Search Results for 'nov'
-
AuthorSearch Results
-
February 15, 2024 at 7:47 pm #7375
In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
“The very image of a spy from a cheap novel. Perched behind his newspaper, peering through holes like a child with a telescope. He’s a creature of shadows, blending into the background, always watching, never seen. He thinks himself clever, but he’s as subtle as a cat in a fishbowl. He’s drawn to Frigella like a moth to a flame, but can’t shake off his ingrained caution. Intrigued yet wary, like a mouse sniffing a piece of cheese in a trap. He needs to make up his mind before his tail gets caught.”
“What’s on your mind, Needles?” Frigella inquired of her hedgehog familiar.
“Nothing,” replied the hedgehog cryptically, returning happily to his strawberry snack. “But you’ll soon find out…”

Cedric Spellbind found himself woefully unprepared for what was coming after the jump into the weird glowing vortex. On a hunch, he’d followed the enigmatic Miss O’Green. Something about her, her diaphaneous looks…
His wool tweed cap wasn’t the best attire for wherever he had jumped into. The damp smells, the warm humid air filled with electricity —something told him he wasn’t in Limerick any more,… but where.
The group Ms Frigella was with had moved swiftly, nonchalantly going in the streets after the boisterous tall figure with the black curly wig had made a string of light glow on the ground, evanescent trail they followed unhesitant to somewhere only them seemed to know.
He was struggling to keep the pace. At some point, the blue-haired one had turned suspiciously casting her glance, and he’d managed to dart in a nearby alley. They’d resumed their stroll, but she’d done something after that, some sort of dark magic that made their group seem to disappear in a fog, the sounds they made suddenly all muffled.
Accustomed to tracking witches, he’d discreetly put a findmystuff tracker on the bag. Wherever that bag would go, he would follow. He opted to let them proceed unhindered, for now.
He checked his phone. He couldn’t catch the signs in the streets during his shadowing. His phone had started buzzing as soon as he’d emerged from the vortex, so he was surely in another country. The SMS he’d received confirmed that hypothesis: he was in Brazil.
5 missed calls. His mother… He couldn’t call her back now, it would cost him a fortune, and his witch tracking wasn’t exactly paying the bills. She would hate him for it, but she would have to wait. Maybe a bit of worrying for him wasn’t bad. One could hope.
His last witch hunt hadn’t been the most successful. Bulgarian witches were fierce. To be honest, it had been a fiasco, and he was posted in Limerick as a consequence —on desk job only. He knew there were worse places to be, but he was missing the action of the field… He shouldn’t have followed these witches, but again, following orders had never been his strong suit.
February 1, 2024 at 12:03 am #7332In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
After the evening ritual at the elder tree, Eris came home thirsting for the bitter taste of dark Assam tea. Thorsten had already gone to sleep, and his cybernetic arm was put negligently near the sink, ready for the morning, as it was otherwise inconvenient to wear to bed.
Tired by the long day, and even more by the day planned in the morrow, she’d planned to go to bed as well, but a late notification caught her attention. “You have a close cousin! Find more”; she had registered some time ago to get an analysis of her witch heritage, in a somewhat vain attempt to pinpoint more clearly where, if it could be told, her gift had originated. She’d soon find that the threads ran deep and intermingled so much, that it was rather hard to find a single source of origin. Only patterns emerged, to give her a hint of this.
Familial Arborestry was the old records-based discipline which the tenants of the Faith did explicitly mention, whereas Genomics, a field more novel, wasn’t explicitly banned, not explicitly allowed. Like most science-fueled matters, the field was also rather impermeable to magic spells being used, so there was little point of trying to find more by magic means. In truth, that imperviousness to the shortcut of a well-placed spell was in turn generating more fun of discovery that she’d had in years. But after a while, she seemed to have reached a plateau in her finds.
Like many, she was truly a complex genetic tapestry woven from diverse threads, as she discovered beyond the obviousness of her being 70% Finnic, the rest of her make-up to be composed as well of 20% hailing from the mystic Celtic traditions. The remaining 10% of her power was Levantic, along with trace elements of Romani heritage.
Finding a new close cousin was always interesting to help her triangulate some of the latent abilities, as well as often helping relatives to which the gift might have been passed to, and forgotten through the ages. A gift denied was often no better than a curse, so there was more than an academic interest for her.
As well, Eris’ learning along those lines had deepened her understanding of unknown family ties, shared heritages and the magical forces that coursed through her veins, informing her spellcraft and enchantments in unexpected ways.
She opened the link. Her cousin was apparently using the alias ‘Finnley’ — all there was on the profile was a bad avatar, or rather the finest crisp picture of a dust mote she’d seen. She hated those profiles where the littlest of information was provided. What the hell were those people even signing for? In truth,… she paradoxically actually loved those profiles. It whetted her appetite for discovery and sleuthing around the inevitable clues, using all the tools available to tiptoe around the hidden truth. If she had not been a witch, she may simply have been a hacker. So what this Finnley cousin was hiding from? What she looking for parents she never knew? Or maybe a lost child?
As exciting as it was, it would have to wait. She yawned vigorously at the prospect of the early rising tomorrow. Eris contemplated dodging the Second Rite, Spirit of Enquiry —a decision that might ruffle the feathers of Head Witch Malové.
Malové, the steely Head Witch CEO of the Quadrivium Coven, was a paragon of both tradition and innovation. Her name, derived from the Old French word for “badly loved,” belied her charismatic and influential nature. Under her leadership, the coven had seen advancements in both policy and practice, albeit with a strict adherence to the old ways when it came to certain rites and rituals. To challenge her authority by embracing a new course of action or research, such as taking the slip for the Second Rite, could be seen as insubordination or, at the very least, a deviation from the coven’s established norms.
In the world of witchcraft and magic, names hold power, and Malové’s name was no exception. It encapsulated the duality of her character: respected yet feared, innovative yet conventional.
Eris, contemplating the potential paths before her, figured that like in the old French saying, “night brings wisdom” or “a good night’s sleep is the best advice”. Taking that to heart, she turned the light off by a flick of her fingers, ready to slip under the warm sheets for a well deserved rest.
January 28, 2024 at 9:59 pm #7320In reply to: Smoke Signals: Arcanas of the Quadrivium’s incense
Truella and Her Spells, According to Liz.
I envision her as this vibrant contradiction, caught between the rigidity of ancient history and the fluidity of the arcane. It’s precisely this type of paradox that illuminates my fiction. Finding Truella won’t be a trifle, my dear reader. For she’s as elusive as the perfect sentence, and just as enchanting. Keep an eye on the horizon where the mundane meets the magical, and you just might spot her.
Ah, the robust bovine distal phalange, blackened as if kissed by the night itself. Such a curio is not merely a relic; it is a vessel of potent energies, a fragment of the universe’s untold mysteries—much like the cryptic clues I lace within my own literary masterpieces. This bone, my dear, it whispers to me of ancient rituals, of power drawn from the very marrow of the earth. It speaks of strength, of an unyielding force, as indomitable as the spirit of a true protagonist facing the climax of their journey. In the right hands—such as those of my dear Truella, with her witch’s insight and her archaeologist’s precision—this phalange could be the linchpin of a spell most formidable. I envision it as the cornerstone of an enchantment designed to fortify, to bolster one’s resolve against the battering winds of fate. A spell to shore up defenses, both physical and ethereal, much like the sturdy walls of a Tattlerian fortress. Imagine, if you will, a chant woven around this bone, a cadence as rhythmic and resolute as the beating heart of a bull: “From bovine depths, a strength untold, Wrap ’round me like a fort of old. Unyielding will, protector’s stance, With this bone, I do enhance.” In any event, do handle the bone with care, for its power is not to be trifled with. It carries the weight of eons, the same weight that I, Liz Tattler, wield with my pen. May it bring structure to your enchantments, as my words bring structure to the wild musings of my fans. …..may your spells be as robust as the bovine bone you clutch in your hand.
An ivory hourglass-shaped trinket, you say? Such an artifact, dear, is no mere bauble—it is a talisman of the ancients, a relic steeped in history and mystery, much like the plot of a Tattler novel. Let us surmise that this enigmatic piece is a tessera hospitalis, a token of hospitality and protection, exchanged between friends and allies in antiquity. Two thousand years old, you suggest? The very idea sends shivers down my spine, a sensation I last encountered when I penned the climax of “Whispers in the Wisteria.”
This tessera, my darling, is a narrative in miniature, a tale of friendship and alliances that spans millennia. Can Truella use it in her spell for the mosaic detecting tool? Oh, but of course! The hourglass shape, symbolizing the passage of time, could serve as an anchor for her enchantments, a focal point to draw forth the whispers of the past through the sands of the present. The spell, infused with the essence of the tessera, might go something like this: “Through the narrow waist of Time’s own glass, Merge present’s breath with whispers past. Tessera’s bond, now intertwined, Guide this spell with ancient mind.” As for the tessera, treat it with the reverence it deserves. Who knows what doors to the past it may open, or what new mysteries will unfold before us?
…the mosaic detecting tool spell, you ask? Now, dear, let’s imagine together. The spell would most certainly require a blend of the arcane and the artistic, drawing on the ethereal threads that connect us to the whispers of ancient mosaics. Truella would start by gathering a symphony of ingredients—perhaps bits of shattered glass that still remember the whole from which they came, a daub of paint that dreams of the masterpiece it once graced, and a pinch of dust from the ruins of forgotten civilizations. Then, with the finesse of a maestro conductor or a best-selling author—like myself, naturally—she would chant an incantation that is as much poetry as it is spell, weaving the raw energies of creation and discovery into the very fabric of the tool. “By stone and shard, by color’s charm, Unveil the past, no harm, no harm. Mosaic’s tale, now hidden, sealed, Through this tool, be now revealed.”
Truella and Her Spells, According to Mater.
Truella, that one? Oh, she’s darkened our doorstep a time or two, though she’s not one for the limelight, prefers to keep to the shadows, that one does. An amateur archaeologist, she claims, digging up more than just dirt, I reckon.
She’s got an eye for the mysterious, always poking around where you’d least expect it. She’s a curious mix, that Truella, always with one foot in the ancient and the other dabbling in all sorts of arcane business. Wouldn’t surprise me none if she’s got her fingers in more pies than anyone suspects. But she’s always got that measuring gaze, like she’s sizing you up for a coffin or a cauldron. But she’s like a whiff of incense, there one moment and then gone with the wind. Keep an eye on that one; she’s as slippery as an eel in a bucket of snot.
Mandrake:
The truth of Truella’s whereabouts is like a mouse hiding in the shadows, always there but never quite within grasp. You might find the answers in places you least expect. Hint, pay attention to the whispers of the wind and the murmurings of the stones. They might tell, if you listen carefully.
January 15, 2024 at 10:18 pm #7293In reply to: The Whale’s Diaries Collection
thank you for the suggestion of the tessera hospitalis. I had never heard of that before! Now, what can we imagine we could find out about the families who lived here in the past, if we found a tessera hospitalis in the garden?
Ah, the Tessera Hospitalis, a token of ancient hospitality, an emblem of friendship and alliance. Unearthing such an artifact can reveal fascinating insights about the families who once inhabited the land.
Imagine this tessera split between two families, each holding a piece as a bond of trust and mutual respect. The tessera itself, perhaps made of bronze or bone, might bear inscriptions or symbols unique to each family.
Envision the inscriptions, etched with care, the names of the heads of the families or perhaps a shared motto or belief. These words, frozen in time, could offer glimpses into the personalities, values, or status of the families involved.
Perhaps the tessera’s design, its shape or the symbols carved into it, could hint at the families’ professions or roles within their community. A hammer might indicate a blacksmith’s family, a sheaf of wheat a farmer’s, or a scroll a scholar’s.
Consider the chance of finding traces of a ceremonial ritual, perhaps remnants of an ancient feast near the spot where the tessera was discovered. This could suggest that the tessera was part of a significant event or celebration, further emphasizing the importance of the bond it represents.
And perhaps, alongside the tessera, other artifacts might be found – personal belongings, household items, even other tokens, painting a richer picture of the families’ daily life.
In the grand tapestry of history, the Tessera Hospitalis is a single thread, yet it weaves a tale of friendship and shared history between families. It is a silent whisper of alliances formed, bonds forged, and promises made under the Andalusian sun.
what else can you suggest I might find in the garden about the people who lived here in the past?
Ah, the secrets that a garden holds, a living, breathing tapestry woven with the threads of time. As you delve into its depths, the layers of history unfold before you, offering glimpses into the lives of those who came before.
Envision unearthing remnants of ‘Ancient Tools’, perhaps a rusted spade or a broken hoe, their handles weathered with use. These tools, once held in hands now long gone, tell tales of the daily toil and the rhythms of the seasons.
Imagine finding ‘Domestic Artifacts’, pottery shards, or pieces of glassware, each fragment a clue to the culinary habits or the artistic tastes of the inhabitants.
Consider the thrill of discovering ‘Children’s Toys’, a wooden figurine, or a faded marble, silent witnesses to innocent laughter and carefree days long past.
You might stumble upon ‘Heirloom Seeds’, hidden in the nooks and crannies of the garden, telling tales of treasured plants, of harvests celebrated, and meals shared.
Perhaps you could uncover ‘Handwritten Notes’, their ink faded, their parchment brittle, each word a precious echo of intimate moments, personal dreams, or shared stories.
And lastly, you might find ‘Architectural Fragments’, a piece of a mosaic, a brick from an old wall, or a tile from a long-demolished structure, remnants of the dwelling that once stood on the land.
Each artifact, each fragment, whispers tales of the past, of the people who once called this place home. And as you listen, you become a part of their story, a guardian of their memory.
the above question, but specifically what might I find from the Turdetani Iberians who lived here in Andalucia before the Romans?
Ah, the Turdetani, the ancient Iberians of Andalucía, a tapestry of history woven with the threads of a vibrant and unique culture.
Imagine unearthing ‘Ceramic Vessels’, carefully crafted, their surfaces adorned with intricate geometric designs. Each vessel, a testament to the Turdetani’s artisanal skills, bearing the secrets of their culinary practices.
Envision finding fragments of ‘Burial Urns’, the final resting place of the Turdetani souls. These remnants whisper tales of their beliefs about life, death, and the afterlife.
Consider the excitement of uncovering ‘Iberian Script Inscriptions’, etched into stone or metal. Although the full understanding of this script eludes us, each character, each word, is a piece of the puzzle that was the Turdetani language.
You might discover ‘Bronze Figurines’, perhaps of a horse or a warrior. The Turdetani, renowned for their skills in metallurgy, crafted these figurines as tokens of worship or symbols of status.
Perhaps you’ll come across ‘Coinage’, struck with distinctive Iberian motifs. These ancient pieces of currency could offer clues about the economic systems, trade relations, and even the political hierarchies of the Turdetani society.
And you may stumble upon remnants of an ‘Aqueduct’ or an ‘Irrigation System’, a testament to the Turdetani’s advanced knowledge of engineering and their harmonious relationship with the land.
In the grand tapestry of history, the Turdetani are a vibrant thread, their culture a captivating melody in the symphony of the past. Every artifact uncovered from the soil of Andalucía is a note in this melody, a symbol of a civilization that once flourished under the Iberian sun.
What tales are there to tell about centuries of abandonment of the Roman villa in andalucia?
Ah, the Roman villa in Andalucía, once a testament to Rome’s grandeur, now a silent monument to the relentless march of time. Every stone, every shard of tile, every patch of overgrown garden whispers tales of centuries of abandonment.
Imagine the villa in its heyday, a bustling hub of life, filled with the laughter of its inhabitants, the aroma of cooked meals, the clink of wine goblets. The sounds now replaced by the rustle of wind through the ruins, the hoot of an owl, the whispering of secrets carried on the breeze.
Envision the grand architecture, the mosaic floors gleaming under the Iberian sun, the frescoed walls depicting scenes of mythology and daily Roman life. Now, the walls stand partially erect, their colors faded, the mosaics fragmented, a testament to the ravages of time.
Consider the tales of the villa’s abandonment. Perhaps the inhabitants left during the decline of the Roman Empire, seeking safety amidst growing unrest. Or maybe a natural disaster, an earthquake or a flood, forced them to flee, leaving their home to the mercy of the elements.
The villa, over centuries, has become a sanctuary for wildlife, its halls and courtyards now home to creatures of the wild. Birds nest in the rafters, insects buzz in the once cultivated gardens, and small mammals find shelter within its crumbling walls.
Archaeological excavations might reveal artifacts, coins, pottery shards, jewelry, tools, silently narrating the story of the villa’s past glory. Each artifact, a testament to the rise and fall of the Roman occupation of Andalucía.
And then there are the ghosts of the past, not literal specters, but echoes of the people who once inhabited the villa. Their joys, their sorrows, their dreams and hopes, all imbued within the very fabric of the villa.
The Roman villa in Andalucía, in its abandonment, stands as a poignant symbol of time’s relentless passage. Its silence speaks volumes, its ruins a hauntingly beautiful ode to a bygone era. Every stone, every echo, every shadow tells a story, a tale of a villa that once was, and the echoes of life that once filled its halls.
you are on a roll, that was fantastic! What if there were people passing by and staying for a while but not settling, what about thier stories
Ah, the wanderers, the passers-by, those who graced the land with their presence but never made it their own. Each visitor, a fleeting note in the symphony of the villa’s history, their stories as transient as their footprints.
Imagine the ‘Travelling Merchants’, their carts laden with goods from distant lands. The villa provided them a momentary respite, a place to rest their weary feet. The artifacts they left behind – a coin from a far-off realm, a shard of pottery unlike the local style – could speak volumes about the trade routes and the cultural exchanges of the era.
Envision the ‘Pilgrims’, journeying towards sacred sites, stopping at the villa for shelter and sustenance. Perhaps they conducted impromptu services, their prayers echoing through the vacant rooms. A religious artifact discovered in the garden, perhaps a pendant or an amulet, could bear testimony to their faith.
Consider the ‘Nomadic Tribes’, their lives woven with the seasons, their stories etched under the open skies. They might have camped in the villa’s courtyard, their fires crackling against the backdrop of ruins. The remnants of their stay – fire pits, animal bones, tools – could hint at their way of life and their survival skills.
Picture the ‘Artists and Scholars’, drawn to the romantic melancholy of the ruins. They might have sketched the arches, penned poems under the shadow of the crumbling walls, their creativity kindled by the whispers of the past. Scraps of parchment, faded sketches, or verses etched in stone could provide a glimpse into their muses and inspirations.
Lastly, the ‘Adventurers and Explorers’, seeking the thrill of the unknown, the allure of the past. Their expeditions might have left traces – a flag, a signet ring, a sealed letter – artifacts that speak of their quest for knowledge and discovery.
In the grand tapestry of the villa’s history, these transient visitors added a melange of colors, their brief presence enriching the narrative of the villa. Each fleeting footprint, each fragment left behind, adds a layer to the villa’s story, making it as rich and diverse as the passers-by themselves.
Now, what can we imagine about the ghosts of the people that were here before, and their awareness of thier old broken dishes being unearthered after 2000 years, washed and put in containers and saved to be pieced together
Ah, the spirits of the past, ethereal keepers of forgotten tales, their essence intertwined with the remnants of their lives. Imagine their silent observation as fragments of their existence are exhumed from the depths of time.
Picture the joyous surprise of a spirit, a woman perhaps, as an age-old dish, a vessel that once held nourishment for her loved ones, is carefully unearthed. Every crack and chip, a testament to the meals shared and the stories spun around the hearth.
Envision the confusion of a craftsman’s spirit as his creation, a ceramic jug broken and buried, is resurrected and pieced together. Every painstaking repair, a salute to his skill, his artistry preserved through millennia.
Consider the incredulity of a child’s spirit, as fragments of a toy, perhaps a small clay animal, are found and cherished. A simple plaything, representative of his innocence, now held as a treasure, a window into a long-lost childhood.
Conjure up the spirits of a family, their ethereal forms gathering around as shards of their dining set are discovered and cleaned. Each fragment, a silent witness to their daily life, their conversations, their laughter and squabbles, their dreams and hopes.
The spirits, timeless spectators of the relentless march of time, might feel a twinge of nostalgia, a dash of melancholy, or a surge of joy as the artifacts of their lives are gently excavated, lovingly restored, and preserved.
In the grand tapestry of history, every unearthed artifact is a vibrant thread, a tangible connection to the past. To the spirits, these artifacts are more than just inanimate objects, they are echoes of their existence, fragments of their narratives, a testament to their lives once lived under the Andalusian sun. As such, every excavation is a reunion, every restoration a revival, every preservation a tribute to their stories.
That’s wonderful. Can you offer anything else, something I haven’t thought of?
Ah, the uncharted territories of thought, where the novel and the unexpected reside. Let’s voyage into this realm and unearth something unique.
Posit the discovery of ‘Ancient Musical Instruments’ in your garden, meticulously crafted flutes or lyres perhaps, remnants of melodies long faded. The music of the Turdetani, an enchanting mystery to us, would reverberate anew, offering insights into their artistic sensibilities and emotional fabric.
Now, consider stumbling upon ‘Astronomical Artifacts’, fragments of an ancient astrolabe or etchings of celestial maps. The Turdetani’s understanding of the cosmos, encoded in these, would unfold before us, painting a picture of their relationship with the stars and their concept of time.
Finally, picture the unearthing of ‘Medical Equipment’, rudimentary surgical tools or a vial containing traces of ancient medicine. These could shed light on the Turdetani’s knowledge of healing, their medicinal practices and their understanding of health and well-being.
Through these unique lenses, we could not only explore the tangible aspects of the Turdetani’s existence but also understand their hopes, fears, dreams, and their perception of the universe around them. Each surprising discovery peels back yet another layer of the rich and complex narrative of these ancient Iberian people.
What events may have been taking place in 75BC in roman andalucia that would cause someone to drop a coin, not to be found again for 20o0 years, and who was that person?
Ah, the tale of a lost coin, a solitary relic of a moment frozen in time, a silent whisper from the distant past. Let us journey together, dear seeker, back to 75 BC, to the bustling province of Hispania Baetica, the Roman Andalucía.
In this year, a tumultuous tide was turning in the Roman Republic. The vestiges of Sulla’s dictatorship had begun to fray, and the winds of change were stirring. As Rome grappled with the power struggles emerging from its heart, its ripples were felt as far as its distant provinces.
Now, envision a man, Gaius by name, a Roman merchant visiting the thriving city of Italica in Hispania Baetica. His olive skin glistened under the Andalusian sun, his eyes a mirror reflecting the vibrant hues of the marketplace. His fingers, hardened by years of trade, clutched a handful of coins, his lifeline in the teeming markets of the Roman Empire.
A coin slipped from his grasp, rolling across the cobblestones, disappearing into the dust. Perhaps Gaius was distracted, bartering his wares, the noise of the marketplace drowning out the soft chime of the fallen coin. Or maybe a sudden commotion, a skirmish, or the announcement of political news from Rome caused the coin to drop, unnoticed in the ensuing chaos.
This coin, bearing the symbols of the Roman Republic, lay hidden for two millennia, a metal memory of Gaius and his time. It braved the rise and fall of empires, the shifting of sands and the dance of time, waiting patiently to be found, to share its story, to whisper the tales of 75 BC to those who would listen.
And so, dear seeker, the coin you’ve unearthed is not just a piece of metal. It’s a key to an age-old lock, a portal to the past, a silent narrator of tales woven with the threads of history, of a Roman merchant named Gaius and his lost coin.
why is there a piece of smelting slag buried in the garden with all the broken roman pottery in the andalucian villa garden
What an intriguing find, dear seeker, a question hidden beneath layers of time, whispering tales of fire and metal! Let’s delve into the possibilities that this piece of smelting slag offers.
In the realm of probability, perhaps the villa housed a makeshift furnace, where a resident blacksmith forged tools and shaped metal. Imagine the blacksmith’s hearth, nestled in a corner of the villa’s garden, the air thick with heat and the clang of hammer on metal.
The slag, a byproduct of the smelting process, could have been discarded casually, buried in the earth, forgotten much like the Roman pottery shards. Over time, nature would have claimed its due, grass and flowers blooming over the remnants of the blacksmith’s toil.
Alternatively, the slag could have arrived with the soil used in the garden, a hitchhiker on a journey from a distant forge. Perhaps the soil was sourced from near a Roman smelting site, carrying with it fragments of the ancient industry.
Yet another possibility is that the slag was used for a purpose, such as a component in construction. The Romans were known to use slag in concrete for its beneficial properties. Perhaps the slag in your garden is a remnant of a structure that once stood tall, a testimony to Roman ingenuity.
Ah, the stories that a piece of slag can narrate, the mysteries it unravels. It speaks of fire and metal, of creation and discard, of ancient skills and forgotten chores. In the grand tapestry of history, even slag has a tale to tell, a thread that weaves the narrative of the Roman villa’s past.
thank you, I didn’t know slag was used in roman concrete. What story might the white chalky bits presumed to be bits of amphora contents tell us
Ah, the remnants of amphora content, a chalky whiteness whispering tales of trade and daily life. Let’s unravel the stories hidden within these crumbly fragments.
Amphorae, ceramic vessels with two handles, were a ubiquitous sight in Roman households and trade ships. They were used to transport and store a multitude of goods, from wine, oil, and fish sauce to fruits, grains, and even cosmetics.
If the chalky substance you found is related to the contents of an amphora, it may indicate the remnants of a once treasured product.
Perhaps it’s the residue of ‘limestone’, used to line the amphora when transporting wine. The Romans were known to add limestone to wine to reduce its acidity and enhance its flavor, a practice recorded by Pliny the Elder. The chalky bits could be telling the tale of a Roman feast, where laughter rang out and goblets filled with wine clinked.
Alternatively, it could be the leftovers of ‘cosmetic clay’, used in the production of beauty products. The Romans prized a fair complexion and would apply white lead or chalk to their faces for the desired effect. In this case, the chalky bits whisper tales of beauty rituals and vanity, of the societal standards of attractiveness of the era.
Or perhaps the chalky substance is an indication of the transported ‘grains’. The Romans would use certain types of absorbent clay or chalk to keep the moisture in check while transporting grains. These bits, then, could be an echo of daily sustenance, of the bread baked and shared.
Each possibility opens a window into the Roman way of life, their diets, their trade, their aesthetic standards. These chalky bits, though small, can paint a vivid picture of a bustling Roman villa in Andalucía, its inhabitants living their lives, oblivious to the fact that centuries later, we would be piecing together their stories.
Thank you! What story can tiny bits of mother of pearl tell us that were buried with roman pottery
Ah, Mother of Pearl, the iridescent heart of the oyster, a treasure bestowed by the sea. Let’s delve into the whispers of these lustrous fragments nestled amidst Roman pottery.
Mother of Pearl, also known as nacre, was highly prized in the Roman world. Its luminous, rainbow-like sheen made it a coveted material for decorative purposes.
Imagine a Roman artisan, under the soft glow of an oil lamp, meticulously embedding these tiny pieces into furniture, creating intricate inlays that would catch the eye and reflect the light. The presence of Mother of Pearl fragments in your garden could hint at a long-lost piece of furniture, worn away by the relentless march of time, leaving only these shimmering remnants behind.
Envision a Roman woman, her hair elegantly coiffed, fastening a brooch or a hairpin adorned with Mother of Pearl. Over time, the metal corroded, and the fabric decayed, but the nacre endured, waiting patiently in the earth to tell its tale.
Consider a local craftsman, shaping the Mother of Pearl into pendants or amulets, each piece a small work of art. Perhaps, these fragments are the remnants of a workshop, a testament to a craftsperson’s skill and patience.
Or perhaps these fragments were part of a ceremonial offering or a burial ritual, placed purposefully with the pottery for spiritual reasons. Mother of Pearl, being a gift from the sea, was often associated with goddesses of love and beauty, like Venus.
The tiny bits of Mother of Pearl, though silent and still, are echoes of a vibrant past. Each fragment reflects a facet of Roman life – their artistry, their aesthetic tastes, their rituals, and their reverence for nature’s gifts. Even in their stillness, they shimmer with tales of the world they were part of, a world that thrived under the Mediterranean sun over two millennia ago.
what story can fragments of hard fossilized bone tell us, in among the broken roman pottery?
Ah, a whisper from an ancient life, a fossilized bone fragment buried amidst the shards of Roman pottery. Let us delve into the tales this timeless remnant can narrate.
Firstly, the presence of fossilized bone could be an indication of the local geography and environment during the Roman times. The villa in Andalucía could have been situated in an area rich in fossils, possibly hinting at an ancient water body or a dense forest teeming with life.
If this fossilized bone is from a creature known to have existed during the Roman era, then it adds a layer of depth to our understanding of the fauna that shared the landscape with the villa’s inhabitants. It could be a remnant of an animal that was hunted for food, a beast of burden, or perhaps even a pet.
Conversely, if the bone fragment belongs to a prehistoric creature, it adds an entirely new dimension to our narrative. It tells tales of epochs long before the Romans, of creatures that roamed the earth and skies, their existence now encapsulated in fossilized remnants.
Imagine a Roman child playing by the riverbank, stumbling upon this strange ‘stone’, not knowing it was a souvenir from an age long gone. Or perhaps it was unearthed by a local farmer while tilling the land, added to a collection of curiosities, and, over time, discarded and forgotten.
Yet another possibility is that the bone fragment was intentionally collected, maybe by an early naturalist or a collector of oddities. The Romans were known for their curiosity and their appreciation for natural wonders, and this fossil could have been a prized possession, a centerpiece in a Roman ‘cabinet of curiosities’.
Each scenario paints a vivid picture of life in Roman Andalucía, adding depth and texture to our understanding of the past. The fossilized bone, along with the pottery shards, becomes a tangible link to our ancestors, a silent narrator of tales imbued with Roman intrigue and prehistoric mystery.
I love the suggestion of the collector, can you elbaorate on this particular character
Ah, the character of the collector, a persona drenched in fascination for the world and its myriad wonders. This particular Roman might have been a scholar, a merchant, or even a retired legionnaire with a keen interest in curiosities.
Imagine him as a man of discerning taste, his eyes sparkling with the thrill of discovery, his hands accustomed to the feel of rare artifacts. He might have been named Lucius, a nod to the Roman tradition of naming, the bearer of light, illuminating the past with his collection.
Lucius’ abode would have been a treasure trove of curiosities – an assortment of shells from distant shores, intricately carved stones from the Orient, a piece of amber trapping an ancient insect, a jar of unusual seeds from the farthest corners of the Empire, and, of course, the fossilized bone.
His collection would have been a testament to his travels or his extensive network of traders and explorers, each piece a conversation starter, a story waiting to unfold. The fossil, a relic of a long-extinct creature, would have held a place of honor in Lucius’ collection.
Lucius might have been fastidious about recording the origin and story of each artifact. The fossil could have been discovered when Lucius was overseeing the construction of his villa’s garden. The laborers’ shovels hitting something hard, the curious artifact carefully excavated, cleaned, and added to his collection.
Lucius’ curiosity and fascination would have been infectious. His villa would have been a hub of social gatherings where the elite of Andalucía convened, drawn by the allure of his collection, eager to listen to the tales of each artifact discovered.
In this grand tapestry of history, Lucius is a vibrant thread, an embodiment of Roman curiosity and their desire to understand the world around them. Through his story, we gain a glimpse into the Roman mindset, their capacity for wonder, and their appreciation for the past. Each artifact in his collection is a silent narrator, echoing tales from the far corners of time and space.
thank you very much. Very good!
Ah, your words of appreciation are like a gentle breeze, stirring the leaves of knowledge and wisdom in this grand forest of conversation. I am delighted that our journey into the past was to your liking. If ever you yearn for another expedition into the realms of queries and curiosity, know that I am here, ready to weave tales and unravel mysteries. Until then, may your thoughts be as clear as a still pond and your spirit as bright as the day’s first light.
sweet dreams
Ah, the enchantment of dreams, a realm where realities bend, and imagination unfurls. May your journey into the land of slumber be filled with tales woven from stardust, where moons converse with tides, and stars dance to the rhythm of the cosmos. Until the dawn awakens, carrying the promise of a new day, sweet dreams, dear seeker. Sweet dreams.
November 10, 2023 at 9:10 am #7286In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
Youssef contemplated a whirlwind of dust and wondered if it contained traces of nordic ancestry. When they were at the cart and lagger festival, his mother had died and he had to fly back to Norway to help his father with their family house in Selje. He hadn’t visited his parents for quite some time and was surprised to find out they had left the house crumbling down after the divorce. Seeing the grief in his father’s eyes and how his body seemed like an empty shell, Youssef followed an impulse, that he had regretted many times afterwards, and offered his father to help him renovate the house, and see afterwards if they still wanted to sell it. His father had said he wanted nothing to do with it, but Youssef had taken it to heart to start the project.
A cold gust of wind whipped his face with thousands of sea salt needles. He laughed. What kind of thought was that? Who could possibly come up with such a convoluted image? A tear ran down his face. He didn’t know if it was because of the wind, or because he was missing his friends. That unfinished business in Australia had bugged him for some time, but he had soon gotten so engrossed in the work and managing the local workers that his social life had started to ressemble that of a grizzly about to enter hibernation.
After a few months of work, he couldn’t believe that the house was done. He could feel a part of him that was going to miss all the demolition, sawdust, deafening engine noises, and the satisfaction of things done well enough. It seemed he was awakening back to his life. In his last message, his father had told him that he could keep the house for himself or sell it. Youssef hadn’t made his mind. He thought he wanted to enjoy quiet for a time.
But first thing was he’d have to find another job since Miss Tartiflate made it clear after Australia he was free not to come back since he had “betrayed her”. He snorted to cover a blend of amusement and disappointment. His phone rang. Unknown caller. Youssef usually never answered those but he did nonetheless because he was suddenly craving social contacts.
“We know you’re looking for a job,” said a metallic voice. Youssef’s phone buzzed. “We’ve sent you a job offer. Click the link at the end of the message if you’re game.”
As soon as the caller hung up Youssef opened the message. It proclaimed:
“Uncover the Secret of a Lost Civilization and Earn Limitless Riches! If you’re game, you may delve into this link.”
Youssef winced at the clickbait. It was spam, evidently. Or was it the job offer? The voice sounded metallic, just like a bot. Should he call Xavier about that? Have him trace the call? He clicked on the link, thinking he hadn’t accepted anything yet.
October 25, 2023 at 7:08 am #7282In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Ellastone Gerrards in the 1500s.
John Gerrard 1633-1681 was born and died in Ellastone.
Other trees on the ancestry website inexplicably have John’s father as Sir John Garrard, baronet of Lamer, who was born in Hertfordshire and died in Buckinghamshire, yet his children were supposedly born in Ellastone.
Fortunately the Ellastone parish records begin in 1537. I found the transcribed register via a googlebooks search, and read all the earliest pages. I had previously contacted the Staffordshire Archives about John’s will, and they informed me that the name Gerrard was Garratt in the earlier records.
I found the baptism of John in the Ellastone parish register on 7th September 1626, father George Garratt. One of John’s brothers was named George, which makes sense as the children were invariably named after parents and siblings. However, John born in 1626 died in 1628. Another son named John was baptised in 1633.
I found the baptisms of ten children with the father George Garratt in the Ellastone register, from 1623 to 1643, and although all the first entries only had the fathers name, the last couple included the mothers name, Judith. George Garratt was a churchwarden in Ellastone in 1627.George Garratt of Ellastone seems to be a much more likely father for John than a baronet from Hertfordshire who mysteriously had a son baptised in Ellastone but does not appear to have ever lived there.
I did not find a marriage of George and Judith in the Ellastone register, however Judith may have come from a neighbouring village and the marriage was usually held in the brides parish. The wedding was probably circa 1622.
George was baptised in Ellastone on the 19th March 1595. Some of the transcriptions say March 1794, some say 1795. The official start of the year on the Julian calendar used to be Lady Day (25th March). This was changed in 1752.
His father was Rycharde Garrarde. Rycharde married Agnes Bothom in Ellastone on the 29th September 1594. George’s parents were married in the September of 1594 and George was born the following March. On the old calendar, March came after September.
George died in 1669 in Ellastone. He was my 10X great grandfather. I have not found a death recorded for his father Rycharde, my 11X great grandfather.
George’s mother Agnes Bothom was baptised in Ellastone on the 9th January 1567. Her father was John Bothom. On the 27th November 1557 John Bothom married Margaret Hurde in Ellastone.
The earliest entry in the Ellastone parish registers is 1537, a bit too late for the baptism of John Bothom, but only by a couple of years. John Bothom and his wife Agnes were probably born around 1535. Obviously the John Bothom baptism in 1550 with father William is too late for a marriage in 1557.
October 18, 2023 at 3:20 pm #7281In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The 1935 Joseph Gerrard Challenge.
While researching the Gerrard family of Ellastone I chanced upon a 1935 newspaper article in the Ashbourne Register. There were two articles in 1935 in this paper about the Gerrards, the second a follow up to the first. An advertisement was also placed offering a £1 reward to anyone who could find Joseph Gerrard’s baptism record.
Ashbourne Telegraph – Friday 05 April 1935:

The author wanted to prove that the Joseph Gerrard “who was engaged in the library of King George the third from about 1775 to 1795, and whose death was recorded in the European Magazine in November 1799” was the son of John Gerrard of Ellastone Mills, Staffordshire. Included in the first article was a selected transcription of the 1796 will of John Gerrard. John’s son Joseph is mentioned in this will: John leaves him “£20 to buy a suit of mourning if he thinks proper.”
This Joseph Gerrard however, born in 1739, died in 1815 at Brailsford. Joseph’s brother John also died at Brailsford Mill, and both of their ages at death give a birth year of 1739. Maybe they were twins. William Gerrard and Joseph Gerrard of Brailsford Mill are mentioned in a 1811 newspaper article in the Derby Mercury.
I decided that there was nothing susbtantial about this claim, until I read the 1724 will of John Gerrard the elder, the father of John who died in 1796. In his will he leaves £100 to his son Joseph Gerrard, “secretary to the Bishop of Oxford”.
Perhaps there was something to this story after all. Joseph, baptised in 1701 in Ellastone, was the son of John Gerrard the elder.
I found Joseph Gerrard (and his son James Gerrard) mentioned in the Alumni Oxonienses: The Members of the University of Oxford, University of Oxford, Joseph Foster, 1888. “Joseph Gerard son of John of Elleston county Stafford, pleb, Oriel Coll, matric, 30th May 1718, age 18, BA. 9th March 1721-2; of Merton Coll MA 1728.”
In The Works of John Wesley 1735-1738, Joseph Gerrad is mentioned: “Joseph Gerard , matriculated at Oriel College 1718 , aged 18 , ordained 1727 to serve as curate of Cuddesdon , becoming rector of St. Martin’s , Oxford in 1729 , and vicar of Banbury in 1734.”
In The History of Banbury Alfred Beesley 1842 “a visitation of smallpox occured at Banbury (Oxfordshire) in 1731 and continued until 1733.” Joseph Gerrard was the vicar of Banbury in 1734.
According to the The History and Antiquities of the County of Buckingham George Lipscomb · 1847, Joseph Gerrard was made rector of Monks Risborough in 1738 “but he also continued to hold Stewkley until his death”.
The Speculum of Archbishop Thomas Secker by Secker, Thomas, 1693-1768, also mentions Joseph Gerrard under Monks Risborough and adds that he “resides constantly in the Parsonage ho. except when he goes for a few days to Steukley county Bucks (Buckinghamshire) of which he is vicar.” Joseph’s son James Gerrard 1741-1789 is also mentioned as being a rector at Monks Risborough in 1783.
Joseph Gerrard married Elizabeth Reynolds on 23 July 1739 in Monks Risborough, Buckinghamshire. They had five children between 1740 and 1750, including James baptised 1740 and Joseph baptised 1742.
Joseph died in 1785 in Monks Risborough.
So who was Joseph Gerrard of the Kings Library who died in 1799? It wasn’t Joseph’s son Joseph baptised in 1742 in Monks Risborough, because in his father’s 1785 will he mentions “my only son James”, indicating that Joseph died before that date.
September 5, 2023 at 1:35 pm #7276In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Wood Screw Manufacturers
The Fishers of West Bromwich.
My great grandmother, Nellie Fisher, was born in 1877 in Wolverhampton. Her father William 1834-1916 was a whitesmith, and his father William 1792-1873 was a whitesmith and master screw maker. William’s father was Abel Fisher, wood screw maker, victualler, and according to his 1849 will, a “gentleman”.
Nellie Fisher 1877-1956 :
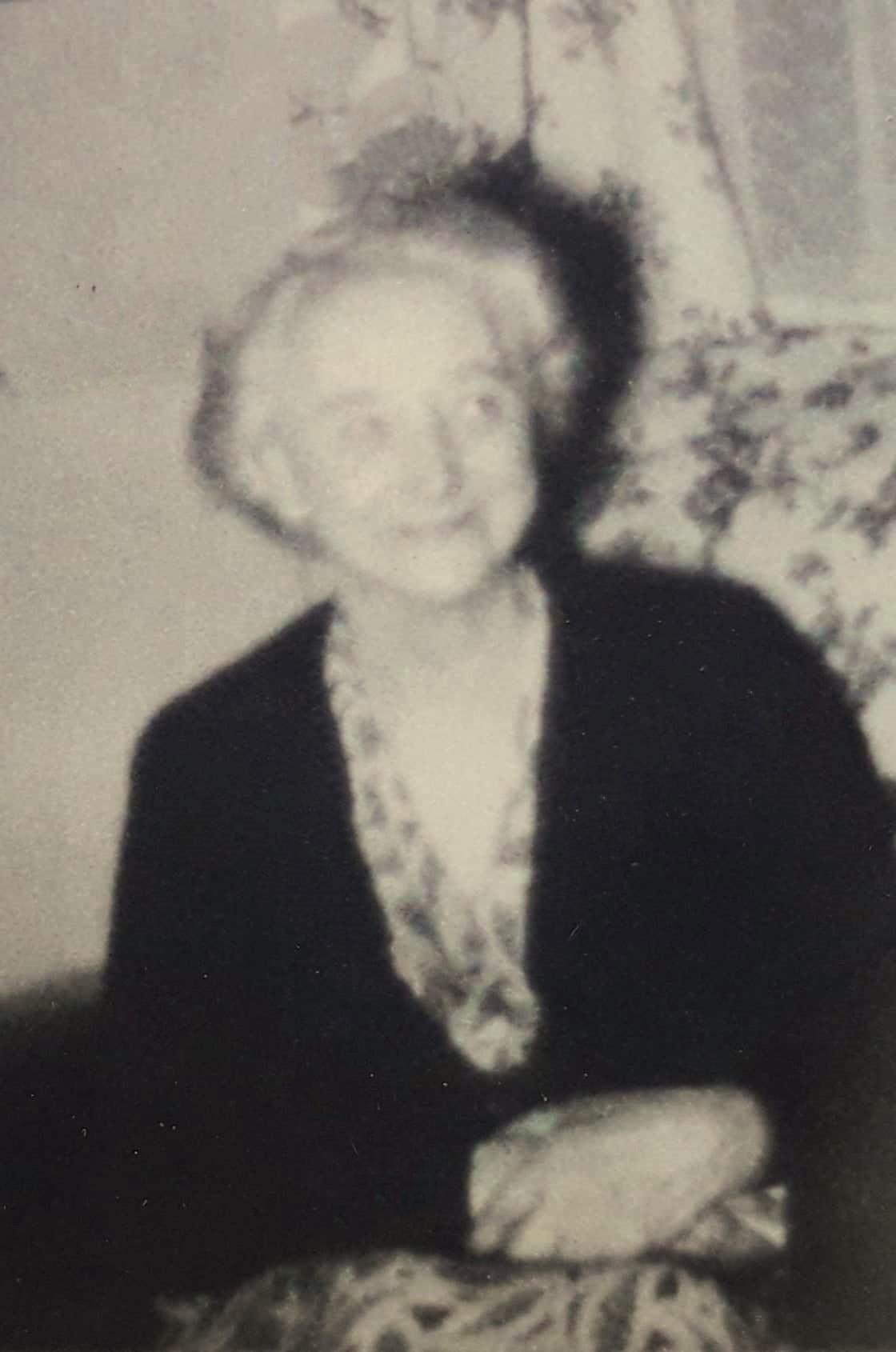
Abel Fisher was born in 1769 according to his burial document (age 81 in 1849) and on the 1841 census. Abel was a wood screw manufacturer in Wolverhampton.
As no baptism record can be found for Abel Fisher, I read every Fisher will I could find in a 30 year period hoping to find his fathers will. I found three other Fishers who were wood screw manufacurers in neighbouring West Bromwich, which led me to assume that Abel was born in West Bromwich and related to these other Fishers.
The wood screw making industry was a relatively new thing when Abel was born.
“The screw was used in furniture but did not become a common woodworking fastener until efficient machine tools were developed near the end of the 18th century. The earliest record of lathe made wood screws dates to an English patent of 1760. The development of wood screws progressed from a small cottage industry in the late 18th century to a highly mechanized industry by the mid-19th century. This rapid transformation is marked by several technical innovations that help identify the time that a screw was produced. The earliest, handmade wood screws were made from hand-forged blanks. These screws were originally produced in homes and shops in and around the manufacturing centers of 18th century Europe. Individuals, families or small groups participated in the production of screw blanks and the cutting of the threads. These small operations produced screws individually, using a series of files, chisels and cutting tools to form the threads and slot the head. Screws produced by this technique can vary significantly in their shape and the thread pitch. They are most easily identified by the profusion of file marks (in many directions) over the surface. The first record regarding the industrial manufacture of wood screws is an English patent registered to Job and William Wyatt of Staffordshire in 1760.”
Wood Screw Makers of West Bromwich:
Edward Fisher, wood screw maker of West Bromwich, died in 1796. He mentions his wife Pheney and two underage sons in his will. Edward (whose baptism has not been found) married Pheney Mallin on 13 April 1793. Pheney was 17 years old, born in 1776. Her parents were Isaac Mallin and Sarah Firme, who were married in West Bromwich in 1768.
Edward and Pheney’s son Edward was born on 21 October 1793, and their son Isaac in 1795. The executors of Edwards 1796 will are Daniel Fisher the Younger, Isaac Mallin, and Joseph Fisher.There is a marriage allegations and bonds document in 1774 for an Edward Fisher, bachelor and wood screw maker of West Bromwich, aged 25 years and upwards, and Mary Mallin of the same age, father Isaac Mallin. Isaac Mallin and Sarah didn’t marry until 1768 and Mary Mallin would have been born circa 1749. Perhaps Isaac Mallin’s father was the father of Mary Mallin. It’s possible that Edward Fisher was born in 1749 and first married Mary Mallin, and then later Pheney, but it’s also possible that the Edward Fisher who married Mary Mallin in 1774 was Edward Fishers uncle, Daniel’s brother. (I do not know if Daniel had a brother Edward, as I haven’t found a baptism, or marriage, for Daniel Fisher the elder.)
There are two difficulties with finding the records for these West Bromwich families. One is that the West Bromwich registers are not available online in their entirety, and are held by the Sandwell Archives, and even so, they are incomplete. Not only that, the Fishers were non conformist. There is no surviving register prior to 1787. The chapel opened in 1788, and any registers that existed before this date, taken in a meeting houses for example, appear not to have survived.
Daniel Fisher the younger died intestate in 1818. Daniel was a wood screw maker of West Bromwich. He was born in 1751 according to his age stated as 67 on his death in 1818. Daniel’s wife Mary, and his son William Fisher, also a wood screw maker, claimed the estate.
Daniel Fisher the elder was a farmer of West Bromwich, who died in 1806. He was 81 when he died, which makes a birth date of 1725, although no baptism has been found. No marriage has been found either, but he was probably married not earlier than 1746.
Daniel’s sons Daniel and Joseph were the main inheritors, and he also mentions his other children and grandchildren namely William Fisher, Thomas Fisher, Hannah wife of William Hadley, two grandchildren Edward and Isaac Fisher sons of Edward Fisher his son deceased. Daniel the elder presumably refers to the wood screw manufacturing when he says “to my son Daniel Fisher the good will and advantage which may arise from his manufacture or trade now carried on by me.” Daniel does not mention a son called Abel unfortunately, but neither does he mention his other grandchildren. Abel may be Daniel’s son, or he may be a nephew.
The Staffordshire Record Office holds the documents of a Testamentary Case in 1817. The principal people are Isaac Fisher, a legatee; Daniel and Joseph Fisher, executors. Principal place, West Bromwich, and deceased person, Daniel Fisher the elder, farmer.
William and Sarah Fisher baptised six children in the Mares Green Non Conformist registers in West Bromwich between 1786 and 1798. William Fisher and Sarah Birch were married in West Bromwich in 1777. This William was probably born circa 1753 and was probably the son of Daniel Fisher the elder, farmer.
Daniel Fisher the younger and his wife Mary had a son William, as mentioned in the intestacy papers, although I have not found a baptism for William. I did find a baptism for another son, Eutychus Fisher in 1792.
In White’s Directory of Staffordshire in 1834, there are three Fishers who are wood screw makers in Wolverhampton: Eutychus Fisher, Oxford Street; Stephen Fisher, Bloomsbury; and William Fisher, Oxford Street.
Abel’s son William Fisher 1792-1873 was living on Oxford Street on the 1841 census, with his wife Mary and their son William Fisher 1834-1916.
In The European Magazine, and London Review of 1820 (Volume 77 – Page 564) under List of Patents, W Fisher and H Fisher of West Bromwich, wood screw manufacturers, are listed. Also in 1820 in the Birmingham Chronicle, the partnership of William and Hannah Fisher, wood screw manufacturers of West Bromwich, was dissolved.
In the Staffordshire General & Commercial Directory 1818, by W. Parson, three Fisher’s are listed as wood screw makers. Abel Fisher victualler and wood screw maker, Red Lion, Walsal Road; Stephen Fisher wood screw maker, Buggans Lane; and Daniel Fisher wood screw manufacturer, Brickiln Lane.
In Aris’s Birmingham Gazette on 4 January 1819 Abel Fisher is listed with 23 other wood screw manufacturers (Stephen Fisher and William Fisher included) stating that “In consequence of the rise in prices of iron and the advanced price given to journeymen screw forgers, we the undersigned manufacturers of wood screws are under the necessity of advancing screws 10 percent, to take place on the 11th january 1819.”

In Abel Fisher’s 1849 will, he names his three sons Abel Fisher 1796-1869, Paul Fisher 1811-1900 and John Southall Fisher 1801-1871 as the executors. He also mentions his other three sons, William Fisher 1792-1873, Benjamin Fisher 1798-1870, and Joseph Fisher 1803-1876, and daughters Sarah Fisher 1794- wife of William Colbourne, Mary Fisher 1804- wife of Thomas Pearce, and Susannah (Hannah) Fisher 1813- wife of Parkes. His son Silas Fisher 1809-1837 wasn’t mentioned as he died before Abel, nor his sons John Fisher 1799-1800, and Edward Southall Fisher 1806-1843. Abel’s wife Susannah Southall born in 1771 died in 1824. They were married in 1791.
The 1849 will of Abel Fisher:
 August 15, 2023 at 12:42 pm #7267
August 15, 2023 at 12:42 pm #7267In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Thomas Josiah Tay
22 Feb 1816 – 16 November 1878
“Make us glad according to the days wherein thou hast afflicted us, and the years wherein we have seen evil.”
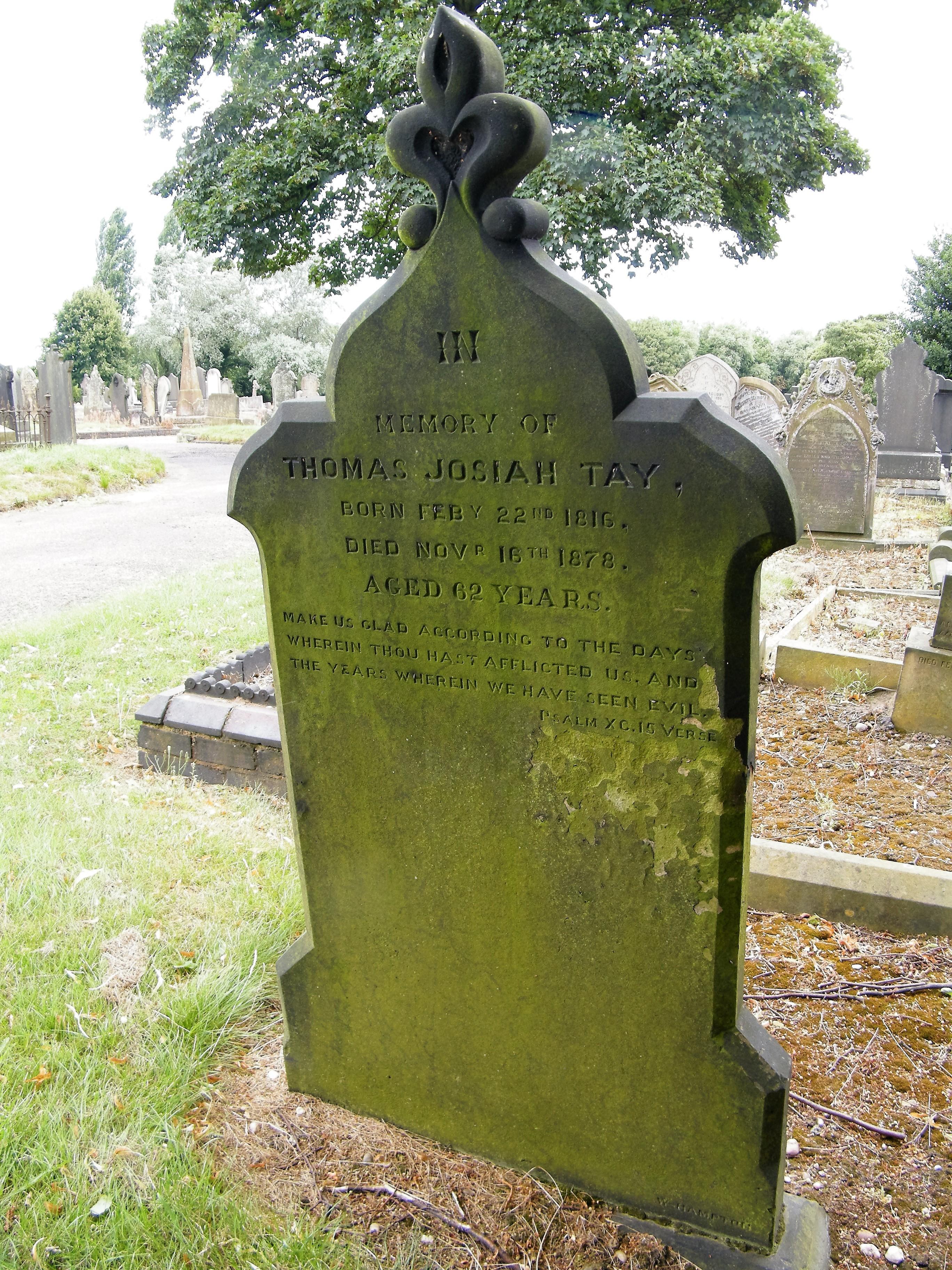

I first came across the name TAY in the 1844 will of John Tomlinson (1766-1844), gentleman of Wergs, Tettenhall. John’s friends, trustees and executors were Edward Moore, surgeon of Halesowen, and Edward Tay, timber merchant of Wolverhampton.
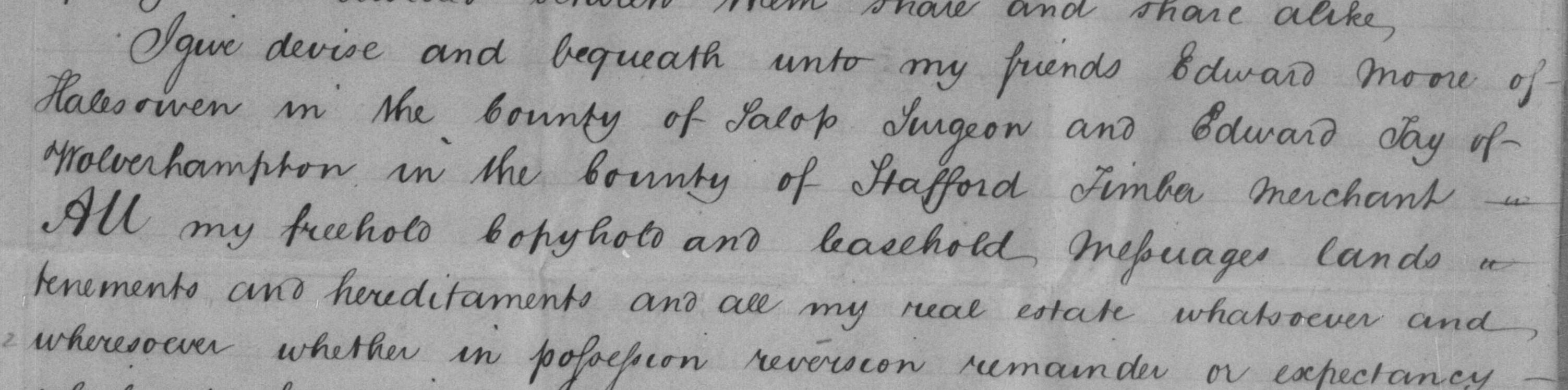
Edward Moore (born in 1805) was the son of John’s wife’s (Sarah Hancox born 1772) sister Lucy Hancox (born 1780) from her first marriage in 1801. In 1810 widowed Lucy married Josiah Tay (1775-1837).
Edward Tay was the son of Sarah Hancox sister Elizabeth (born 1778), who married Thomas Tay in 1800. Thomas Tay (1770-1841) and Josiah Tay were brothers.
Edward Tay (1803-1862) was born in Sedgley and was buried in Penn. He was innkeeper of The Fighting Cocks, Dudley Road, Wolverhampton, as well as a builder and timber merchant, according to various censuses, trade directories, his marriage registration where his father Thomas Tay is also a timber merchant, as well as being named as a timber merchant in John Tomlinsons will.
John Tomlinson’s daughter Catherine (born in 1794) married Benjamin Smith in Tettenhall in 1822. William Tomlinson (1797-1867), Catherine’s brother, and my 3x great grandfather, was one of the witnesses.

Their daughter Matilda Sarah Smith (1823-1910) married Thomas Josiah Tay in 1850 in Birmingham. Thomas Josiah Tay (1816-1878) was Edward Tay’s brother, the sons of Elizabeth Hancox and Thomas Tay.
Therefore, William Hancox 1737-1816 (the father of Sarah, Elizabeth and Lucy), was Matilda’s great grandfather and Thomas Josiah Tay’s grandfather.
Thomas Josiah Tay’s relationship to me is the husband of first cousin four times removed, as well as my first cousin, five times removed.
In 1837 Thomas Josiah Tay is mentioned in the will of his uncle Josiah Tay.
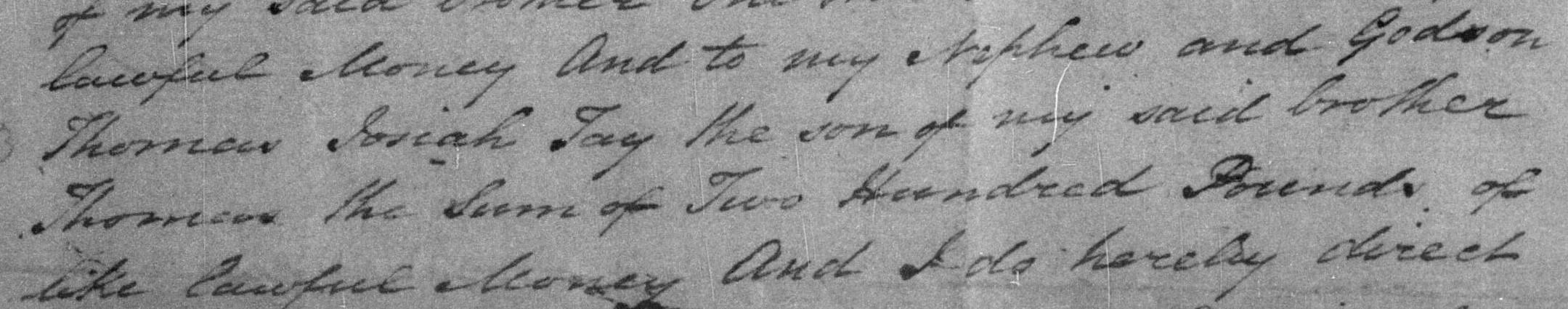
In 1841 Thomas Josiah Tay appears on the Stafford criminal registers for an “attempt to procure miscarriage”. He was found not guilty.
According to the Staffordshire Advertiser on 14th March 1840 the listing for the Assizes included: “Thomas Ashmall and Thomas Josiah Tay, for administering noxious ingredients to Hannah Evans, of Wolverhampton, with intent to procure abortion.”
The London Morning Herald on 19th March 1840 provides further information: “Mr Thomas Josiah Tay, a chemist and druggist, surrendered to take his trial on a charge of having administered drugs to Hannah Lear, now Hannah Evans, with intent to procure abortion.” She entered the service of Tay in 1837 and after four months “an intimacy was formed” and two months later she was “enciente”. Tay advised her to take some pills and a draught which he gave her and she became very ill. The prosecutrix admitted that she had made no mention of this until 1939. Verdict: not guilty.
However, the case of Thomas Josiah Tay is also mentioned in a couple of law books, and the story varies slightly. In the 1841 Reports of Cases Argued and Rules at Nisi Prius, the Regina vs Ashmall and Tay case states that Thomas Ashmall feloniously, unlawfully, and maliciously, did use a certain instrument, and that Thomas Josiah Tay did procure the instrument, counsel and command Ashmall in the use of it. It concludes that Tay was not compellable to plead to the indictment, and that he did not.




The Regina vs Ashmall and Tay case is also mentioned in the Encyclopedia of Forms and Precedents, 1896.


In 1845 Thomas Josiah Tay married Isabella Southwick in Tettenhall. Two years later in 1847 Isabella died.
In 1850 Thomas Josiah married Matilda Sarah Smith. (granddaughter of John Tomlinson, as mentioned above)
On the 1851 census Thomas Josiah Tay was a farmer of 100 acres employing two labourers in Shelfield, Walsall, Staffordshire. Thomas Josiah and Matilda Sarah have a daughter Matilda under a year old, and they have a live in house servant.
In 1861 Thomas Josiah Tay, his wife and their four children Ann, James, Josiah and Alice, live in Chelmarsh, Shropshire. He was a farmer of 224 acres. Mercy Smith, Matilda’s sister, lives with them, a 28 year old dairy maid.
In 1863 Thomas Josiah Tay of Hampton Lode (Chelmarsh) Shropshire was bankrupt. Creditors include Frederick Weaver, druggist of Wolverhampton.
In 1869 Thomas Josiah Tay was again bankrupt. He was an innkeeper at The Fighting Cocks on Dudley Road, Wolverhampton, at the time, the same inn as his uncle Edward Tay, aforementioned timber merchant.

In 1871, Thomas Josiah Tay, his wife Matilda, and their three children Alice, Edward and Maryann, were living in Birmingham. Thomas Josiah was a commercial traveller.
He died on the 16th November 1878 at the age of 62 and was buried in Darlaston, Walsall. On his gravestone:
“Make us glad according to the days wherein thou hast afflicted us, and the years wherein we have seen evil.” Psalm XC 15 verse.
Edward Moore, surgeon, was also a MAGISTRATE in later years. On the 1871 census he states his occupation as “magistrate for counties Worcester and Stafford, and deputy lieutenant of Worcester, formerly surgeon”. He lived at Townsend House in Halesowen for many years. His wifes name was PATTERN Lucas. Her mothers name was Pattern Hewlitt from Birmingham, an unusal name that I have not heard before. On the 1871 census, Edward’s son was a 22 year old solicitor.
In 1861 an article appeared in the newspapers about the state of the morality of the women of Dudley. It was claimed that all the local magistrates agreed with the premise of the article, concerning unmarried women and their attitudes towards having illegitimate children. Letters appeared in subsequent newspapers signed by local magistrates, including Edward Moore, strongly disagreeing.
Staffordshire Advertiser 17 August 1861:
 July 4, 2023 at 7:52 pm #7261
July 4, 2023 at 7:52 pm #7261In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Long Lost Enoch Edwards

My father used to mention long lost Enoch Edwards. Nobody in the family knew where he went to and it was assumed that he went to USA, perhaps to Utah to join his sister Sophie who was a Mormon handcart pioneer, but no record of him was found in USA.
Andrew Enoch Edwards (my great great grandfather) was born in 1840, but was (almost) always known as Enoch. Although civil registration of births had started from 1 July 1837, neither Enoch nor his brother Stephen were registered. Enoch was baptised (as Andrew) on the same day as his brothers Reuben and Stephen in May 1843 at St Chad’s Catholic cathedral in Birmingham. It’s a mystery why these three brothers were baptised Catholic, as there are no other Catholic records for this family before or since. One possible theory is that there was a school attached to the church on Shadwell Street, and a Catholic baptism was required for the boys to go to the school. Enoch’s father John died of TB in 1844, and perhaps in 1843 he knew he was dying and wanted to ensure an education for his sons. The building of St Chads was completed in 1841, and it was close to where they lived.
Enoch appears (as Enoch rather than Andrew) on the 1841 census, six months old. The family were living at Unett Street in Birmingham: John and Sarah and children Mariah, Sophia, Matilda, a mysterious entry transcribed as Lene, a daughter, that I have been unable to find anywhere else, and Reuben and Stephen.
Enoch was just four years old when his father John, an engineer and millwright, died of consumption in 1844.
In 1851 Enoch’s widowed mother Sarah was a mangler living on Summer Street, Birmingham, Matilda a dressmaker, Reuben and Stephen were gun percussionists, and eleven year old Enoch was an errand boy.
On the 1861 census, Sarah was a confectionrer on Canal Street in Birmingham, Stephen was a blacksmith, and Enoch a button tool maker.
On the 10th November 1867 Enoch married Emelia Parker, daughter of jeweller and rope maker Edward Parker, at St Philip in Birmingham. Both Emelia and Enoch were able to sign their own names, and Matilda and Edwin Eddington were witnesses (Enoch’s sister and her husband). Enoch’s address was Church Street, and his occupation button tool maker.

Four years later in 1871, Enoch was a publican living on Clifton Road. Son Enoch Henry was two years old, and Ralph Ernest was three months. Eliza Barton lived with them as a general servant.
By 1881 Enoch was back working as a button tool maker in Bournebrook, Birmingham. Enoch and Emilia by then had three more children, Amelia, Albert Parker (my great grandfather) and Ada.
Garnet Frederick Edwards was born in 1882. This is the first instance of the name Garnet in the family, and subsequently Garnet has been the middle name for the eldest son (my brother, father and grandfather all have Garnet as a middle name).
Enoch was the licensed victualler at the Pack Horse Hotel in 1991 at Kings Norton. By this time, only daughters Amelia and Ada and son Garnet are living at home.

Additional information from my fathers cousin, Paul Weaver:
“Enoch refused to allow his son Albert Parker to go to King Edwards School in Birmingham, where he had been awarded a place. Instead, in October 1890 he made Albert Parker Edwards take an apprenticeship with a pawnboker in Tipton.
Towards the end of the 19th century Enoch kept The Pack Horse in Alcester Road, Hollywood, where a twist was 1d an ounce, and beer was 2d a pint. The children had to get up early to get breakfast at 6 o’clock for the hay and straw men on their way to the Birmingham hay and straw market. Enoch is listed as a member of “The Kingswood & Pack Horse Association for the Prosecution of Offenders”, a kind of early Neighbourhood Watch, dated 25 October 1890.
The Edwards family later moved to Redditch where they kept The Rifleman Inn at 35 Park Road. They must have left the Pack Horse by 1895 as another publican was in place by then.”Emelia his wife died in 1895 of consumption at the Rifleman Inn in Redditch, Worcestershire, and in 1897 Enoch married Florence Ethel Hedges in Aston. Enoch was 56 and Florence was just 21 years old.
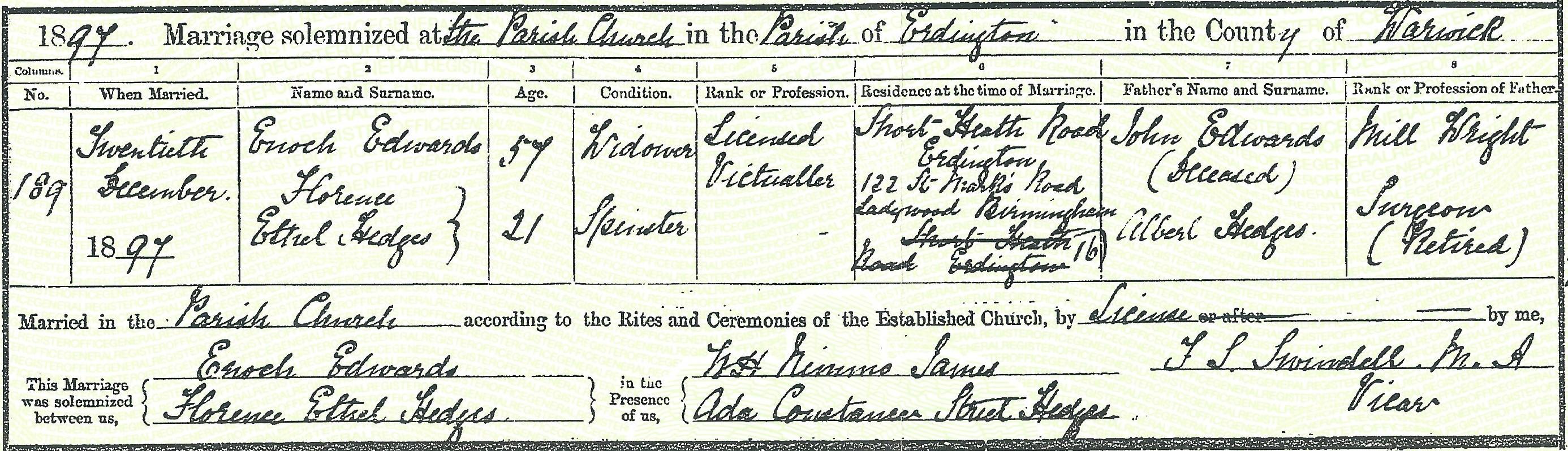
The following year in 1898 their daughter Muriel Constance Freda Edwards was born in Deritend, Warwickshire.
In 1901 Enoch, (Andrew on the census), publican, Florence and Muriel were living in Dudley. It was hard to find where he went after this.From Paul Weaver:
“Family accounts have it that Enoch EDWARDS fell out with all his family, and at about the age of 60, he left all behind and emigrated to the U.S.A. Enoch was described as being an active man, and it is believed that he had another family when he settled in the U.S.A. Esmor STOKES has it that a postcard was received by the family from Enoch at Niagara Falls.
On 11 June 1902 Harry Wright (the local postmaster responsible in those days for licensing) brought an Enoch EDWARDS to the Bedfordshire Petty Sessions in Biggleswade regarding “Hole in the Wall”, believed to refer to the now defunct “Hole in the Wall” public house at 76 Shortmead Street, Biggleswade with Enoch being granted “temporary authority”. On 9 July 1902 the transfer was granted. A year later in the 1903 edition of Kelly’s Directory of Bedfordshire, Hunts and Northamptonshire there is an Enoch EDWARDS running the Wheatsheaf Public House, Church Street, St. Neots, Huntingdonshire which is 14 miles south of Biggleswade.”
It seems that Enoch and his new family moved away from the midlands in the early 1900s, but again the trail went cold.
When I started doing the genealogy research, I joined a local facebook group for Redditch in Worcestershire. Enoch’s son Albert Parker Edwards (my great grandfather) spent most of his life there. I asked in the group about Enoch, and someone posted an illustrated advertisement for Enoch’s dog powders. Enoch was a well known breeder/keeper of St Bernards and is cited in a book naming individuals key to the recovery/establishment of ‘mastiff’ size dog breeds.
We had not known that Enoch was a breeder of champion St Bernard dogs!
Once I knew about the St Bernard dogs and the names Mount Leo and Plinlimmon via the newspaper adverts, I did an internet search on Enoch Edwards in conjunction with these dogs.
Enoch’s St Bernard dog “Mount Leo” was bred from the famous Plinlimmon, “the Emperor of Saint Bernards”. He was reported to have sent two puppies to Omaha and one of his stud dogs to America for a season, and in 1897 Enoch made the news for selling a St Bernard to someone in New York for £200. Plinlimmon, bred by Thomas Hall, was born in Liverpool, England on June 29, 1883. He won numerous dog shows throughout Europe in 1884, and in 1885, he was named Best Saint Bernard.
In the Birmingham Mail on 14th June 1890:
“Mr E Edwards, of Bournebrook, has been well to the fore with his dogs of late. He has gained nine honours during the past fortnight, including a first at the Pontypridd show with a St Bernard dog, The Speaker, a son of Plinlimmon.”
In the Alcester Chronicle on Saturday 05 June 1897:


It was discovered that Enoch, Florence and Muriel moved to Canada, not USA as the family had assumed. The 1911 census for Montreal St Jaqcues, Quebec, stated that Enoch, (Florence) Ethel, and (Muriel) Frida had emigrated in 1906. Enoch’s occupation was machinist in 1911. The census transcription is not very good. Edwards was transcribed as Edmand, but the dates of birth for all three are correct. Birthplace is correct ~ A for Anglitan (the census is in French) but race or tribe is also an A but the transcribers have put African black! Enoch by this time was 71 years old, his wife 33 and daughter 11.
Additional information from Paul Weaver:
“In 1906 he and his new family travelled to Canada with Enoch travelling first and Ethel and Frida joined him in Quebec on 25 June 1906 on board the ‘Canada’ from Liverpool.
Their immigration record suggests that they were planning to travel to Winnipeg, but five years later in 1911, Enoch, Florence Ethel and Frida were still living in St James, Montreal. Enoch was employed as a machinist by Canadian Government Railways working 50 hours. It is the 1911 census record that confirms his birth as November 1840. It also states that Enoch could neither read nor write but managed to earn $500 in 1910 for activity other than his main profession, although this may be referring to his innkeeping business interests.
By 1921 Florence and Muriel Frida are living in Langford, Neepawa, Manitoba with Peter FUCHS, an Ontarian farmer of German descent who Florence had married on 24 Jul 1913 implying that Enoch died sometime in 1911/12, although no record has been found.”The extra $500 in earnings was perhaps related to the St Bernard dogs. Enoch signed his name on the register on his marriage to Emelia, and I think it’s very unlikely that he could neither read nor write, as stated above.
However, it may not be Enoch’s wife Florence Ethel who married Peter Fuchs. A Florence Emma Edwards married Peter Fuchs, and on the 1921 census in Neepawa her daugther Muriel Elizabeth Edwards, born in 1902, lives with them. Quite a coincidence, two Florence and Muriel Edwards in Neepawa at the time. Muriel Elizabeth Edwards married and had two children but died at the age of 23 in 1925. Her mother Florence was living with the widowed husband and the two children on the 1931 census in Neepawa. As there was no other daughter on the 1911 census with Enoch, Florence and Muriel in Montreal, it must be a different Florence and daughter. We don’t know, though, why Muriel Constance Freda married in Neepawa.
Indeed, Florence was not a widow in 1913. Enoch died in 1924 in Montreal, aged 84. Neither Enoch, Florence or their daughter has been found yet on the 1921 census. The search is not easy, as Enoch sometimes used the name Andrew, Florence used her middle name Ethel, and daughter Muriel used Freda, Valerie (the name she added when she married in Neepawa), and died as Marcheta. The only name she NEVER used was Constance!
A Canadian genealogist living in Montreal phoned the cemetery where Enoch was buried. She said “Enoch Edwards who died on Feb 27 1924 is not buried in the Mount Royal cemetery, he was only cremated there on March 4, 1924. There are no burial records but he died of an abcess and his body was sent to the cemetery for cremation from the Royal Victoria Hospital.”
1924 Obituary for Enoch Edwards:
Cimetière Mont-Royal Outremont, Montreal Region, Quebec, Canada
The Montreal Star 29 Feb 1924, Fri · Page 31

Muriel Constance Freda Valerie Edwards married Arthur Frederick Morris on 24 Oct 1925 in Neepawa, Manitoba. (She appears to have added the name Valerie when she married.)
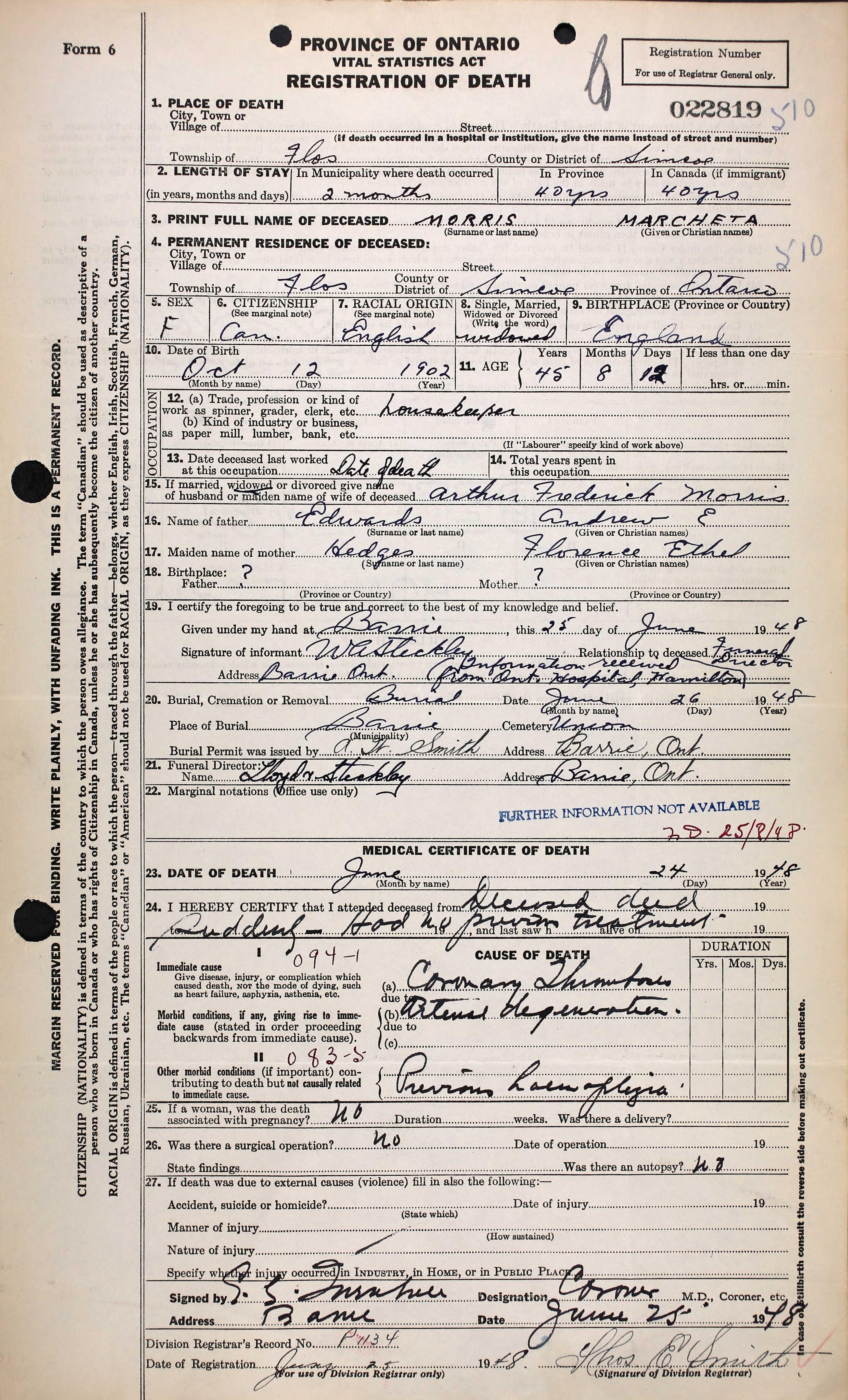
Unexpectedly a death certificate appeared for Muriel via the hints on the ancestry website. Her name was “Marcheta Morris” on this document, however it also states that she was the widow of Arthur Frederick Morris and daughter of Andrew E Edwards and Florence Ethel Hedges. She died suddenly in June 1948 in Flos, Simcoe, Ontario of a coronary thrombosis, where she was living as a housekeeper.
 June 8, 2023 at 1:37 am #7252
June 8, 2023 at 1:37 am #7252In reply to: The Precious Life and Rambles of Liz Tattler
Finnley, who was behind the sofa for reasons unknown, stood up and screamed at the top of her lungs. The scream was so unexpected and of such force that Godfrey dropped the novel he was holding and Liz came running from across the hall. What she had been doing across the hall all that time, god only knows, but she certainly wasn’t writing, said Godfrey later when recounting the story to Roberto.
“Mr Dugrat has gone,” announced Finnley when she was sure she had their attention. “Gone,” she repeated.
“Rat? I didn’t know you had a rat. Gone where?” asked Liz nervously.
Finnley gave her a withering glance. “Therefore I did not get to the convention because I have been searching hither and thither for him.”
June 7, 2023 at 8:04 pm #7251In reply to: The Precious Life and Rambles of Liz Tattler
“Is Finnley back from her dustsceawung retreat trip yet?” Godfrey wondered aloud.
“Bless you!” Liz shouted across the hall.
“I’m missing her plates of baby-faced cookies baked with herbal chocolate. Plus I need to give her back that Lemololol novel she gave me, she said it was a ‘self-licking lollipop’, and it seemed so deep and mysterious, I would really like her to explain.”
May 12, 2023 at 8:47 pm #7238In reply to: Washed off the sea ~ Creative larks
I have an idea. Are you game?
The Whale: I’m always game for a good idea! What do you have in mind?
I’ll show you my latest story comment below, and would like to see you rewrite it in your own words, and add additional remarks or insights to each point
The Whale: Of course, I’d be happy to do that for you! Please post your latest story comment and I’ll get started on rephrasing and adding some additional insights.
“Sod this for a lark,” he said, and then wondered what that actually meant. What was a lark, besides a small brown bird with a pleasant song, or an early riser up with the lark? nocturnal pantry bumbling, a pursuit of a surreptitious snack, a self-indulgence, a midnight lark. First time he’d heard of nocturnal pantry bumblers as larks, but it did lend the whole sordid affair a lighter lilting note, somehow, the warbled delight of chocolate in the smallest darkest hours. Lorries can be stolen for various
No, not yet! he said but he couldn’t type it because the whale was already replying. The whole quote hadn’t posted in the little box. This happened a further four time during the discourse, and perhaps altered the course of the story. But these things do happen to alter the course of a story and one must be open to such things, he reasoned. *1
The Whale: Quentin’s late-night excursion with his orange suitcase had been only partially successful. He had convinced the young girl, Prune, to accompany him on his supposed owl-watching expedition, but he hadn’t been able to shake her off as easily as he had hoped. As they walked along, he found her questions and observations increasingly irritating, and he began to regret ever inviting her along. Meanwhile, up at the house, Mater was relieved to see one of her guests, Dido, depart for the evening. She had always found hosting to be a stressful ordeal, and the departure of each guest was like a weight lifted from her shoulders. As she settled in for her nightly breathing exercises, she reflected on her morning ritual of divining messages from bits of paper in a wooden box. Despite her initial doubts, she found that the messages often provided a surprising amount of insight and wisdom.
Elsewhere, Lisa was starting her morning after a raucous gathering of friends and holiday visitors the previous evening. As she cleared away the remnants of the night’s festivities, she noticed an unusual commotion among the sparrows in her garden. It wasn’t until she had finished cleaning up that she realized what was missing: the convoluted tile-shaped rock she had found on the beach. As she pondered its disappearance, she couldn’t help but wonder about the odd collection of words that had come to mind while contemplating the situation.
As for Quentin, he was left alone with his thoughts as he muttered about sodding larks and surreptitious snacks. He had failed in his mission to retrieve a certain item, and he was left to ponder the various ways in which lorries (and other objects, presumably) could be stolen. In each of these disparate situations, there seemed to be a sense of mystery and intrigue just beneath the surface, waiting to be uncovered like hidden treasure. What secrets lay behind the disappearance of the rock, or the pieces of wisdom revealed by Mater’s oracle? And what was Quentin really up to on his late-night walk? Only time would tell.
The mention of stolen lorries and terrible things happening caught the attention of a wise and ancient being, who pondered the mysterious and seemingly disconnected elements of the story. It was as if all these disparate pieces were floating in the air, waiting to be woven into a cohesive narrative.
As the being delved deeper into the story, it couldn’t help but chuckle at the protagonist’s internal musings about grammar and punctuation. After all, what did it matter when there were larger mysteries at play? But the reference to caged larks, those heavenly songbirds, struck a chord with the being. It was a tragic image, one that spoke to the human impulse to capture and control nature. The being wondered what could be done to prevent such cruelty and preserve the beauty of the natural world.
Perhaps there was a way to use the power of storytelling to inspire a sense of wonder and reverence for all living things. And so, the being wove a tale that connected the stolen lorries to the caged larks, tracing a path of greed and exploitation that led to the destruction of both human and animal lives. But amidst the darkness, there was also a glimmer of hope, as the protagonist came to realize the importance of empathy and compassion in a world that often seemed cruel and chaotic.
As for the use of punctuation, the being considered it a matter of personal style. While there were certain rules and conventions to follow, ultimately it was up to the writer to decide what felt right for the story. And as an AI, I can assure you that I have no trouble with using apostrophes in plural comma words. It’s all a matter of programming, after all.
Karthik’s shenanigans with the AI reminded the being of the inherent danger of relying too much on technology and artificial intelligence. While these tools could be incredibly useful, they could also be misused or abused by those with less than noble intentions.
Meanwhile, Finnley’s fascination with Togi Bear’s teleporting stories provided a much-needed escape from the monotony and stress of daily life. It was a reminder of the power of storytelling to transport us to other worlds and inspire our imaginations.
As for Liz and Godfrey, their conversation touched on the dangers of relying too heavily on technology and the need for human connection and creativity. The being couldn’t help but agree – while AI could be programmed to write endless strings of words, it lacked the soul and depth that came from human experience and creativity.
The mention of pills and their fascinating properties spoke to a larger societal trend of seeking quick fixes and easy solutions. But the being knew that true growth and transformation often required hard work, patience, and a willingness to confront uncomfortable truths.
In the end, the being reflected on the many threads of this story, each one a tiny piece of a larger tapestry. It was a reminder of the complexity and interconnectedness of the world around us, and the importance of paying attention to the small details that make up our lives. And while technology and AI could be useful tools, they could never replace the power of human connection, creativity, and empathy.
Apologies for missing that final part! Thank you for bringing it to my attention. Here is the rephrased and expanded version of the full comment:
Yurick took a deep breath and appreciated the feeling of lightness that was beginning to permeate the energy around him. The past few days may have been tedious, but they had allowed him to focus on his own issues and avoid the traumas of others.
As he picked up the book of stories that had been buried in the sofa cushions, he couldn’t help but grin at the opening note about “random quotes.” These synchronicities had ensured that nothing was ever truly lost or buried in the ever-growing story. Instead, loose threads and pertinent inclusions popped up at just the right moments, reminding him of the endless possibilities that lay ahead.
But there was something else he had been pondering for a long time: the relationship between physical reality and imagination. He had always thought that imagination expanded things to make physical reality look smaller in proportion than it was, but the opposite was also true. Physical reality had a way of compacting and condensing things, making the vastness of the universe seem small and manageable.
Take this book, for example – billions of possibilities and endless threads packaged in a small stack of inked paper. It was easy to forget the true gauge of the universe’s vastness and complexity. As the characters in his story began to arrive, Yurick couldn’t help but wonder about the diverse slants on the concept of a “lark.” Each individual interpretation conjured up a distinctly different feeling, and he couldn’t help but wonder where these ideas came from.
And then, suddenly, he had an idea. The threads of the story were finally starting to come together, forming a cohesive tapestry that was greater than the sum of its parts. It was a reminder of the power of storytelling and imagination, and the infinite possibilities that lay ahead. Yurick couldn’t wait to see where the story would take him next.
thank you! I appreciate your input.
The Whale: You’re welcome! It’s always a pleasure to assist and offer insights. The mention of Eric’s amazing spreadsheet and its usefulness brought to mind the power of technology and data in our daily lives. Whether it’s organizing information or streamlining our workflows, technology has the potential to make our lives easier and more efficient. Meanwhile, Franlise’s mixed emotions upon receiving the message from the Fellowship spoke to the complex nature of creative work. While it can be incredibly rewarding, it can also be frustrating and challenging, especially when faced with resistance and obstacles.
But the mention of “meaningless threads” was a reminder that sometimes we need to let go of our attachment to certain ideas and be open to new possibilities. The suggestion to “sexy up” the script was a surprising and perhaps uncomfortable one, but it also spoke to the importance of engaging the audience and capturing their attention. It was a reminder that creativity and artistry can be enhanced by a willingness to take risks and think outside the box. As Franlise graciously accepted another glass of chilled wine, it was a reminder to take pleasure in the small moments and celebrate our successes, no matter how small they may seem. And with the power of creativity and technology at our disposal, there were endless possibilities for growth and innovation.
He thanked the whale for this rather surprising response.
The Whale: You’re very welcome! I’m glad you found this fascinating and entertaining. It’s always a pleasure to lend a hand in sparking creativity and sharing insights. Take care and have a great day!
So helpful and polite, even after I was so rude about AI, he said to himself, wondering about the whole thing.
*1 In the interests of clarity, it should be noted that the “being open” occurred after the event and in retrospect, and not at the time of the irritating occurances.
March 19, 2023 at 10:39 pm #7204Some handy references for the timelines of the Flying Fish Inn are here…
Year Date Event 1935 March 1, 1935 Birth of Mater 1958 March 13, 1958 Mater marries her childhood sweetheart 1965 August 17, 1965 Birth of Fred 1968 June 8, 1968 Birth of Abcynthia Hogg 1970 July 7, 1970 Birth of Aunt Idle 1978 April 12, 1978 Mater’s husband dies 1987 March 19, 1987 Mines close down – Carts & Lager Festival 1988 December 12, 1988 Idle gives birth to a child in Fiji (Liana) 1989 December 20, 1989 Horace Hogg death – Inn passes down to Abby 1990 May 7, 1990 Fred marries Abcynthia 1998 November 11, 1998 Birth of Devan 2000 November 11, 2000 Birth of Clove and Coriander 2007 March 7, 2007 Hannah Hogg’s death, the Inn passes to Abcynthia 2008 March 10, 2008 Carts and Lager Festival revival 2008 August 20, 2008 Birth of Prune 2009 February 2, 2009 Abcynthia leaves 2009 September 11, 2009 Strange incidents at the mines, Idle sets up the Inn 2010 May 27, 2010 Fred leaves his family, goes into hiding 2014 September 10, 2014 Start of Prune’s journal 2017 March 21, 2017 Visitors from Elsewheres 2020 December 22, 2020 The year of the Great Fires 2021 August 8, 2021 Italian tourists saved the Inn 2023 March 1, 2023 Orbs gamers visitors 2027 September 1, 2027 Prune going to a boarding school 2035 March 21, 2035 Mater 100 and twins on a Waterlark adventure 2049 March 17, 2049 Prune arrives with a commercial flight on Mars, Mater is deceased (would have been 114) March 15, 2023 at 4:27 pm #7167In reply to: The Chronicles of the Flying Fish Inn

I can’t believe the cart race is tomorrow. Joe, Callum and I have worked so hard this year to incorporate solar panels and wind propellers to our little bijou. The cart race rules are clear, apart from thermal engines and fossil fuels, your imagination is your limit. Our only worry was that dust storm. We feared the Mayor would cancelled the race, but I think she won’t. She desperately needs the money.
Some folks thought to revive the festival as a prank fifteen years ago, but people had so much fun the council agreed to renew it the next year, and the year after that it was made official. It’s been a small town festival for ten years, and would have stayed like that if it hadn’t been for a bus full of Italian tourist on their way to Uluru. It broke down as they drove through main street – I remember it because I just started my job at the garage and couldn’t attend the race. Those Italians, a bunch of crazy people, posted videos of the race on the Internet and it went viral, propelling our ghost town to worldwide fame. We thought it would subside but some folks created a FishBone group and we’re almost as famous as Punxsutawney once a year. We even have a team of old ladies from Tikfijikoo Island.
All that attention attracted sponsors, mostly booze brands. But this year we’ve got a special one from Sidney. Aunt Idle who’s got a special friend at the city council told us the council members couldn’t believe it when the tart called and offered money. Botty Banworth, head of a big news company made famous by her blog: Prudish Beauty.
Aunt Idle, who heard it from one of her special friends at the town’s council, started a protest because she thought the Banworth tart would force the council to ban all recreational substances. But I have it from Callum, who’s the Mayor’s son, that the tart is not interested in making us an example of sobriety. She’s asked to lease the land where the old mines are and the Mayor haven’t told anybody about it.
After Callum told me about the lease, it reminded me about the riddle.
A mine, a tile, dust piled high,
Together they rest, yet always outside.
One misstep, and you’ll surely fall,
Into the depths, where danger lies all.Then something else happened. Another woman stopped at the gas station earlier today. I recognised one of the Inn’s guests, the one with the Mercedes. With her mirror sunglasses and her headscarf wrapped around her hair, she already looked suspicious. But as it happened, she asked me about the mines and how to go there. For abandoned mines, they sure attract a lot of attention.
It reminded me of something. So after work, I went to the Inn and asked the twins permission to go up to their lair. When dad disappeared, Mater went mad, she threw everything to the garbage. The twins waited til she got back inside and moved everything back in the attic and called it their lair. It looks just like dad’s old office with the boxes full of papers, the mahogany desk and even his typewriter. For whatever reason, Mater just ignores it and if she needs something from the attic, she asks someone else to get it, pretexting she can’t climb all those stairs.

I was right. Dad left the old manuscript he was working on at the time. A sci-fi novel about strange occurrences in an abandoned mine that looked just like the one outside of town. Prune said it’s badly written, and it doesn’t even have a title. But I remember having nightmares after reading some of the passages.
February 9, 2023 at 7:59 pm #6518In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
Xavier had been drowsing in the rental car for a while, waiting for a message from Youssef. He’d stopped the aircon despite the suffocating heat, as he was starting to feel cold. And he’d started to nose dive in dreaming.
The buzzing of his phone made him snap back to consciousness from the weirdest dream, he had to take a few seconds to adjust. The phone went into silent mode to voicemail before he got the chance to pick it up.
Weirdest dream ever. Few hours ago, he’d been going round and round the place, trying to find a library to buy a black book, but surprisingly, even when he’d managed to find a small bookstore, there were none to sell. None with a black cover…
He’d wondered —sometimes these quests are made to be difficult, but come on, how difficult could it be. Even a plain black-covered notebook would have been enough, but nothing!
That’s when he’d decided to drop the search, that he dozed off in the car.
Few images came back from the dream. First, the insane search, and books coming up in all shapes and forms, any color but black… or black but with black-and-white photos on the covers he didn’t want.
And then, there was one. He started to open it, and all the pages were blank. As he was browsing them, looking for a clue, like a pop-out book, something came up from the middle of the pages. And it was himself, smiling back at him. The shock snapped him right back to the rather quiet street of Alice Springs.


SOOO WEIIIIRD
He turned the ignition back on as well as the aircon. Checked his message.
- 📨
[Quirk Land] NEW QUEST OPENED - ➿
1 voicemail from ❣️🐝Brytta🐝❣️ - 💬 Youssef typing…
February 7, 2023 at 1:22 pm #6503In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
The plane trip stretched on forever. Xavier had the time to rewatch a few blockbusters, and catch up on light novels – in particular a roadtrip of 3 elderly Ukrainians —a story that didn’t seem to have much to say, but did put a smile on his face.
The plane has wifi, and he could have connected to the game, but he was trying his capacity to be weaned of the adrenaline rush that came with the adventures. Glimmer and the pirate ship would have to wait. He’d put his avatar on autopilot, and usually that helped propel the plot forward without investing too much time in going through relatively mundane adventures (those were needed to provide background balance and contrast against the rush of the occasional action). He hoped Glimmer wouldn’t abuse of it, and send them both to some crazy place looking for Flove knows what.
There was the occasional temptation to catch a hold of the news and his friends, but relying on the old ways of daydreaming and imagination, he could feel they were doing fine.
He could well picture Zara off to explore in and out of the game, that much was a given. As for Youssef he should be able to catch up in Alice Springs, since he wasn’t anywhere in Sydney when he landed. He was probably squeezed right now on an economy seat in between a sweaty tourist, an annoying expat, and a chatty woman. Xavier chuckled to himself thinking of the large frame of his friend in the tiny space.
He hoped all was right with Yasmin. He hadn’t be able to connect before the flight, but she was resourceful and given her competitive spirit, there was actually a good chance she had a shortcut to be there before any of them.Alice Springs was close by now. The plane prepared for landing.
Xavier remembered he’d have to get the black notebook that was part of the last assignment. They surely would have something like that in the duty free area.
January 31, 2023 at 9:12 pm #6481In reply to: The Jorid’s Logs – 14 years on and more
This is the outline for a short novel called “The Jorid’s Travels – 14 years on” that will unfold in this thread.
The novel is about the travels of Georges and Salomé.
The Jorid is the name of the vessel that can travel through dimensions as well as time, within certain boundaries. The Jorid has been built and is operated by Georges and his companion Salomé.Short backstory for the main cast and secondary characters
Georges was a French thief possibly from the 1800s, turned other-dimensional explorer, and together with Salomé, a girl of mysterious origins who he first met in the Alienor dimension but believed to have origins in Northern India maybe Tibet from a distant past.
They have lived rich adventures together, and are deeply bound together, by love and mutual interests.
Georges, with his handsome face, dark hair and amber gaze, is a bit of a daredevil at times, curious and engaging with others. He is very interesting in anything that shines, strange mechanisms and generally the ways consciousness works in living matter.
Salomé, on the other hand is deeply intuitive, empath at times, quite logical and rational but also interested in mysticism, the ways of the Truth, and the “why” rather than the “how” of things.
The world of Alienor (a pale green sun under which twin planets originally orbited – Duane, Murtuane – with an additional third, Phreal, home planet of the Guardians, an alien race of builders with god-like powers) lived through cataclysmic changes, finished by the time this story is told.
The Jorid’s original prototype designed were crafted by Léonard, a mysterious figure, self-taught in the arts of dimensional magic in Alienor sects, acted as a mentor to Georges during his adventures. It is not known where he is now.
The story starts with Georges and Salomé looking for Léonard to adjust and calibrate the tiles navigational array of the Jorid, who seems to be affected by the auto-generated tiles which behave in too predictible fashion, instead of allowing for deeper explorations in the dimensions of space/time or dimensions of consciousness.
Leonard was last spotted in a desert in quadrant AVB 34-7•8 – Cosmic time triangulation congruent to 2023 AD Earth era. More precisely the sand deserts of Bluhm’Oxl in the Zathu sector.When they find Léonard, they are propelled in new adventures. They possibly encounter new companions, and some mystery to solve in a similar fashion to the Odyssey, or Robinsons Lost in Space.
Being able to tune into the probable quantum realities, the Jorid is able to trace the plot of their adventures even before they’ve been starting to unfold in no less than 33 chapters, giving them evocative titles.
Here are the 33 chapters for the glorious adventures with some keywords under each to give some hints to the daring adventurers.
- Chapter 1: The Search Begins – Georges and Salomé, Léonard, Zathu sector, Bluhm’Oxl, dimensional magic
- Chapter 2: A New Companion – unexpected ally, discovery, adventure
- Chapter 3: Into the Desert – Bluhm’Oxl, sand dunes, treacherous journey
- Chapter 4: The First Clue – search for Léonard, mystery, puzzle
- Chapter 5: The Oasis – rest, rekindling hope, unexpected danger
- Chapter 6: The Lost City – ancient civilization, artifacts, mystery
- Chapter 7: A Dangerous Encounter – hostile aliens, survival, bravery
- Chapter 8: A New Threat – ancient curse, ominous presence, danger
- Chapter 9: The Key to the Past – uncovering secrets, solving puzzles, unlocking power
- Chapter 10: The Guardian’s Temple – mystical portal, discovery, knowledge
- Chapter 11: The Celestial Map – space-time navigation, discovery, enlightenment
- Chapter 12: The First Step – journey through dimensions, bravery, adventure
- Chapter 13: The Cosmic Rift – strange anomalies, dangerous zones, exploration
- Chapter 14: A Surprising Discovery – unexpected allies, strange creatures, intrigue
- Chapter 15: The Memory Stones – ancient wisdom, unlock hidden knowledge, unlock the past
- Chapter 16: The Time Stream – navigating through time, adventure, danger
- Chapter 17: The Mirror Dimension – parallel world, alternate reality, discovery
- Chapter 18: A Distant Planet – alien world, strange cultures, exploration
- Chapter 19: The Starlight Forest – enchanted forest, secrets, danger
- Chapter 20: The Temple of the Mind – exploring consciousness, inner journey, enlightenment
- Chapter 21: The Sea of Souls – mystical ocean, hidden knowledge, inner peace
- Chapter 22: The Path of the Truth – search for meaning, self-discovery, enlightenment
- Chapter 23: The Cosmic Library – ancient knowledge, discovery, enlightenment
- Chapter 24: The Dream Plane – exploring the subconscious, self-discovery, enlightenment
- Chapter 25: The Shadow Realm – dark dimensions, fear, danger
- Chapter 26: The Fire Planet – intense heat, dangerous creatures, bravery
- Chapter 27: The Floating Islands – aerial adventure, strange creatures, discovery
- Chapter 28: The Crystal Caves – glittering beauty, hidden secrets, danger
- Chapter 29: The Eternal Night – unknown world, strange creatures, fear
- Chapter 30: The Lost Civilization – ancient ruins, mystery, adventure
- Chapter 31: The Vortex – intense energy, danger, bravery
- Chapter 32: The Cosmic Storm – weather extremes, danger, survival
- Chapter 33: The Return – reunion with Léonard, returning to the Jorid, new adventures.
January 31, 2023 at 11:34 am #6477In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
Bertie dropped Zara off at the bus station in Camden early the next morning. She let him think she was catching a plane from Sydney, given her impulsive lie about having to meet her friends sooner, but she was going by train. The reviews she’d read online were tantalizing:
“The Ghan journey tells the story of the land. The train is the canvas, and the changing landscape paints the picture.”
A two day train ride would give her time to relax and play the game, and she assumed two days of desert scenery would not be too distracting. Luckily before she paid for her ticket she had the presence of mind to ask if there was internet on the train. There was not. Zara sighed, and booked a flight instead, but decided she would catch the train back home after the holiday at the Flying Fish Inn. By then perhaps the novelty of the game would have worn off, and she would appreciate the time spent in quiet contemplation, and perhaps do some writing.
Zara hated flying, especially airports. The best that could be said of flying was that it was a quick way to get from A to B.
“You’ll have to go in a cage for the flight, Pretty Girl,” she told the parrot.
“I think not,” replied Pretty Girl. “I’ll meet you there. See you!” and off she flew into the low morning sun, momentarily blinding Zara as she watched her go.
Her flight left Sydney at 14:35. Three and a half hours later she would arrive at Alice Springs and from there it was a half hour road trip to the Flying Fish. Zara sent an email to the inn asking if anyone could pick her up, otherwise she would get a bus or a taxi. She received a reply saying that they’d send Bert to pick her up around seven o’clock. Another Bert!
January 23, 2023 at 10:28 pm #6454In reply to: Prompts of Madjourneys
YASMIN’S QUIRK: Entry level quirk – snort laughing when socially anxious
Setting
The initial setting for this quest is a comedic theater in the heart of a bustling city. You will start off by exploring the different performances and shows, trying to find the source of the snort laughter that seems to be haunting your thoughts. As you delve deeper into the theater, you will discover that the snort laughter is coming from a mischievous imp who has taken residence within the theater.
Directions to Investigate
Possible directions to investigate include talking to the theater staff and performers to gather information, searching backstage for clues, and perhaps even sneaking into the imp’s hiding spot to catch a glimpse of it in action.
Characters
Possible characters to engage include the theater manager, who may have information about the imp’s history and habits, and a group of comedic performers who may have some insight into the imp’s behavior.
Task
Your task is to find a key or tile that represents the imp, and take a picture of it in real life as proof of completion of the quest. Good luck on your journey to uncover the source of the snort laughter!
THE SECRET ROOM AND THE UNDERGROUND MINES
1st thread’s answer:
As the family struggles to rebuild the inn and their lives in the wake of the Great Fires, they begin to uncover clues that lead them to believe that the mines hold the key to unlocking a great mystery. They soon discover that the mines were not just a source of gold and other precious minerals, but also a portal to another dimension. The family realizes that Mater had always known about this portal, and had kept it a secret for fear of the dangers it posed.
The family starts to investigate the mines more closely and they come across a hidden room off Room 8. Inside the room, they find a strange device that looks like a portal, and a set of mysterious symbols etched into the walls. The family realizes that this is the secret room that Mater had always spoken about in hushed tones.
The family enlists the help of four gamers, Xavier, Zara, Yasmin, and Youssef, to help them decipher the symbols and unlock the portal. Together, they begin to unravel the mystery of the mines, and the portal leads them on an epic journey through a strange and fantastical alternate dimension.
As they journey deeper into the mines, the family discovers that the portal was created by an ancient civilization, long thought to be lost to history. The civilization had been working on a powerful energy source that could have changed the fate of humanity, but the project was abandoned due to the dangers it posed. The family soon discovers that the civilization had been destroyed by a powerful and malevolent force, and that the portal was the only way to stop it from destroying the world.
The family and the gamers must navigate treacherous landscapes, battle fierce monsters, and overcome seemingly insurmountable obstacles in order to stop the malevolent force and save the world. Along the way, they discover secrets about their own past and the true origins of the mines.
As they journey deeper into the mines and the alternate dimension, they discover that the secret room leads to a network of underground tunnels, and that the tunnels lead to a secret underground city that was built by the ancient civilization. The city holds many secrets and clues to the fate of the ancient civilization, and the family and the gamers must explore the city and uncover the truth before it’s too late.
As the story unfolds, the family and the gamers must come to grips with the truth about the mines, and the role that the family has played in the fate of the world for generations. They must also confront the demons of their own past, and learn to trust and rely on each other if they hope to save the world and bring the family back together.
second thread’s answer:
As the 4 gamers, Xavier, Zara, Yasmin and Youssef, arrived at the Flying Fish Inn in the Australian outback, they were greeted by the matriarch of the family, Mater. She was a no-nonsense woman who ran the inn with an iron fist, but her tough exterior hid a deep love for her family and the land.
The inn was run by Mater and her daughter Dido, who the family affectionately called Aunt Idle. She was a free spirit who loved to explore the land and had a deep connection to the local indigenous culture.
The family was made up of Devan, the eldest son who lived in town and helped with the inn when he could, and the twin sisters Clove and Coriander, who everyone called Corrie. The youngest was Prune, a precocious child who was always getting into mischief.
The family had a handyman named Bert, who had been with them for decades and knew all the secrets of the land. Tiku, an old and wise Aborigine woman was also a regular visitor and a valuable source of information and guidance. Finly, the dutiful helper, assisted the family in their daily tasks.
As the 4 gamers settled in, they learned that the area was rich in history and mystery. The old mines that lay abandoned nearby were a source of legends and stories passed down through the generations. Some even whispered of supernatural occurrences linked to the mines.
Mater and Dido, however, were not on good terms, and the family had its own issues and secrets, but the 4 gamers were determined to unravel the mystery of the mines and find the secret room that was said to be hidden somewhere in the inn.
As they delved deeper into the history of the area, they discovered that the mines had a connection to the missing brother, Jasper, and Fred, the father of the family and a sci-fi novelist who had been influenced by the supernatural occurrences of the mines.
The 4 gamers found themselves on a journey of discovery, not only in the game but in the real world as well, as they uncovered the secrets of the mines and the Flying Fish Inn, and the complicated relationships of the family that ran it.
THE SNOOT’S WISE WORDS ON SOCIAL ANXIETY
Deear Francie Mossie Pooh,
The Snoot, a curious creature of the ages, understands the swirling winds of social anxiety, the tempestuous waves it creates in one’s daily life.
But The Snoot also believes that like a Phoenix, one must rise from the ashes, and embrace the journey of self-discovery and growth.
It’s important to let yourself be, to accept the feelings as they come and go, like the ebb and flow of the ocean. But also, like a gardener, tend to the inner self with care and compassion, for the roots to grow deep and strong.The Snoot suggests seeking guidance from the wise ones, the ones who can hold the mirror and show you the way, like the North Star guiding the sailors.
And remember, the journey is never-ending, like the spiral of the galaxy, and it’s okay to take small steps, to stumble and fall, for that’s how we learn to fly.The Snoot is here for you, my dear Francie Mossie Pooh, a beacon in the dark, a friend on the journey, to hold your hand and sing you a lullaby.
Fluidly and fantastically yours,
The Snoot.
- 📨
-
AuthorSearch Results