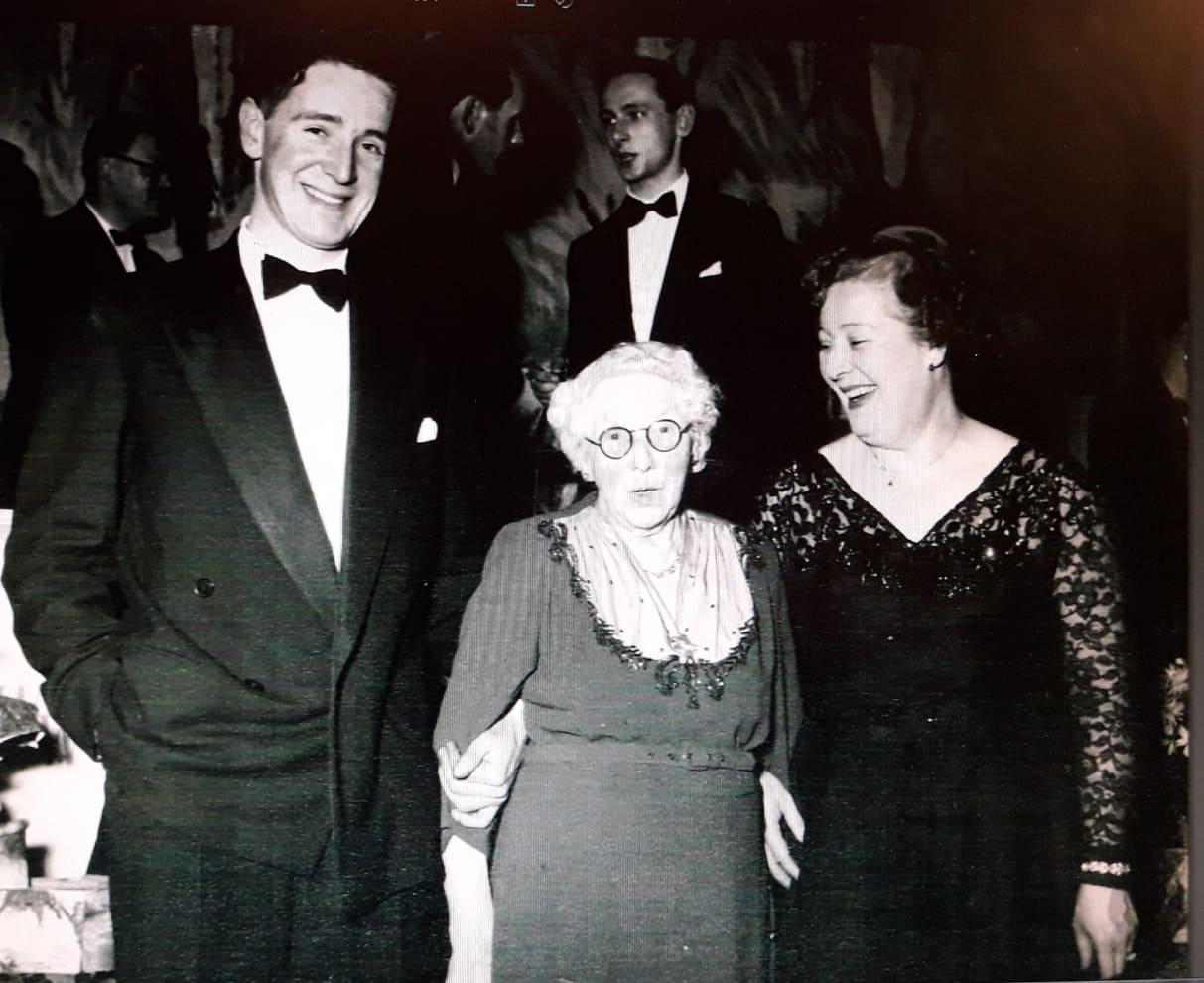
Annie was referred to in later years as Grandma E, probably to differentiate between her and my fathers Grandma T, as both lived to a great age.
Annie with her grandson Reg on the left and her daughter in law Peggy on the right, in the early 1950s:

Annie at my christening in 1959:

Annie died 30 Dec 1961, aged 90, at Ravenscourt nursing home, Redditch. Her obituary in the Droitwich Guardian in January 1962:

Note that this obituary contains an obvious error: Annie’s father was Frederick Stokes, and Thomas was his father.
October 11, 2022 at 2:58 pm #6334In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The House on Penn Common
Toi Fang and the Duke of Sutherland
Tomlinsons

Grassholme
Charles Tomlinson (1873-1929) my great grandfather, was born in Wolverhampton in 1873. His father Charles Tomlinson (1847-1907) was a licensed victualler or publican, or alternatively a vet/castrator. He married Emma Grattidge (1853-1911) in 1872. On the 1881 census they were living at The Wheel in Wolverhampton.
Charles married Nellie Fisher (1877-1956) in Wolverhampton in 1896. In 1901 they were living next to the post office in Upper Penn, with children (Charles) Sidney Tomlinson (1896-1955), and Hilda Tomlinson (1898-1977) . Charles was a vet/castrator working on his own account.
In 1911 their address was 4, Wakely Hill, Penn, and living with them were their children Hilda, Frank Tomlinson (1901-1975), (Dorothy) Phyllis Tomlinson (1905-1982), Nellie Tomlinson (1906-1978) and May Tomlinson (1910-1983). Charles was a castrator working on his own account.
Charles and Nellie had a further four children: Charles Fisher Tomlinson (1911-1977), Margaret Tomlinson (1913-1989) (my grandmother Peggy), Major Tomlinson (1916-1984) and Norah Mary Tomlinson (1919-2010).
My father told me that my grandmother had fallen down the well at the house on Penn Common in 1915 when she was two years old, and sent me a photo of her standing next to the well when she revisted the house at a much later date.
Peggy next to the well on Penn Common:

My grandmother Peggy told me that her father had had a racehorse called Toi Fang. She remembered the racing colours were sky blue and orange, and had a set of racing silks made which she sent to my father.
Through a DNA match, I met Ian Tomlinson. Ian is the son of my fathers favourite cousin Roger, Frank’s son. Ian found some racing silks and sent a photo to my father (they are now in contact with each other as a result of my DNA match with Ian), wondering what they were.
When Ian sent a photo of these racing silks, I had a look in the newspaper archives. In 1920 there are a number of mentions in the racing news of Mr C Tomlinson’s horse TOI FANG. I have not found any mention of Toi Fang in the newspapers in the following years.
The Scotsman – Monday 12 July 1920:

The other story that Ian Tomlinson recalled was about the house on Penn Common. Ian said he’d heard that the local titled person took Charles Tomlinson to court over building the house but that Tomlinson won the case because it was built on common land and was the first case of it’s kind.

Penn Common Right of Way Case:
Staffordshire Advertiser March 9, 1912In the chancery division, on Tuesday, before Mr Justice Joyce, it was announced that a settlement had been arrived at of the Penn Common Right of Way case, the hearing of which occupied several days last month. The action was brought by the Duke of Sutherland (as Lord of the Manor of Penn) and Mr Harry Sydney Pitt (on behalf of himself and other freeholders of the manor having a right to pasturage on Penn Common) to restrain Mr James Lakin, Carlton House, Penn; Mr Charles Tomlinson, Mayfield Villa, Wakely Hill, Penn; and Mr Joseph Harold Simpkin, Dudley Road, Wolverhampton, from drawing building materials across the common, or otherwise causing injury to the soil.
The real point in dispute was whether there was a public highway for all purposes running by the side of the defendants land from the Turf Tavern past the golf club to the Barley Mow.
Mr Hughes, KC for the plaintiffs, now stated that the parties had been in consultation, and had come to terms, the substance of which was that the defendants admitted that there was no public right of way, and that they were granted a private way. This, he thought, would involve the granting of some deed or deeds to express the rights of the parties, and he suggested that the documents should be be settled by some counsel to be mutually agreed upon.His lordship observed that the question of coal was probably the important point. Mr Younger said Mr Tomlinson was a freeholder, and the plaintiffs could not mine under him. Mr Hughes: The coal actually under his house is his, and, of course, subsidence might be produced by taking away coal some distance away. I think some document is required to determine his actual rights.
Mr Younger said he wanted to avoid anything that would increase the costs, but, after further discussion, it was agreed that Mr John Dixon (an expert on mineral rights), or failing him, another counsel satisfactory to both parties, should be invited to settle the terms scheduled in the agreement, in order to prevent any further dispute.
The name of the house is Grassholme. The address of Mayfield Villas is the house they were living in while building Grassholme, which I assume they had not yet moved in to at the time of the newspaper article in March 1912.
What my grandmother didn’t tell anyone was how her father died in 1929:

On the 1921 census, Charles, Nellie and eight of their children were living at 269 Coleman Street, Wolverhampton.
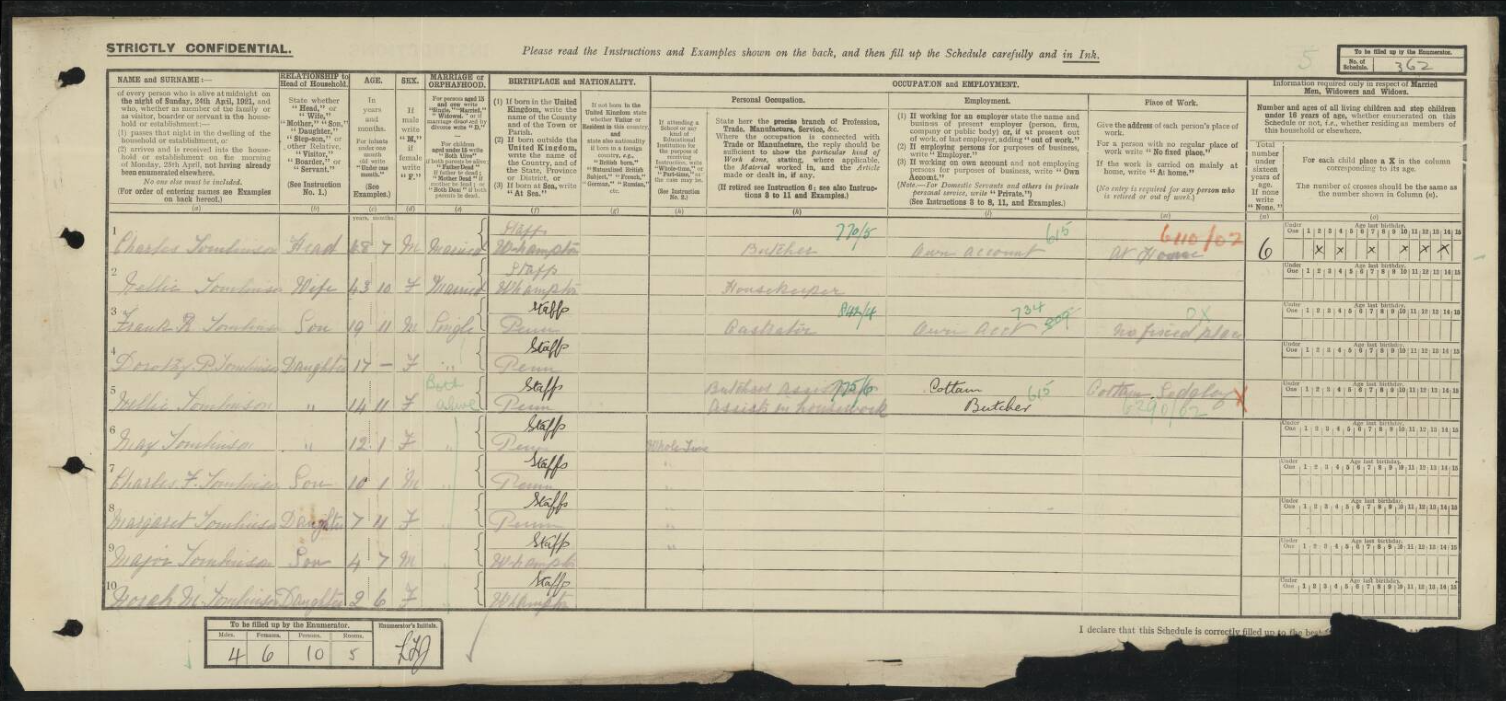
They were living on Coleman Street in 1915 when Charles was fined for staying open late.
Staffordshire Advertiser – Saturday 13 February 1915:

What is not yet clear is why they moved from the house on Penn Common sometime between 1912 and 1915. And why did he have a racehorse in 1920?
June 10, 2022 at 1:39 pm #6305In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
The Hair’s and Leedham’s of Netherseal
Samuel Warren of Stapenhill married Catherine Holland of Barton under Needwood in 1795. Catherine’s father was Thomas Holland; her mother was Hannah Hair.
Hannah was born in Netherseal, Derbyshire, in 1739. Her parents were Joseph Hair 1696-1746 and Hannah.
Joseph’s parents were Isaac Hair and Elizabeth Leedham. Elizabeth was born in Netherseal in 1665. Isaac and Elizabeth were married in Netherseal in 1686.Marriage of Isaac Hair and Elizabeth Leedham: (variously spelled Ledom, Leedom, Leedham, and in one case mistranscribed as Sedom):

Isaac was buried in Netherseal on 14 August 1709 (the transcript says the 18th, but the microfiche image clearly says the 14th), but I have not been able to find a birth registered for him. On other public trees on an ancestry website, Isaac Le Haire was baptised in Canterbury and was a Huguenot, but I haven’t found any evidence to support this.
Isaac Hair’s death registered 14 August 1709 in Netherseal:

A search for the etymology of the surname Hair brings various suggestions, including:
“This surname is derived from a nickname. ‘the hare,’ probably affixed on some one fleet of foot. Naturally looked upon as a complimentary sobriquet, and retained in the family; compare Lightfoot. (for example) Hugh le Hare, Oxfordshire, 1273. Hundred Rolls.”
From this we may deduce that the name Hair (or Hare) is not necessarily from the French Le Haire, and existed in England for some considerable time before the arrival of the Huguenots.
Elizabeth Leedham was born in Netherseal in 1665. Her parents were Nicholas Leedham 1621-1670 and Dorothy. Nicholas Leedham was born in Church Gresley (Swadlincote) in 1621, and died in Netherseal in 1670.
Nicholas was a Yeoman and left a will and inventory worth £147.14s.8d (one hundred and forty seven pounds fourteen shillings and eight pence).
The 1670 inventory of Nicholas Leedham:

According to local historian Mark Knight on the Netherseal History facebook group, the Seale (Netherseal and Overseal) parish registers from the year 1563 to 1724 were digitized during lockdown.
via Mark Knight:
“There are five entries for Nicholas Leedham.
On March 14th 1646 he and his wife buried an unnamed child, presumably the child died during childbirth or was stillborn.
On November 28th 1659 he buried his wife, Elizabeth. He remarried as on June 13th 1664 he had his son William baptised.
The following year, 1665, he baptised a daughter on November 12th. (Elizabeth) On December 23rd 1672 the parish record says that Dorithy daughter of Dorithy was buried. The Bishops Transcript has Dorithy a daughter of Nicholas. Nicholas’ second wife was called Dorithy and they named a daughter after her. Alas, the daughter died two years after Nicholas. No further Leedhams appear in the record until after 1724.”Dorothy daughter of Dorothy Leedham was buried 23 December 1672:

William, son of Nicholas and Dorothy also left a will. In it he mentions “My dear wife Elizabeth. My children Thomas Leedom, Dorothy Leedom , Ann Leedom, Christopher Leedom and William Leedom.”
1726 will of William Leedham:

I found a curious error with the the parish register entries for Hannah Hair. It was a transcription error, but not a recent one. The original parish registers were copied: “HO Copy of ye register of Seale anno 1739.” I’m not sure when the copy was made, but it wasn’t recently. I found a burial for Hannah Hair on 22 April 1739 in the HO copy, which was the same day as her baptism registered on the original. I checked both registers name by name and they are exactly copied EXCEPT for Hannah Hairs. The rector, Richard Inge, put burial instead of baptism by mistake.
The original Parish register baptism of Hannah Hair:

The HO register copy incorrectly copied:
 June 6, 2022 at 12:58 pm #6303
June 6, 2022 at 12:58 pm #6303In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
The Hollands of Barton under Needwood
Samuel Warren of Stapenhill married Catherine Holland of Barton under Needwood in 1795.
I joined a Barton under Needwood History group and found an incredible amount of information on the Holland family, but first I wanted to make absolutely sure that our Catherine Holland was one of them as there were also Hollands in Newhall. Not only that, on the marriage licence it says that Catherine Holland was from Bretby Park Gate, Stapenhill.
Then I noticed that one of the witnesses on Samuel’s brother Williams marriage to Ann Holland in 1796 was John Hair. Hannah Hair was the wife of Thomas Holland, and they were the Barton under Needwood parents of Catherine. Catherine was born in 1775, and Ann was born in 1767.
The 1851 census clinched it: Catherine Warren 74 years old, widow and formerly a farmers wife, was living in the household of her son John Warren, and her place of birth is listed as Barton under Needwood. In 1841 Catherine was a 64 year old widow, her husband Samuel having died in 1837, and she was living with her son Samuel, a farmer. The 1841 census did not list place of birth, however. Catherine died on 31 March 1861 and does not appear on the 1861 census.
Once I had established that our Catherine Holland was from Barton under Needwood, I had another look at the information available on the Barton under Needwood History group, compiled by local historian Steve Gardner.
Catherine’s parents were Thomas Holland 1737-1828 and Hannah Hair 1739-1822.
Steve Gardner had posted a long list of the dates, marriages and children of the Holland family. The earliest entries in parish registers were Thomae Holland 1562-1626 and his wife Eunica Edwardes 1565-1632. They married on 10th July 1582. They were born, married and died in Barton under Needwood. They were direct ancestors of Catherine Holland, and as such my direct ancestors too.
The known history of the Holland family in Barton under Needwood goes back to Richard De Holland. (Thanks once again to Steve Gardner of the Barton under Needwood History group for this information.)
“Richard de Holland was the first member of the Holland family to become resident in Barton under Needwood (in about 1312) having been granted lands by the Earl of Lancaster (for whom Richard served as Stud and Stock Keeper of the Peak District) The Holland family stemmed from Upholland in Lancashire and had many family connections working for the Earl of Lancaster, who was one of the biggest Barons in England. Lancaster had his own army and lived at Tutbury Castle, from where he ruled over most of the Midlands area. The Earl of Lancaster was one of the main players in the ‘Barons Rebellion’ and the ensuing Battle of Burton Bridge in 1322. Richard de Holland was very much involved in the proceedings which had so angered Englands King. Holland narrowly escaped with his life, unlike the Earl who was executed.
From the arrival of that first Holland family member, the Hollands were a mainstay family in the community, and were in Barton under Needwood for over 600 years.”Continuing with various items of information regarding the Hollands, thanks to Steve Gardner’s Barton under Needwood history pages:
“PART 6 (Final Part)
Some mentions of The Manor of Barton in the Ancient Staffordshire Rolls:
1330. A Grant was made to Herbert de Ferrars, at le Newland in the Manor of Barton.
1378. The Inquisitio bonorum – Johannis Holand — an interesting Inventory of his goods and their value and his debts.
1380. View of Frankpledge ; the Jury found that Richard Holland was feloniously murdered by his wife Joan and Thomas Graunger, who fled. The goods of the deceased were valued at iiij/. iijj. xid. ; one-third went to the dead man, one-third to his son, one- third to the Lord for the wife’s share. Compare 1 H. V. Indictments. (1413.)
That Thomas Graunger of Barton smyth and Joan the wife of Richard de Holond of Barton on the Feast of St. John the Baptist 10 H. II. (1387) had traitorously killed and murdered at night, at Barton, Richard, the husband of the said Joan. (m. 22.)
The names of various members of the Holland family appear constantly among the listed Jurors on the manorial records printed below : —
1539. Richard Holland and Richard Holland the younger are on the Muster Roll of Barton
1583. Thomas Holland and Unica his wife are living at Barton.
1663-4. Visitations. — Barton under Needword. Disclaimers. William Holland, Senior, William Holland, Junior.
1609. Richard Holland, Clerk and Alice, his wife.
1663-4. Disclaimers at the Visitation. William Holland, Senior, William Holland, Junior.”I was able to find considerably more information on the Hollands in the book “Some Records of the Holland Family (The Hollands of Barton under Needwood, Staffordshire, and the Hollands in History)” by William Richard Holland. Luckily the full text of this book can be found online.
William Richard Holland (Died 1915) An early local Historian and author of the book:

‘Holland House’ taken from the Gardens (sadly demolished in the early 60’s):
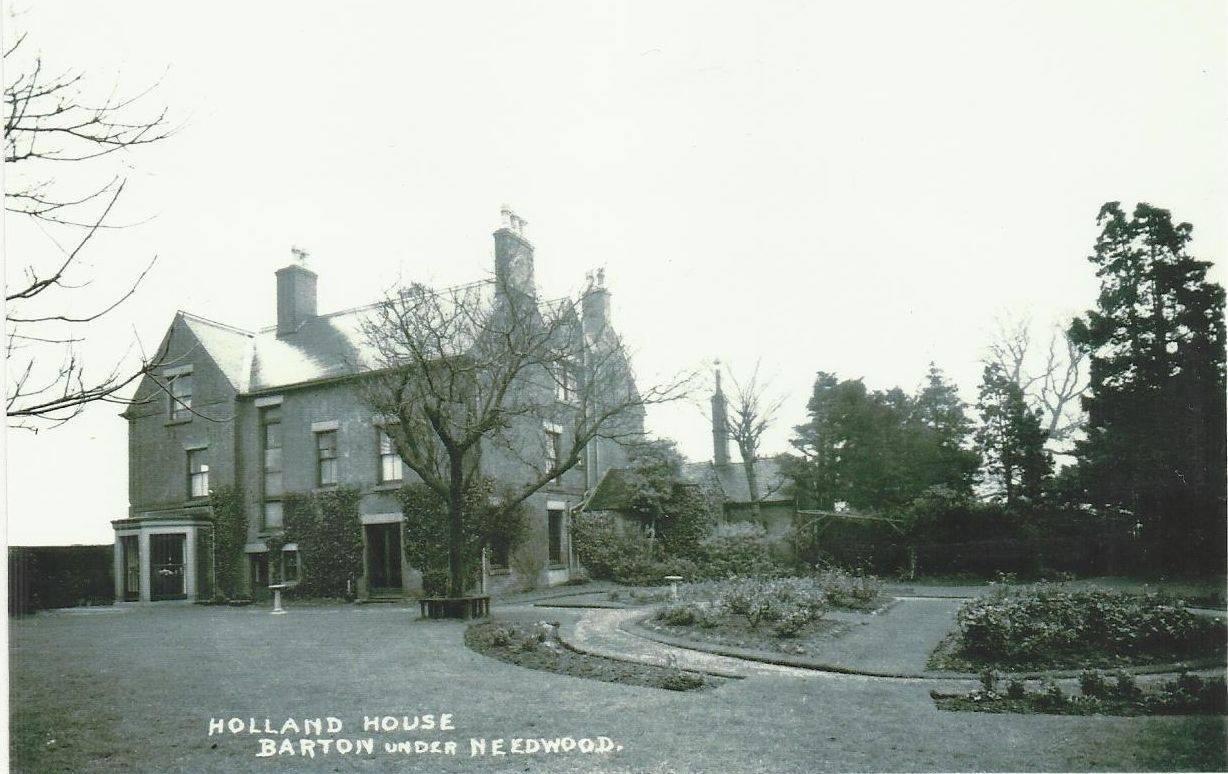

Excerpt from the book:
“The charter, dated 1314, granting Richard rights and privileges in Needwood Forest, reads as follows:
“Thomas Earl of Lancaster and Leicester, high-steward of England, to whom all these present shall come, greeting: Know ye, that we have given, &c., to Richard Holland of Barton, and his heirs, housboot, heyboot, and fireboot, and common of pasture, in our forest of Needwood, for all his beasts, as well in places fenced as lying open, with 40 hogs, quit of pawnage in our said forest at all times in the year (except hogs only in fence month). All which premises we will warrant, &c. to the said Richard and his heirs against all people for ever”
“The terms “housboot” “heyboot” and “fireboot” meant that Richard and his heirs were to have the privilege of taking from the Forest, wood needed for house repair and building, hedging material for the repairing of fences, and what was needful for purposes of fuel.”
Further excerpts from the book:
“It may here be mentioned that during the renovation of Barton Church, when the stone pillars were being stripped of the plaster which covered them, “William Holland 1617” was found roughly carved on a pillar near to the belfry gallery, obviously the work of a not too devout member of the family, who, seated in the gallery of that time, occupied himself thus during the service. The inscription can still be seen.”
“The earliest mention of a Holland of Upholland occurs in the reign of John in a Final Concord, made at the Lancashire Assizes, dated November 5th, 1202, in which Uchtred de Chryche, who seems to have had some right in the manor of Upholland, releases his right in fourteen oxgangs* of land to Matthew de Holland, in consideration of the sum of six marks of silver. Thus was planted the Holland Tree, all the early information of which is found in The Victoria County History of Lancaster.
As time went on, the family acquired more land, and with this, increased position. Thus, in the reign of Edward I, a Robert de Holland, son of Thurstan, son of Robert, became possessed of the manor of Orrell adjoining Upholland and of the lordship of Hale in the parish of Childwall, and, through marriage with Elizabeth de Samlesbury (co-heiress of Sir Wm. de Samlesbury of Samlesbury, Hall, near to Preston), of the moiety of that manor….
* An oxgang signified the amount of land that could be ploughed by one ox in one day”
“This Robert de Holland, son of Thurstan, received Knighthood in the reign of Edward I, as did also his brother William, ancestor of that branch of the family which later migrated to Cheshire. Belonging to this branch are such noteworthy personages as Mrs. Gaskell, the talented authoress, her mother being a Holland of this branch, Sir Henry Holland, Physician to Queen Victoria, and his two sons, the first Viscount Knutsford, and Canon Francis Holland ; Sir Henry’s grandson (the present Lord Knutsford), Canon Scott Holland, etc. Captain Frederick Holland, R.N., late of Ashbourne Hall, Derbyshire, may also be mentioned here.*”
Thanks to the Barton under Needwood history group for the following:
WALES END FARM:
In 1509 it was owned and occupied by Mr Johannes Holland De Wallass end who was a well to do Yeoman Farmer (the origin of the areas name – Wales End). Part of the building dates to 1490 making it probably the oldest building still standing in the Village: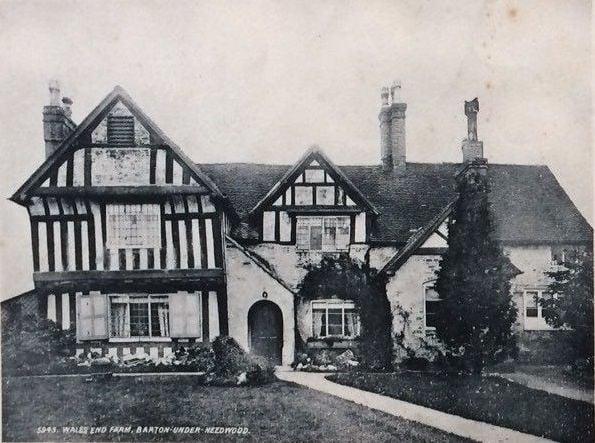
I found records for all of the Holland’s listed on the Barton under Needwood History group and added them to my ancestry tree. The earliest will I found was for Eunica Edwardes, then Eunica Holland, who died in 1632.
A page from the 1632 will and inventory of Eunica (Unice) Holland:

I’d been reading about “pedigree collapse” just before I found out her maiden name of Edwardes. Edwards is my own maiden name.
“In genealogy, pedigree collapse describes how reproduction between two individuals who knowingly or unknowingly share an ancestor causes the family tree of their offspring to be smaller than it would otherwise be.
Without pedigree collapse, a person’s ancestor tree is a binary tree, formed by the person, the parents, grandparents, and so on. However, the number of individuals in such a tree grows exponentially and will eventually become impossibly high. For example, a single individual alive today would, over 30 generations going back to the High Middle Ages, have roughly a billion ancestors, more than the total world population at the time. This apparent paradox occurs because the individuals in the binary tree are not distinct: instead, a single individual may occupy multiple places in the binary tree. This typically happens when the parents of an ancestor are cousins (sometimes unbeknownst to themselves). For example, the offspring of two first cousins has at most only six great-grandparents instead of the normal eight. This reduction in the number of ancestors is pedigree collapse. It collapses the binary tree into a directed acyclic graph with two different, directed paths starting from the ancestor who in the binary tree would occupy two places.” via wikipediaThere is nothing to suggest, however, that Eunica’s family were related to my fathers family, and the only evidence so far in my tree of pedigree collapse are the marriages of Orgill cousins, where two sets of grandparents are repeated.
A list of Holland ancestors:
Catherine Holland 1775-1861
her parents:
Thomas Holland 1737-1828 Hannah Hair 1739-1832
Thomas’s parents:
William Holland 1696-1756 Susannah Whiteing 1715-1752
William’s parents:
William Holland 1665- Elizabeth Higgs 1675-1720
William’s parents:
Thomas Holland 1634-1681 Katherine Owen 1634-1728
Thomas’s parents:
Thomas Holland 1606-1680 Margaret Belcher 1608-1664
Thomas’s parents:
Thomas Holland 1562-1626 Eunice Edwardes 1565- 1632March 21, 2022 at 7:05 am #6284In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
To Australia
Grettons
Charles Herbert Gretton 1876-1954
Charles Gretton, my great grandmothers youngest brother, arrived in Sydney Australia on 12 February 1912, having set sail on 5 January 1912 from London. His occupation on the passenger list was stockman, and he was traveling alone. Later that year, in October, his wife and two sons sailed out to join him.
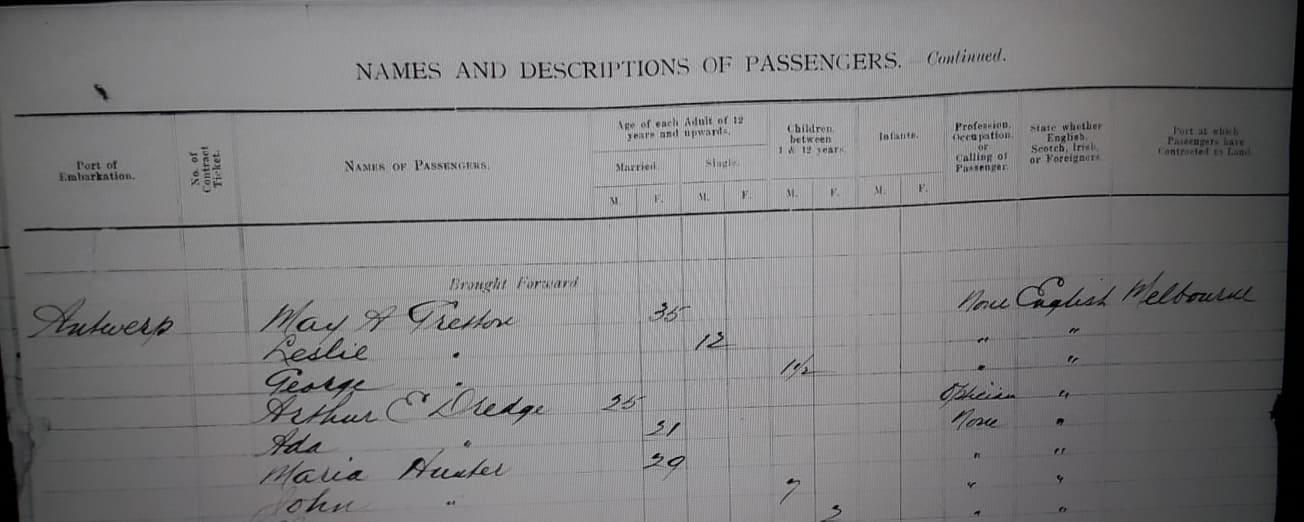
Charles was born in Swadlincote. He married Mary Anne Illsley, a local girl from nearby Church Gresley, in 1898. Their first son, Leslie Charles Bloemfontein Gretton, was born in 1900 in Church Gresley, and their second son, George Herbert Gretton, was born in 1910 in Swadlincote. In 1901 Charles was a colliery worker, and on the 1911 census, his occupation was a sanitary ware packer.
Charles and Mary Anne had two more sons, both born in Footscray: Frank Orgill Gretton in 1914, and Arthur Ernest Gretton in 1920.
On the Australian 1914 electoral rolls, Charles and Mary Ann were living at 72 Moreland Street, Footscray, and in 1919 at 134 Cowper Street, Footscray, and Charles was a labourer. In 1924, Charles was a sub foreman, living at 3, Ryan Street E, Footscray, Australia. On a later electoral register, Charles was a foreman. Footscray is a suburb of Melbourne, and developed into an industrial zone in the second half of the nineteenth century.
Charles died in Victoria in 1954 at the age of 77. His wife Mary Ann died in 1958.

Charles and Mary Ann Gretton:

Leslie Charles Bloemfontein Gretton 1900-1955
Leslie was an electrician. He married Ethel Christine Halliday, born in 1900 in Footscray, in 1927. They had four children: Tom, Claire, Nancy and Frank. By 1943 they were living in Yallourn. Yallourn, Victoria was a company town in Victoria, Australia built between the 1920s and 1950s to house employees of the State Electricity Commission of Victoria, who operated the nearby Yallourn Power Station complex. However, expansion of the adjacent open-cut brown coal mine led to the closure and removal of the town in the 1980s.
On the 1954 electoral registers, daughter Claire Elizabeth Gretton, occupation teacher, was living at the same address as Leslie and Ethel.
Leslie died in Yallourn in 1955, and Ethel nine years later in 1964, also in Yallourn.
George Herbert Gretton 1910-1970
George married Florence May Hall in 1934 in Victoria, Australia. In 1942 George was listed on the electoral roll as a grocer, likewise in 1949. In 1963 his occupation was a process worker, and in 1968 in Flinders, a horticultural advisor.
George died in Lang Lang, not far from Melbourne, in 1970.
Frank Orgill Gretton 1914-
Arthur Ernest Gretton 1920-
Orgills
John Orgill 1835-1911
John Orgill was Charles Herbert Gretton’s uncle. He emigrated to Australia in 1865, and married Elizabeth Mary Gladstone 1845-1926 in Victoria in 1870. Their first child was born in December that year, in Dandenong. They had seven children, and their three sons all have the middle name Gladstone.
John Orgill was a councillor for the Shire of Dandenong in 1873, and between 1876 and 1879.
John Orgill:

John Orgill obituary in the South Bourke and Mornington Journal, 21 December 1911:

John’s wife Elizabeth Orgill, a teacher and a “a public spirited lady” according to newspaper articles, opened a hydropathic hospital in Dandenong called Gladstone House.
Elizabeth Gladstone Orgill:
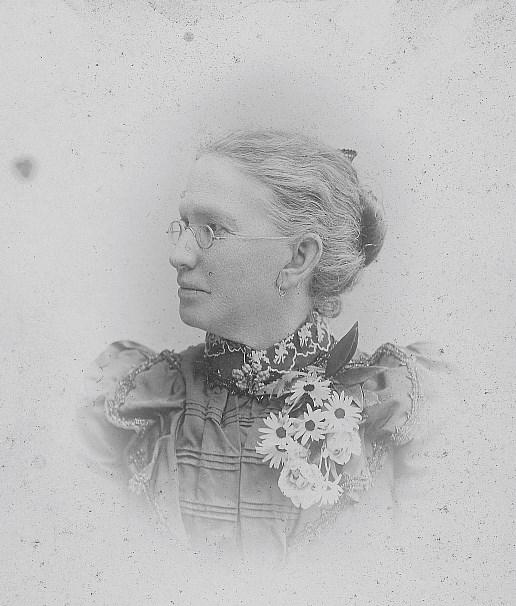
On the Old Dandenong website:
Gladstone House hydropathic hospital on the corner of Langhorne and Foster streets (153 Foster Street) Dandenong opened in 1896, working on the theory of water therapy, no medicine or operations. Her husband passed away in 1911 at 77, around similar time Dr Barclay Thompson obtained control of the practice. Mrs Orgill remaining on in some capacity.
Elizabeth Mary Orgill (nee Gladstone) operated Gladstone House until at least 1911, along with another hydropathic hospital (Birthwood) on Cheltenham road. She was the daughter of William Gladstone (Nephew of William Ewart Gladstone, UK prime minister in 1874).
Around 1912 Dr A. E. Taylor took over the location from Dr. Barclay Thompson. Mrs Orgill was still working here but no longer controlled the practice, having given it up to Barclay. Taylor served as medical officer for the Shire for before his death in 1939. After Taylor’s death Dr. T. C. Reeves bought his practice in 1939, later that year being appointed medical officer,
Gladstone Road in Dandenong is named after her family, who owned and occupied a farming paddock in the area on former Police Paddock ground, the Police reserve having earlier been reduced back to Stud Road.
Hydropathy (now known as Hydrotherapy) and also called water cure, is a part of medicine and alternative medicine, in particular of naturopathy, occupational therapy and physiotherapy, that involves the use of water for pain relief and treatment.
Gladstone House, Dandenong:
John’s brother Robert Orgill 1830-1915 also emigrated to Australia. I met (online) his great great grand daughter Lidya Orgill via the Old Dandenong facebook group.
John’s other brother Thomas Orgill 1833-1908 also emigrated to the same part of Australia.
Thomas Orgill:

One of Thomas Orgills sons was George Albert Orgill 1880-1949:

A letter was published in The South Bourke & Mornington Journal (Richmond, Victoria, Australia) on 17 Jun 1915, to Tom Orgill, Emerald Hill (South Melbourne) from hospital by his brother George Albert Orgill (4th Pioneers) describing landing of Covering Party prior to dawn invasion of Gallipoli:

Another brother Henry Orgill 1837-1916 was born in Measham and died in Dandenong, Australia. Henry was a bricklayer living in Measham on the 1861 census. Also living with his widowed mother Elizabeth at that address was his sister Sarah and her husband Richard Gretton, the baker (my great great grandparents). In October of that year he sailed to Melbourne. His occupation was bricklayer on his death records in 1916.
Two of Henry’s sons, Arthur Garfield Orgill born 1888 and Ernest Alfred Orgill born 1880 were killed in action in 1917 and buried in Nord-Pas-de-Calais, France. Another son, Frederick Stanley Orgill, died in 1897 at the age of seven.
A fifth brother, William Orgill 1842- sailed from Liverpool to Melbourne in 1861, at 19 years of age. Four years later in 1865 he sailed from Victoria, Australia to New Zealand.
I assumed I had found all of the Orgill brothers who went to Australia, and resumed research on the Orgills in Measham, in England. A search in the British Newspaper Archives for Orgills in Measham revealed yet another Orgill brother who had gone to Australia.
Matthew Orgill 1828-1907 went to South Africa and to Australia, but returned to Measham.
The Orgill brothers had two sisters. One was my great great great grandmother Sarah, and the other was Hannah. Hannah married Francis Hart in Measham. One of her sons, John Orgill Hart 1862-1909, was born in Measham. On the 1881 census he was a 19 year old carpenters apprentice. Two years later in 1883 he was listed as a joiner on the passenger list of the ship Illawarra, bound for Australia. His occupation at the time of his death in Dandenong in 1909 was contractor.
An additional coincidental note about Dandenong: my step daughter Emily’s Australian partner is from Dandenong.
Housleys
Charles Housley 1823-1856
Charles Housley emigrated to Australia in 1851, the same year that his brother George emigrated to USA. Charles is mentioned in the Narrative on the Letters by Barbara Housley, and appears in the Housley Letters chapters.
Rushbys
George “Mike” Rushby 1933-
Mike moved to Australia from South Africa. His story is a separate chapter.
-
AuthorSearch Results