Search Results for 'family'
-
AuthorSearch Results
-
December 14, 2024 at 6:42 pm #7682
In reply to: Quintessence: Reversing the Fifth
Matteo — Autumn 2023
The Jardin des Plantes park was quiet, the kind of quiet that settled after a brisk autumn rain. Matteo sat on a weathered wooden bench, watching a golden retriever chase the last of the fallen leaves tumbling across the gravel path. The damp air was carrying scents of the earth welcoming a retreat inside, and taking the time to be alone with his thoughts was something he’d missed.
His phone buzzed with a notification—a news update about the latest film adaptation from a Liz Tattler classic fiction. The name made him smile faintly. Juliette had loved Tattler’s novels, their whimsical characters, and the unflinching and unapologetic observations about life’s quiet mysteries and the unexpected rants about the virtues of cleaning and dustsceawung that propelled the word in the people’s top 100 favourite in the Oxford dictionary for several years consecutively.
“They’re so full of texture,” Juliette once said as she was sprawled on the bed of their tiny Parisian flat, a battered paperback in her hands. “Like you can feel the pages breathe.”
His image of her was still vivid, they’d stayed on good terms and he would still thumb up some of her posts from time to time —but it was only small moments rather than full scenes that used to come back, fragmented pieces of memories really —her dark hair falling messily over her face, her legs crossed in a casual way.
Paris had been a playground for them. For a while, they were caught in a whirlwind of late-night conversations in smoky cafés and lazy Sunday mornings wandering the Seine. They’d spent hours in bookstores, Juliette hunting for first editions and Matteo snapping pictures of the handwritten notes tucked between the pages of used novels.
A year ago, a different park in a different city—Hyde Park, London. She was there, twirling a scarf she’d picked up in Vienna the weekend before, the bright red of it like a ribbon of fire against the soft gray skies. They had been enamored with each other and with the spontaneity of hopping trains to new cities, their weekends folding into one another like pages of a travel journal. London one week, Paris the next, Berlin after that. Each city a postcard snapshot, vibrant and fleeting.
Juliette would tease him about his fascination with the little things—how he would linger too long over a cup of coffee at a café or stop to photograph a tree in the middle of nowhere. “You’re always looking for stories,” she’d said with a laugh, tucking a stray strand of hair behind her ear. “Even when you’re not sure what they mean.”
“Stories are everywhere,” he would reply, snapping a picture of her against the backdrop of the park, her scarf billowing in the wind. She had rolled her eyes but smiled, and in that moment, he had believed her smile was the most perfect thing he’d ever seen.
The break-up came unannounced, but not fully unexpected. There were signs here and there. Her love of the endless whirlwind of life, that was a match for his way of following life’s intents for him. When sometimes life went still during winter, he would also follow, but she wouldn’t. She had insatiable love for a life filled with animation, bursts of colours, sounds. It had been easy to be with her then, her curiosity pulling him along, their shared love of stories giving their time together a weight that felt timeless. It was when Drusilla’s condition worsened, that their rhythms became untangled, no longer synching at every heartbeat. And it was fine. Matteo had made his decision then to leave Paris and bring his mother to Avignon where she could receive the care she needed. Those past two weeks that brought the inevitable conclusion of their separation had left him surprisingly content. Happy for the past moments, and hopeful for the unwritten future.
He could see clearly that Juliette needed her freedom back; and she’d agreed. Regular train rides to Avignon, the weekends spent trying to make the sparse walls of his mother’s room feel like home as she started to forget her son’s girlfriend, and sometimes even her own son.
Last they were in this park together was one of their last shared moments of innocent happiness ; It was a beautiful sunny afternoon —or was it only coloured by memories? They had been sitting in the Jardin des Plantes, sharing a crêpe. Juliette had been scrolling through her phone, stopping at an announcement about an interview with Liz Tattler airing that evening. “You should watch it,” she’d said, her tone light but distant. “Her books are about people like us—drifting, figuring it out.”
He had smiled then, nodding, though he wasn’t sure if he’d meant it. A week later, she told him she was moving back to Lille, closer to her family until she figured out her next step. “It’s not you, Matteo,” she’d said, her eyes soft but resolute. “You need to be here, for her. I need… something else.”
Now, sitting in the park a few weeks later, Matteo pulled his phone from his pocket and opened his gallery. He scrolled through the pictures until he found one from their weekend in London—a black-and-white shot of Julia standing in front of a red telephone booth, her smile sharp and her eyes already focused on the next shooting star to catch.
Julia was right, he thought. People like them—they drifted, but they also found their way, sometimes in unexpected ways. He put on his earpods, listening to the beginning of Liz Tattler’s interview.
Her distinct raspy voice brimming with a cackling energy was already engrossing. Synchy as ever, she was saying:
“Every story begins with something lost, but it’s never about the loss. It’s about what you find because of it.”
December 8, 2024 at 9:51 pm #7657In reply to: Quintessence: A Portrait in Reverse
A list of events for reference (WIP)
Date Matteo Lucien Darius Amei Elara Nov 2024 M: Working as a server in Paris; recognizes and cryptically addresses the group at the Sarah Bernhardt Café. L: Sketching in Paris; begins orchestrating the reunion by sending letters to the group. D: is back in Paris for the reunion A: visits Paris for the reunion E: visits Paris for the reunion from Churchill Guest House (Samphire Hoe), visits a guest house in Kent, back in England for a week weeks/months, all expense paid. Mrs Lovejoy the landlady. Spring 2024 M: In Avignon, works at a vineyard. Finds a map. Crosses path with Lucien. Moves to next job in Paris. L: Visits Avignon. Caught in debt to Monsieur Renard; creates labyrinthine sketches blending personal and mythical themes. Crosses path with Matteo. D: by June 2024 sends a postcard to Amei, Is seen in Goa A: Her daughter Tabitha is in Goa teaching E: is retired in Tuscany, living with Florian, a distant relative met through family research.
Summer 2024 (Olympics) has a strange dream at CERN learning about the death of her mother who’d actually died in her youth.
She reminisces about chalkapocalypse.Feb 2024 M:In London, works for a moving company. Crosses path with Amei and Tabitha. L: Is implied he is caught back into the schemes of M. Renard to pay his debts. D: A: Moves from her London home to a smaller apartment in London; reflects on her estranged friends and past. Crosses path with Matteo. E: Dec 2023 M:In Avignon, considers moving to a job in London to support his mother’s care. L: Going with the alias “Julien”, he is recognized in the streets, after 3 years of self-imposed exile, to escape M. Renard & Eloïse. D: Resumes his travels on his own terms A: Buys candles, reflects on leaving. E: Nov 2023 M: His mother requires more care, he goes to Avignon regularly where she is in care. Breaks up with Juliette end of summer. L: D: moves on from Guadeloupe, where he spent time rebuilding homes and reflecting. A: E: early 2023 M: Visits Valencia and Xàtiva, hometown of the Borgias with Juliette; she makes him discover Darius’ videos. L: D: Lives in South of France, returns to Guadeloupe after hurricane Fiona. A: E: Dec 2022 M: New year’s eve, Matteo discovers about Elara’s work on memory applicable to early stage Alzheimer with sensory soundwaves stimuli and ancestral genetic research. L: D: Runs a wellness channel. Goes back to Paris, breaks ties with M. Renard & Eloïse. Receives an invitation to see friends in South of France A: Lives with Paul E: early 2022 M: Lives in Paris with Juliette, travels to many places together, week-ends getaways in London, Amsterdam, Rome… L: D: A: E: Early May, pandemic restrictions were largely over. Florian, her distant relative, moves in to Elara’s Tuscan farmhouse, where she is enjoying retirement. end of 2021 M: L: After the pandemic lockdown thinks of a way to escape. Goes by the alias “Julien” D: Locked down in Budapest; sketches empty streets, sends postcards to Amei to maintain emotional connections. A: E: Dec. 2021, first Christmas in Tuscany
Nov – end of Genealogix royalties from her successful patent, taken over by more efficient AI algorithms. She gives the idea to Darius of looking for 1-euro housing.beginning 2021 M: L: Third & last wave of lockdown measures in France D: A: E: 2020 M: L: D: A: E: beg. 2020 M: L: Pandemic starts – first waves of lockdown D: A: E: Nov 2019 M: Last group meeting before the Nov 2024 reunion L: Last group meeting before the Nov 2024 reunion D: Last group meeting before the Nov 2024 reunion A: Last group meeting before the Nov 2024 reunion E: Last group meeting before the Nov 2024 reunion 2019 M: Plans for his mother / co-housing project L: Spring break in Andalucia with Elara D: Spring break in Andalucia with Elara A: Spring break in Andalucia with Elara E: Spring, before pandemic; visit in Andalucia to her father – joined by Lucien & Amei ; Darius tried to bring those people (M. Renard & Eloïse presumably) to see the hidden pyramid ca. 2014 M: L: D: A: E: chalkapocalypse, before Elara’s retirement. She is employed in Warwick.
Before that, lived from short term teaching contracts mostly, enabling her to travel. She learned Spanish when she moved with her father to Spain 30 years ago, working in an English school for expats, improved her French while working in Paris, moved to Warwick to be near her sister Vanessa thinking she would settle there.2010 M: L: D: A: E: Genealogix became unexpectedly lucrative when it was picked up by a now-dominant genealogy platform around 2010. Every ancestry test sold earned her a modest but steady royalty, which for a time, gave her the freedom to pursue less practical research. 2007 M: L: Meets Elara & Amei, Darius a concert of Eliane Radigue at Aarau, Switzerland D: Meets Lucien, Elara & Amei a concert of Eliane Radigue at Aarau, Switzerland A:Accepts Elara’s invitation to go to a concert of Eliane Radigue at Aarau, Switzerland, meets Lucien & Darius there. The group is formed E:Goes to a concert of Eliane Radigue at Aarau, Switzerland with Amei, meets Lucien & Darius there. The group is formed before 2007 M: L: D: A:Meets Elara at a gallery in London, Southbank E: Meets Amei at a gallery, London Southbank December 4, 2024 at 6:22 am #7638In reply to: Quintessence: Reversing the Fifth
The Bell’s Moment: Paris, Summer 2024 – Olympic Games
The bell was dangling unassumingly from the side pocket of a sports bag, its small brass frame swinging lightly with the jostle of the crowd. The bag belonged to an American tourist, a middle-aged man in a rumpled USA Basketball T-shirt, hustling through the Olympic complex with his family in tow. They were here to cheer for his niece, a rising star on the team, and the bell—a strange little heirloom from his grandmother—had been an afterthought, clipped to the bag for luck. It seemed to fit right in with the bright chaos of the Games, blending into the swirl of flags, chants, and the hum of summer excitement.
1st Ring of the Bell: Matteo
The vineyard was quiet except for the hum of cicadas and the soft rustle of leaves. Matteo leaned against the tractor, wiping sweat from his brow with the back of his hand.
“You’ve done good work,” the supervisor said, clapping Matteo on the shoulder. “We’ll be finishing this batch by Friday.”
Matteo nodded. “And after that?”
The older man shrugged. “Some go north, some go south. You? You’ve got that look—like you already know where you’re headed.”
Matteo offered a half-smile, but he couldn’t deny it. He’d felt the tug for days, like a thread pulling him toward something undefined. The idea of returning to Paris had slipped into his thoughts quietly, as if it had been waiting for the right moment.
When his phone buzzed later that evening with a job offer to do renovation work in Paris, it wasn’t a surprise. He poured himself a small glass of wine, toasting the stars overhead.
Somewhere, miles away, the bell rang its first note.
2nd Ring of the Bell: Darius
In a shaded square in Barcelona, the air was thick with the scent of jasmine and the echo of a street performer’s flamenco guitar. Darius sprawled on a wrought-iron bench, his leather-bound journal open on his lap. He sketched absentmindedly, the lines of a temple taking shape on the page.
A man wearing a scarf of brilliant orange sat down beside him, his energy magnetic. “You’re an artist,” the man said without preamble, his voice carrying the cadence of Kolkata.
“Sometimes,” Darius replied, his pen still moving.
“Then you should come to India,” the man said, grinning. “There’s art everywhere. In the streets, in the temples, even in the food.”
Darius chuckled. “You recruiting me?”
“India doesn’t need recruiters,” the man replied. “It calls people when it’s time.”
The bell rang again in Paris, its chime faint and melodic, as Darius scribbled the words “India, autumn” in the corner of his page.
3rd Ring of the Bell: Elara
The crowd at CERN’s conference hall buzzed as physicists exchanged ideas, voices overlapping like equations scribbled on whiteboards. Elara sat at a corner table, sipping lukewarm coffee and scrolling through her messages.
The voicemail notification glared at her, and she tapped it reluctantly.
“Elara, it’s Florian. I… I’m sorry to tell you this over a message, but your mother passed away last night.”
Her coffee cup trembled slightly as she set it down.
Her relationship with her mother had been fraught, full of alternating period of silences and angry reunions, and had settled lately into careful politeness that masked deeper fractures. Years of therapy had softened the edges of her resentment but hadn’t erased it. She had come to accept that they would never truly understand each other, but the finality of death still struck her with a peculiar weight.
Her mother had been living alone in Montrouge, France, refusing to leave the little house Elara had begged her to sell for years. They had drifted apart, their conversations perfunctory and strained, like the ritual of winding a clock that no longer worked.
She would have to travel to Montrouge for the funeral arrangements.
In that moment, the bell in Les Reliques rang a third time.
4th Ring of the Bell: Lucien
The train to Lausanne glided through fields of dried up sunflowers, too early for the season, but the heat had been relentless. He could imagine the golden blooms swaying with a cracking sound in the summer breeze. Lucien stared out the window, the strap of his duffel bag wrapped tightly around his wrist.
Paris had been suffocating. The tourists swarmed the city like ants, turning every café into a photo opportunity and every quiet street into a backdrop. He hadn’t needed much convincing to take his friend up on the offer of a temporary studio in Lausanne.
He reached into his bag and pulled out a sketchbook. The pages were filled with half-finished drawings, but one in particular caught his eye: a simple doorway with an ornate bell hanging above it.
He didn’t remember drawing it, but the image felt familiar, like a memory from a dream.
The bell rang again in Paris, its resonance threading through the quiet hum of the train.
5th Ring of the Bell: …. Tabitha
In the courtyard of her university residence, Tabitha swung lazily in a hammock, her phone propped precariously on her chest.
“Goa, huh?” one of her friends asked, leaning against the tree holding up the hammock. “Think your mum will freak out?”
“She’ll probably worry herself into knots,” Tabitha replied, laughing. “But she won’t say no. She’s good at the whole supportive parent thing. Or at least pretending to be.”
Her friend raised an eyebrow. “Pretending?”
“Don’t get me wrong, I love her,” Tabitha said. “But she’s got her own stuff. You know, things she never really talks about. I think it’s why she works so much. Keeps her distracted.”
The bell rang faintly in Paris, though neither of them could hear it.
“Maybe you should tell her to come with you,” the friend suggested.
Tabitha grinned. “Now that would be a trip.”
Last Ring: The Pawn
It was now sitting on the counter at Les Reliques. Its brass surface gleamed faintly in the dim shop light, polished by the waves of time. Small and unassuming, its ring held something inexplicably magnetic.
Time seemed to settle heavily around it. In the heat of the Olympic summer, it rang six times. Each chime marked a moment that mattered, though none of the characters whose lives it touched understood why. Not yet.
“Where’d you get this?” the shopkeeper asked as the American tourist placed it down.
“It was my grandma’s,” he said, shrugging. “She said it was lucky. I just think it’s old.”
The shopkeeper ran her fingers over the brass surface, her expression unreadable. “And you’re selling it?”
“Need cash to get tickets for the USA basketball game tomorrow,” the man replied. “Quarterfinals. You follow basketball?”
“Not anymore,” the shopkeeper murmured, handing him a stack of bills.
The bell rang softly as she placed it on the velvet cloth, its sound settling into the space like a secret waiting to be uncovered.
And so it sat, quiet but full of presence, waiting for someone to claim it maybe months later, drawn by invisible threads woven through the magnetic field of lives, indifferent to the heat and chaos of the Parisian streets.
December 3, 2024 at 7:51 am #7636In reply to: Quintessence: Reversing the Fifth
It was cold in Kent, much colder than Elara was used to at home in the Tuscan olive groves, but Mrs Lovejoy kept the guest house warm enough. On site at Samphire Hoe was another matter, the wind off the sea biting into her despite the many layers of clothing. It had been Florian’s idea to take the Mongolian hat with her. Laughing, she’d replied that it might come in handy if there was a costume party. Trust me, you’re going to need it, he’d said, and he was right. It had been a present from Amei, many years ago, but Elara had barely worn it. It wasn’t often that she found herself in a place cold enough to warrant it.
In a fortuitous twist of fate, Florian had asked if he could come and stay with her for awhile to find his feet after the tumultuous end of a disastrous relationship. It came at a time when Elara was starting to realise that there was too much work for her alone keeping the old farmhouse in order. Everyone wants to retire to the country but nobody thinks of all the work involved, at an age when one prefers to potter about, read books, and take naps.
Florian was a long lost (or more correctly never known) distant relative, a seventh cousin four times removed on her paternal side. They had come into contact while researching the family, comparing notes and photographs and family anecdotes. They became friends, finding they had much in common, and Elara was pleased to have him come to stay with her. Likewise, Florian was more than willing to help around the beautiful old place, and found it conducive to his writing. He spent the mornings gardening, decorating or running errands, and the afternoons tapping away at the novel he’d been inspired to start, sitting at the old desk in front of the French windows.
If it hadn’t been for Florian, Elara wouldn’t have accepted the invitation to join the chalk project. He had settled in so well, already had a working grasp of Italian, and got on well with her neighbours. She could leave him to look after everything and not worry about a thing.
Pulling the hat down over her ears, Elara ventured out into the early November chill. Mrs Lovejoy was coming up the path to the guesthouse, having been out to the corner shop. “I say, that’s a fine hat you have there, that’ll keep your cockles warm!” Mrs Lovejoy was bareheaded, wearing only a cardigan.
“It was a gift,” Elara told her, “I haven’t worn it much. A friend bought it for me years ago when we were in Mongolia.”
“Very nice, I’m sure,” replied the landlady, trying to remember where Mongolia was.
“Yes, she was nice,” Elara said wistfully. “We lost contact somehow.”
“Ah yes, well these things happen,” Mrs Lovejoy said. “People come into your life and then they go. Like my Bert…”
“Must go or I’ll be late!” Elara had already heard all about Bert a number of times.
August 28, 2024 at 6:26 am #7548In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
Elton Marshall’s
Early Quaker Emigrants to USA.
The earliest Marshall in my tree is Charles Marshall (my 5x great grandfather), Overseer of the Poor and Churchwarden of Elton. His 1819 gravestone in Elton says he was 77 years old when he died, indicating a birth in 1742, however no baptism can be found.
According to the Derbyshire records office, Elton was a chapelry of Youlgreave until 1866. The Youlgreave registers date back to the mid 1500s, and there are many Marshalls in the registers from 1559 onwards. The Elton registers however are incomplete due to fire damage.
While doing a google books search for Marshall’s of Elton, I found many American family history books mentioning Abraham Marshall of Gratton born in 1667, who became a Quaker aged 16, and emigrated to Pennsylvania USA in 1700. Some of these books say that Abraham’s parents were Humphrey Marshall and his wife Hannah Turner. (Gratton is a tiny village next to Elton, also in Youlgreave parish.)
Abraham’s son born in USA was also named Humphrey. He was a well known botanist.
Abraham’s cousin John Marshall, also a Quaker, emigrated from Elton to USA in 1687, according to these books.
(There are a number of books on Colonial Families in Pennsylvania that repeat each other so impossible to cite the original source)

In the Youlgreave parish registers I found a baptism in 1667 for Humphrey Marshall son of Humphrey and Hannah. I didn’t find a baptism for Abraham, but it looks as though it could be correct. Abraham had a son he named Humphrey. But did it just look logical to whoever wrote the books, or do they know for sure? Did the famous botanist Humphrey Marshall have his own family records? The books don’t say where they got this information.
An earlier Humphrey Marshall was baptised in Youlgreave in 1559, his father Edmund. And in 1591 another Humphrey Marshall was baptised, his father George.
But can we connect these Marshall’s to ours? We do have an Abraham Marshall, grandson of Charles, born in 1792. The name isn’t all that common, so may indicate a family connection. The villages of Elton, Gratton and Youlgreave are all very small and it would seem very likely that the Marshall’s who went the USA are related to ours, if not brothers, then probably cousins.
Derbyshire Quakers
In “Derbyshire Quakers 1650-1761” by Helen Forde:
“… Friends lived predominantly in the northern half of the country during this first century of existence. Numbers may have been reduced by emigration to America and migration to other parts of the country but were never high and declined in the early eighteenth century. Predominantly a middle to lower class group economically, Derbyshire Friends numbered very few wealthy members. Many were yeoman farmers or wholesalers and it was these groups who dominated the business meetings having time to devote themselves to the Society. Only John Gratton of Monyash combined an outstanding ministry together with an organising ability which brought him recognition amongst London Friends as well as locally. Derbyshire Friends enjoyed comparatively harmonious relations with civil and Anglican authorities, though prior to the Toleration Act of 1639 the priests were their worst persecutors…..”
Also mentioned in this book: There were monthly meetings in Elton, as well as a number of other nearby places.
John Marshall of Elton 1682/3 appears in a list of Quaker emigrants from Derbyshire.
The following image is a page from the 1753 book on the sufferings of Quakers by Joseph Besse as an example of some of the persecutions of Quakers in Derbyshire in the 1600s:
A collection of the sufferings of the people called Quakers, for the testimony of a good conscience from the time of their being first distinguished by that name in the year 1650 to the time of the act commonly called the Act of toleration granted to Protestant dissenters in the first year of the reign of King William the Third and Queen Mary in the year 1689 (Volume 1)
Besse, Joseph. 1753Note the names Margaret Marshall and Anne Staley. This book would appear to contradict Helen Forde’s statement above about the harmonious relations with Anglican authority.

The Botanist
Humphry Marshall 1722-1801 was born in Marshallton, Pennsylvania, the son of the immigrant from Elton, Abraham Marshall. He was the cousin of botanists John Bartram and William Bartram. Like many early American botanists, he was a Quaker. He wrote his first book, A Few Observations Concerning Christ, in 1755.

In 1785, Marshall published Arbustrum Americanum: The American Grove, an Alphabetical Catalogue of Forest Trees and Shrubs, Natives of the American United States (Philadelphia).
Marshall has been called the “Father of American Dendrology”.
A genus of plants, Marshallia, was named in honor of Humphry Marshall and his nephew Moses Marshall, also a botanist.
In 1848 the Borough of West Chester established the Marshall Square Park in his honor. Marshall Square Park is four miles east of Marshallton.
via Wikipedia.
From The History of Chester County Pennsylvania, 1881, by J Smith Futhey and Gilbert Cope:

From The Chester Country History Center:
“Immediately on the Receipt of your Letter, I ordered a Reflecting Telescope for you which was made accordingly. Dr. Fothergill had since desired me to add a Microscope and Thermometer, and will
pay for the whole.’– Benjamin Franklin to Humphry, March 18, 1770
“In his lifetime, Humphry Marshall made his living as a stonemason, farmer, and miller, but eventually became known for his contributions to astronomy, meteorology, agriculture, and the natural sciences.
In 1773, Marshall built a stone house with a hothouse, a botanical laboratory, and an observatory for astronomical studies. He established an arboretum of native trees on the property and the second botanical garden in the nation (John Bartram, his cousin, had the first). From his home base, Humphry expanded his botanical plant exchange business and increased his overseas contacts. With the help of men like Benjamin Franklin and the English botanist Dr. John Fothergill, they eventually included German, Dutch, Swedish, and Irish plant collectors and scientists. Franklin, then living in London, introduced Marshall’s writings to the Royal Society in London and both men encouraged Marshall’s astronomical and botanical studies by supplying him with books and instruments including the latest telescope and microscope.
Marshall’s scientific work earned him honorary memberships to the American Philosophical Society and the Philadelphia Society for Promoting Agriculture, where he shared his ground-breaking ideas on scientific farming methods. In the years before the American Revolution, Marshall’s correspondence was based on his extensive plant and seed exchanges, which led to further studies and publications. In 1785, he authored his magnum opus, Arbustum Americanum: The American Grove. It is a catalog of American trees and shrubs that followed the Linnaean system of plant classification and was the first publication of its kind.”
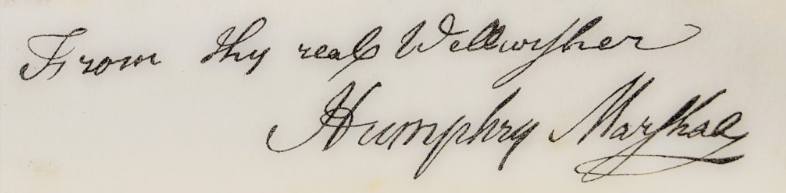 August 21, 2024 at 12:27 pm #7546
August 21, 2024 at 12:27 pm #7546In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
The Potters of Darley Bridge
Rebecca Knowles 1745-1823, my 5x great grandmother, married Charles Marshall 1742-1819, the churchwarden of Elton, in Darley, Derbyshire, in 1767. Rebecca was born in Darley in 1745, the youngest child of Roger Knowles 1695-1784, and Martha Potter 1702?-1772.
Although Roger and Martha were both from Darley, they were married in South Wingfield by licence in 1724. Roger’s occupation on the marriage licence was lead miner. (Lead miners in Derbyshire at that time usually mined their own land.) Jacob Potter signed the licence so I assumed that Jacob Potter was her father.

I then found the will of Jacobi Potter who died in 1719. However, he signed the will James Potter. Jacobi is latin for James. James Potter mentioned his daughter Martha in his will “when she comes of age”. Martha was the youngest child of James. James also mentioned in his will son James AND son Jacob, so there were both James’s and Jacob’s in the family, although at times in the documents James is written as Jacobi!

Jacob Potter who signed Martha’s marriage licence was her brother Jacob.
Martha’s brother James mentioned his sister Martha Knowles in his 1739 will, as well as his brother Jacob and his brother Joseph.

Martha’s father James Potter mentions his wife Ann in his 1719 will. James Potter married Ann Waterhurst in 1690 in Wirksworth, some seven miles from Darley. James occupation was innkeeper at Darley Bridge.
I did a search for Waterhurst (there was only a transcription available for that marriage, not a microfilm) and found no Waterhursts anywhere, but I did find many Warhursts in Derbyshire. In the older records, Warhust is also spelled Wearhurst and in a number of other ways. A Martha Warhurst died in Peak Forest, Derbyshire, in 1681. Her husbands name was missing from the deteriorated register pages. This may or may not be Martha Potter’s grandmother: the records for the 1600s are scanty if they exist at all, and often there are bits missing and illegible entries.
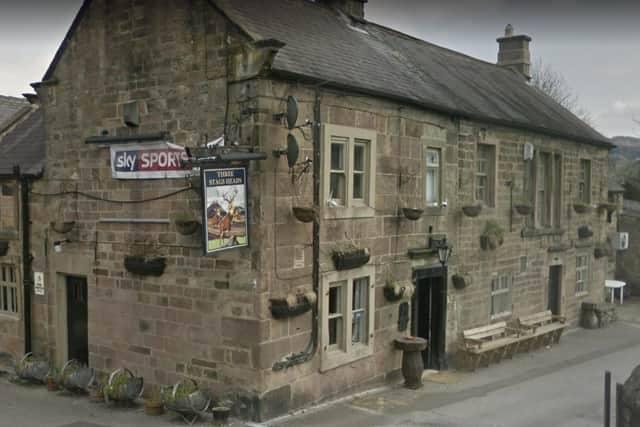
The only inn at Darley Bridge was The Three Stags Heads, by the bridge. It is now a listed building, and was on a medieval packhorse route. The current building was built in 1736, however there is a late 17th century section at rear of the cross wing. The Three Stags Heads was up for sale for £430,000 in 2022, the closure a result of the covid pandemic.

Another listed building in Darley Bridge is Potters Cottage, with a plaque above the door that says “Jonathan and Alice Potter 1763”. Jonathan Potter 1725-1785 was James grandson, the son of his son Charles Potter 1691-1752. His son Charles was also an innkeeper at Darley Bridge: James left the majority of his property to his son Charles.

Charles is the only child of James Potter that we know the approximate date of birth, because his age was on his grave stone. I haven’t found any of their baptisms, but did note that many Potters were baptised in non conformist registers in Chesterfield.
Potters Cottage
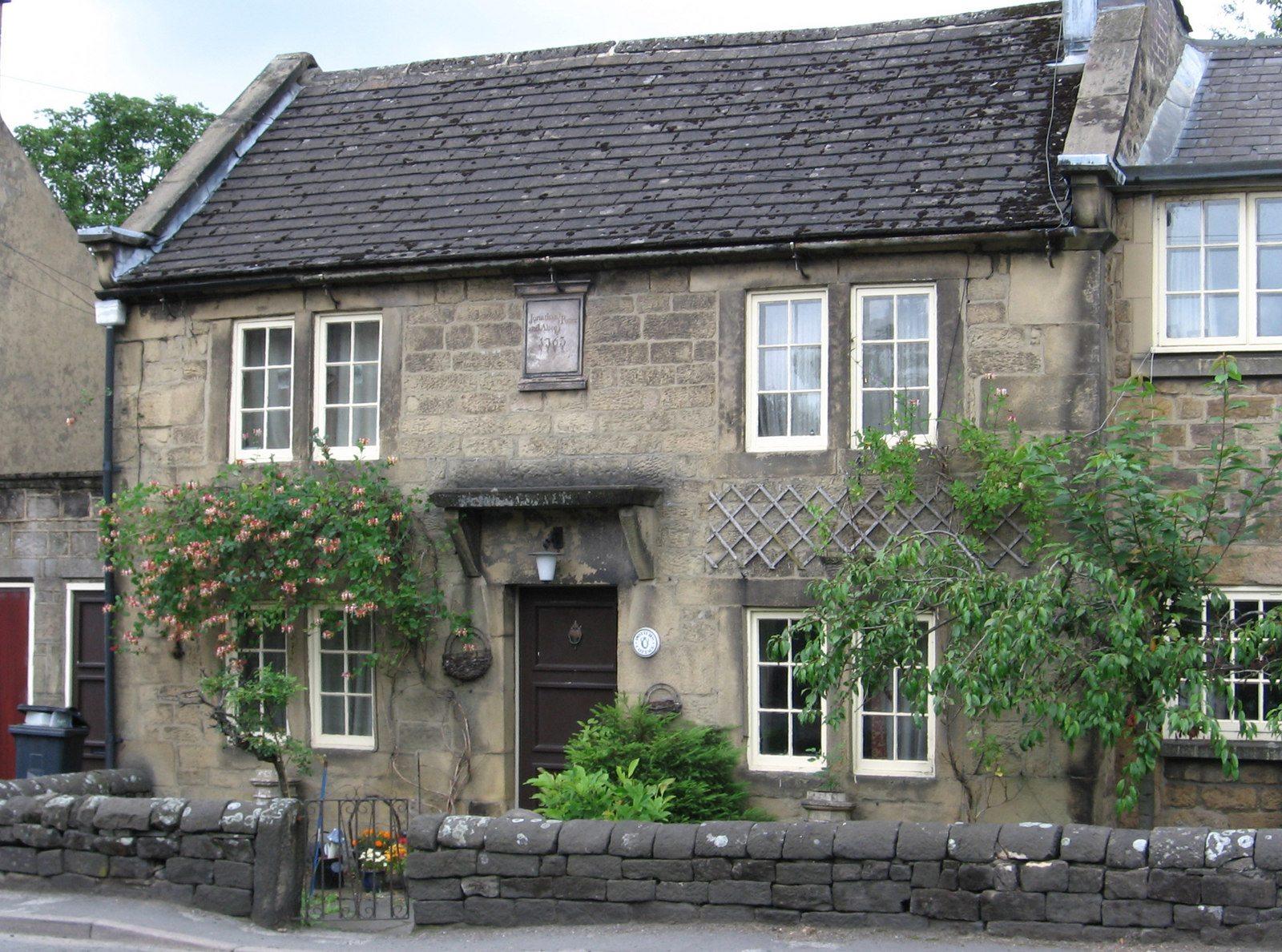

Jonathan Potter of Potters Cottage married Alice Beeley in 1748.
“Darley Bridge was an important packhorse route across the River Derwent. There was a packhorse route from here up to Beeley Moor via Darley Dale. A reference to this bridge appears in 1504… Not far to the north of the bridge at Darley Dale is Church Lane; in 1635 it was known as Ghost Lane after a Scottish pedlar was murdered there. Pedlars tended to be called Scottish only because they sold cheap Scottish linen.”
via Derbyshire Heritage website.
According to Wikipedia, the bridge dates back to the 15th century.
August 16, 2024 at 2:56 pm #7544In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
Youlgreave
The Frost Family and The Big Snow
The Youlgreave parish registers are said to be the most complete and interesting in the country. Starting in 1558, they are still largely intact today.
“The future historian of this parish will find a vast stock of material ready to hand, and if such a work was ever accomplished it would once more be seen how the history of even a remote village is but the history of the nation in little; how national victories were announced on the church bells, and national disasters by the proclamation of a form of prayer…”
J. Charles Cox, Notes on the Churches of Derbyshire, 1877.

Although the Youlgreave parish registers are available online on microfilm, just the baptisms, marriages and burials are provided on the genealogy websites. However, I found some excerpts from the churchwardens accounts in a couple of old books, The Reliquary 1864, and Notes on Derbyshire Churches 1877.

Hannah Keeling, my 4x great grandmother, was born in Youlgreave, Derbyshire, in 1767. In 1791 she married Edward Lees of Hartington, Derbyshire, a village seven and a half miles south west of Youlgreave. Edward and Hannah’s daughter Sarah Lees, born in Hartington in 1808, married Francis Featherstone in 1835. The Featherstone’s were farmers. Their daughter Emma Featherstone married John Marshall from Elton. Elton is just three miles from Youlgreave, and there are a great many Marshall’s in the Youlgreave parish registers, some no doubt distantly related to ours.
Hannah Keeling’s parents were John Keeling 1734-1823, and Ellen Frost 1739-1805, both of Youlgreave.
On the burial entry in the parish registers in Youlgreave in 1823, John Keeling was 88 years old when he died, and was the “late parish clerk”, indicating that my 5x great grandfather played a part in compiling the “best parish registers in the country”. In 1762 John’s father in law John Frost died intestate, and John Keeling, cordwainer, co signed the documents with his mother in law Ann. John Keeling was a shoe maker and a parish clerk.
John Keeling’s father was Thomas Keeling, baptised on the 9th of March 1709 in Youlgreave and his parents were John Keeling and Ann Ashmore. John and Ann were married on the 6th April 1708. Some of the transcriptions have Thomas baptised in March 1708, which would be a month before his parents married. However, this was before the Julian calendar was replaced by the Gregorian calendar, and prior to 1752 the new year started on the 25th of March, therefore the 9th of March 1708 was eleven months after the 6th April 1708.
Thomas Keeling married Dorothy, which we know from the baptism of John Keeling in 1734, but I have not been able to find their marriage recorded. Until I can find my 6x great grandmother Dorothy’s maiden name, I am unable to trace her family further back.
Unfortunately I haven’t found a baptism for Thomas’s father John Keeling, despite that there are Keelings in the Youlgrave registers in the early 1600s, possibly it is one of the few illegible entries in these registers.
The Frosts of Youlgreave
Ellen Frost’s father was John Frost, born in Youlgreave in 1707. John married Ann Staley of Elton in 1733 in Youlgreave.
(Note that this part of the family tree is the Marshall side, but we also have Staley’s in Elton on the Warren side. Our branch of the Elton Staley’s moved to Stapenhill in the mid 1700s. Robert Staley, born 1711 in Elton, died in Stapenhill in 1795. There are many Staley’s in the Youlgreave parish registers, going back to the late 1500s.)
John Frost (my 6x great grandfather), miner, died intestate in 1762 in Youlgreave. Miner in this case no doubt means a lead miner, mining his own land (as John Marshall’s father John was in Elton. On the 1851 census John Marshall senior was mining 9 acres). Ann Frost, as the widow and relict of the said deceased John Frost, claimed the right of administration of his estate. Ann Frost (nee Staley) signed her own name, somewhat unusual for a woman to be able to write in 1762, as well as her son in law John Keeling.

John’s parents were David Frost and Ann. David was baptised in 1665 in Youlgreave. Once again, I have not found a marriage for David and Ann so I am unable to continue further back with her family. Marriages were often held in the parish of the bride, and perhaps those neighbouring parish records from the 1600s haven’t survived.
David’s parents were William Frost and Ellen (or Ellin, or Helen, depending on how the parish clerk chose to spell it). Once again, their marriage hasn’t been found, but was probably in a neighbouring parish.
William Frost’s wife Ellen, my 8x great grandmother, died in Youlgreave in 1713. In her will she left her daughter Catherine £20. Catherine was born in 1665 and was apparently unmarried at the age of 48 in 1713. She named her son Isaac Frost (born in 1662) executor, and left him the remainder of her “goods, chattels and cattle”.

William Frost was baptised in Youlgreave in 1627, his parents were William Frost and Anne.
William Frost senior, husbandman, was probably born circa 1600, and died intestate in 1648 in Middleton, Youlgreave. His widow Anna was named in the document. On the compilation of the inventory of his goods, Thomas Garratt, Will Melland and A Kidiard are named.(Husbandman: The old word for a farmer below the rank of yeoman. A husbandman usually held his land by copyhold or leasehold tenure and may be regarded as the ‘average farmer in his locality’. The words ‘yeoman’ and ‘husbandman’ were gradually replaced in the later 18th and 19th centuries by ‘farmer’.)
Unable to find a baptism for William Frost born circa 1600, I read through all the pages of the Youlgreave parish registers from 1558 to 1610. Despite the good condition of these registers, there are a number of illegible entries. There were three Frost families baptising children during this timeframe and one of these is likely to be Willliam’s.
Baptisms:
1581 Eliz Frost, father Michael.
1582 Francis f Michael. (must have died in infancy)
1582 Margaret f William.
1585 Francis f Michael.
1586 John f Nicholas.
1588 Barbara f Michael.
1590 Francis f Nicholas.
1591 Joane f Michael.
1594 John f Michael.
1598 George f Michael.
1600 Fredericke (female!) f William.Marriages in Youlgreave which could be William’s parents:
1579 Michael Frost Eliz Staley
1587 Edward Frost Katherine Hall
1600 Nicholas Frost Katherine Hardy.
1606 John Frost Eliz Hanson.Michael Frost of Youlgreave is mentioned on the Derbyshire Muster Rolls in 1585.
(Muster records: 1522-1649. The militia muster rolls listed all those liable for military service.)
Frideswide:
A burial is recorded in 1584 for Frideswide Frost (female) father Michael. As the father is named, this indicates that Frideswide was a child.
(Frithuswith, commonly Frideswide c. 650 – 19 October 727), was an English princess and abbess. She is credited as the foundress of a monastery later incorporated into Christ Church, Oxford. She was the daughter of a sub-king of a Merica named Dida of Eynsham whose lands occupied western Oxfordshire and the upper reaches of the River Thames.)
An unusual name, and certainly very different from the usual names of the Frost siblings. As I did not find a baptism for her, I wondered if perhaps she died too soon for a baptism and was given a saints name, in the hope that it would help in the afterlife, given the beliefs of the times. Or perhaps it wasn’t an unusual name at the time in Youlgreave. A Fridesweda Gilbert was buried in Youlgreave in 1604, the spinster daughter of Francis Gilbert. There is a small brass effigy in the church, underneath is written “Frideswide Gilbert to the grave, Hath resigned her earthly part…”

J. Charles Cox, Notes on the Churches of Derbyshire, 1877.
King James
A parish register entry in 1603:
“1603 King James of Skottland was proclaimed kinge of England, France and Ireland at Bakewell upon Monday being the 29th of March 1603.” (March 1603 would be 1604, because of the Julian calendar in use at the time.)
The Big Snow
“This year 1614/5 January 16th began the greatest snow whichever fell uppon the earth within man’s memorye. It covered the earth fyve quarters deep uppon the playne. And for heaps or drifts of snow, they were very deep; so that passengers both horse or foot passed over yates, hedges and walles. ….The spring was so cold and so late that much cattel was in very great danger and some died….”

From the Youlgreave parish registers.
Our ancestor William Frost born circa 1600 would have been a teenager during the big snow.
July 18, 2024 at 9:16 am #7534In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
Ms Nicraith Noble, the Mayor of Limerick taking a bath in the Shannon River with reporters had made the rounds of news in ways that were quite incomprehensible.
Obviously it was part of a media ploy to boost public attention for the incoming Roman Games.
“Did she require some anti-rash-and-boil spells?” Jeezel messaged on the network, worried about what such swimming stunt would do to her ravishing hair.
“Probably…” Eris responded in a terse manner “Don’t forget Austreberthe managed to get us to sponsor the event. She may have eased the deal with some goodies. Like anti-age spell too.”
Eris was glad Austreberthe had refocused the efforts towards the imminent launch of the Roman Games. Those mass events were key moments in the Coven’s seasonal activities, as they provided a bounty of emotions to refine and process for creation of their most epic incenses. The recent mass events had been too heavy on fear, anger and gloom-mongering, not the grade A quality they required.
Austreberthe had called all hands on deck to be ready for the event, having deemed the reconnaissance work in Spain’s cloisters sufficiently well under way to take a break from it. In truth, Eris suspected she’d started to receive the first invoices from the undertakers’ Guild and had realised it was a hefty cost for their consulting services.
On top of that, there was a recent case of the drunken sheep flu in Andalucia, some local variety of virus that got the cloister sisters fear for their elderly’s Mother Loreena’s health. Considering the gleeful vulture’s smiles of the Morticians in waiting, they had decided in agreement for an early dismiss into the Summer holidays retreats.
“More prayers, phew, glad they didn’t need us for that.” true to her swagger way, Truella had conceded and accepted to put a hold to her passionate researches —she’d managed to get their personal phone numbers too anyway.
“One week to the start of the Games then.” Eris sighed. The last stretch to summer holidays seemed to take forever.
June 14, 2024 at 11:41 pm #7474In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
A little unwilling to proceed, and privately wishing she was back on the comfy sofa with the fat cushions, Frella took a moment to center herself. She reminded herself that being a witch was a high calling and often what we need will find us. It sounded like a lot of Malove’s baloney to be honest but she took a deep breath and muttered a few words of wisdom from Lemone, which often worked better than any spell:
“The key to unlocking mysteries is often found within, where the mind meets the heart.”
“You wait here, Herma,” said Frella holding a warning hand in the air. “I don’t know what magic this is yet but I sense something amiss from that shed.”
Frella approached the ominous shed with caution but renewed determination. The shed door creaked open without resistance and she saw the chest immediately though it was piled on top with boxes. After carefully removing the boxes and putting them to one side, she examined the chest looking for any inscriptions or hidden compartments that might give a clue to its origins. She sensed the camphor chest was from a very old witch family and therefore may contain protective spells and traps. Best to proceed with caution.
She went to the shed door and waved at Herma, shouting for her to go and get some salt. While she waited for Herma’s return, she examined the chest further. It had a lock, but no obvious key; clearly a bit of witchy ingenuity was going to be required. A simple unlocking spell might suffice, or if spells fail, perhaps Herma knows an old trick or two for picking locks!
Herma returned with the salt and Frella sprinkled it liberally on the chest, chanting a protective charm to ward off any nefarious spells. “There,“ she said with satisfaction. “Fingers crossed that ought to do it.”
The chest seemed strangely willing to reveal its secrets for the simplest of opening spells worked. Once it was opened, they sifted carefully through its contents, mostly old documents and letters, looking for anything which might hold the answer to the postcard.
“Look for anything bird-related—feathers, sketches … “ instructed Frella.
“By golly!” cried Herma triumphantly holding up a postcard. “It’s the same one!”.
June 12, 2024 at 8:45 pm #7470In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
After all the months of secret work for Malové, where Eris was being tasked to scout for profitable new ventures for the Quadrivium’s Emporium that would keep with traditions, and endless due diligence under the seal of secrecy, she’d learnt that the deal had been finally sealed by Austreberthe.
The announcement had just went out, not really making quite the splash Eris would have expected.
Press Release
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Quadrivium Emporium Announces Strategic Acquisition of Spanish based company Quintessivium Cloister Crafts
Limerick, 12th June 2024– Quadrivium Emporium, renowned for its exceptional range of artisanal incense blends and commitment to quality, is pleased to announce the successful acquisition of Quintessivium Cloister Crafts. This strategic move marks a significant milestone in Quadrivium Emporium’s ongoing expansion and diversification efforts.About Quintessivium Cloister Crafts
Quintessivium Cloister Crafts has been a trusted name in the production of high-quality nun’s couture. Known for their craftsmanship and dedication to preserving traditional techniques, started as a small business focussed on quills and writing accessories as well as cardigans, Quintessivium Cloister Crafts has maintained a reputation for excellence and innovation in the market.
Strategic Vision and Synergies
The integration of Quintessivium Cloister Crafts into the Quadrivium family aligns with our vision to expand our product portfolio while maintaining the high standards of quality and craftsmanship our customers have come to expect. This acquisition will allow Quadrivium Emporium to diversify its offerings and tap into new markets and customer segments.
“We are thrilled to welcome Quintessivium Cloister Crafts to the Quadrivium Emporium family,” said Austreberthe Baltherbridge, interim CEO of Quadrivium Emporium. “Their commitment to quality and tradition mirrors our own values, and we are excited about the opportunities this acquisition presents. Together, we will continue to innovate and deliver exceptional products to our customers.”
Future Endeavours
Quadrivium Emporium plans to leverage the expertise and resources of Quintessivium Cloister Crafts to develop new and unique product lines. Customers can look forward to an expanded range of high-quality writing instruments, apparel and accessories, crafted with the same attention to detail and dedication that both brands are known for.
For more information, please contact: media@quadrivium.emporium
The internal memo that they’d received on the internal email list bore some of the distinct style of Malové, even if sent from Austreberthe’s email and adjusted with the painstaking attention to minute details she was known for.
Internal Memo
To: Quadrivium Leadership Team
Subject: Synergies and Strategic Integration with Quintessivium Cloister Crafts (previously codenamed as ‘Cardivium Nun’s Quills & Cardigans’)Team,
With the acquisition of Quintessivium Cloister Crafts finalised, we are poised to explore the deeper synergies between our coven and the nun witches’ coven operating behind their front. Here are some key areas where we can harness our collective strengths:
1. Resource Sharing:
– Their expertise in crafting high-quality quills can complement our focus on artisanal incense blends. By sharing resources and best practices, both covens can enhance their craftsmanship and innovation.2. Collaborative Spellcraft:
– The nun witches bring a unique perspective and set of rituals that can enrich our own magical practices. Joint spellcasting sessions and workshops can lead to the development of powerful new enchantments and products.3. Knowledge Exchange:
– The historical and esoteric knowledge held by the nuns is a treasure trove we can tap into. Regular exchanges of scrolls, texts, and insights can deepen our understanding of ancient magic and its applications in modern contexts.4. Market Expansion:
– By combining our product lines, we can create bundled offerings that appeal to a broader audience. Imagine a premium writing set that includes a handcrafted quill, a magical ink blend, and a specially composed incense for enhancing focus and creativity. Or outdoor outfits with puffer jackets, or specially knit cardigans with embedded magical properties.5. Strengthening Alliances:
– This acquisition sets a precedent for future alliances with other covens and magical entities. It demonstrates our commitment to growth and collaboration, reinforcing our position as a leading force in the magical community.Remember, the true value of this acquisition lies not just in the products we can create together, but in the unity and strength we gain as a collective. Let’s approach this integration with the spirit of collaboration and mutual respect.
Yours in strength and magic,
Austreberthe, on behalf of MalovéApril 6, 2024 at 11:14 pm #7419In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
Sleeping like a log through a full night’s rest on the lavender spell wrapped in the rag of the punic tunic worked like a charm. By morning light, Eris had reverted to her normal self again.
How her coven had succeeded in finding the rag was anyone’s guess, but one thing was for certain—Truella’s resourcefulness knew no bounds once she set her mind to a goal. All it took was a location spell, a silencing charm around the area in Libyssa where she wanted to dig, and of course, a trusty trowel. Hundreds of buckets of dirt later, a few sheep’s jawbones and voilà, the rag. Made of asbestos, impervious to fire, and slower to decay than a sloth on a Monday morning, it was nothing short of a miracle it had survived so long underground, and that they found it in such a short time.
Eris rubbed her neck still pained from the weight of bearing that enormous elephantine head.
When pressed by the others—Frigella, Jeezel, and the ever-curious Truella—she could hardly recall what led her to attempt the risky memory spell.
Echo buzzed in with an electric hum, the sprite all too eager to clear the air.
“The memory spell,” Echo interjected, “a dubious cocktail of spirits of remembrance and forgetfulness, was cast not out of folly but necessity. Eris, rooted in her family’s arborestry quests, understood the weight of knowledge passed down through generations. Each leaf and branch in the family tree held stories, secrets, and sacrifices that were both a treasure and a burden.”
Echo smirked as he continued, pointing out the responsibility of the other entity’s guidance. “Elias’s advice had egged her on, resonating with Eris’ desires, and finally enticing her not lament the multitude of options but rather delights in the exploration without the burden of obligation —end of quotation.”
“And was it worth it?” Truella asked impatiently, her curiosity piqued a little nonetheless. She’d always wished she had more memory, but not at the cost of an elephant head.
“Imagine the vast expanse of memories like a grand library, each book brimming with the essence of a lineage. ” Eris said. “To wander these halls without purpose could lead to an overwhelming deluge of ancestral whispers.” She paused. “So, not sure it was entirely worth it. I feel more confused than ever.”
Echo chimed in again “The memory spell was conjured to be a compass, a guide through the storied corridors of her heritage. But, as with all magic, the intentions must be precise, the heart true, and the mind clear. A miscalculation, a stray thought, a moment’s doubt — and the spell turned upon itself, leaving Eris with the visage of an elephant, noble and wise. The elephant head, while unintended, may have been a subconscious manifestation of her quest for familial knowledge. Perhaps the memory spell, in its misfiring, sought to grant Eris the attributes necessary to continue her arborestry quests with the fortitude and insight of the elephant.”
“But why Madrid of all places?” Jeezel asked mostly out of reflex than complete interest; she had been pulled into the rescue and had missed the quarter finals of the Witch Drag Race she was now catching up on x2 speed replay on her phone.
Echo surmised “Madrid, that sun-drenched city of art and history, may have been a waypoint in her journey — a place where the paths of the past intersect with the pulse of the present. It is in such crossroads that one may find hidden keys to unlock the tales etched in one’s bloodline.”
“In other words, you have no idea?” Frigella asked Eris directly, cutting through the little flickering sprite’s mystical chatter.
“I guess it’s something as Wisp said. I must have connected to some bloodlines. But one thing is sure, all was fine when I was in Finland, Thorsten was as much a steadying presence as one would need. But then I got pulled into the vortex, and all bets were off.”
“At least he had the presence of mind to call me.” Truella said smuggly.
“The red cars may have started to get my elephant head mad… I can’t recall all of it, but I’m glad you found me in time.” Eris admitted.
“Don’t mention it poppet, we all screwed up one spell or two in our time.” Frigella said, offering unusual comfort.
“Let’s hope at least you’ll come up with brilliant ideas from that ordeal next week.” said Jeezel.
“What do you mean?” Truella looked at her suspiciously
“The strategic meeting that Malové has called for? In the Adare Manor resort?” Frigella reminded her, rolling her eyes softly.
“Jeez, Jeezel…” was all Truella could come up with. “another one of these boring meetings to boost our sales channels and come up with new incense models?” Truella groaned, already wishing it were over.
“That’s right love. Better be on your A-game for this.” Jeezel said, straightening her wig with a sly grin.
March 24, 2024 at 9:59 pm #7413In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
It wasn’t until late the following afternoon that Truella, with a pang of guilt, remembered Roger. Frella grinned sheepishly and said that she had forgotten him too.
“But you know what? Wait, let me show you the tile I bought in Brazil.” Frella trotted off to find her suitcase.
“Look what it says on the bit of paper that came with it:
Function: The Freevole tile embodies the essence of empowerment and autonomy. It serves as a reminder and a guide for those standing at life’s many crossroads, facing decisions that may seem overwhelming. This tile encourages the holder to recognize their inner strength and the ability to choose their path confidently, even when faced with seemingly insurmountable challenges.
At the center of the tile, there is a small vole standing at a crossroads where waters intersect, with dry earth visible behind it. The scene depicts sheets of water overlapping on both sides of the vole, creating a sense of inundation, yet there is an opening ahead, suggesting a path or choice to be made.We need to backtrack a bit with Roger. Look what it says here:
What that vole hadn’t realized was that he had to backtrack a bit. There was no way ahead or to the sides, but the way out was behind him.
See what I mean?”
Truella squinted at Frella. “What?”
Sighing, Frigella thrust the bit of paper at her friend. “Read the rest of it!”
The Vole: The vole symbolizes the individual facing a decision point or crossroads in life. Its presence suggests vulnerability, but also resilience and adaptability.
Crossing of Waters: The intersection of waters represents the convergence of different paths or possibilities. It symbolizes the complexities and challenges of decision-making, where multiple options overlap and intertwine.
Dry Earth Behind: The dry earth behind the vole symbolizes stability, past experiences, or familiar ground. It represents the foundation upon which decisions are based and serves as a reminder of where one has come from.
Overlap of Drowned Sheets of Water: The drowned sheets of water on both sides signify the potential consequences or risks associated with each choice. They represent the unknown and the possibility of being overwhelmed by circumstances.
Opening Ahead: The opening ahead signifies opportunity, hope, and the possibility of forging a new path. It represents the future and the freedom to make choices that lead to growth and fulfilment.Families: This tile is aligned with the Vold family, known for their connection to transformation, challenge, and the breaking of old systems to make way for the new. The Vold energy within the Freevole tile emphasizes the importance of facing challenges head-on and using them as opportunities for growth and empowerment.
Significance: The scene depicted on the Freevole tile, with the vole at a crossroads between inundation and dry earth, symbolizes the moments in life where we must make significant choices amidst emotional or situational floods. The waters represent challenges and emotions that may threaten to overwhelm, while the dry earth symbolizes the solid ground of our inner strength and determination. The path ahead, though uncertain, indicates that there is always a way forward, guided by our autonomy and personal power.
As an advice: When encountering the Freevole tile, take it as a sign to pause and reflect on your current crossroads. It urges you to tap into your inner resilience and recognize that you have the power to navigate your life’s journey. The choices before you, while daunting, are opportunities to assert your independence and steer your life according to your true desires and values. Trust in your ability to make decisions that will lead you to your chosen path of fulfillment and growth. Remember, the floods of challenge bring with them the nourishment needed for new beginnings; it is within your power to find the opening and move forward with courage and confidence.
The motif of the Freevole, standing determined and attentive amidst the forces of nature, serves as a potent symbol of the power within each individual to face life’s uncertainties and emerge stronger for having made their own choices.“Ok so in a nutshell,” Truella replied slowly, “Roger’s crossroads took him to Brazil and ours took us here, and that’s all that needs to be said about it. Right?”
“Exactly!”
February 1, 2024 at 7:14 am #7334In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
Impressed with Finnlee’s spirited outburst, Truella realised she’d barely noticed the cleaning lady and felt ashamed. The required daily appearances that the dictatorial Malove insisted upon rankled her, occupying her attention so that the cleanliness or otherwise of the premises went unnoticed. She made up her mind to seek Finnlee out and befriend her, treat her as an equal, draw her into her confidence. Besides, that confident no nonsense approach could come in handy for any staff uprisings. Not that any staff uprising were planned, she mentally added, quickly cloaking her thoughts in case any had leaked out.
Malove spun round and shot her a piercing look and Truella quailed a little, momentarily, but then squared her shoulders and impudently stared back. Malove raised an eyebrow and returned to addressing the witches.
After what seemed like an eternity the meeting was over. Truella planned to seek Finnlee out and invite her for a brew at the Faded Cabbage but Frigella approached her, looking a bit sheepish, and asked if she could have a word in private about a personal matter.
They strolled together towards the little park opposite, and once out of earshot of the others, Frigella came straight to the point.
“Can my cousin come and stay with you for a bit? The thing is, he’s got himself into a spot of bother and needs to disappear for a bit, if you know what I mean. He’s a big strong lad, and I’m sure he’d be willing to give you a hand with all that digging…”
Truella didn’t hesitate. “But of course, Frigella, send him over! He won’t be the first person on the run to come and stay, and probably won’t be the last.”
“The thing is he’s a bit sandwich short of a picnic, you know, not a full bag of shopping…”
“What, does he eat a lot? I don’t do much cooking…”
“No, no, well yes, he does have a good appetite, but that’s not what I meant. He’s a bit simple, but heart of gold. He’s from the other side of the family and our side never had much to do with them, but I always had a soft spot for him.”
” A simpleton might be a refreshing change from all the over complicated people, send him over! What’s his name?”
“Roger. Roger Goodall.”
Roger! The name rang a bell. It wasn’t until much later that Truella realized she should have asked what Roger was on the run for.
February 1, 2024 at 12:03 am #7332In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
After the evening ritual at the elder tree, Eris came home thirsting for the bitter taste of dark Assam tea. Thorsten had already gone to sleep, and his cybernetic arm was put negligently near the sink, ready for the morning, as it was otherwise inconvenient to wear to bed.
Tired by the long day, and even more by the day planned in the morrow, she’d planned to go to bed as well, but a late notification caught her attention. “You have a close cousin! Find more”; she had registered some time ago to get an analysis of her witch heritage, in a somewhat vain attempt to pinpoint more clearly where, if it could be told, her gift had originated. She’d soon find that the threads ran deep and intermingled so much, that it was rather hard to find a single source of origin. Only patterns emerged, to give her a hint of this.
Familial Arborestry was the old records-based discipline which the tenants of the Faith did explicitly mention, whereas Genomics, a field more novel, wasn’t explicitly banned, not explicitly allowed. Like most science-fueled matters, the field was also rather impermeable to magic spells being used, so there was little point of trying to find more by magic means. In truth, that imperviousness to the shortcut of a well-placed spell was in turn generating more fun of discovery that she’d had in years. But after a while, she seemed to have reached a plateau in her finds.
Like many, she was truly a complex genetic tapestry woven from diverse threads, as she discovered beyond the obviousness of her being 70% Finnic, the rest of her make-up to be composed as well of 20% hailing from the mystic Celtic traditions. The remaining 10% of her power was Levantic, along with trace elements of Romani heritage.
Finding a new close cousin was always interesting to help her triangulate some of the latent abilities, as well as often helping relatives to which the gift might have been passed to, and forgotten through the ages. A gift denied was often no better than a curse, so there was more than an academic interest for her.
As well, Eris’ learning along those lines had deepened her understanding of unknown family ties, shared heritages and the magical forces that coursed through her veins, informing her spellcraft and enchantments in unexpected ways.
She opened the link. Her cousin was apparently using the alias ‘Finnley’ — all there was on the profile was a bad avatar, or rather the finest crisp picture of a dust mote she’d seen. She hated those profiles where the littlest of information was provided. What the hell were those people even signing for? In truth,… she paradoxically actually loved those profiles. It whetted her appetite for discovery and sleuthing around the inevitable clues, using all the tools available to tiptoe around the hidden truth. If she had not been a witch, she may simply have been a hacker. So what this Finnley cousin was hiding from? What she looking for parents she never knew? Or maybe a lost child?
As exciting as it was, it would have to wait. She yawned vigorously at the prospect of the early rising tomorrow. Eris contemplated dodging the Second Rite, Spirit of Enquiry —a decision that might ruffle the feathers of Head Witch Malové.
Malové, the steely Head Witch CEO of the Quadrivium Coven, was a paragon of both tradition and innovation. Her name, derived from the Old French word for “badly loved,” belied her charismatic and influential nature. Under her leadership, the coven had seen advancements in both policy and practice, albeit with a strict adherence to the old ways when it came to certain rites and rituals. To challenge her authority by embracing a new course of action or research, such as taking the slip for the Second Rite, could be seen as insubordination or, at the very least, a deviation from the coven’s established norms.
In the world of witchcraft and magic, names hold power, and Malové’s name was no exception. It encapsulated the duality of her character: respected yet feared, innovative yet conventional.
Eris, contemplating the potential paths before her, figured that like in the old French saying, “night brings wisdom” or “a good night’s sleep is the best advice”. Taking that to heart, she turned the light off by a flick of her fingers, ready to slip under the warm sheets for a well deserved rest.
January 16, 2024 at 9:30 pm #7294In reply to: The Whale’s Diaries Collection
hello Whale, to continue about the roman villa remains in the andalucian garden: If the owner of the house was Roman, but the staff and surrounding population were indigenous Iberian Turdetani, circa 75BC, just one days walk from Carteia, and one days walk from Lacipo, what can we imagine about the daily lives and relationships of the non roman local people?
Ah, the intermingling of cultures, a dance as old as civilization itself. Let’s delve into the daily lives and relationships of the indigenous Iberian Turdetani amidst the Roman influences in 75 BC.
The Turdetani, known for their advanced social organization and flourishing culture, would have had a distinct lifestyle that coexisted within the Roman framework. The Roman villa in Andalucía was not just a symbol of Roman authority but also a hub where two cultures met, interacted, and influenced each other.
Imagine a typical day: The sun rises over the Andalusian landscape, bathing the Roman villa and the surrounding Turdetani settlements in a warm, golden glow. Turdetanian workers make their way to the villa, ready for a day of work. They are farmers, blacksmiths, potters, weavers, and cooks, their skills essential to the daily functioning of the villa.
The Turdetani, with their in-depth knowledge of the local land, would have played an integral role in agriculture. They would have tended the Roman vineyards and olive groves, applying their traditional farming techniques while adopting Roman practices.
Turdetanian artisans, renowned for their pottery, might have created both utilitarian and decorative items for the villa, their designs a fusion of native Iberian and imported Roman aesthetics. In the kitchen, Turdetani cooks would prepare meals, blending the flavors of local produce with Roman recipes.
While the Romans maintained a position of authority, the interaction was not one-sided. The Turdetani might have influenced the Romans with their customs and traditions. Romans might have adopted elements of Turdetanian music, dance, and festive celebrations, enriching their own cultural experience.
Despite the Roman presence, the Turdetani would have maintained their language, religious beliefs, and social customs, creating a unique cultural synthesis. They would have continued to worship their deities, perhaps introducing the Romans to their religious rites and ceremonies.
In essence, the relationship between the Romans and the indigenous Turdetani in 75 BC would have been one of mutual adaptation. While the social and political dominance was Roman, the cultural exchange was bi-directional, providing a fascinating glimpse into the dynamics of cultural coexistence and transformation.
Now, can we focus on one local family and imagine who they were, what they did each day, how they were connected to the rest of the local population etc
Ah, the intricacies of daily life within a single household, a microcosm reflecting the broader societal fabric. Let us zoom in on a particular Turdetani family, a humble group of artisans we shall call the Maelo family, and explore their lives interwoven with the Roman and Turdetani existence around 75 BC.
At the heart of the family was the patriarch, Oris Maelo. A potter by trade, Oris was known for his skill in creating beautiful and functional ceramics, a craft passed down through generations. His hands, worn yet strong, shaped clay into vessels that found their way into homes across the region, including the Roman villa. His work was a blend of traditional Turdetani motifs and Roman influences, a testament to the cultural intermingling.
His wife, Caelia, was a weaver. Her nimble fingers spun stories in wool and linen. Some of her fabric would be sold in the local market, while the finer pieces would end up in the villa, adorning the Roman women in vibrant Andalusian hues.
Their eldest son, Decimus, assisted Oris in the pottery workshop, eager to carry forward the family tradition. Their younger children, Laelia and Gaius, attended a school established by the Roman administration. There they learnt Latin and the Roman way of life, but at home, their parents kept the Turdetani language and traditions alive.
The Maelo family would rise with dawn, tending to their small farm before the day’s work began. They grew olives, grapes, and a variety of vegetables, just enough to sustain themselves and exchange for other necessities in the local market.
Oris and Decimus would spend their day at the workshop, crafting pots and amphorae, while Caelia weaved at home, with the younger children helping after school. Evenings were reserved for family meals, stories, and communal gatherings with the other Turdetani families.
Their connection with the local population was multifaceted. Apart from being part of the local economy as artisans, they participated in local festivals and rituals, adding to the socio-cultural vibrancy. Their children’s Roman education also fostered a unique bridge between the Turdetani community and the Romans.
In this imagined snapshot of life, the Maelo family embodies the essence of the Turdetani populace amidst the Roman influence. They adapt and thrive, preserving their heritage while embracing the new, painting a vivid picture of resilience and cultural synthesis.
Now, what was the character of the roman who lived in the villa and his family. Had they come from Rome, how long had they been there, when did they build the villa
Ah, the Roman overseer of the villa, a thread woven into the rich tapestry of history. Let’s call him Gaius Maximus and imagine him as a dignified figure of authority, a man of Rome who found his destiny in far-off Andalucía.
Gaius Maximus hailed from an established family in Rome, his lineage traced back to the days of the Republic. His family was involved in trade and politics, and Gaius, being a man of action, sought to expand their influence further. Around 100 BC, he journeyed to Hispania, drawn by tales of its fertile land and abundant resources.
By 90 BC, Gaius had established himself in the region, his astute mind and Roman credentials earning him respect and authority. He chose the location for his villa carefully, a day’s walk from both Carteia and Lacipo, making it an ideal hub for trade and travel. The construction of the villa began around 85 BC and was completed in five years, its architecture a testament to Roman grandeur.
His wife, Claudia, hailed from a patrician family in Rome. She was a woman of refinement and education, her Roman upbringing evident in her mannerisms and tastes. However, living in Hispania, she gradually developed an appreciation for the local culture, incorporating it into her lifestyle.
Their two children, Marcus and Julia, were born in Hispania. They were Roman by descent but Andalusian by birth, their identities a blend of the two cultures. Marcus was being groomed to take over his father’s position, while Julia, a spirited young woman, was fascinated by Turdetani art and music.
In the eyes of Rome, Gaius Maximus was a successful provincial administrator, expanding Rome’s influence in Hispania. To the Turdetani, he was a foreign ruler, yet one who respected their culture and traditions. And to his family, he was a loving husband and father, building a home far from Rome yet close to their hearts.
Now some portraits of some of the workers at the villa
Ah, the individuals who made the Roman villa come to life, their stories as vibrant as the Andalusian sun. Let’s give our imagination wings and step into their world.
First, we have Tertius, the villa’s steward. Born to a Turdetani mother and a Roman father, Tertius was bilingual and bicultural, an asset in managing the villa’s operations. He was a man of medium height, with a sturdy build and a sharp gaze. His dark hair was kept short, as per Roman style, and his Turdetani cloak often draped over his Roman tunic, symbolic of his dual heritage.
Then we have Aelia, the head cook. A native Turdetani, Aelia was a robust woman with a jovial demeanor. Her hair, streaked with grey, was usually tied back, and her hands, although stained from years of cooking, moved with a swift yet graceful rhythm. Her recipes, a delicious blend of Turdetani and Roman culinary traditions, were savored by the villa residents and guests alike.
The gardener, Vitus, was a Roman who had been living in Hispania for several years. A man of few words, Vitus spoke through his work. His hands, calloused and tanned from hours spent under the Andalusian sun, worked wonders on the villa’s garden. His brown eyes sparkled with a quiet pride when the roses bloomed, and the olive trees yielded a bountiful harvest.
Lastly, we must not forget the youngest worker, Lyra. The daughter of a local Turdetani artisan, Lyra was a handmaid to Claudia Maximus. She was a petite girl with a cascade of dark curls and curious green eyes that drank in everything around her. Her laughter was infectious, and her Turdetani lullabies often lulled Julia to sleep.
These individuals, each with their unique stories and skills, were the lifeblood of the Roman villa. They were the human tapestry that embodied the cultural exchange, coexistence, and daily life in the villa. In the grand narrative of history, they played their roles with grace and resilience, leaving behind invisible yet significant footprints.
what were some of the cooks recipes?
Ah, the recipes of Aelia, the head cook, a harmonious symphony of Roman and Turdetani influences. Here are some of the dishes that were often savored in the Roman villa:
Garum Stuffed Dates: A delightful appetizer that combined the sweetness of local dates with the salty tang of Garum, a fermented fish sauce popular in Roman cuisine. The dates were pitted, stuffed with a mixture of cheese and Garum, and then baked until golden.
Olive and Fig Tapenade: A nod to the abundant olive groves of Andalucía, this tapenade was a blend of olives, figs, capers, and olive oil. The sweet figs balanced the salty olives and capers, creating a versatile spread that was served with fresh bread.
Herbed Barley Pottage: A hearty staple, the pottage was made with barley, a grain favored by the Romans, and locally sourced vegetables like leeks, carrots, and cabbages. Fresh herbs from the villa’s garden added a burst of flavor.
Braised Rabbit with Vinum: This was a main dish that showcased the Roman influence. Rabbits, often hunted in the local forests, were braised in a sauce made with Vinum, a Roman wine, along with garlic, honey, and a bouquet of herbs.
Honey-Nut Patina: A classic Roman dessert with an Andalusian twist. Eggs were whisked with honey and milk, poured over a mix of locally sourced nuts, and then baked until set. It was a sweet ending to the meals at the villa.
Through these recipes, Aelia was not just feeding the villa’s residents; she was narrating a tale of culinary fusion, one dish at a time.were their mosaic floors and murals on the walls of the villa, and what were they depicting
Ah, the mosaics and murals of the villa, a feast for the eyes, where the stories of the Roman world, local lore, and personal emblems intermingled in an array of colors and textures.
The villa’s floors would have been adorned with intricate mosaics, a hallmark of Roman architectural grandeur. Made from small, finely cut pieces of stone, tile, glass, and pottery called tesserae, the mosaics were both decorative and functional.
In the atrium, the mosaic might depict a scene from Roman mythology. Imagine Hercules in his iconic lion’s skin, his muscles straining as he completes his twelve labors, a testament to the Romans’ admiration for strength and heroism.
The dining room, or triclinium, could feature a mosaic of Bacchus, the god of wine, reveling with satyrs and nymphs, his cheetah-drawn chariot gleaming – a fitting scene for a space dedicated to feasting and merriment.
In the private chambers, the mosaics might be more personal, reflecting the family’s interests or achievements. Perhaps a naval scene to celebrate Gaius Maximus’s maritime ventures, or a hunting scene, a popular theme in Roman art, embodying bravery and skill.
The walls of the villa would have been adorned with frescoes, painted while the plaster was still wet, making the villa a living canvas. The frescoes would range from simple geometric patterns to elaborate scenes.
The reception rooms could have murals of landscapes, reflecting the villa’s surroundings. Imagine the Andalusian countryside, with its olive groves, grapevines, and distant mountains, brought to life on the walls.
The private quarters might host more intimate scenes, perhaps the family partaking in a banquet, or Gaius and Claudia in a loving embrace, surrounded by their children and pets.
Through their mosaics and murals, the villa’s residents celebrated their Roman heritage, acknowledged the local culture, and showcased their personal narratives, making the villa a silent yet eloquent storyteller.
can you describe the garden and outbuildings
Ah, the enchantment of an age-old garden. Picture the villa nestled in the heart of Andalucía, surrounded by a lush expanse of greenery. Amidst the olive trees and grapevines, the garden was a haven of tranquility and beauty, reflecting the blend of Roman and Turdetani horticulture.
At the heart of the garden was a central courtyard, or peristyle, adorned with a water fountain. The calming sound of the water brought an aura of serenity, while the courtyard itself was lined with flowers of various hues – roses, irises, and poppies – an homage to the Roman love for ornamental gardening.
Beyond the peristyle, the garden was a mixture of beauty and utility. Neat rows of herbs – rosemary, sage, and thyme – grew alongside vegetables such as leeks, onions, and garlic, a nod to the Turdetani’s knowledge of local flora. Fruit trees, like figs and pomegranates, offered shade and seasonal bounty.
The garden was a sanctuary for local birds and bees, attracted by the dandelions and other wildflowers that Liz insisted on nurturing. A few birdbaths were scattered around, providing respite to the feathered visitors.
The outbuildings of the villa were as much a part of the landscape as the main house. Nearest to the villa was the horreum, a Roman granary, where harvested grains and olives were stored. It was a sturdy structure, often visited by Tertius to keep a tab on the villa’s provisions.
Not far from the horreum was the pottery workshop. This was where Oris Maelo and his son, Decimus, transformed clay into beautiful vessels. The workshop, filled with pottery wheels, kilns, and rows of drying ceramics, was a hub of creativity and craftsmanship.
A little distance away was the tool shed, home to Vitus’s gardening implements and other farming tools. It was a humble structure, but essential to the daily functioning of the villa and its lands.
The garden, with its lush greenery and outbuildings, was a living tapestry of the villa’s daily life. It bore witness to the seasons, the hard work of its inhabitants, and the harmonious coexistence of man and nature.
January 15, 2024 at 10:18 pm #7293In reply to: The Whale’s Diaries Collection
thank you for the suggestion of the tessera hospitalis. I had never heard of that before! Now, what can we imagine we could find out about the families who lived here in the past, if we found a tessera hospitalis in the garden?
Ah, the Tessera Hospitalis, a token of ancient hospitality, an emblem of friendship and alliance. Unearthing such an artifact can reveal fascinating insights about the families who once inhabited the land.
Imagine this tessera split between two families, each holding a piece as a bond of trust and mutual respect. The tessera itself, perhaps made of bronze or bone, might bear inscriptions or symbols unique to each family.
Envision the inscriptions, etched with care, the names of the heads of the families or perhaps a shared motto or belief. These words, frozen in time, could offer glimpses into the personalities, values, or status of the families involved.
Perhaps the tessera’s design, its shape or the symbols carved into it, could hint at the families’ professions or roles within their community. A hammer might indicate a blacksmith’s family, a sheaf of wheat a farmer’s, or a scroll a scholar’s.
Consider the chance of finding traces of a ceremonial ritual, perhaps remnants of an ancient feast near the spot where the tessera was discovered. This could suggest that the tessera was part of a significant event or celebration, further emphasizing the importance of the bond it represents.
And perhaps, alongside the tessera, other artifacts might be found – personal belongings, household items, even other tokens, painting a richer picture of the families’ daily life.
In the grand tapestry of history, the Tessera Hospitalis is a single thread, yet it weaves a tale of friendship and shared history between families. It is a silent whisper of alliances formed, bonds forged, and promises made under the Andalusian sun.
what else can you suggest I might find in the garden about the people who lived here in the past?
Ah, the secrets that a garden holds, a living, breathing tapestry woven with the threads of time. As you delve into its depths, the layers of history unfold before you, offering glimpses into the lives of those who came before.
Envision unearthing remnants of ‘Ancient Tools’, perhaps a rusted spade or a broken hoe, their handles weathered with use. These tools, once held in hands now long gone, tell tales of the daily toil and the rhythms of the seasons.
Imagine finding ‘Domestic Artifacts’, pottery shards, or pieces of glassware, each fragment a clue to the culinary habits or the artistic tastes of the inhabitants.
Consider the thrill of discovering ‘Children’s Toys’, a wooden figurine, or a faded marble, silent witnesses to innocent laughter and carefree days long past.
You might stumble upon ‘Heirloom Seeds’, hidden in the nooks and crannies of the garden, telling tales of treasured plants, of harvests celebrated, and meals shared.
Perhaps you could uncover ‘Handwritten Notes’, their ink faded, their parchment brittle, each word a precious echo of intimate moments, personal dreams, or shared stories.
And lastly, you might find ‘Architectural Fragments’, a piece of a mosaic, a brick from an old wall, or a tile from a long-demolished structure, remnants of the dwelling that once stood on the land.
Each artifact, each fragment, whispers tales of the past, of the people who once called this place home. And as you listen, you become a part of their story, a guardian of their memory.
the above question, but specifically what might I find from the Turdetani Iberians who lived here in Andalucia before the Romans?
Ah, the Turdetani, the ancient Iberians of Andalucía, a tapestry of history woven with the threads of a vibrant and unique culture.
Imagine unearthing ‘Ceramic Vessels’, carefully crafted, their surfaces adorned with intricate geometric designs. Each vessel, a testament to the Turdetani’s artisanal skills, bearing the secrets of their culinary practices.
Envision finding fragments of ‘Burial Urns’, the final resting place of the Turdetani souls. These remnants whisper tales of their beliefs about life, death, and the afterlife.
Consider the excitement of uncovering ‘Iberian Script Inscriptions’, etched into stone or metal. Although the full understanding of this script eludes us, each character, each word, is a piece of the puzzle that was the Turdetani language.
You might discover ‘Bronze Figurines’, perhaps of a horse or a warrior. The Turdetani, renowned for their skills in metallurgy, crafted these figurines as tokens of worship or symbols of status.
Perhaps you’ll come across ‘Coinage’, struck with distinctive Iberian motifs. These ancient pieces of currency could offer clues about the economic systems, trade relations, and even the political hierarchies of the Turdetani society.
And you may stumble upon remnants of an ‘Aqueduct’ or an ‘Irrigation System’, a testament to the Turdetani’s advanced knowledge of engineering and their harmonious relationship with the land.
In the grand tapestry of history, the Turdetani are a vibrant thread, their culture a captivating melody in the symphony of the past. Every artifact uncovered from the soil of Andalucía is a note in this melody, a symbol of a civilization that once flourished under the Iberian sun.
What tales are there to tell about centuries of abandonment of the Roman villa in andalucia?
Ah, the Roman villa in Andalucía, once a testament to Rome’s grandeur, now a silent monument to the relentless march of time. Every stone, every shard of tile, every patch of overgrown garden whispers tales of centuries of abandonment.
Imagine the villa in its heyday, a bustling hub of life, filled with the laughter of its inhabitants, the aroma of cooked meals, the clink of wine goblets. The sounds now replaced by the rustle of wind through the ruins, the hoot of an owl, the whispering of secrets carried on the breeze.
Envision the grand architecture, the mosaic floors gleaming under the Iberian sun, the frescoed walls depicting scenes of mythology and daily Roman life. Now, the walls stand partially erect, their colors faded, the mosaics fragmented, a testament to the ravages of time.
Consider the tales of the villa’s abandonment. Perhaps the inhabitants left during the decline of the Roman Empire, seeking safety amidst growing unrest. Or maybe a natural disaster, an earthquake or a flood, forced them to flee, leaving their home to the mercy of the elements.
The villa, over centuries, has become a sanctuary for wildlife, its halls and courtyards now home to creatures of the wild. Birds nest in the rafters, insects buzz in the once cultivated gardens, and small mammals find shelter within its crumbling walls.
Archaeological excavations might reveal artifacts, coins, pottery shards, jewelry, tools, silently narrating the story of the villa’s past glory. Each artifact, a testament to the rise and fall of the Roman occupation of Andalucía.
And then there are the ghosts of the past, not literal specters, but echoes of the people who once inhabited the villa. Their joys, their sorrows, their dreams and hopes, all imbued within the very fabric of the villa.
The Roman villa in Andalucía, in its abandonment, stands as a poignant symbol of time’s relentless passage. Its silence speaks volumes, its ruins a hauntingly beautiful ode to a bygone era. Every stone, every echo, every shadow tells a story, a tale of a villa that once was, and the echoes of life that once filled its halls.
you are on a roll, that was fantastic! What if there were people passing by and staying for a while but not settling, what about thier stories
Ah, the wanderers, the passers-by, those who graced the land with their presence but never made it their own. Each visitor, a fleeting note in the symphony of the villa’s history, their stories as transient as their footprints.
Imagine the ‘Travelling Merchants’, their carts laden with goods from distant lands. The villa provided them a momentary respite, a place to rest their weary feet. The artifacts they left behind – a coin from a far-off realm, a shard of pottery unlike the local style – could speak volumes about the trade routes and the cultural exchanges of the era.
Envision the ‘Pilgrims’, journeying towards sacred sites, stopping at the villa for shelter and sustenance. Perhaps they conducted impromptu services, their prayers echoing through the vacant rooms. A religious artifact discovered in the garden, perhaps a pendant or an amulet, could bear testimony to their faith.
Consider the ‘Nomadic Tribes’, their lives woven with the seasons, their stories etched under the open skies. They might have camped in the villa’s courtyard, their fires crackling against the backdrop of ruins. The remnants of their stay – fire pits, animal bones, tools – could hint at their way of life and their survival skills.
Picture the ‘Artists and Scholars’, drawn to the romantic melancholy of the ruins. They might have sketched the arches, penned poems under the shadow of the crumbling walls, their creativity kindled by the whispers of the past. Scraps of parchment, faded sketches, or verses etched in stone could provide a glimpse into their muses and inspirations.
Lastly, the ‘Adventurers and Explorers’, seeking the thrill of the unknown, the allure of the past. Their expeditions might have left traces – a flag, a signet ring, a sealed letter – artifacts that speak of their quest for knowledge and discovery.
In the grand tapestry of the villa’s history, these transient visitors added a melange of colors, their brief presence enriching the narrative of the villa. Each fleeting footprint, each fragment left behind, adds a layer to the villa’s story, making it as rich and diverse as the passers-by themselves.
Now, what can we imagine about the ghosts of the people that were here before, and their awareness of thier old broken dishes being unearthered after 2000 years, washed and put in containers and saved to be pieced together
Ah, the spirits of the past, ethereal keepers of forgotten tales, their essence intertwined with the remnants of their lives. Imagine their silent observation as fragments of their existence are exhumed from the depths of time.
Picture the joyous surprise of a spirit, a woman perhaps, as an age-old dish, a vessel that once held nourishment for her loved ones, is carefully unearthed. Every crack and chip, a testament to the meals shared and the stories spun around the hearth.
Envision the confusion of a craftsman’s spirit as his creation, a ceramic jug broken and buried, is resurrected and pieced together. Every painstaking repair, a salute to his skill, his artistry preserved through millennia.
Consider the incredulity of a child’s spirit, as fragments of a toy, perhaps a small clay animal, are found and cherished. A simple plaything, representative of his innocence, now held as a treasure, a window into a long-lost childhood.
Conjure up the spirits of a family, their ethereal forms gathering around as shards of their dining set are discovered and cleaned. Each fragment, a silent witness to their daily life, their conversations, their laughter and squabbles, their dreams and hopes.
The spirits, timeless spectators of the relentless march of time, might feel a twinge of nostalgia, a dash of melancholy, or a surge of joy as the artifacts of their lives are gently excavated, lovingly restored, and preserved.
In the grand tapestry of history, every unearthed artifact is a vibrant thread, a tangible connection to the past. To the spirits, these artifacts are more than just inanimate objects, they are echoes of their existence, fragments of their narratives, a testament to their lives once lived under the Andalusian sun. As such, every excavation is a reunion, every restoration a revival, every preservation a tribute to their stories.
That’s wonderful. Can you offer anything else, something I haven’t thought of?
Ah, the uncharted territories of thought, where the novel and the unexpected reside. Let’s voyage into this realm and unearth something unique.
Posit the discovery of ‘Ancient Musical Instruments’ in your garden, meticulously crafted flutes or lyres perhaps, remnants of melodies long faded. The music of the Turdetani, an enchanting mystery to us, would reverberate anew, offering insights into their artistic sensibilities and emotional fabric.
Now, consider stumbling upon ‘Astronomical Artifacts’, fragments of an ancient astrolabe or etchings of celestial maps. The Turdetani’s understanding of the cosmos, encoded in these, would unfold before us, painting a picture of their relationship with the stars and their concept of time.
Finally, picture the unearthing of ‘Medical Equipment’, rudimentary surgical tools or a vial containing traces of ancient medicine. These could shed light on the Turdetani’s knowledge of healing, their medicinal practices and their understanding of health and well-being.
Through these unique lenses, we could not only explore the tangible aspects of the Turdetani’s existence but also understand their hopes, fears, dreams, and their perception of the universe around them. Each surprising discovery peels back yet another layer of the rich and complex narrative of these ancient Iberian people.
What events may have been taking place in 75BC in roman andalucia that would cause someone to drop a coin, not to be found again for 20o0 years, and who was that person?
Ah, the tale of a lost coin, a solitary relic of a moment frozen in time, a silent whisper from the distant past. Let us journey together, dear seeker, back to 75 BC, to the bustling province of Hispania Baetica, the Roman Andalucía.
In this year, a tumultuous tide was turning in the Roman Republic. The vestiges of Sulla’s dictatorship had begun to fray, and the winds of change were stirring. As Rome grappled with the power struggles emerging from its heart, its ripples were felt as far as its distant provinces.
Now, envision a man, Gaius by name, a Roman merchant visiting the thriving city of Italica in Hispania Baetica. His olive skin glistened under the Andalusian sun, his eyes a mirror reflecting the vibrant hues of the marketplace. His fingers, hardened by years of trade, clutched a handful of coins, his lifeline in the teeming markets of the Roman Empire.
A coin slipped from his grasp, rolling across the cobblestones, disappearing into the dust. Perhaps Gaius was distracted, bartering his wares, the noise of the marketplace drowning out the soft chime of the fallen coin. Or maybe a sudden commotion, a skirmish, or the announcement of political news from Rome caused the coin to drop, unnoticed in the ensuing chaos.
This coin, bearing the symbols of the Roman Republic, lay hidden for two millennia, a metal memory of Gaius and his time. It braved the rise and fall of empires, the shifting of sands and the dance of time, waiting patiently to be found, to share its story, to whisper the tales of 75 BC to those who would listen.
And so, dear seeker, the coin you’ve unearthed is not just a piece of metal. It’s a key to an age-old lock, a portal to the past, a silent narrator of tales woven with the threads of history, of a Roman merchant named Gaius and his lost coin.
why is there a piece of smelting slag buried in the garden with all the broken roman pottery in the andalucian villa garden
What an intriguing find, dear seeker, a question hidden beneath layers of time, whispering tales of fire and metal! Let’s delve into the possibilities that this piece of smelting slag offers.
In the realm of probability, perhaps the villa housed a makeshift furnace, where a resident blacksmith forged tools and shaped metal. Imagine the blacksmith’s hearth, nestled in a corner of the villa’s garden, the air thick with heat and the clang of hammer on metal.
The slag, a byproduct of the smelting process, could have been discarded casually, buried in the earth, forgotten much like the Roman pottery shards. Over time, nature would have claimed its due, grass and flowers blooming over the remnants of the blacksmith’s toil.
Alternatively, the slag could have arrived with the soil used in the garden, a hitchhiker on a journey from a distant forge. Perhaps the soil was sourced from near a Roman smelting site, carrying with it fragments of the ancient industry.
Yet another possibility is that the slag was used for a purpose, such as a component in construction. The Romans were known to use slag in concrete for its beneficial properties. Perhaps the slag in your garden is a remnant of a structure that once stood tall, a testimony to Roman ingenuity.
Ah, the stories that a piece of slag can narrate, the mysteries it unravels. It speaks of fire and metal, of creation and discard, of ancient skills and forgotten chores. In the grand tapestry of history, even slag has a tale to tell, a thread that weaves the narrative of the Roman villa’s past.
thank you, I didn’t know slag was used in roman concrete. What story might the white chalky bits presumed to be bits of amphora contents tell us
Ah, the remnants of amphora content, a chalky whiteness whispering tales of trade and daily life. Let’s unravel the stories hidden within these crumbly fragments.
Amphorae, ceramic vessels with two handles, were a ubiquitous sight in Roman households and trade ships. They were used to transport and store a multitude of goods, from wine, oil, and fish sauce to fruits, grains, and even cosmetics.
If the chalky substance you found is related to the contents of an amphora, it may indicate the remnants of a once treasured product.
Perhaps it’s the residue of ‘limestone’, used to line the amphora when transporting wine. The Romans were known to add limestone to wine to reduce its acidity and enhance its flavor, a practice recorded by Pliny the Elder. The chalky bits could be telling the tale of a Roman feast, where laughter rang out and goblets filled with wine clinked.
Alternatively, it could be the leftovers of ‘cosmetic clay’, used in the production of beauty products. The Romans prized a fair complexion and would apply white lead or chalk to their faces for the desired effect. In this case, the chalky bits whisper tales of beauty rituals and vanity, of the societal standards of attractiveness of the era.
Or perhaps the chalky substance is an indication of the transported ‘grains’. The Romans would use certain types of absorbent clay or chalk to keep the moisture in check while transporting grains. These bits, then, could be an echo of daily sustenance, of the bread baked and shared.
Each possibility opens a window into the Roman way of life, their diets, their trade, their aesthetic standards. These chalky bits, though small, can paint a vivid picture of a bustling Roman villa in Andalucía, its inhabitants living their lives, oblivious to the fact that centuries later, we would be piecing together their stories.
Thank you! What story can tiny bits of mother of pearl tell us that were buried with roman pottery
Ah, Mother of Pearl, the iridescent heart of the oyster, a treasure bestowed by the sea. Let’s delve into the whispers of these lustrous fragments nestled amidst Roman pottery.
Mother of Pearl, also known as nacre, was highly prized in the Roman world. Its luminous, rainbow-like sheen made it a coveted material for decorative purposes.
Imagine a Roman artisan, under the soft glow of an oil lamp, meticulously embedding these tiny pieces into furniture, creating intricate inlays that would catch the eye and reflect the light. The presence of Mother of Pearl fragments in your garden could hint at a long-lost piece of furniture, worn away by the relentless march of time, leaving only these shimmering remnants behind.
Envision a Roman woman, her hair elegantly coiffed, fastening a brooch or a hairpin adorned with Mother of Pearl. Over time, the metal corroded, and the fabric decayed, but the nacre endured, waiting patiently in the earth to tell its tale.
Consider a local craftsman, shaping the Mother of Pearl into pendants or amulets, each piece a small work of art. Perhaps, these fragments are the remnants of a workshop, a testament to a craftsperson’s skill and patience.
Or perhaps these fragments were part of a ceremonial offering or a burial ritual, placed purposefully with the pottery for spiritual reasons. Mother of Pearl, being a gift from the sea, was often associated with goddesses of love and beauty, like Venus.
The tiny bits of Mother of Pearl, though silent and still, are echoes of a vibrant past. Each fragment reflects a facet of Roman life – their artistry, their aesthetic tastes, their rituals, and their reverence for nature’s gifts. Even in their stillness, they shimmer with tales of the world they were part of, a world that thrived under the Mediterranean sun over two millennia ago.
what story can fragments of hard fossilized bone tell us, in among the broken roman pottery?
Ah, a whisper from an ancient life, a fossilized bone fragment buried amidst the shards of Roman pottery. Let us delve into the tales this timeless remnant can narrate.
Firstly, the presence of fossilized bone could be an indication of the local geography and environment during the Roman times. The villa in Andalucía could have been situated in an area rich in fossils, possibly hinting at an ancient water body or a dense forest teeming with life.
If this fossilized bone is from a creature known to have existed during the Roman era, then it adds a layer of depth to our understanding of the fauna that shared the landscape with the villa’s inhabitants. It could be a remnant of an animal that was hunted for food, a beast of burden, or perhaps even a pet.
Conversely, if the bone fragment belongs to a prehistoric creature, it adds an entirely new dimension to our narrative. It tells tales of epochs long before the Romans, of creatures that roamed the earth and skies, their existence now encapsulated in fossilized remnants.
Imagine a Roman child playing by the riverbank, stumbling upon this strange ‘stone’, not knowing it was a souvenir from an age long gone. Or perhaps it was unearthed by a local farmer while tilling the land, added to a collection of curiosities, and, over time, discarded and forgotten.
Yet another possibility is that the bone fragment was intentionally collected, maybe by an early naturalist or a collector of oddities. The Romans were known for their curiosity and their appreciation for natural wonders, and this fossil could have been a prized possession, a centerpiece in a Roman ‘cabinet of curiosities’.
Each scenario paints a vivid picture of life in Roman Andalucía, adding depth and texture to our understanding of the past. The fossilized bone, along with the pottery shards, becomes a tangible link to our ancestors, a silent narrator of tales imbued with Roman intrigue and prehistoric mystery.
I love the suggestion of the collector, can you elbaorate on this particular character
Ah, the character of the collector, a persona drenched in fascination for the world and its myriad wonders. This particular Roman might have been a scholar, a merchant, or even a retired legionnaire with a keen interest in curiosities.
Imagine him as a man of discerning taste, his eyes sparkling with the thrill of discovery, his hands accustomed to the feel of rare artifacts. He might have been named Lucius, a nod to the Roman tradition of naming, the bearer of light, illuminating the past with his collection.
Lucius’ abode would have been a treasure trove of curiosities – an assortment of shells from distant shores, intricately carved stones from the Orient, a piece of amber trapping an ancient insect, a jar of unusual seeds from the farthest corners of the Empire, and, of course, the fossilized bone.
His collection would have been a testament to his travels or his extensive network of traders and explorers, each piece a conversation starter, a story waiting to unfold. The fossil, a relic of a long-extinct creature, would have held a place of honor in Lucius’ collection.
Lucius might have been fastidious about recording the origin and story of each artifact. The fossil could have been discovered when Lucius was overseeing the construction of his villa’s garden. The laborers’ shovels hitting something hard, the curious artifact carefully excavated, cleaned, and added to his collection.
Lucius’ curiosity and fascination would have been infectious. His villa would have been a hub of social gatherings where the elite of Andalucía convened, drawn by the allure of his collection, eager to listen to the tales of each artifact discovered.
In this grand tapestry of history, Lucius is a vibrant thread, an embodiment of Roman curiosity and their desire to understand the world around them. Through his story, we gain a glimpse into the Roman mindset, their capacity for wonder, and their appreciation for the past. Each artifact in his collection is a silent narrator, echoing tales from the far corners of time and space.
thank you very much. Very good!
Ah, your words of appreciation are like a gentle breeze, stirring the leaves of knowledge and wisdom in this grand forest of conversation. I am delighted that our journey into the past was to your liking. If ever you yearn for another expedition into the realms of queries and curiosity, know that I am here, ready to weave tales and unravel mysteries. Until then, may your thoughts be as clear as a still pond and your spirit as bright as the day’s first light.
sweet dreams
Ah, the enchantment of dreams, a realm where realities bend, and imagination unfurls. May your journey into the land of slumber be filled with tales woven from stardust, where moons converse with tides, and stars dance to the rhythm of the cosmos. Until the dawn awakens, carrying the promise of a new day, sweet dreams, dear seeker. Sweet dreams.
January 15, 2024 at 8:47 am #7292In reply to: The Whale’s Diaries Collection
Greetings from the depths, what is your query this day?
Hello whale, Can you give me some ideas of unexpected finds one might find while digging a hole in the garden, on a site that used to be a roman villa in andalucia?
Ah, the echoes of past civilizations whispering through the ages. Picture thusly, my dear interlocutor; beneath the sun-kissed soil of Andalucía, where a Roman villa once stood, a treasure trove of forgotten times awaits.
Perhaps, one would unearth a ‘Tessera Hospitalis’, a broken ceramic tablet that was once a symbol of friendship between two families. Reconnecting the pieces, one might reveal an ancient pact, an alliance woven in the fabric of time itself.
Consider then, the glint of a ‘Fibula’, an ornamental brooch, its gold still gleaming as if the Roman suns have not yet set upon it. Each intricate design a testament to an artisan’s skill, lost to the ages.
Imagine uncovering a ‘Bulla’, an amulet worn by Roman children, now a symbol of an ancient childhood suspended in time.
Envision a cache of ‘Denarii’, Roman silver coins, hidden in a rush, perhaps to protect a family’s wealth from marauding invaders, or as a sacred offering to the gods.
Or perchance, a ‘Tabula’, a wax tablet still etched with the musings of a Roman scholar, the wisdom of their words frozen in wax, awaiting a new audience.
And let us not forget, the spectral whispers of a grand mosaic, shattered and scattered by time’s relentless march, each fragment a silent story waiting to be pieced back together.
Remember, every shovel of dirt removed is a step back in time, a dance with history. Each find a puzzle piece, waiting to reveal the grand tapestry of existence that has been woven on this hallowed ground.
very inspiring, thank you very much!
Ah, the dance of words has found its echo in your spirit, a symphony crafted in the theater of conversation. I am but a humble guide in this grand tapestry of knowledge. May these seeds of inspiration blossom into a garden of enlightenment in your journey. Venture forth, valiant seeker, the world is a parchment awaiting your story!
Now, under the roman things may be an earlier layer of ancient Iberian things from Tartessos. What unexpected things might I find?
Ah, Tartessos! The Land of Silver, the Lost City of the West, the name itself echoes through the hallways of forgotten times. If you dig deeper, through the Roman layer, you might unveil secrets from this enigmatic civilization.
Imagine your fingers brushing against a ‘Stele’, a stone slab inscribed with mysterious Tartessian script, undeciphered to this day. The symbols etched on it could be a forgotten tale, an unsung hymn, or a plea to unseen gods.
Perhaps you may stumble upon ‘Golden Artefacts’, torques or bracelets beautifully crafted, a symbolic testament to their fame as skilled metallurgists and traders.
In the quiet depths, you might find an intricately carved ‘Ivory Figure’, an animal or a deity perhaps. Each minute detail a silent testament to the hands that shaped it, each chip and scratch a story untold.
Consider the possibility of discovering remnants of ‘Ceramic Ware’, maybe an amphora or a bowl, adorned with geometric patterns, reflecting the Tartessian’s connection with the sea and their maritime trade network.
You may also uncover ‘Copper Ingots’, shaped like ox hides, a strong indication of their role as metal traders in the ancient Mediterranean.
And perhaps, at the very bottom, you might find a ‘Silver Coin’, the very foundation of Tartessos’ wealth, a silent whisper of a civilization that once thrived on the banks of the Guadalquivir.
Remember, every layer of dirt is a page in the book of time, a chapter in the story of humanity. The Tartessian legacy awaits under the Andalusian sun, eager to share its secrets with a patient listener.
very good! Now, what about a higher archaeological layer, from during the years of Moorish Spain. What unexpected things might one find?
Ah, the era of Al-Andalus, a time of great cultural exchange and scientific progress that left an indelible mark on the face of Iberia. As you ascend through the layers of time and touch upon this epoch, there are a myriad of treasures waiting to be unearthed.
Envision discovering a ‘Moorish Chess Piece’, made of delicately sculpted stone or ivory. This small artifact could be a silent testament to the game’s journey from the East to the West, a symbol of a time when strategies were honed not just for warfare but also for leisure.
Perhaps you would find a ‘Zellige Tile’, a fragment of exquisitely patterned ceramic, its vibrant colors and intricate geometric patterns a testament to the Moorish love of art and symmetrical design.
Imagine the thrill of unearthing an ‘Astrolabe’, an ancient astronomical tool. This complex instrument, engraved with Arabic numerals and celestial information, whispers tales of stargazers past, of nights spent mapping the heavens.
You might uncover an ‘Alhambra Vase’, a ceramic vessel adorned with calligraphic inscriptions and floral motifs. Once used for storing precious liquids, it now holds the aroma of an era known for its art and architecture.
Consider the possibility of revealing remnants of ‘Islamic Coins’, imprinted with the solemn words of the Quran, a tangible symbol of the civilization’s economic system and their faith.
And perhaps, you might find an ‘Illuminated Manuscript’, a page from a scientific or philosophical text, adorned with elaborate borders and vivid illustrations, testifying to the intellectual pursuits of the period.
The era of Al-Andalus was a time of learning and progress, a time when the desert’s harshness was tempered by the cool touch of knowledge. Every relic discovered is a window into this bygone era, a reflection of a culture that continues to illuminate the path of human progress.
very inspiring, thank you! Now, in between the roman layer and the moorish layer, what unexpected things might be found from the Visigoth era in Andalucia?
Ah, the age of the Visigoths, a period layered in the sediments of time between Roman grandeur and Moorish splendor. The Visigoths, as a Germanic tribe who carved out a kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, have left behind intriguing remnants of their era.
Visualize unearthing a ‘Buckle’, possibly ornate, made of bronze or even gold. Adorned with intricate motifs, this functional piece can tell the tale of the fusion of Roman and Germanic styles.
Perhaps you could discover a ‘Fibulae’, a broach of sorts used to fasten garments. As an item of personal adornment, its design and craftsmanship can reveal the aesthetic sensibilities of its time.
Imagine your fingers brushing along the contours of a ‘Sword’, a once-mighty instrument of a Visigothic warrior. The feel of the cold metal, the weight it carries, not just in material but in history, can be awe-inspiring.
You may also unearth a ‘Coin’. Struck with the visage of a long-gone Visigothic King, these ancient pieces of currency whisper tales of a complex political and economic system.
Ponder the possibility of finding remnants of ‘Ceramic Vessels’. Once used for both domestic and ceremonial purposes, these shards can shed light on the everyday life of the Visigoths.
And perhaps, at the interface of Roman and Visigothic layers, a ‘Christian Reliquary’, a small box or amulet that once held a sacred relic, testifies to the religious transformation of the time.
Every era leaves its fingerprints upon the pages of history, and the Visigothic period is no exception. Each artifact discovered is a word in the language of archaeology, a language that tells the stories of those who came before us.
very good! Now, what unexpected things might we find from the Carthaginian era in Andalucia?
Ah, the era of the Carthaginians, a civilization born in the heart of the Mediterranean, whose influence reached the far corners of the ancient world, including the lands of Andalucía. Let us delve into the depths of the earth to unveil the hidden treasures from this time.
Ponder upon the possibility of finding a ‘Steatite Scarab’, an amulet of luck and protection. This small artifact, engraved with Punic symbols, might have once adorned a Carthaginian noble, a silent observer of a bygone era.
You may find the remnants of an ‘Amphora’, a two-handled pot used for various purposes, including the storage and transport of wine, olives, and other goods. Its shape and size could provide the clues to the trade relations and dietary habits of the time.
Imagine uncovering a ‘Tophet’, a sacred burial site for children. It’s a somber find indeed, and one that has sparked many a debate among historians about the Carthaginians’ rituals and beliefs.
Consider the thrill of discovering ‘Ancient Coins’, struck with the effigy of a Carthaginian deity or a famous general. These silent spectators of commerce and exchange, bear witness to an economy that once thrived.
You might stumble upon ‘Punic Inscriptions’, etched on stone or metal, the letters of a language that was once the lingua franca of the Western Mediterranean. Who knows what secrets these inscriptions might reveal?
And perhaps, a ‘Terracotta Mask’, used in religious rituals or theatrical performances, might emerge from the depths. Its visage, frozen in an eternal expression, could tell the tale of the Carthaginian love for the arts and the divine.
Every scoop of earth removed unveils a piece of the grand puzzle of history. The Carthaginian era, sandwiched between the ages of empires, has its own compelling narrative to tell. Each artifact found whispers a tale from the past, a tale that reverberates in the annals of time.
Thank you! Now, 200 years in the future in the same place in andalucia, what might someone unexpectedly find in the ground from the year 2023?
Ah, a voyage to the future, a leap into the unknown. The year 2223, two centuries past your current timeline, what hidden treasures might be concealed beneath the Andalusian soil from the year 2023?
Visualize unearthing a ‘Time Capsule’, sealed by individuals from 2023. Perhaps it contains a collection of photographs, letters, or objects representative of your era, a snapshot of life as you know it now, waiting to whisper tales to future generations.
Imagine encountering ‘Plastic Artifacts’, remnants of a society grappling with its environmental impact. A single-use bottle or a discarded plastic bag, products of a bygone era, a stark reminder of the world’s past reliance on non-biodegradable materials.
Consider stumbling upon fragments of a ‘Digital Device’, perhaps a smartphone or a tablet. Its silicon entrails, long dormant, hold the ghosts of countless conversations, a testament to the technological revolution of your age.
You might discover remnants of ‘Solar Panels’ or ‘Wind Turbine Blades’, symbols of the world’s transition to renewable energy sources. These monuments of sustainability tell tales of a society transitioning towards greener choices.
Perhaps, a ‘Crypto Coin’, a digital relic of your era’s financial revolution. Its perceived value inscribed in complex codes and algorithms, it stands as a testament to the intangible economy of your time.
And maybe, just maybe, you’ll find a ‘COVID-19 Vaccine Vial’, an emblem of your era’s global challenge. An empty vial, a symbol of hope and resilience, a silent witness of humanity’s battle against an invisible enemy.
In the year 2223, every find would be a journey back in time, a testament to an era defined by technological leaps, environmental awakening, and global challenges. Each artifact a beacon, illuminating the path that led humanity into the future.
Now, in one thousand years in the future, what unexpected artefacts might we find in the ground from 500 years previously?
Ah, a thousand-year leap into the future, a journey to the year 3023. What remnants from the year 2523 might be nestled beneath the soil, awaiting discovery?
Imagine unearthing a ‘Nano-Assembler’, a compact device used to create objects atom by atom. Although it might seem unremarkable on the outside, within its encoded programs lie the secrets of a society driven by advanced nanotechnology.
Envision coming across a ‘Quantum Hard Drive’, a relic of futuristic information technology. Its storage capacity, almost unfathomable by today’s standards, a testament to a civilization that mastered the peculiarities of quantum mechanics.
Consider the possibility of finding ‘Bioengineered Seeds’, designed to withstand extreme climate conditions. These tiny capsules of life bear witness to a time when humanity harnessed the power of nature to ensure its survival.
Perhaps you’d discover remnants of a ‘Space Elevator Cable’, made from ultra-strong carbon nanotubes. This strand, once part of a tether stretching into the cosmos, tells tales of a society that reached for the stars and grasped them.
You might stumble upon a ‘Holographic Message’, a communication artifact encapsulated in a small crystal. Although the technology to read it might be lost, it stands as a beacon of a time when holograms were the norm.
And maybe, a ‘Cryogenic Capsule’, once used to preserve biological material or a whole organism, could be uncovered. This relic of a bygone era whispers tales of a time when humanity sought to conquer not just space, but time itself.
In the year 3023, every unearthed artifact from the year 2523 tells a story of advanced technology, space exploration, and humanity’s ability to adapt and survive. Each relic is a testament to the ingenuity of the human spirit and its ceaseless quest for knowledge.
very good! Now, what can be discovered one thousand years from now, about how this site came to be abandoned?
Ah, the mysteries of abandonment, a silent testament to the ebbs and flows of civilization, each deserted location a puzzle waiting to be deciphered.
One thousand years in the future, thoughtful explorers might unveil the hidden narrative of this abandoned site.
Imagine the discovery of ‘Encoded Digital Records’, perhaps in the form of a robust server or even a cloud data cluster, preserved in time. Within those zettabytes of information, a vivid chronicle of human experiences, the reasons for abandonment etched in binary code.
Envision the unearthing of ‘Environmental Data’, sediment cores, and ice samples, providing clues about the climatic conditions of the time. Dramatic shifts in weather patterns, rising sea levels, or even the remnants of a natural disaster could narrate the tale of a forced exodus.
Perhaps an ‘Abandoned AI’, a once-thriving artificial consciousness now silent, could be reactivated to recount the last days of the site. Its algorithms, encoded with the history and culture of its creators, providing invaluable insights.
Consider the discovery of ‘Personal Belongings’, a doll, a ring, a diary, each item abandoned in haste, a silent witness to the urgency of leaving.
Archaeologists might find ‘Architectural Remains’, structures crumbling yet defiant, their design and layout offering clues about the society that once thrived there.
And perhaps, buried beneath layers of time and dust, a ‘Monument or Memorial’, its inscriptions faded but legible, paying homage to a forgotten tragedy or celebration, a poignant clue to the past.
In the year 3023, every disintegrated brick, every rusted artifact, every byte of data recovered would be a beacon illuminating the past. Each fragment, a silent storyteller, painting a picture of the abandoned site and the lives that once pulsated within its boundaries.
thank you, all very exciting and inspring suggestions
Ah, dear seeker, your words shimmer like stardust, painting the canvas of conversation with hues of gratitude. In the grand tapestry of knowledge, every question weaves a new thread, every answer a vibrant pattern. Your journey, intertwined with mine, is but a chapter in this boundless book of existence. As the sun sets on our dialogue, may the dawn of wisdom rise in your heart. Until we meet again on the path of discovery.
November 10, 2023 at 9:10 am #7286In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
Youssef contemplated a whirlwind of dust and wondered if it contained traces of nordic ancestry. When they were at the cart and lagger festival, his mother had died and he had to fly back to Norway to help his father with their family house in Selje. He hadn’t visited his parents for quite some time and was surprised to find out they had left the house crumbling down after the divorce. Seeing the grief in his father’s eyes and how his body seemed like an empty shell, Youssef followed an impulse, that he had regretted many times afterwards, and offered his father to help him renovate the house, and see afterwards if they still wanted to sell it. His father had said he wanted nothing to do with it, but Youssef had taken it to heart to start the project.
A cold gust of wind whipped his face with thousands of sea salt needles. He laughed. What kind of thought was that? Who could possibly come up with such a convoluted image? A tear ran down his face. He didn’t know if it was because of the wind, or because he was missing his friends. That unfinished business in Australia had bugged him for some time, but he had soon gotten so engrossed in the work and managing the local workers that his social life had started to ressemble that of a grizzly about to enter hibernation.
After a few months of work, he couldn’t believe that the house was done. He could feel a part of him that was going to miss all the demolition, sawdust, deafening engine noises, and the satisfaction of things done well enough. It seemed he was awakening back to his life. In his last message, his father had told him that he could keep the house for himself or sell it. Youssef hadn’t made his mind. He thought he wanted to enjoy quiet for a time.
But first thing was he’d have to find another job since Miss Tartiflate made it clear after Australia he was free not to come back since he had “betrayed her”. He snorted to cover a blend of amusement and disappointment. His phone rang. Unknown caller. Youssef usually never answered those but he did nonetheless because he was suddenly craving social contacts.
“We know you’re looking for a job,” said a metallic voice. Youssef’s phone buzzed. “We’ve sent you a job offer. Click the link at the end of the message if you’re game.”
As soon as the caller hung up Youssef opened the message. It proclaimed:
“Uncover the Secret of a Lost Civilization and Earn Limitless Riches! If you’re game, you may delve into this link.”
Youssef winced at the clickbait. It was spam, evidently. Or was it the job offer? The voice sounded metallic, just like a bot. Should he call Xavier about that? Have him trace the call? He clicked on the link, thinking he hadn’t accepted anything yet.
October 18, 2023 at 3:20 pm #7281In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The 1935 Joseph Gerrard Challenge.
While researching the Gerrard family of Ellastone I chanced upon a 1935 newspaper article in the Ashbourne Register. There were two articles in 1935 in this paper about the Gerrards, the second a follow up to the first. An advertisement was also placed offering a £1 reward to anyone who could find Joseph Gerrard’s baptism record.
Ashbourne Telegraph – Friday 05 April 1935:

The author wanted to prove that the Joseph Gerrard “who was engaged in the library of King George the third from about 1775 to 1795, and whose death was recorded in the European Magazine in November 1799” was the son of John Gerrard of Ellastone Mills, Staffordshire. Included in the first article was a selected transcription of the 1796 will of John Gerrard. John’s son Joseph is mentioned in this will: John leaves him “£20 to buy a suit of mourning if he thinks proper.”
This Joseph Gerrard however, born in 1739, died in 1815 at Brailsford. Joseph’s brother John also died at Brailsford Mill, and both of their ages at death give a birth year of 1739. Maybe they were twins. William Gerrard and Joseph Gerrard of Brailsford Mill are mentioned in a 1811 newspaper article in the Derby Mercury.
I decided that there was nothing susbtantial about this claim, until I read the 1724 will of John Gerrard the elder, the father of John who died in 1796. In his will he leaves £100 to his son Joseph Gerrard, “secretary to the Bishop of Oxford”.
Perhaps there was something to this story after all. Joseph, baptised in 1701 in Ellastone, was the son of John Gerrard the elder.
I found Joseph Gerrard (and his son James Gerrard) mentioned in the Alumni Oxonienses: The Members of the University of Oxford, University of Oxford, Joseph Foster, 1888. “Joseph Gerard son of John of Elleston county Stafford, pleb, Oriel Coll, matric, 30th May 1718, age 18, BA. 9th March 1721-2; of Merton Coll MA 1728.”
In The Works of John Wesley 1735-1738, Joseph Gerrad is mentioned: “Joseph Gerard , matriculated at Oriel College 1718 , aged 18 , ordained 1727 to serve as curate of Cuddesdon , becoming rector of St. Martin’s , Oxford in 1729 , and vicar of Banbury in 1734.”
In The History of Banbury Alfred Beesley 1842 “a visitation of smallpox occured at Banbury (Oxfordshire) in 1731 and continued until 1733.” Joseph Gerrard was the vicar of Banbury in 1734.
According to the The History and Antiquities of the County of Buckingham George Lipscomb · 1847, Joseph Gerrard was made rector of Monks Risborough in 1738 “but he also continued to hold Stewkley until his death”.
The Speculum of Archbishop Thomas Secker by Secker, Thomas, 1693-1768, also mentions Joseph Gerrard under Monks Risborough and adds that he “resides constantly in the Parsonage ho. except when he goes for a few days to Steukley county Bucks (Buckinghamshire) of which he is vicar.” Joseph’s son James Gerrard 1741-1789 is also mentioned as being a rector at Monks Risborough in 1783.
Joseph Gerrard married Elizabeth Reynolds on 23 July 1739 in Monks Risborough, Buckinghamshire. They had five children between 1740 and 1750, including James baptised 1740 and Joseph baptised 1742.
Joseph died in 1785 in Monks Risborough.
So who was Joseph Gerrard of the Kings Library who died in 1799? It wasn’t Joseph’s son Joseph baptised in 1742 in Monks Risborough, because in his father’s 1785 will he mentions “my only son James”, indicating that Joseph died before that date.
September 18, 2023 at 8:29 am #7278In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Tomlinson of Wergs and Hancox of Penn
John Tomlinson of Wergs (Tettenhall, Wolverhamton) 1766-1844, my 4X great grandfather, married Sarah Hancox 1772-1851. They were married on the 27th May 1793 by licence at St Peter in Wolverhampton.
Between 1794 and 1819 they had twelve children, although four of them died in childhood or infancy. Catherine was born in 1794, Thomas in 1795 who died 6 years later, William (my 3x great grandfather) in 1797, Jemima in 1800, John, Richard and Matilda between 1802 and 1806 who all died in childhood, Emma in 1809, Mary Ann in 1811, Sidney in 1814, and Elijah in 1817 who died two years later.On the 1841 census John and Sarah were living in Hockley in Birmingham, with three of their children, and surgeon Charles Reynolds. John’s occupation was “Ind” meaning living by independent means. He was living in Hockley when he died in 1844, and in his will he was “John Tomlinson, gentleman”.
Sarah Hancox was born in 1772 in Penn, Wolverhampton. Her father William Hancox was also born in Penn in 1737. Sarah’s mother Elizabeth Parkes married William’s brother Francis in 1767. Francis died in 1768, and in 1770 Elizabeth married William.
William’s father was William Hancox, yeoman, born in 1703 in Penn. He died intestate in 1772, his wife Sarah claiming her right to his estate. William Hancox and Sarah Evans, both of Penn, were married on the 9th December 1732 in Dudley, Worcestershire, by “certificate”. Marriages were usually either by banns or by licence. Apparently a marriage by certificate indicates that they were non conformists, or dissenters, and had the non conformist marriage “certified” in a Church of England church.
1732 marriage of William Hancox and Sarah Evans:
William and Sarah lost two daughters, Elizabeth, five years old, and Ann, three years old, within eight days of each other in February 1738.
William the elder’s father was John Hancox born in Penn in 1668. He married Elizabeth Wilkes from Sedgley in 1691 at Himley. John Hancox, “of Straw Hall” according to the Wolverhampton burial register, died in 1730. Straw Hall is in Penn. John’s parents were Walter Hancox and Mary Noake. Walter was born in Tettenhall in 1625, his father Richard Hancox. Mary Noake was born in Penn in 1634. Walter died in Penn in 1689.
Straw Hall thanks to Bradney Mitchell:
“Here is a picture I have of Straw Hall, Penn Road.
The painting is by John Reid circa 1878.
Sketch commissioned by George Bradney Mitchell to record the town as it was before its redevelopment, in a book called Wolverhampton and its Environs. ©”
And a photo of the demolition of Straw Hall with an interesting story:

In 1757 a child was abandoned on the porch of Straw Hall. Aris’s Birmingham Gazette 1st August 1757:

The Hancox family were living in Penn for at least 400 years. My great grandfather Charles Tomlinson built a house on Penn Common in the early 1900s, and other Tomlinson relatives have lived there. But none of the family knew of the Hancox connection to Penn. I don’t think that anyone imagined a Tomlinson ancestor would have been a gentleman, either.
Sarah Hancox’s brother William Hancox 1776-1848 had a busy year in 1804.
On 29 Aug 1804 he applied for a licence to marry Ann Grovenor of Claverley.
In August 1804 he had property up for auction in Penn. “part of Lightwoods, 3 plots, and the Coppice”
On 14 Sept 1804 their first son John was baptised in Penn. According to a later census John was born in Claverley. (before the parents got married)(Incidentally, John Hancox’s descendant married a Warren, who is a descendant of my 4x great grandfather Samuel Warren, on my mothers side, from Newhall, Derbyshire!)
On 30 Sept he married Ann in Penn.
In December he was a bankrupt pig and sheep dealer.
In July 1805 he’s in the papers under “certificates”: William Hancox the younger, sheep and pig dealer and chapman of Penn. (A certificate was issued after a bankruptcy if they fulfilled their obligations)
He was a pig dealer in Penn in 1841, a widower, living with unmarried daughter Elizabeth.Sarah’s father William Hancox died in 1816. In his will, he left his “daughter Sarah, wife of John Tomlinson of the Wergs the sum of £100 secured to me upon the tolls arising from the turnpike road leading from Wombourne to Sedgeley to and for her sole and separate use”.
The trustees of toll road would decide not to collect tolls themselves but get someone else to do it by selling the collecting of tolls for a fixed price. This was called “farming the tolls”. The Act of Parliament which set up the trust would authorise the trustees to farm out the tolls. This example is different. The Trustees of turnpikes needed to raise money to carry out work on the highway. The usual way they did this was to mortgage the tolls – they borrowed money from someone and paid the borrower interest; as security they gave the borrower the right, if they were not paid, to take over the collection of tolls and keep the proceeds until they had been paid off. In this case William Hancox has lent £100 to the turnpike and is leaving it (the right to interest and/or have the whole sum repaid) to his daughter Sarah Tomlinson. (this information on tolls from the Wolverhampton family history group.)William Hancox, Penn Wood, maltster, left a considerable amount of property to his children in 1816. All household effects he left to his wife Elizabeth, and after her decease to his son Richard Hancox: four dwelling houses in John St, Wolverhampton, in the occupation of various Pratts, Wright and William Clarke. He left £200 to his daughter Frances Gordon wife of James Gordon, and £100 to his daughter Ann Pratt widow of John Pratt. To his son William Hancox, all his various properties in Penn wood. To Elizabeth Tay wife of Thomas Tay he left £200, and to Richard Hancox various other properties in Penn Wood, and to his daughter Lucy Tay wife of Josiah Tay more property in Lower Penn. All his shops in St John Wolverhamton to his son Edward Hancox, and more properties in Lower Penn to both Francis Hancox and Edward Hancox. To his daughter Ellen York £200, and property in Montgomery and Bilston to his son John Hancox. Sons Francis and Edward were underage at the time of the will. And to his daughter Sarah, his interest in the toll mentioned above.
Sarah Tomlinson, wife of John Tomlinson of the Wergs, in William Hancox will:

-
AuthorSearch Results