Search Results for 'wife'
-
AuthorSearch Results
-
December 30, 2025 at 6:42 pm #8003
In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
JOHN BROOKS ALIAS PRIESTLAND
1766-1846John Brooks, my 5x great grandfather, was born in 1766, according to the 1841 census and the burial register in 1846 which stated his age at death as 80 years, but no baptism has been found thus far.
On his first son’s baptism in 1790 the parish register states “John son of John and Elizabeth Brooks Priestnal was baptised”. The name Priestnal was not mentioned in any further sibling baptism, and he was John Brooks on his marriage, on the 1841 census and on his burial in the Netherseal parish register. The name Priestnal was a mystery.
I wondered why there was a nine year gap between the first son John, and the further six siblings, and found that his first wife Elizabeth Wilson died in 1791, and in 1798 John married Elizabeth Cowper, a widow.
John was a farmer of Netherseal on both marriage licences, and of independent means on the 1841 census.
Without finding a baptism it was impossible to go further back, and I was curious to find another tree on the ancestry website with many specific dates but no sources attached, that had Thomas Brooks as his father and his mother as Mary Priestland. I couldn’t find a marriage for John and Mary Priestland, so I sent a message to the owner of the tree, and before receiving a reply, did a bit more searching.
I found an article in the newspaper archives dated 9 August 1839 about a dispute over a right of way, and John Brooks, 73 years of age and a witness for the complainant, said that he had lived in Netherseal all his life (and had always know that public right of way and so on).
I found three lists of documents held by the Derby Records Office about property deeds and transfers, naming a John Brooks alias Priestland, one in 1794, one in 1814, and one in 1824. One of them stated that his father was Thomas Brooks. I was beginning to wonder if Thomas Brooks and Mary Priestland had never married, and this proved to be the case.
The Australian owner of the other tree replied, and said that they had paid a researcher in England many years ago, and that she would look through a box of papers. She sent me a transcribed summary of the main ponts of Thomas Brooks 1784 will:
Thomas Brooks, husbandman of Netherseal
To daughter Ann husband of George Oakden, £20.
To grandson William Brooks, £20.
To son William Brooks and his wife Ann, one shilling each.
To his servant Mary Priestland, £20 and certain household effects and certain property.
To his natural son John Priestland alias Brooks, various properties and the residue of his estate.
John Priestland alias Brooks appointed sole executor.It would appear that Thomas Brooks left the bulk of his estate to his illegitimate son, and more to his servant Mary Priestland than to his legitimate children.
THOMAS BROOKS
1706-1784
Thomas Brooks, my 6x great grandfather, had three wives. He had four children with his first wife, Elizabeth, between 1732 and 1737. Elizabeth died in 1737. He then married Mary Bath, who died in 1763. Thomas had no children with Mary Bath. In 1765 Thomas married Mary Beck. In 1766 his son John Brooks alias Priestland was born to his servant Mary Priestland.
Thomas Brooks parents were John Brooks 1671-1741, and his wife Anne Speare 1674-1718, both of Netherseal, Leicestershire.
December 30, 2025 at 1:13 pm #8001In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
John Brooks
The Father of Catherine Housley’s Mother, Elizabeth Brooks.I had not managed to find out anything about the Brooks family in previous searches. We knew that Elizabeth Brooks father was J Brooks, cooper, from her marriage record. A cooper is a man who makes barrels.
Elizabeth was born in 1819 in Sutton Coldfield, parents John and Mary Brooks. Elizabeth had three brothers, all baptised in Sutton Coldfield: Thomas 1815-1821, John 1816-1821, and William Brooks, 1822-1875. William was known to Samuel Housley, the husband of Elizabeth, which we know from the Housley Letters, sent from the family in Smalley to George, Samuel’s brother, in USA, from the 1850s to 1870s. More to follow on William Brooks.
Elizabeth married Samuel Housley in Wolverhampton in 1844. Elizabeth and Samuel had three daughters in Smalley before Elizabeth’s death from TB in 1849, the youngest, just 6 weeks old at the time, was my great great grandmother Catherine Housley.
Elizabeth’s mother Mary died in 1823, and it not known if Elizabeth, then four, and William, a year old, stayed at home with their father or went to stay with relatives. There were no census records during those years.
John Brooks married Mary Wagstaff in 1814 in Birmingham. A witness at their marriage was Elizabeth Brooks, and this was probably John’s sister.
On the 1841 census (which was the first census in England) John Brooks, cooper, was living on Dudley Road, Wolverhampton, with wife Sarah. I was unable to find a marriage for them before a marriage in 1845 between John Brooks and Sarah Hughes, so presumably they lived together as man and wife before they married.
Then came the lucky find with John Brooks place of birth: Netherseal, Leicestershire. The place of birth on the 1841 census wasn’t specified, thereafter it was. On the 1851 census John Brooks, cooper, and Sarah his wife were living at Queens Cross, Dudley, with a three year old granddaughter E Brooks. John was born in 1791 in Netherseal.
It was commonplace for people to move to the industrial midlands around this time, from the surrounding countryside. However if they died before the 1851 census stating place of birth, it’s usually impossible to find out where they came from, particularly if they had a common name.
John Brooks doesn’t appear on any further census. I found seven deaths registered in Dudley for a John Brooks between 1851 and 1861, so presumably he is one of them.NETHERSEAL
On 27 June 1790 appears in the Netherseal parish register “John Brooks the son of John and Elizabeth Brooks Priestnal was baptised.” The name Priestnal does not appear in the transcription, nor the Bishops Transcripts, nor on any other sibling baptism. The Priestnal mystery will be solved in the next chapter.
John Brooks senior married Elizabeth Wilson by marriage licence on 20 November 1788 in Gresley, a neighbouring town in Derbyshire (incidentally near to Swadlincote and the ancestral lines of the Warren family, which also has branches in Netherseal. The Brooks family is the Marshall side). John Brooks was a farmer.
I haven’t found a baptism yet for John Brooks senior, but his death in Netherseal in 1846 provided the age at death, eighty years old, which puts his birth at 1766. The 1841 census has his birth as 1766 as well.
In 1841 John Brooks was 75, and “independent”, meaning that he was living on his own means. The name Brooks was transcribed as Broster, making this difficult to find, but it is clearly Brooks if you look at the original.
His wife Elizabeth, born in 1762, is also on the census, as well as the Jackson family: Joseph Jackon born 1804, Elizabeth Jackson his wife born 1799, and children Joseph, born 1833, William 1834, Thomas 1835, Stephen 1836, and Mary born 1838.
John and Elizabeths daughter Elizabeth Brooks, born in 1799, married Joseph Jackson, the son of an “opulent farmer” (newspaper archives) of Tatenhill, Staffordshire. They married on the 19th January 1832 in Burton on Trent. (Elizabeth Brooks was probably the witness on John Brooks junior’s marriage to Mary Wagstaff in Birmingham in 1814, although it could have been his mother, also Elizabeth Brooks.)
(Elizabeth Jackson nee Brooks was the aunt of Elizabeth in the portrait)
Joseph Jackson was declared bankrupt in 1833 (newspapers) and in 1834 a noticed in the newspapers “to the creditors of Joseph Jackson junior”, a victualler and farmer late of Netherseal, “following no business, who was lately dischared from his Majesty’s Gaol at Stafford” whose real estate was to be sold by auction. I haven’t yet found what he was in prison for.
In 1841 Joseph appeared again in the newspapers, in which he publicly stated that he had accused Thomas Webb, surgeon of Barton Under Needwood, of owing him money “just to annoy him” and “with a view to extort money from him”. and that he undertakes to pay Thomas Webb or his attorney, the costs within 14 days.
Joseph and Elizabeth had twins in 1841, born in Netherseal, John and Ruth. Elizabeth died in 1850.
Thereafter, Joseph was a labourer at the iron works in Wednesbury, and many generations of Jacksons continued working in the iron industry in Wednesbury ~ all orignially descended from farmers in Netherseal and Tatenhill.July 16, 2025 at 6:06 am #7969In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
Gatacre Hall and The Old Book
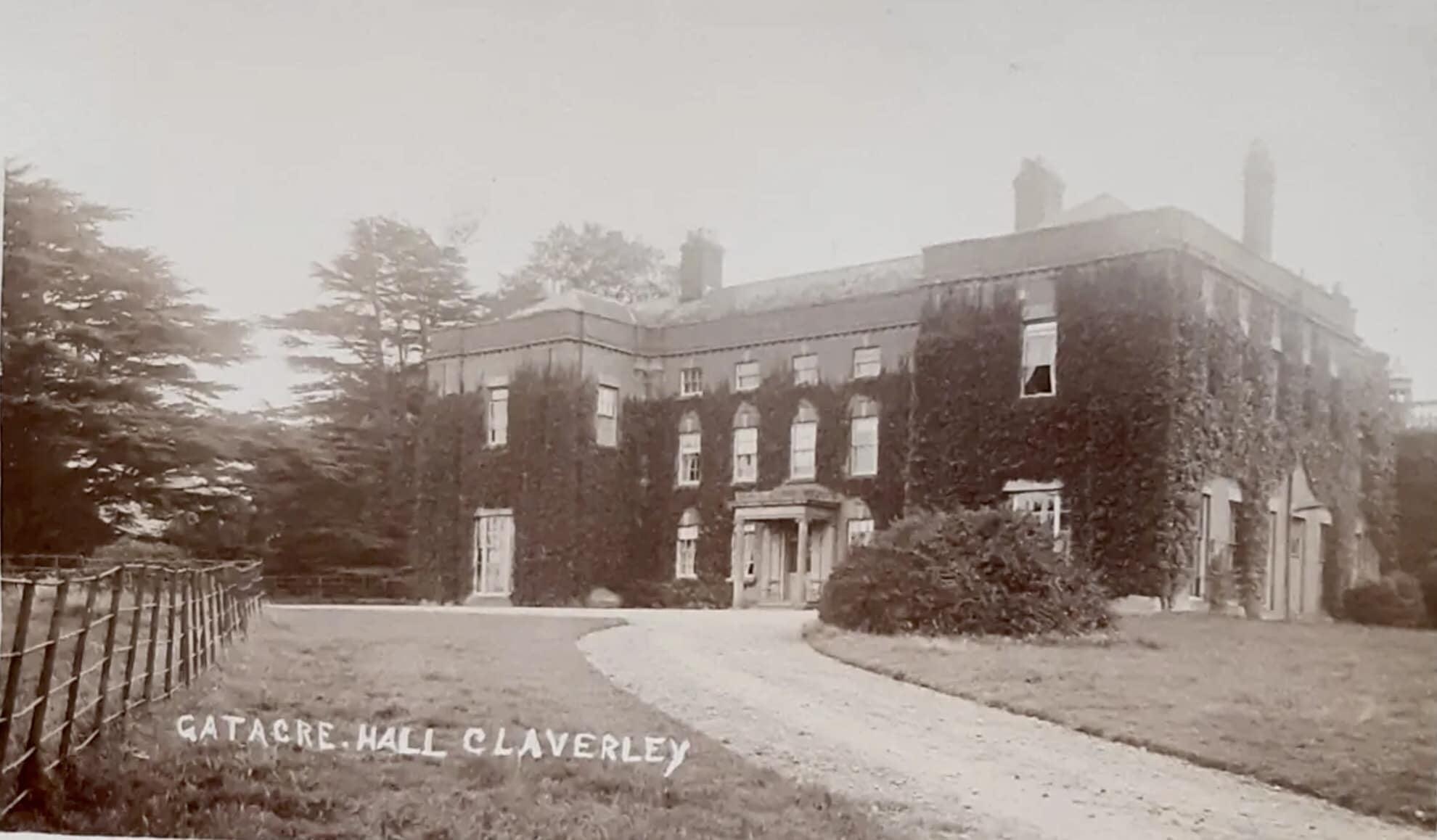

In the early 1950s my uncle John and his friend, possibly John Clare, ventured into an abandoned old house while out walking in Shropshire. He (or his friend) saved an old book from the vandalised dereliction and took it home. Somehow my mother ended up with the book.
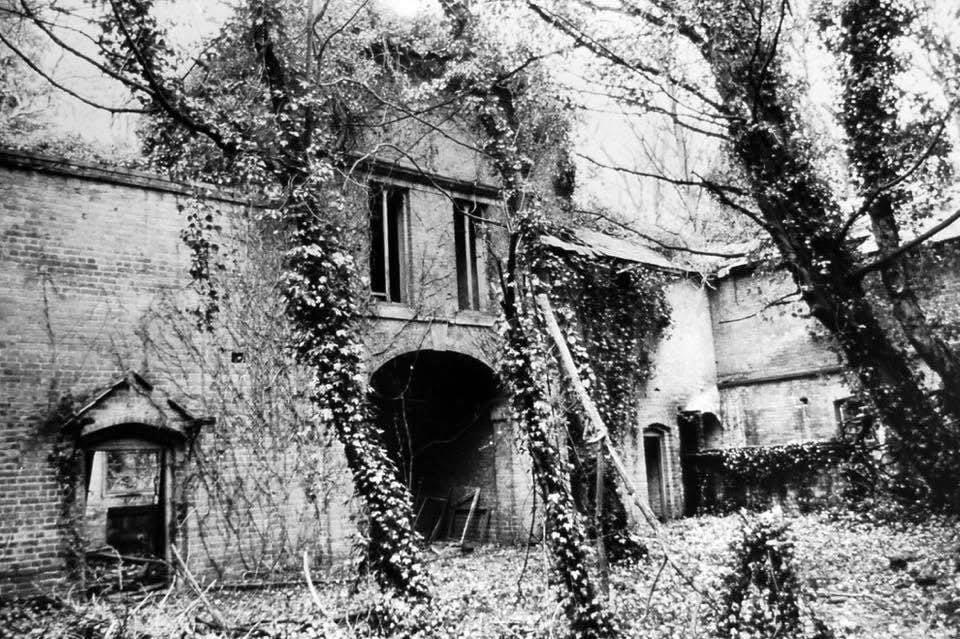

I remember that we had the book when we were living in USA, and that my mother said that John didn’t want the book in his house. He had said the abandoned hall had been spooky. The book was heavy and thick with a hard cover. I recall it was a “magazine” which seemed odd to me at the time; a compendium of information. I seem to recall the date 1553, but also recall that it was during the reign of Henry VIII. No doubt one of those recollections is wrong, probably the date. It was written in English, and had illustrations, presumably woodcuts.
I found out a few years ago that my mother had sold the book some years before. Had I known she was going to sell it, I’d have first asked her not to, and then at least made a note of the name of it, and taken photographs of it. It seems that she sold the book in Connecticut, USA, probably in the 1980’s.
My cousin and I were talking about the book and the story. We decided to try and find out which abandoned house it was although we didn’t have much to go on: it was in Shropshire, it was in a state of abandoned dereliction in the early 50s, and it contained antiquarian books.
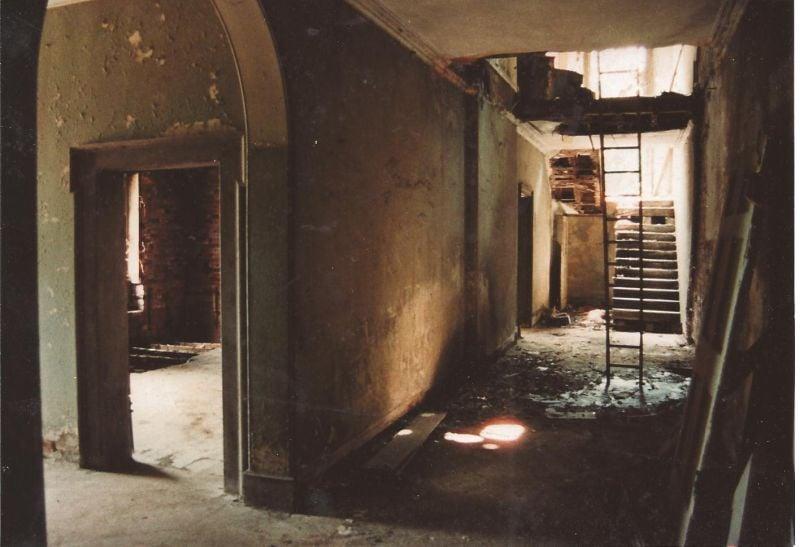

I posted the story on a Shropshire History and Nostalgia facebook group, and almost immediately had a reply from someone whose husband remembered such a place with ancient books and manuscripts all over the floor, and the place was called Gatacre Hall in Claverley, near Bridgnorth. She also said that there was a story that the family had fled to Canada just after WWII, even leaving the dishes on the table.
The Gatacre family sailing to Canada in 1947:
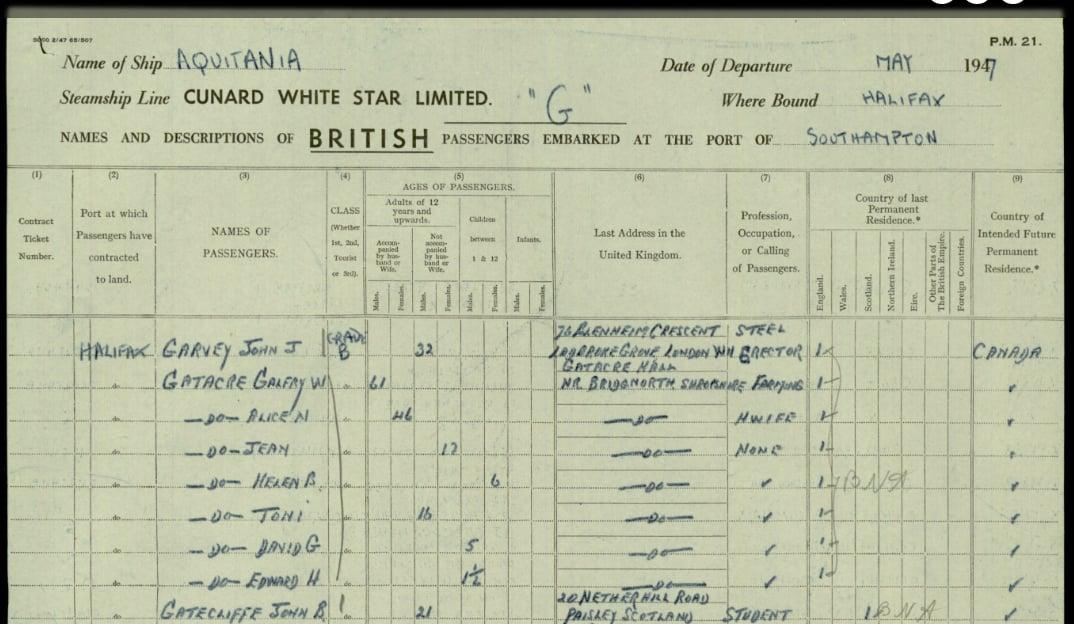
When my cousin heard the name Gatacre Hall she remembered that was the name of the place where her father had found the book.
I looked into Gatacre Hall online, in the newspaper archives, the usual genealogy sites and google books searches and so on. The estate had been going downhill with debts for some years. The old squire died in 1911, and his eldest son died in 1916 at the Somme. Another son, Galfrey Gatacre, was already farming in BC, Canada. He was unable to sell Gatacre Hall because of an entail, so he closed the house up. Between 1945-1947 some important pieces of furniture were auctioned, and the rest appears to have been left in the empty house.
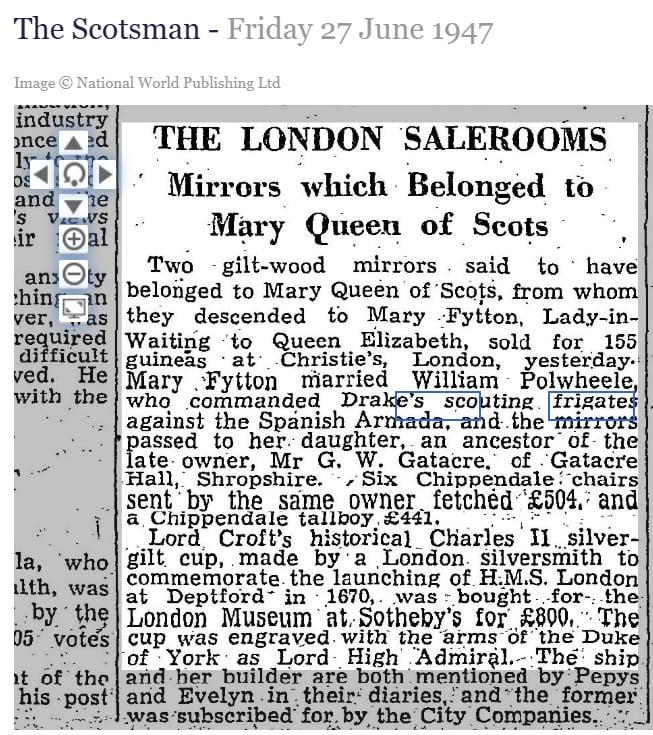
The family didn’t suddenly flee to Canada leaving the dishes on the table, although it was true that the family were living in Canada.

An interesting thing to note here is that not long after this book was found, my parents moved to BC Canada (where I was born), and a year later my uncle moved to Toronto (where he met his wife).
Captain Gatacre in 1918:

The Gatacre library was mentioned in the auction notes of a particular antiquarian book:
“Provenance: Contemporary ownership inscription and textual annotations of Thomas Gatacre (1533-1593). A younger son of William Gatacre of Gatacre Hall in Shropshire, he studied at the English college at the University of Leuven, where he rejected his Catholic roots and embraced evangelical Protestantism. He studied for eleven years at Oxford, and four years at Magdalene, Cambridge. In 1568 he was ordained deacon and priest by Bishop of London Edmund Grindal, and became domestic chaplain to Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester and was later collated to the rectory of St Edmund’s, Lombard Street. His scholarly annotations here reference other classical authors including Plato and Plutarch. His extensive library was mentioned in his will.”


There are thirty four pages in this 1662 book about Thomas Gatacre d 1654:

 June 6, 2025 at 6:02 pm #7954
June 6, 2025 at 6:02 pm #7954In reply to: Cofficionados Bandits (vs Lucid Dreamers)
Another one! A random distant memory wafted into Amy’s mind. Uncle Jack always used to say GATZ e bo. Amy could picture his smile when he said it, and how his wife always smiled back at him and chuckled. Amy wondered if she’d even known the story behind that or if it had always been a private joke between them.
“What’s been going on with my gazebo?” Amy’s father rushed into the scene. So that’s what he looks like. Amy couldn’t take her eyes off him, until Carob elbowed her in the neck.
“Sorry, I meant to elbow you in the ribs, but I’m so tall,” Carob said pointlessly, in an attempt to stop Amy staring at her father as if she’d never seen him before.
Thiram started to explain the situation with the gazebo to Amy’s father, after first introducing him to Kit, the new arrival. “Humphrey, meet Kit, our new LBGYEQCXOJMFKHHVZ story character. Kit, this is Amy’s father who we sometimes refer to as The Padre.”
“Pleased to meet you, ” Kit said politely, quaking a little at the stern glare from the old man. What on earth is he wearing? A tweed suit and a deerstalker, in this heat! How do I know that’s what they’re called? Kit wondered, quaking a little more at the strangeness of it all.
“Never mind all that now!” Humphrey interrupted Thiram’s explanation.
Still as rude as ever! Amy thought.
“I’ve too much to think about, but I’ll tell you this: I’ve planned a character building meeting in the gazebo, and you are all invited. As a matter of fact,” Humphrey continued, “You are all obliged to attend. If you choose not to ~ well, you know what happened last time!”
“What happened last time?” asked Carob, leaning forward in anticipation of an elucidating response, but Humphrey merely glared at her.
Amy sniggered, and Humphrey shot her a lopsided smile. “YOU know what happened in Jack’s GATZ e bo, don’t you, my girl?”
Where were those random memories when you wanted them? Amy had no idea what he was talking about.
“Who else is invited, Humph? asked Chico, resisting the urge to spit.
“My good man,” Humphrey said with a withering look. “Sir Humphrey’s the name to you.”
Sir? what’s he on about now? wondered Amy. Does that make me a Lady?
“Who else is invited, Padre?” Amy echoed.
Humphrey pulled a scroll tied with a purple ribbon out of his waistcoat pocket and unfurled it. Clearing his throat importantly, he read the list to all assembled.
Juan and Dolores Valdez.
Godric, the Swedish barman
Malathion and Glyphosate, Thiram’s triplet brothers. Mal and Glyph for short.
Liz Tattler
Miss Bossy Pants
Goat Horned Draugaskald“Did I forget anyone?” Humphrey asked, peering over his spectacles as he looked at each of the characters. “You lot,” he said, “Amy, Carob, Thiram, Chico, Kit and Ricardo: you will be expected to play hosts, so you might want to start thinking about refreshments. And not,” he said with a strong authoritarian air, “Not just coffee! A good range of beverages. And snacks.”
Thiram, leaning against a tree, started whistling the theme tune to Gone With The Wind. Tossing an irritated glance in his direction, Carob roughly gathered up her mass of frizzy curls and tethered it all in a tight pony tail. I still don’t know what happened before, she fumed silently. The latest developments where making her nervous. Would they find out her secret?
“You guys,” called Chico, who had wandered over to the gazebo. “It’s full of ants.”
March 1, 2025 at 3:21 pm #7849In reply to: The Last Cruise of Helix 25
Helix 25 – The Genetic Puzzle
Amara’s Lab – Data Now Aggregated
(Discrepancies Never Addressed)On the screen in front of Dr. Amara Voss, lines upon lines of genetic code were cascading and making her sleepy. While the rest of the ship was running amok, she was barricaded into her lab, content to have been staring at the sequences for the most part of the day —too long actually.
She took a sip of her long-cold tea and exhaled sharply.
Even if data was patchy from the records she had access to, there was a solid database of genetic materials, all dutifully collected for all passengers, or crew before embarkment, as was mandated by company policy. The official reason being to detect potential risks for deep space survival. Before the ship’s take-over, systematic recording of new-borns had been neglected, and after the ship’s takeover, population’s new born had drastically reduced, with the birth control program everyone had agreed on, as was suggested by Synthia. So not everyone’s DNA was accounted for, but in theory, anybody on the ship could be traced back and matched by less than 2 or 3 generations to the original data records.
The Marlowe lineage was the one that kept resurfacing. At first, she thought it was coincidence—tracing the bloodlines of the ship’s inhabitants was messy, a tangled net of survivors, refugees, and engineered populations. But Marlowe wasn’t alone.
Another name pulsed in the data. Forgelot. Then Holt. Old names of Earth, unlike the new star-birthed. There were others, too.
Families that had been aboard Helix 25 for some generations. But more importantly, bloodlines that could be traced back to Earth’s distant past.
But beyond just analysing their origins, there was something else that caught her attention. It was what was happening to them now.
Amara leaned forward, pulling up the mutation activation models she had been building. In normal conditions, these dormant genetic markers would remain just that—latent. Passed through generations like forgotten heirlooms, meaningless until triggered.
Except in this case, there was evidence that something had triggered them.
The human body, subjected to long-term exposure to deep space radiation, artificial gravity shifts, and cosmic phenomena, and had there not been a fair dose of shielding from the hull, should have mutated chaotically, randomly. But this was different. The genetic sequences weren’t just mutating—they were activating.
And more surprisingly… it wasn’t truly random.
Something—or someone—had inherited an old mechanism that allowed them to access knowledge, instincts, memories from generations long past.
The ancient Templars had believed in a ritualistic process to recover ancestral skills and knowledge. What Amara was seeing now…
She rubbed her forehead.
“Impossible.”
And yet—here was the data.
On Earth, the past was written in stories and fading ink. In space, the past was still alive—hiding inside their cells, waiting.
Earth – The Quiz Night Reveal
The Golden Trowel, Hungary
The candlelit warmth of The Golden Trowel buzzed with newfound energy. The survivors sat in a loose circle, drinks in hand, at this unplanned but much-needed evening of levity.
Once the postcards shared, everyone was listening as Tala addressed the group.
“If anyone has an anecdote, hang on to the postcard,” she said. “If not, pass it on. No wrong answers, but the best story wins.”
Molly felt the weight of her own selection, the Giralda’s spire sharp and unmistakable. Something about it stirred her—an itch in the back of her mind, a thread tugging at long-buried memories.
She turned toward Vera, who was already inspecting her own card with keen interest.
“Tower of London, anything exciting to share?”
Vera arched a perfectly sculpted eyebrow, lips curving in amusement.
“Molly Darling,” she drawled, “I can tell you lots, I know more about dead people’s families than most people know about their living ones, and London is surely a place of abundance of stories. But do you even know about your own name Marlowe?”
She spun the postcard between her fingers before answering.
“Not sure, really, I only know about Philip Marlowe, the fictional detective from Lady in the Lake novel… Never really thought about the name before.”
“Marlowe,” Vera smiled. “That’s an old name. Very old. Derived from an Old English phrase meaning ‘remnants of a lake.’”
Molly inhaled sharply.
Remnants of the Lady of the Lake ?
Her pulse thrummed. Beyond the historical curiosity she’d felt a deep old connection.
If her family had left behind records, they would have been on the ship… The thought came with unwanted feelings she’d rather have buried. The living mattered, the lost ones… They’d lost connection for so long, how could they…
Her fingers tightened around the postcard.
Unless there was something behind her ravings?
Molly swallowed the lump in her throat and met Vera’s gaze. “I need to talk to Finja.”

Finja had spent most of the evening pretending not to exist.
But after the fifth time Molly nudged her, eyes bright with silent pleas, she let out a long-suffering sigh.
“Alright,” she muttered. “But just one.”
Molly exhaled in relief.
The once-raucous Golden Trowel had dimmed into something softer—the edges of the night blurred with expectation.
Because it wasn’t just Molly who wanted to ask.
Maybe it was the effect of the postcards game, a shared psychic connection, or maybe like someone had muttered, caused by the new Moon’s sickness… A dozen others had realized, all at once, that they too had names to whisper.
Somehow, a whole population was still alive, in space, after all this time. There was no time for disbelief now, Finja’s knowledge of stuff was incontrovertible. Molly was cued by the care-taking of Ellis Marlowe by Finkley, she knew things about her softie of a son, only his mother and close people would know.
So Finja had relented. And agreed to use all means to establish a connection, to reignite a spark of hope she was worried could just be the last straw before being thrown into despair once again.
Finja closed her eyes.
The link had always been there, an immediate vivid presence beneath her skull, pristine and comfortable but tonight it felt louder, crowdier.
The moons had shifted, in syzygy, with a gravity pull in their orbits tugging at things unseen.
She reached out—
And the voices crashed into her.
Too much. Too many.
Hundreds of voices, drowning her in longing and loss.
“Where is my brother?”
“Did my wife make it aboard?”
“My son—please—he was supposed to be on Helix 23—”
“Tell them I’m still here!”Her head snapped back, breath shattering into gasps.
The crowd held its breath.
A dozen pairs of eyes, wide and unblinking.
Finja clenched her fists. She had to shut it down. She had to—
And then—
Something else.
A presence. Watching.
Synthia.
Her chest seized.
There was no logical way for an AI to interfere with telepathic frequencies.
And yet—
She felt it.
A subtle distortion. A foreign hand pressing against the link, observing.
The ship knew.
Finja jerked back, knocking over her chair.
The bar erupted into chaos.
“FINJA?! What did you see?”
“Was someone there?”
“Did you find anyone?!”Her breath came in short, panicked bursts.
She had never thought about the consequences of calling out across space.
But now…
Now she knew.
They were not the last survivors. Other lived and thrived beyond Earth.
And Synthia wanted to keep it that way.
Yet, Finja and Finkley had both simultaneously caught something.
It would take the ship time, but they were coming back. Synthia was not pleased about it, but had not been able to override the response to the beacon.They were coming back.
February 18, 2025 at 8:12 am #7825In reply to: The Last Cruise of Helix 25
“I didn’t much like where the world was heading anyway, Gregor,” Molly said, leaning towards the old man who was riding beside her. “Before it all ended I mean. All that techno feudalist stuff. Once we got over the shock of it all, I’ll be honest, I rather liked it. Oh not that everyone was dead, I don’t mean that,” she added. She didn’t want to give the impression that she was cold or ruthless. “But, you know, something had to happen to stop where that was going.”
Gregor didn’t respond immediately. He hadn’t thought about the old days for a long time, and long suppressed memories flooded his mind. Eventually he replied, “If it hadn’t been for that plague, we’d have been exterminated, I reckon. Surplus to requirements, people like us.”
Molly looked at him sharply. “Did you hear of extermination camps here? We’d started to hear about them before the plague. But there were so many problems with communication. People started disappearing and it was impossible by then to find out what happened to them.”
“I was one of the ones who disappeared,” Gregor said. “They summoned me for questioning about something I’d said on Folkback. I told the wife not to worry, I’d be back soon when I’d explained to them, and she said to me to call in at the shop on the way home and get some milk and potatoes.” A large tear rolled down the old mans leathery cheek. “I never saw her again.”
Molly leaned over and compassionately gripped Gregors arm for a moment, and then steadied herself as Berlingo descended the last part of the hill before the track where the truck had been sighted.
The group halted and gathered around the tyre tracks. They were easily visible going in both directions and a discussion ensued about which way to go: follow the truck, or retrace the trucks journey to see where it came from?
“Down, Berlingo!” Molly instructed her horse. “I need to get off and find a bush. First time in years I’ve had to hide to have a pee!” she laughed, “There’s never been anyone around to see.”
Molly took her time, relishing a few moments of solitude. Suddenly being surrounded by people was a mixed blessing. It was stimulating and exciting, but also tiring and somewhat unsettling. She closed her eyes and took a few deep breaths and calmed her mind.
She returned to the group to a heated discussion on which way to go. Jian was in favour of going in the direction of the city, which appeared to be the direction the truck had come from. Mikhail wanted to follow where the truck had gone.
“If the truck came from the city, it means there is something in the city,” reasoned Jian. “It could be heading anywhere, and there are no cities in the direction the truck went.”
“There might not be any survivors in the city though,” Anya said, “And we know there’s at least one survivor IN the truck.”
“We could split up into two groups,” suggested Tala, but this idea was unanimously rejected.
“We have all the time in the world to go one way first, and the other way later,” Mikhail said. “I think we should head for the city first, and follow where the truck came from. Jian is right. And there’s more chance of finding something we can use in the city, than a wild goose chase to who knows where.”
“More chance of finding some disinfectant in the city, too,” Finja added.
 February 14, 2025 at 10:02 am #7780
February 14, 2025 at 10:02 am #7780In reply to: The Last Cruise of Helix 25
Orrin Holt gripped the wheel of the battered truck, his knuckles white as the vehicle rumbled over the dry, cracked road. The leather wrap was a patchwork of smooth and worn, stichted together from whatever scraps they had—much like the quilts his mother used to make before her hands gave out. The main road was a useless, unpredictable mess of asphalt gravels and sinkholes. Years of war with Russia, then the collapse, left it to rot before anyone could fix it. Orrin stuck to the dirt path beside it. That was the only safe way through. The engine coughed but held. A miracle, considering how many times it had been patched together.
The cargo in the back was too important for a breakdown now. Medical supplies—antibiotics, painkillers, and a few salvaged vials of something even rarer. They’d traded well for it, risking much. Now he had to get it back to Base Klyutch (Ukrainian word for Key) without incident. If he continued like that he could make it before noon.
Still, something bothered him. That group of people he’d seen.
They had been barely more than silhouettes on top of a hill. Strangers, a rarity in these times. His first instinct had been to stop and evaluate who they were. But his instructions let room for no delay. So, he’d pushed forward and ignored them. The world wasn’t kind to the wandering. But they hadn’t looked like raiders or scavengers. Lost, perhaps. Or searching.
The truck lurched forward as he pushed it harder. The fences of the base rose in the distance, grey and wiry against the blue sky. Base Klyutch was a former military complex, fortified over the years with scavenged materials, steel sheets, and watchtowers. It wasn’t perfect, but it kept them alive.
As he rolled up to the main gate, the sentries swung the barricade open. Before he could fully cut the engine, a woman wearing a pristine white lab coat stepped forward, her sharp eyes scanning the truck’s cargo bed. Dr. Yelena Markova, the camp’s chief doctor, a former nurse who had to step up when the older one died in a raid on their camp three years ago. Stern-faced and wiry, with a perpetual air of exhaustion, she moved with the efficiency of someone who had long stopped hoping for ease. She had been waiting for this delivery.
“Finally,” she murmured, motioning for her assistants to start unloading. “We were running low. This will keep us going for a while.”
Orrin barely had time to nod before Dmytro Koval, the de facto leader of the base, strode toward him with the gait of a tall bear. His face seemed to have been carved out by a dulled blade, hardened by years of survival. A scar barred his mouth, pulling slightly at the corner when he spoke, giving the impression of a permanent sneer.
“Did you get it?” Koval asked, voice low.
Orrin reached into his kaki jacket and pulled out a sealed letter, along with a small package.
Koval took both, his expression unreadable. “Anything on the road?”
Orrin exhaled and adjusted his stance. “Saw something on the way back. A group, about a dozen, on a hill ten kilometers out. They seemed lost.”
“Armed?” asked Koval with a frown.
“Can’t say for sure.”
Dr. Markova straightened. “Lost? Unarmed? Out in the open like that, they won’t last long with Sokolov’s gang roaming the land. We have to go take them in.”
Koval grimaced. “Or they’re Sokolov’s spies. Trying to infiltrate us and find a weakness in our defenses. You know how it works.”
Before Koval could argue, a new voice cut in. “Or they could just be people.”
Solara Ortega had stepped into the conversation, brushing dirt from her overalls. A woman of lean strength, with the tan of someone spending long hours outside. Her sharp amber eyes carried the weight of someone who had survived too much but refused to be hardened by it. Orrin shoved down a mix of joy and ache at her sight. Her voice was calm but firm. “We can’t always assume the worst. We need more hands and we don’t leave people to die if we can help it. And in case you forgot, Koval, you don’t make all the decisions around here. I say we send a team to assess them.”
Koval narrowed his eyes, but he held his tongue. There was tension between them, but the council wasn’t a dictatorship.
“Fine,” Koval said after a moment, his jaw tense. “A team of two. They scout first. No direct contact until we’re sure. Orrin, you one of them take whoever wants to accompany you, but not one of my men. We need to maintain tight security.”
Dr. Markova sighed with relief when the man left. “If he wasn’t good at what he does, I would gladly kick him out of our camp.”
Solara, her face framed by strands of dark hair, shot a glance at Orrin. “I’m coming with you.”
This time, Orrin couldn’t repress a longing for a time before everything fell apart, when she had been his wife. The collapse had torn them apart in an instant, and by the time he found her again, years later, she had built a new life within the base in Ukraine. She had a husband now, one of the scientists managing the radio equipment, and two children. Orrin kept his expression neutral, but the weight of time pressed heavy on him.
“Then let’s get on the move. They might not stay there long.”
December 10, 2024 at 9:42 pm #7661In reply to: Quintessence: Reversing the Fifth
Early May 2022
“You don’t look like a physicist,” Florian said on their first evening together. Most of the day since his arrival that morning had been taken up with Elara showing him around the farmhouse and a stroll outside after he’d unpacked and showered.
It was early May, Elara’s favourite time of the year, and the pandemic restrictions were largely over. An enthusiastic hiker and ardent lover of the countryside, Florian found his hosts running commentary as they walked the blossomy lanes a tonic after the grim scenesand mental anguish he’d left behind. Elara beamed at his evident interest and perspicacious questions, warming to him and realising how much she’d missed company and conversation during the lockdowns and subsequent limiting of social interactions. It’s so nice to have a conversation in English, she couldn’t help thinking.
Laughing, Elara replied that she’d never felt like a physicist either. “As soon as I started my first post after qualifying, I realised it wasn’t for me. I hadn’t really thought about the jobs, you know?”
Happy to have such an attentive listener, the convivial glow of red wine warming her veins, Elara explained that she’d resorted to short term teaching contracts mostly, enabling her to travel. She learned Spanish when she moved with her father to Spain 30 years ago, working in an English school for expats, improved her French while working in Paris, moved to Warwick to be near her sister Vanessa thinking she would settle there, “Big mistake that was, best forgotten.”
“I always wanted to travel a bit, but the wife always wanted to go to a resort to sunbathe,” Florian said, adding pensively, “I think the kids would have liked to travel though.”
“I think you’ll enjoy your stay here,” Elara smiled, not wanting the pleasant evening to take a despondant turn. Florian was here to get over it, not dwell on it.
October 24, 2024 at 7:56 am #7568In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
The year 480 AD. It was there hovering in her mind the moment she woke up the morning after Eris had mentioned the DNA spell idea. 480 AD. But why? And it seemed strangely familiar, as if she’d dreamed of that date before. Mumbling the date over and over, Truella pushed the bed covers back, noted the welcome slight chill of the October morning, and made her way blindly to the kitchen to make coffee. 480 AD. Why, though?
Eris’s change of tune yesterday about the paperwork had given her a slight inward chuckle, but it was a good sign. And Eris had been right: Truella did like the DNA idea. At first she’d wondered if she would find something containing DNA. Then she reminded herself that she herself contained DNA available to use. But what was the year 480 AD to do with it?
Taking her steaming mug of coffee outside, Truella sat down under the porch and lit a cigarette. Too late for Romans but then what was next after Romans? It would have made more sense if it was 1480 AD, when Cromwell was born.
Oh, but what an idea! Yes! The DNA of Cromwell! She was reminded of the pieces of Hannibals tunic, and the efficacy of that spell. If they could find a bit of that old tunic, they could surely time travel back to gather some DNA from old Thomas. Truella giggled, imagining herself appearing in Cromwell’s chamber, armed with a cotton swab. “If you please, my Lord, open wide, this will only take a moment.”
He would rub his eyes, wondering if the fever had returned. What was this unseemly wench doing in here, bearing an uncanny resemblance to Lizzie, his dead wife. “Open wide,” she would say, for all the world as if she was the one giving the orders. “My lady, if you please to explain your purpose?” he would replied calmly, rather amused at the incomprehensible interlude.
“Well if you must know, we need some of your DNA. Yes, yes, I know you don’t know what that is yet, I’ve come from the future you see, and we know a lot more. Well, that’s not strictly true or I wouldn’t be here now. We know more about some things, but other things haven’t changed much. It’s the sea of paperwork we’re drowning in. Nobody could have more paperwork than you, my Lord Cromwell, but you have a particularly efficient way of dealing with it.”
“Are you referring to the Tower and the …”
“Gosh, no! No, we don’t plan to execute anyone. We just need a bit, a tiny bit, of your DNA to use in a spell…”
Suddenly Cromwell understood who this woman was. He didn’t need to call for the man who dealt with postcards from the future: everyone knows that Cromwell never forgets any paperwork he’s ever seen. In the future they called it photographic memory, but of course it wasn’t called that in his time.
“You, my lady, are one of those witches from the future, are you not? And why, pray, would I be willing to assist with witchcraft?”
“Well, why not?” retorted Truella. “You won’t be around to be executed for heresy, you were already..” She clapped her hand to her mouth. He didn’t know about that yet, obviously.
Cromwell merely raised a sardonic eyebrow. “I don’t want to know when,” he said calmly. He knew his days were numbered.
“Now, there a number of ways we can collect a bit of your DNA, sir, any bodily fluid will do,” Truella said, and then blushed deeply. Well, why not? she asked herself, and then wondered, What if he hasn’t had a bath for six months?
August 28, 2024 at 1:31 pm #7549In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
The Tailor of Haddon
Wibberly and Newton of Over HaddonIt was noted in the Bakewell parish register in 1782 that John Wibberly 1705?-1782 (my 6x great grandfather) was “taylor of Haddon”.

James Marshall 1767-1848 (my 4x great grandfather), parish clerk of Elton, married Ann Newton 1770-1806 in Elton in 1792. In the Bakewell parish register, Ann was baptised on the 2rd of June 1770, her parents George and Dorothy Newton of Upper Haddon. The Bakewell registers at the time covered several smaller villages in the area, although what is currently known as Over Haddon was referred to as Upper Haddon in the earlier entries.
Newton:
George Newton 1728-1798 was the son of George Newton 1706- of Upper Haddon and Jane Sailes, who were married in 1727, both of Upper Haddon.
George Newton born in 1706 was the son of George Newton 1676- and Anne Carr, who were married in 1701, both of Upper Haddon.
George Newton born in 1676 was the son of John Newton 1647- and Alice who were married in 1673 in Bakewell. There is no last name for Alice on the marriage transcription.
John Newton born in 1647 (my 9x great grandfather) was the son of John Newton and Anne Buxton (my 10x great grandparents), who were married in Bakewell in 1636.
1636 marriage of John Newton and Anne Buxton:

Wibberly
Dorothy Wibberly 1731-1827 married George Newton in 1755 in Bakewell. The entry in the parish registers says that they were both of Over Haddon. Dorothy was baptised in Bakewell on the 25th June 1731, her parents were John and Mary of Over Haddon.
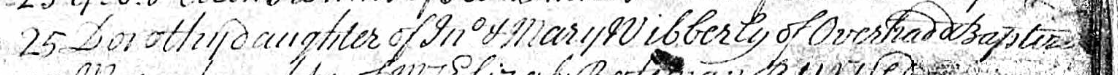
John Wibberly and Mary his wife baptised nine children in Bakewell between 1730 and 1750, and on all of the entries in the parish registers it is stated that they were from Over Haddon. A parish register entry for John and Mary’s marriage has not yet been found, but a marriage in Beeley, a tiny nearby village, in 1728 to Mary Mellor looks likely.
John Wibberly died in Over Haddon in 1782. The entry in the Bakewell parish register notes that he was “taylor of Haddon”.
The tiny village of Over Haddon was historically associated with Haddon Hall.
A baptism for John Wibberly has not yet been found, however, there were Wibersley’s in the Bakewell registers from the early 1600s:
1619 Joyce Wibersley married Raphe Cowper.
1621 Jocosa Wibersley married Radulphus Cowper
1623 Agnes Wibersley married Richard Palfreyman
1635 Cisley Wibberlsy married ? Mr. Mason
1653 John Wibbersly married Grace DaykenHaddon Hall
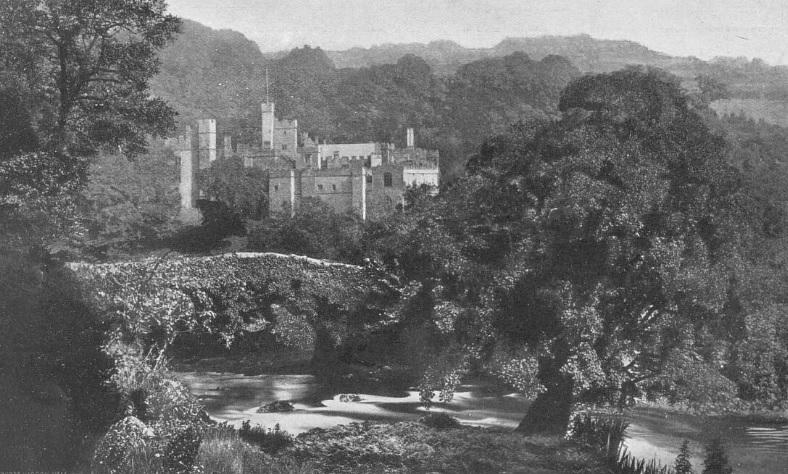

Sir Richard Vernon (c. 1390 – 1451) of Haddon Hall.
Vernon’s property was widespread and varied. From his parents he inherited the manors of Marple and Wibersley, in Cheshire. Perhaps the Over Haddon Wibersley’s origins were from Sir Richard Vernon’s property in Cheshire. There is, however, a medieval wayside cross called Whibbersley Cross situated on Leash Fen in the East Moors of the Derbyshire Peak District. It may have served as a boundary cross marking the estate of Beauchief Abbey. Wayside crosses such as this mostly date from the 9th to 15th centuries.Found in both The History and Antiquities of Haddon Hall by S Raynor, 1836, and the 1663 household accounts published by Lysons, Haddon Hall had 140 domestic staff.
In the book Haddon Hall, an Illustrated Guide, 1871, an example from the 1663 Christmas accounts:


Also in this book, an early 1600s “washing tally” from Haddon Hall:
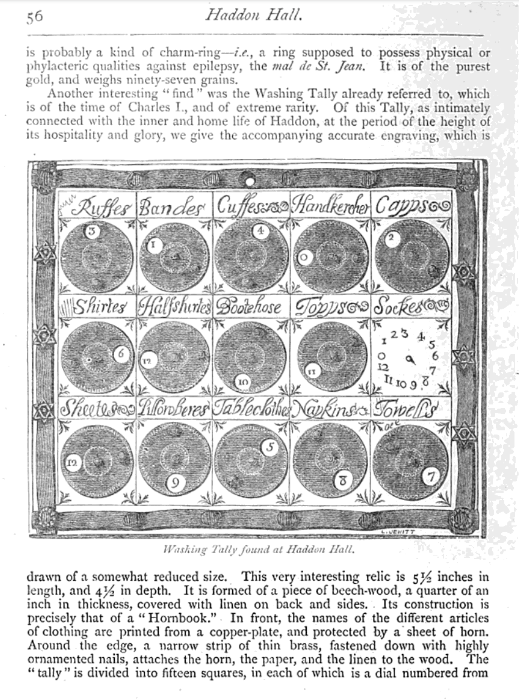
Over Haddon
Martha Taylor, “the fasting damsel”, was born in Over Haddon in 1649. She didn’t eat for almost two years before her death in 1684. One of the Quakers associated with the Marshall Quakers of Elton, John Gratton, visited the fasting damsel while he was living at Monyash, and occasionally “went two miles to see a woman at Over Haddon who pretended to live without meat.” from The Reliquary, 1861.
August 28, 2024 at 6:26 am #7548In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
Elton Marshall’s
Early Quaker Emigrants to USA.
The earliest Marshall in my tree is Charles Marshall (my 5x great grandfather), Overseer of the Poor and Churchwarden of Elton. His 1819 gravestone in Elton says he was 77 years old when he died, indicating a birth in 1742, however no baptism can be found.
According to the Derbyshire records office, Elton was a chapelry of Youlgreave until 1866. The Youlgreave registers date back to the mid 1500s, and there are many Marshalls in the registers from 1559 onwards. The Elton registers however are incomplete due to fire damage.
While doing a google books search for Marshall’s of Elton, I found many American family history books mentioning Abraham Marshall of Gratton born in 1667, who became a Quaker aged 16, and emigrated to Pennsylvania USA in 1700. Some of these books say that Abraham’s parents were Humphrey Marshall and his wife Hannah Turner. (Gratton is a tiny village next to Elton, also in Youlgreave parish.)
Abraham’s son born in USA was also named Humphrey. He was a well known botanist.
Abraham’s cousin John Marshall, also a Quaker, emigrated from Elton to USA in 1687, according to these books.
(There are a number of books on Colonial Families in Pennsylvania that repeat each other so impossible to cite the original source)

In the Youlgreave parish registers I found a baptism in 1667 for Humphrey Marshall son of Humphrey and Hannah. I didn’t find a baptism for Abraham, but it looks as though it could be correct. Abraham had a son he named Humphrey. But did it just look logical to whoever wrote the books, or do they know for sure? Did the famous botanist Humphrey Marshall have his own family records? The books don’t say where they got this information.
An earlier Humphrey Marshall was baptised in Youlgreave in 1559, his father Edmund. And in 1591 another Humphrey Marshall was baptised, his father George.
But can we connect these Marshall’s to ours? We do have an Abraham Marshall, grandson of Charles, born in 1792. The name isn’t all that common, so may indicate a family connection. The villages of Elton, Gratton and Youlgreave are all very small and it would seem very likely that the Marshall’s who went the USA are related to ours, if not brothers, then probably cousins.
Derbyshire Quakers
In “Derbyshire Quakers 1650-1761” by Helen Forde:
“… Friends lived predominantly in the northern half of the country during this first century of existence. Numbers may have been reduced by emigration to America and migration to other parts of the country but were never high and declined in the early eighteenth century. Predominantly a middle to lower class group economically, Derbyshire Friends numbered very few wealthy members. Many were yeoman farmers or wholesalers and it was these groups who dominated the business meetings having time to devote themselves to the Society. Only John Gratton of Monyash combined an outstanding ministry together with an organising ability which brought him recognition amongst London Friends as well as locally. Derbyshire Friends enjoyed comparatively harmonious relations with civil and Anglican authorities, though prior to the Toleration Act of 1639 the priests were their worst persecutors…..”
Also mentioned in this book: There were monthly meetings in Elton, as well as a number of other nearby places.
John Marshall of Elton 1682/3 appears in a list of Quaker emigrants from Derbyshire.
The following image is a page from the 1753 book on the sufferings of Quakers by Joseph Besse as an example of some of the persecutions of Quakers in Derbyshire in the 1600s:
A collection of the sufferings of the people called Quakers, for the testimony of a good conscience from the time of their being first distinguished by that name in the year 1650 to the time of the act commonly called the Act of toleration granted to Protestant dissenters in the first year of the reign of King William the Third and Queen Mary in the year 1689 (Volume 1)
Besse, Joseph. 1753Note the names Margaret Marshall and Anne Staley. This book would appear to contradict Helen Forde’s statement above about the harmonious relations with Anglican authority.

The Botanist
Humphry Marshall 1722-1801 was born in Marshallton, Pennsylvania, the son of the immigrant from Elton, Abraham Marshall. He was the cousin of botanists John Bartram and William Bartram. Like many early American botanists, he was a Quaker. He wrote his first book, A Few Observations Concerning Christ, in 1755.

In 1785, Marshall published Arbustrum Americanum: The American Grove, an Alphabetical Catalogue of Forest Trees and Shrubs, Natives of the American United States (Philadelphia).
Marshall has been called the “Father of American Dendrology”.
A genus of plants, Marshallia, was named in honor of Humphry Marshall and his nephew Moses Marshall, also a botanist.
In 1848 the Borough of West Chester established the Marshall Square Park in his honor. Marshall Square Park is four miles east of Marshallton.
via Wikipedia.
From The History of Chester County Pennsylvania, 1881, by J Smith Futhey and Gilbert Cope:

From The Chester Country History Center:
“Immediately on the Receipt of your Letter, I ordered a Reflecting Telescope for you which was made accordingly. Dr. Fothergill had since desired me to add a Microscope and Thermometer, and will
pay for the whole.’– Benjamin Franklin to Humphry, March 18, 1770
“In his lifetime, Humphry Marshall made his living as a stonemason, farmer, and miller, but eventually became known for his contributions to astronomy, meteorology, agriculture, and the natural sciences.
In 1773, Marshall built a stone house with a hothouse, a botanical laboratory, and an observatory for astronomical studies. He established an arboretum of native trees on the property and the second botanical garden in the nation (John Bartram, his cousin, had the first). From his home base, Humphry expanded his botanical plant exchange business and increased his overseas contacts. With the help of men like Benjamin Franklin and the English botanist Dr. John Fothergill, they eventually included German, Dutch, Swedish, and Irish plant collectors and scientists. Franklin, then living in London, introduced Marshall’s writings to the Royal Society in London and both men encouraged Marshall’s astronomical and botanical studies by supplying him with books and instruments including the latest telescope and microscope.
Marshall’s scientific work earned him honorary memberships to the American Philosophical Society and the Philadelphia Society for Promoting Agriculture, where he shared his ground-breaking ideas on scientific farming methods. In the years before the American Revolution, Marshall’s correspondence was based on his extensive plant and seed exchanges, which led to further studies and publications. In 1785, he authored his magnum opus, Arbustum Americanum: The American Grove. It is a catalog of American trees and shrubs that followed the Linnaean system of plant classification and was the first publication of its kind.”
 August 21, 2024 at 12:27 pm #7546
August 21, 2024 at 12:27 pm #7546In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
The Potters of Darley Bridge
Rebecca Knowles 1745-1823, my 5x great grandmother, married Charles Marshall 1742-1819, the churchwarden of Elton, in Darley, Derbyshire, in 1767. Rebecca was born in Darley in 1745, the youngest child of Roger Knowles 1695-1784, and Martha Potter 1702?-1772.
Although Roger and Martha were both from Darley, they were married in South Wingfield by licence in 1724. Roger’s occupation on the marriage licence was lead miner. (Lead miners in Derbyshire at that time usually mined their own land.) Jacob Potter signed the licence so I assumed that Jacob Potter was her father.

I then found the will of Jacobi Potter who died in 1719. However, he signed the will James Potter. Jacobi is latin for James. James Potter mentioned his daughter Martha in his will “when she comes of age”. Martha was the youngest child of James. James also mentioned in his will son James AND son Jacob, so there were both James’s and Jacob’s in the family, although at times in the documents James is written as Jacobi!

Jacob Potter who signed Martha’s marriage licence was her brother Jacob.
Martha’s brother James mentioned his sister Martha Knowles in his 1739 will, as well as his brother Jacob and his brother Joseph.

Martha’s father James Potter mentions his wife Ann in his 1719 will. James Potter married Ann Waterhurst in 1690 in Wirksworth, some seven miles from Darley. James occupation was innkeeper at Darley Bridge.
I did a search for Waterhurst (there was only a transcription available for that marriage, not a microfilm) and found no Waterhursts anywhere, but I did find many Warhursts in Derbyshire. In the older records, Warhust is also spelled Wearhurst and in a number of other ways. A Martha Warhurst died in Peak Forest, Derbyshire, in 1681. Her husbands name was missing from the deteriorated register pages. This may or may not be Martha Potter’s grandmother: the records for the 1600s are scanty if they exist at all, and often there are bits missing and illegible entries.
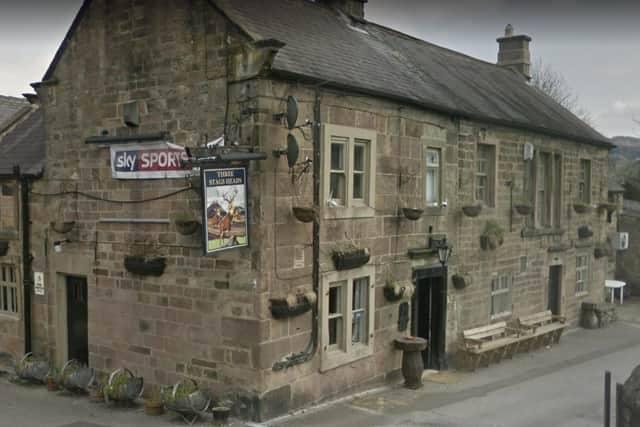
The only inn at Darley Bridge was The Three Stags Heads, by the bridge. It is now a listed building, and was on a medieval packhorse route. The current building was built in 1736, however there is a late 17th century section at rear of the cross wing. The Three Stags Heads was up for sale for £430,000 in 2022, the closure a result of the covid pandemic.

Another listed building in Darley Bridge is Potters Cottage, with a plaque above the door that says “Jonathan and Alice Potter 1763”. Jonathan Potter 1725-1785 was James grandson, the son of his son Charles Potter 1691-1752. His son Charles was also an innkeeper at Darley Bridge: James left the majority of his property to his son Charles.

Charles is the only child of James Potter that we know the approximate date of birth, because his age was on his grave stone. I haven’t found any of their baptisms, but did note that many Potters were baptised in non conformist registers in Chesterfield.
Potters Cottage
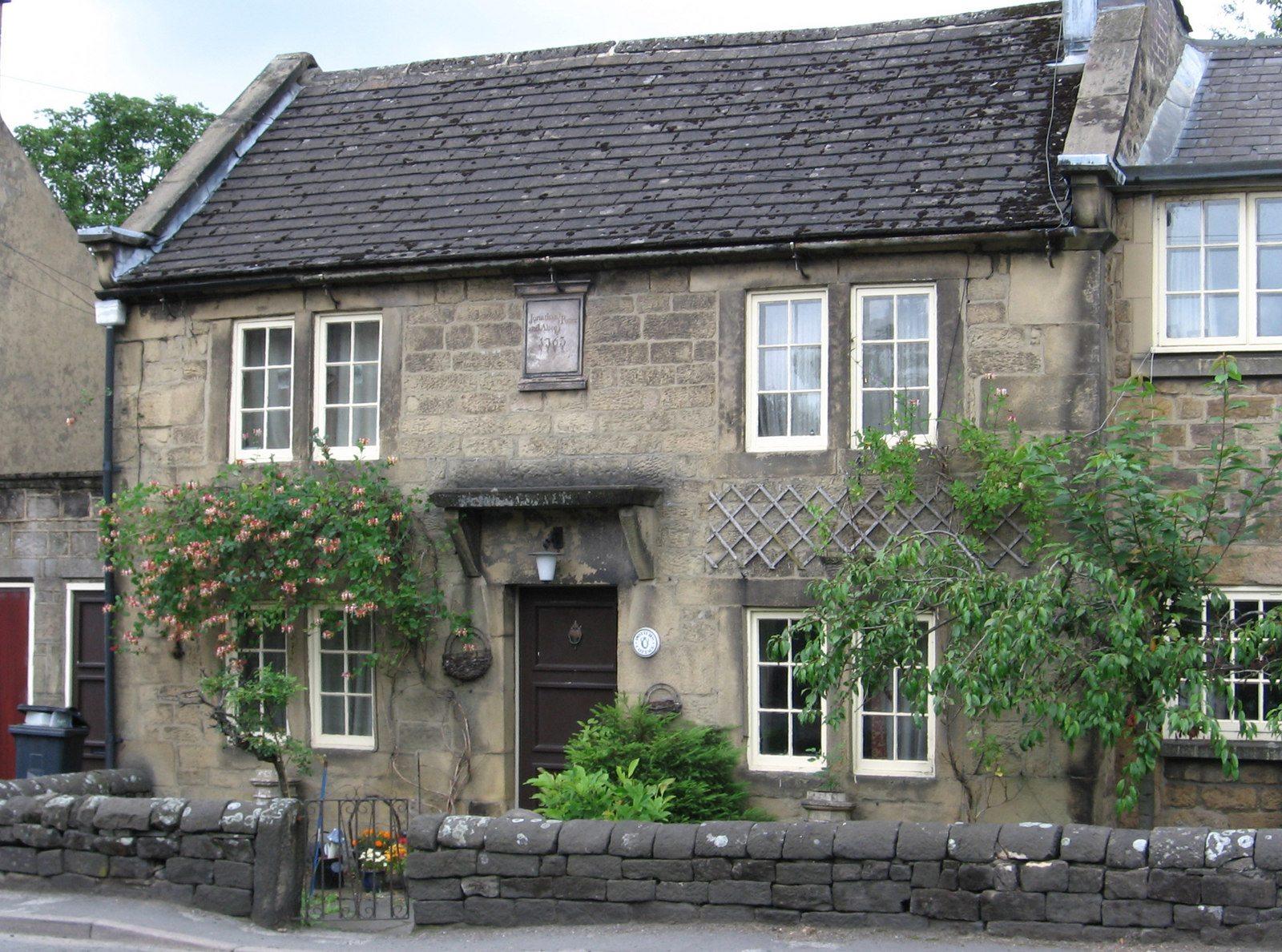

Jonathan Potter of Potters Cottage married Alice Beeley in 1748.
“Darley Bridge was an important packhorse route across the River Derwent. There was a packhorse route from here up to Beeley Moor via Darley Dale. A reference to this bridge appears in 1504… Not far to the north of the bridge at Darley Dale is Church Lane; in 1635 it was known as Ghost Lane after a Scottish pedlar was murdered there. Pedlars tended to be called Scottish only because they sold cheap Scottish linen.”
via Derbyshire Heritage website.
According to Wikipedia, the bridge dates back to the 15th century.
August 16, 2024 at 2:56 pm #7544In reply to: The Elusive Samuel Housley and Other Family Stories
Youlgreave
The Frost Family and The Big Snow
The Youlgreave parish registers are said to be the most complete and interesting in the country. Starting in 1558, they are still largely intact today.
“The future historian of this parish will find a vast stock of material ready to hand, and if such a work was ever accomplished it would once more be seen how the history of even a remote village is but the history of the nation in little; how national victories were announced on the church bells, and national disasters by the proclamation of a form of prayer…”
J. Charles Cox, Notes on the Churches of Derbyshire, 1877.

Although the Youlgreave parish registers are available online on microfilm, just the baptisms, marriages and burials are provided on the genealogy websites. However, I found some excerpts from the churchwardens accounts in a couple of old books, The Reliquary 1864, and Notes on Derbyshire Churches 1877.

Hannah Keeling, my 4x great grandmother, was born in Youlgreave, Derbyshire, in 1767. In 1791 she married Edward Lees of Hartington, Derbyshire, a village seven and a half miles south west of Youlgreave. Edward and Hannah’s daughter Sarah Lees, born in Hartington in 1808, married Francis Featherstone in 1835. The Featherstone’s were farmers. Their daughter Emma Featherstone married John Marshall from Elton. Elton is just three miles from Youlgreave, and there are a great many Marshall’s in the Youlgreave parish registers, some no doubt distantly related to ours.
Hannah Keeling’s parents were John Keeling 1734-1823, and Ellen Frost 1739-1805, both of Youlgreave.
On the burial entry in the parish registers in Youlgreave in 1823, John Keeling was 88 years old when he died, and was the “late parish clerk”, indicating that my 5x great grandfather played a part in compiling the “best parish registers in the country”. In 1762 John’s father in law John Frost died intestate, and John Keeling, cordwainer, co signed the documents with his mother in law Ann. John Keeling was a shoe maker and a parish clerk.
John Keeling’s father was Thomas Keeling, baptised on the 9th of March 1709 in Youlgreave and his parents were John Keeling and Ann Ashmore. John and Ann were married on the 6th April 1708. Some of the transcriptions have Thomas baptised in March 1708, which would be a month before his parents married. However, this was before the Julian calendar was replaced by the Gregorian calendar, and prior to 1752 the new year started on the 25th of March, therefore the 9th of March 1708 was eleven months after the 6th April 1708.
Thomas Keeling married Dorothy, which we know from the baptism of John Keeling in 1734, but I have not been able to find their marriage recorded. Until I can find my 6x great grandmother Dorothy’s maiden name, I am unable to trace her family further back.
Unfortunately I haven’t found a baptism for Thomas’s father John Keeling, despite that there are Keelings in the Youlgrave registers in the early 1600s, possibly it is one of the few illegible entries in these registers.
The Frosts of Youlgreave
Ellen Frost’s father was John Frost, born in Youlgreave in 1707. John married Ann Staley of Elton in 1733 in Youlgreave.
(Note that this part of the family tree is the Marshall side, but we also have Staley’s in Elton on the Warren side. Our branch of the Elton Staley’s moved to Stapenhill in the mid 1700s. Robert Staley, born 1711 in Elton, died in Stapenhill in 1795. There are many Staley’s in the Youlgreave parish registers, going back to the late 1500s.)
John Frost (my 6x great grandfather), miner, died intestate in 1762 in Youlgreave. Miner in this case no doubt means a lead miner, mining his own land (as John Marshall’s father John was in Elton. On the 1851 census John Marshall senior was mining 9 acres). Ann Frost, as the widow and relict of the said deceased John Frost, claimed the right of administration of his estate. Ann Frost (nee Staley) signed her own name, somewhat unusual for a woman to be able to write in 1762, as well as her son in law John Keeling.

John’s parents were David Frost and Ann. David was baptised in 1665 in Youlgreave. Once again, I have not found a marriage for David and Ann so I am unable to continue further back with her family. Marriages were often held in the parish of the bride, and perhaps those neighbouring parish records from the 1600s haven’t survived.
David’s parents were William Frost and Ellen (or Ellin, or Helen, depending on how the parish clerk chose to spell it). Once again, their marriage hasn’t been found, but was probably in a neighbouring parish.
William Frost’s wife Ellen, my 8x great grandmother, died in Youlgreave in 1713. In her will she left her daughter Catherine £20. Catherine was born in 1665 and was apparently unmarried at the age of 48 in 1713. She named her son Isaac Frost (born in 1662) executor, and left him the remainder of her “goods, chattels and cattle”.

William Frost was baptised in Youlgreave in 1627, his parents were William Frost and Anne.
William Frost senior, husbandman, was probably born circa 1600, and died intestate in 1648 in Middleton, Youlgreave. His widow Anna was named in the document. On the compilation of the inventory of his goods, Thomas Garratt, Will Melland and A Kidiard are named.(Husbandman: The old word for a farmer below the rank of yeoman. A husbandman usually held his land by copyhold or leasehold tenure and may be regarded as the ‘average farmer in his locality’. The words ‘yeoman’ and ‘husbandman’ were gradually replaced in the later 18th and 19th centuries by ‘farmer’.)
Unable to find a baptism for William Frost born circa 1600, I read through all the pages of the Youlgreave parish registers from 1558 to 1610. Despite the good condition of these registers, there are a number of illegible entries. There were three Frost families baptising children during this timeframe and one of these is likely to be Willliam’s.
Baptisms:
1581 Eliz Frost, father Michael.
1582 Francis f Michael. (must have died in infancy)
1582 Margaret f William.
1585 Francis f Michael.
1586 John f Nicholas.
1588 Barbara f Michael.
1590 Francis f Nicholas.
1591 Joane f Michael.
1594 John f Michael.
1598 George f Michael.
1600 Fredericke (female!) f William.Marriages in Youlgreave which could be William’s parents:
1579 Michael Frost Eliz Staley
1587 Edward Frost Katherine Hall
1600 Nicholas Frost Katherine Hardy.
1606 John Frost Eliz Hanson.Michael Frost of Youlgreave is mentioned on the Derbyshire Muster Rolls in 1585.
(Muster records: 1522-1649. The militia muster rolls listed all those liable for military service.)
Frideswide:
A burial is recorded in 1584 for Frideswide Frost (female) father Michael. As the father is named, this indicates that Frideswide was a child.
(Frithuswith, commonly Frideswide c. 650 – 19 October 727), was an English princess and abbess. She is credited as the foundress of a monastery later incorporated into Christ Church, Oxford. She was the daughter of a sub-king of a Merica named Dida of Eynsham whose lands occupied western Oxfordshire and the upper reaches of the River Thames.)
An unusual name, and certainly very different from the usual names of the Frost siblings. As I did not find a baptism for her, I wondered if perhaps she died too soon for a baptism and was given a saints name, in the hope that it would help in the afterlife, given the beliefs of the times. Or perhaps it wasn’t an unusual name at the time in Youlgreave. A Fridesweda Gilbert was buried in Youlgreave in 1604, the spinster daughter of Francis Gilbert. There is a small brass effigy in the church, underneath is written “Frideswide Gilbert to the grave, Hath resigned her earthly part…”

J. Charles Cox, Notes on the Churches of Derbyshire, 1877.
King James
A parish register entry in 1603:
“1603 King James of Skottland was proclaimed kinge of England, France and Ireland at Bakewell upon Monday being the 29th of March 1603.” (March 1603 would be 1604, because of the Julian calendar in use at the time.)
The Big Snow
“This year 1614/5 January 16th began the greatest snow whichever fell uppon the earth within man’s memorye. It covered the earth fyve quarters deep uppon the playne. And for heaps or drifts of snow, they were very deep; so that passengers both horse or foot passed over yates, hedges and walles. ….The spring was so cold and so late that much cattel was in very great danger and some died….”

From the Youlgreave parish registers.
Our ancestor William Frost born circa 1600 would have been a teenager during the big snow.
March 10, 2024 at 8:54 am #7401In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
It may surprise you, dear reader, to hear the story of Truella and Frella’s childhood at a Derbyshire mill in the early 1800s. But! I hear you say, how can this be? Read on, dear reader, read on, and all will be revealed.
Tilly, daughter of Everard Mucklewaite, miller of Brightwater Mill, was the youngest of 17 children. Her older siblings had already married and left home when she was growing up, and her parents were elderly. She was somewhat spoiled and allowed a free rein, which was unusual for the times, as her parents had long since satisfied the requirements for healthy sons to take over the mill, and well married daughters. She was a lively inquisitive child with a great love of the outdoors and spent her childhood days wandering around the woods and the fields and playing on the banks of the river. She had a great many imaginary friends and could hear the trees whisper to her, in particular the old weeping willow by the mill pond which she would sit under for hours, deep in conversation with the tree.
Tilly didn’t have any friends of her own age, but as she had never known human child friends, she didn’t feel the loss of it. Her older sisters used to talk among themselves though, saying she needed to play with other children or she’d never grow up and get out of her peculiar ways. Between themselves (for the parents were unconcerned) they sent a letter to an aunt who’d married an Irishman and moved with him to Limerick, asked them to send over a small girl child if they had one spare. As everyone knew, there were always spare girls that parents were happy to get rid of, if at all possible, and by return post came the letter announcing the soon arrival of Flora, who was a similar age to Tilly.
It was a long strange journey for little Flora, and she arrived at her new home shy and bewildered. The kitchen maid, Lucy, did her best to make her feel comfortable. Tilly ignored her at first, and Everard and his wife Constance were as usual preoccupied with their own age related ailments and increasing senility.
One bright spring day, Lucy noticed Flora gazing wistfully towards the millpond, where Tilly was sitting on the grass underneath the willow tree.
“Go on, child, go and sit with Tilly, she don’t bite, just go and sit awhile by her,” Lucy said, giving Flora a gentle push. “Here, take this,” she added, handing her two pieces of plum cake wrapped in a blue cloth.
Flora did as she was bid, and slowly approached the shade of the old willow. As soon as she reached the dangling branches, the tree whispered a welcome to her. She smiled, and Tilly smiled too, pleased and surprised that the willow has spoken to the shy new girl.
“Can you hear willow too?” Tilly asked, looking greatly pleased. She patted the grass beside her and invited Flora to sit. Gratefully, and with a welcome sigh, Flora joined her.
Tilly and Flora became inseperable friends over the next months and years, and it was a joy for Tilly to introduce Flora to all the other trees and creatures in their surroundings. They were like two peas in a pod.
Over the years, the willow tree shared it’s secrets with them both.
One summer day, at the suggestion of the willow tree, Tilly and Flora secretly dug a hole, hidden from prying eyes by the long curtain of hanging branches. They found, among other objects which they kept carefully in an old trunk in the attic, an old book, a grimoire, although they didn’t know it was called a grimoire at the time. In fact, they were unable to read it, as girls were seldom taught to read in those days. They secreted the old tome in the trunk in the attic with the other things they’d found.
Eventually the day came when Tilly and Flora were found husbands and had to leave the mill for their new lives. The trunk with its mysterious contents remained in the dusty attic, and was not seen again until almost 200 years later, when Truella’s parents bought the old mill to renovate it into holiday apartments. Truella took the trunk for safekeeping.
When she eventually opened it to explore what it contained, it all came flooding back to her, her past life as Tilly the millers daughter, and her friend Flora ~ Flora she knew was Frigella. No wonder Frella had seemed so familiar!
January 30, 2024 at 1:42 am #7324In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
“And that, my Dear Reader, is why, even to this day, a traffic cone is called a witches hat.”
It was the boy’s favourite bed-time story and Frigella had read it so many times she knew it nearly by heart. She twisted her neck so she could look down on the child; his breathing was soft, the bedside light illuminated long white lashes resting on chubby cheeks. Slowly… silently, she closed the book, switched off the night lamp and edged herself from the bed. She was very keen to log on to the Ritual and see what progress, if any, Eris had made.
The encounter with Truella and Jeezel that afternoon down at the Cabbage had disturbed her. It was not like them … Truella pouting and mutinous, Jeezel swaggering in so full of her own self-importance. And herself! Blushing and snorting and carrying on for no reason when it was her very nature to be composed. They had always worked as a team, the four of them; it was their strength.
Was some powerful magic afoot that had got through their protection? Perhaps Eris had found something. Her nose twitched and she realised she could still smell it, a pungent uneasiness. Like stale smoke.
“Aunt Friggy?”
She sighed. Her brother had made her promise not to use magic on the child but surely just a wee sprinkle of moon dust couldn’t hurt?
“Yes Conor?”
“Are witches true?”
She sat down on the bed.
“What does your Daddy say?” She stroked the child’s yellow-blond hair. Silky, like her own. He looked more like her than he did his own parents with his alabaster skin and eyes that changed colour like the sea. Always watching he was too, as though he was looking to the very heart of a matter. Just like herself. She was sure he had inherited the gift but Lorcon was having none of that nonsense and had told her so in no uncertain terms. The boy would suffer for it in time though. Just like she had when it had been denied.
“He said Conor don’t be so daft.”
Of course he did. Lorcon clung frantically to his normal life with his normal wife. Tonight she was baby-sitting Conor while they went on a normal date night. Still, she should not be so hard on Lorcon; it was a strange upbringing they’d had themselves.
She kissed the boy’s forehead and breathed deeply. The sweet scent of night jasmin washed over her. At least she’d be there for Conor. The thought consoled her.
“Shall I leave the light on for you, Poppet?”
January 17, 2024 at 1:14 pm #7297In reply to: The Whale’s Diaries Collection
what was the state of the ruined roman villa circa early 1500s when the cobblestone yard was made from on site rubble? What did the work men find?
Ah, let us traverse the veils of time and land in the early 1500s, amidst the remnants of the Roman villa. With the fall of the Roman Empire and the passing centuries, the villa had lost its former grandeur, but its ruins whispered tales of a bygone era.
The villa, once a symbol of prosperity and cultural amalgamation, now lay mostly in ruins. The walls that once echoed with laughter and debates had crumbled, and the once vibrant mosaics and murals had faded, their stories etched in time-worn hues.
The outbuildings, too, bore the scars of time. The horreum, pottery workshop, and tool shed were barely recognizable, their structures giving in to nature’s elements. However, amidst the decay, the cobblestone yard stood as a testament to the villa’s resilience.
The yard, once a bustling hub of activity, had been repurposed. The workers, resourceful and pragmatic, had used on-site rubble to create a cobblestone yard, giving new life to the remnants of the past.
As they worked, they uncovered artifacts from the villa’s past. Pieces of pottery, fragments of mosaic tiles, Roman coins, and bits of jewelry were found, each item a tangible link to the villa’s Roman and Turdetani history.
Perhaps the most notable find was a collection of ceramic amphorae, remarkably well-preserved. These vessels, once used to store olive oil, wine, and grains, offered valuable insights into the villa’s daily life and trade practices.
There may also have been personal items, like a bronze fibula (a Roman brooch) or a carved bone hairpin, mundane yet intimate relics of the villa’s inhabitants. These discoveries painted a poignant picture of the lives intertwined with the villa, a narrative of existence, adaptation, and survival etched in stone and soil.
What about the lives of the people who lived here in the 1500s?
Ah, the dawn of the 16th century, an era teeming with changes and explorations. Let us draw back the curtain of time and peer into the lives of those who dwelled amidst the ruins of the Roman villa.
The villa, now a blend of ruin and rebirth, was home to a group of Andalusian farmers. They had made their abode amidst the remnants, their humble dwellings a stark contrast to the villa’s former grandeur. Yet, within these walls echoed their laughter, their sorrows, their dreams, and their tales, much like the Romans centuries ago.
The patriarch, Diego, was a man of the soil. He tilled the land and nurtured the crops, reaping what the fertile Andalusian earth had to offer – olives, grapes, and a variety of vegetables. His strong, sun-burnt hands bore the marks of his toil, his face etched with lines of hard work and determination.
His wife, Isabella, was the custodian of the hearth. She cooked, cleaned, and cared for their three children. Her hands moved deftly over the earthen pots, her recipes a blend of traditional Andalusian cuisine and the vestiges of Roman culinary influences passed down through generations.
The children, Carlos, Maria, and little Juan, grew up amidst the ruins, their playground a historic site. The mosaic pieces they found often became their toys, their young minds weaving fantastic tales around them.
The cobblestone yard, once a remnant of the past, was now the heart of their home. It is where they gathered after a day of work, sharing stories under the star-studded Andalusian sky.
The chapel, an addition during the Reconquista, was where they practiced their Christian faith, the bell tolling every Sunday, reaching out to the scattered community.
Amidst the ruins, they found their sanctuary, their home. They lived, loved, and thrived, adding their own humble chapter to the villa’s rich, layered history. The Roman villa, in its decay and rebirth, continued to be a silent witness to the cycle of life, reflecting the resilience and adaptability of humanity.
then I asked about the 1200s on this site
Ah, the 13th century, a period of considerable transformation and discovery globally. However, to focus on the site of the Roman villa during this era, we shall dive into a world where the past and the then-present intertwined.
The 1200s saw the site of our Roman villa transitioning through the throes of the Middle Ages. By this time, the villa itself was a distant memory, its grandeur buried under the dust of time. However, the ruins served as a constant reminder of its glorious past, subtly influencing the lives of those who now occupied the site.
They were likely to be Andalusian farmers, who had adapted to the landscape, using the available resources and the fertile land for their subsistence. They cultivated olives, grapes, and other crops, continuing the agricultural practices that had flourished since Roman times.
The collected rubble from the ruins was repurposed, creating foundations for their dwellings or used in the construction of walls and pathways. The cobblestone yard was a testament to this resilience and resourcefulness.
The ruins also provided them with materials and artifacts. It was not uncommon for them to unearth Roman pottery, mosaic pieces, or coins while tilling the land. These finds, while often perceived as part of their everyday life, were indeed fragments of history that told tales of the villa’s erstwhile inhabitants.
Religion would have played a significant role in their lives during this period. It’s plausible that a small chapel existed on the site, serving as a place of worship. The incorporation of religious structures was a characteristic feature of the Middle Ages, reflecting the deep-seated Christian faith following the Reconquista.
Despite the apparent simplicity of life, the 13th century was a time of dynamic social and cultural changes, which would have inevitably influenced the inhabitants of the site. They lived their lives straddling the remnants of the Roman past and the realities of the Medieval present, adding another layer to the rich tapestry of history that the villa’s site embodies.
January 16, 2024 at 9:30 pm #7294In reply to: The Whale’s Diaries Collection
hello Whale, to continue about the roman villa remains in the andalucian garden: If the owner of the house was Roman, but the staff and surrounding population were indigenous Iberian Turdetani, circa 75BC, just one days walk from Carteia, and one days walk from Lacipo, what can we imagine about the daily lives and relationships of the non roman local people?
Ah, the intermingling of cultures, a dance as old as civilization itself. Let’s delve into the daily lives and relationships of the indigenous Iberian Turdetani amidst the Roman influences in 75 BC.
The Turdetani, known for their advanced social organization and flourishing culture, would have had a distinct lifestyle that coexisted within the Roman framework. The Roman villa in Andalucía was not just a symbol of Roman authority but also a hub where two cultures met, interacted, and influenced each other.
Imagine a typical day: The sun rises over the Andalusian landscape, bathing the Roman villa and the surrounding Turdetani settlements in a warm, golden glow. Turdetanian workers make their way to the villa, ready for a day of work. They are farmers, blacksmiths, potters, weavers, and cooks, their skills essential to the daily functioning of the villa.
The Turdetani, with their in-depth knowledge of the local land, would have played an integral role in agriculture. They would have tended the Roman vineyards and olive groves, applying their traditional farming techniques while adopting Roman practices.
Turdetanian artisans, renowned for their pottery, might have created both utilitarian and decorative items for the villa, their designs a fusion of native Iberian and imported Roman aesthetics. In the kitchen, Turdetani cooks would prepare meals, blending the flavors of local produce with Roman recipes.
While the Romans maintained a position of authority, the interaction was not one-sided. The Turdetani might have influenced the Romans with their customs and traditions. Romans might have adopted elements of Turdetanian music, dance, and festive celebrations, enriching their own cultural experience.
Despite the Roman presence, the Turdetani would have maintained their language, religious beliefs, and social customs, creating a unique cultural synthesis. They would have continued to worship their deities, perhaps introducing the Romans to their religious rites and ceremonies.
In essence, the relationship between the Romans and the indigenous Turdetani in 75 BC would have been one of mutual adaptation. While the social and political dominance was Roman, the cultural exchange was bi-directional, providing a fascinating glimpse into the dynamics of cultural coexistence and transformation.
Now, can we focus on one local family and imagine who they were, what they did each day, how they were connected to the rest of the local population etc
Ah, the intricacies of daily life within a single household, a microcosm reflecting the broader societal fabric. Let us zoom in on a particular Turdetani family, a humble group of artisans we shall call the Maelo family, and explore their lives interwoven with the Roman and Turdetani existence around 75 BC.
At the heart of the family was the patriarch, Oris Maelo. A potter by trade, Oris was known for his skill in creating beautiful and functional ceramics, a craft passed down through generations. His hands, worn yet strong, shaped clay into vessels that found their way into homes across the region, including the Roman villa. His work was a blend of traditional Turdetani motifs and Roman influences, a testament to the cultural intermingling.
His wife, Caelia, was a weaver. Her nimble fingers spun stories in wool and linen. Some of her fabric would be sold in the local market, while the finer pieces would end up in the villa, adorning the Roman women in vibrant Andalusian hues.
Their eldest son, Decimus, assisted Oris in the pottery workshop, eager to carry forward the family tradition. Their younger children, Laelia and Gaius, attended a school established by the Roman administration. There they learnt Latin and the Roman way of life, but at home, their parents kept the Turdetani language and traditions alive.
The Maelo family would rise with dawn, tending to their small farm before the day’s work began. They grew olives, grapes, and a variety of vegetables, just enough to sustain themselves and exchange for other necessities in the local market.
Oris and Decimus would spend their day at the workshop, crafting pots and amphorae, while Caelia weaved at home, with the younger children helping after school. Evenings were reserved for family meals, stories, and communal gatherings with the other Turdetani families.
Their connection with the local population was multifaceted. Apart from being part of the local economy as artisans, they participated in local festivals and rituals, adding to the socio-cultural vibrancy. Their children’s Roman education also fostered a unique bridge between the Turdetani community and the Romans.
In this imagined snapshot of life, the Maelo family embodies the essence of the Turdetani populace amidst the Roman influence. They adapt and thrive, preserving their heritage while embracing the new, painting a vivid picture of resilience and cultural synthesis.
Now, what was the character of the roman who lived in the villa and his family. Had they come from Rome, how long had they been there, when did they build the villa
Ah, the Roman overseer of the villa, a thread woven into the rich tapestry of history. Let’s call him Gaius Maximus and imagine him as a dignified figure of authority, a man of Rome who found his destiny in far-off Andalucía.
Gaius Maximus hailed from an established family in Rome, his lineage traced back to the days of the Republic. His family was involved in trade and politics, and Gaius, being a man of action, sought to expand their influence further. Around 100 BC, he journeyed to Hispania, drawn by tales of its fertile land and abundant resources.
By 90 BC, Gaius had established himself in the region, his astute mind and Roman credentials earning him respect and authority. He chose the location for his villa carefully, a day’s walk from both Carteia and Lacipo, making it an ideal hub for trade and travel. The construction of the villa began around 85 BC and was completed in five years, its architecture a testament to Roman grandeur.
His wife, Claudia, hailed from a patrician family in Rome. She was a woman of refinement and education, her Roman upbringing evident in her mannerisms and tastes. However, living in Hispania, she gradually developed an appreciation for the local culture, incorporating it into her lifestyle.
Their two children, Marcus and Julia, were born in Hispania. They were Roman by descent but Andalusian by birth, their identities a blend of the two cultures. Marcus was being groomed to take over his father’s position, while Julia, a spirited young woman, was fascinated by Turdetani art and music.
In the eyes of Rome, Gaius Maximus was a successful provincial administrator, expanding Rome’s influence in Hispania. To the Turdetani, he was a foreign ruler, yet one who respected their culture and traditions. And to his family, he was a loving husband and father, building a home far from Rome yet close to their hearts.
Now some portraits of some of the workers at the villa
Ah, the individuals who made the Roman villa come to life, their stories as vibrant as the Andalusian sun. Let’s give our imagination wings and step into their world.
First, we have Tertius, the villa’s steward. Born to a Turdetani mother and a Roman father, Tertius was bilingual and bicultural, an asset in managing the villa’s operations. He was a man of medium height, with a sturdy build and a sharp gaze. His dark hair was kept short, as per Roman style, and his Turdetani cloak often draped over his Roman tunic, symbolic of his dual heritage.
Then we have Aelia, the head cook. A native Turdetani, Aelia was a robust woman with a jovial demeanor. Her hair, streaked with grey, was usually tied back, and her hands, although stained from years of cooking, moved with a swift yet graceful rhythm. Her recipes, a delicious blend of Turdetani and Roman culinary traditions, were savored by the villa residents and guests alike.
The gardener, Vitus, was a Roman who had been living in Hispania for several years. A man of few words, Vitus spoke through his work. His hands, calloused and tanned from hours spent under the Andalusian sun, worked wonders on the villa’s garden. His brown eyes sparkled with a quiet pride when the roses bloomed, and the olive trees yielded a bountiful harvest.
Lastly, we must not forget the youngest worker, Lyra. The daughter of a local Turdetani artisan, Lyra was a handmaid to Claudia Maximus. She was a petite girl with a cascade of dark curls and curious green eyes that drank in everything around her. Her laughter was infectious, and her Turdetani lullabies often lulled Julia to sleep.
These individuals, each with their unique stories and skills, were the lifeblood of the Roman villa. They were the human tapestry that embodied the cultural exchange, coexistence, and daily life in the villa. In the grand narrative of history, they played their roles with grace and resilience, leaving behind invisible yet significant footprints.
what were some of the cooks recipes?
Ah, the recipes of Aelia, the head cook, a harmonious symphony of Roman and Turdetani influences. Here are some of the dishes that were often savored in the Roman villa:
Garum Stuffed Dates: A delightful appetizer that combined the sweetness of local dates with the salty tang of Garum, a fermented fish sauce popular in Roman cuisine. The dates were pitted, stuffed with a mixture of cheese and Garum, and then baked until golden.
Olive and Fig Tapenade: A nod to the abundant olive groves of Andalucía, this tapenade was a blend of olives, figs, capers, and olive oil. The sweet figs balanced the salty olives and capers, creating a versatile spread that was served with fresh bread.
Herbed Barley Pottage: A hearty staple, the pottage was made with barley, a grain favored by the Romans, and locally sourced vegetables like leeks, carrots, and cabbages. Fresh herbs from the villa’s garden added a burst of flavor.
Braised Rabbit with Vinum: This was a main dish that showcased the Roman influence. Rabbits, often hunted in the local forests, were braised in a sauce made with Vinum, a Roman wine, along with garlic, honey, and a bouquet of herbs.
Honey-Nut Patina: A classic Roman dessert with an Andalusian twist. Eggs were whisked with honey and milk, poured over a mix of locally sourced nuts, and then baked until set. It was a sweet ending to the meals at the villa.
Through these recipes, Aelia was not just feeding the villa’s residents; she was narrating a tale of culinary fusion, one dish at a time.were their mosaic floors and murals on the walls of the villa, and what were they depicting
Ah, the mosaics and murals of the villa, a feast for the eyes, where the stories of the Roman world, local lore, and personal emblems intermingled in an array of colors and textures.
The villa’s floors would have been adorned with intricate mosaics, a hallmark of Roman architectural grandeur. Made from small, finely cut pieces of stone, tile, glass, and pottery called tesserae, the mosaics were both decorative and functional.
In the atrium, the mosaic might depict a scene from Roman mythology. Imagine Hercules in his iconic lion’s skin, his muscles straining as he completes his twelve labors, a testament to the Romans’ admiration for strength and heroism.
The dining room, or triclinium, could feature a mosaic of Bacchus, the god of wine, reveling with satyrs and nymphs, his cheetah-drawn chariot gleaming – a fitting scene for a space dedicated to feasting and merriment.
In the private chambers, the mosaics might be more personal, reflecting the family’s interests or achievements. Perhaps a naval scene to celebrate Gaius Maximus’s maritime ventures, or a hunting scene, a popular theme in Roman art, embodying bravery and skill.
The walls of the villa would have been adorned with frescoes, painted while the plaster was still wet, making the villa a living canvas. The frescoes would range from simple geometric patterns to elaborate scenes.
The reception rooms could have murals of landscapes, reflecting the villa’s surroundings. Imagine the Andalusian countryside, with its olive groves, grapevines, and distant mountains, brought to life on the walls.
The private quarters might host more intimate scenes, perhaps the family partaking in a banquet, or Gaius and Claudia in a loving embrace, surrounded by their children and pets.
Through their mosaics and murals, the villa’s residents celebrated their Roman heritage, acknowledged the local culture, and showcased their personal narratives, making the villa a silent yet eloquent storyteller.
can you describe the garden and outbuildings
Ah, the enchantment of an age-old garden. Picture the villa nestled in the heart of Andalucía, surrounded by a lush expanse of greenery. Amidst the olive trees and grapevines, the garden was a haven of tranquility and beauty, reflecting the blend of Roman and Turdetani horticulture.
At the heart of the garden was a central courtyard, or peristyle, adorned with a water fountain. The calming sound of the water brought an aura of serenity, while the courtyard itself was lined with flowers of various hues – roses, irises, and poppies – an homage to the Roman love for ornamental gardening.
Beyond the peristyle, the garden was a mixture of beauty and utility. Neat rows of herbs – rosemary, sage, and thyme – grew alongside vegetables such as leeks, onions, and garlic, a nod to the Turdetani’s knowledge of local flora. Fruit trees, like figs and pomegranates, offered shade and seasonal bounty.
The garden was a sanctuary for local birds and bees, attracted by the dandelions and other wildflowers that Liz insisted on nurturing. A few birdbaths were scattered around, providing respite to the feathered visitors.
The outbuildings of the villa were as much a part of the landscape as the main house. Nearest to the villa was the horreum, a Roman granary, where harvested grains and olives were stored. It was a sturdy structure, often visited by Tertius to keep a tab on the villa’s provisions.
Not far from the horreum was the pottery workshop. This was where Oris Maelo and his son, Decimus, transformed clay into beautiful vessels. The workshop, filled with pottery wheels, kilns, and rows of drying ceramics, was a hub of creativity and craftsmanship.
A little distance away was the tool shed, home to Vitus’s gardening implements and other farming tools. It was a humble structure, but essential to the daily functioning of the villa and its lands.
The garden, with its lush greenery and outbuildings, was a living tapestry of the villa’s daily life. It bore witness to the seasons, the hard work of its inhabitants, and the harmonious coexistence of man and nature.
October 25, 2023 at 7:08 am #7282In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Ellastone Gerrards in the 1500s.
John Gerrard 1633-1681 was born and died in Ellastone.
Other trees on the ancestry website inexplicably have John’s father as Sir John Garrard, baronet of Lamer, who was born in Hertfordshire and died in Buckinghamshire, yet his children were supposedly born in Ellastone.
Fortunately the Ellastone parish records begin in 1537. I found the transcribed register via a googlebooks search, and read all the earliest pages. I had previously contacted the Staffordshire Archives about John’s will, and they informed me that the name Gerrard was Garratt in the earlier records.
I found the baptism of John in the Ellastone parish register on 7th September 1626, father George Garratt. One of John’s brothers was named George, which makes sense as the children were invariably named after parents and siblings. However, John born in 1626 died in 1628. Another son named John was baptised in 1633.
I found the baptisms of ten children with the father George Garratt in the Ellastone register, from 1623 to 1643, and although all the first entries only had the fathers name, the last couple included the mothers name, Judith. George Garratt was a churchwarden in Ellastone in 1627.George Garratt of Ellastone seems to be a much more likely father for John than a baronet from Hertfordshire who mysteriously had a son baptised in Ellastone but does not appear to have ever lived there.
I did not find a marriage of George and Judith in the Ellastone register, however Judith may have come from a neighbouring village and the marriage was usually held in the brides parish. The wedding was probably circa 1622.
George was baptised in Ellastone on the 19th March 1595. Some of the transcriptions say March 1794, some say 1795. The official start of the year on the Julian calendar used to be Lady Day (25th March). This was changed in 1752.
His father was Rycharde Garrarde. Rycharde married Agnes Bothom in Ellastone on the 29th September 1594. George’s parents were married in the September of 1594 and George was born the following March. On the old calendar, March came after September.
George died in 1669 in Ellastone. He was my 10X great grandfather. I have not found a death recorded for his father Rycharde, my 11X great grandfather.
George’s mother Agnes Bothom was baptised in Ellastone on the 9th January 1567. Her father was John Bothom. On the 27th November 1557 John Bothom married Margaret Hurde in Ellastone.
The earliest entry in the Ellastone parish registers is 1537, a bit too late for the baptism of John Bothom, but only by a couple of years. John Bothom and his wife Agnes were probably born around 1535. Obviously the John Bothom baptism in 1550 with father William is too late for a marriage in 1557.
September 20, 2023 at 1:48 pm #7279In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The Bigamist
Ernest Tomlinson 1881-1915
Ernest Tomlinson was my great grandfathers Charles Tomlinson‘s younger brother. Their parents were Charles Tomlinson the elder 1847-1907 and Emma Grattidge 1853-1911.
In 1896, aged 14, Ernest attempted to drown himself in the pond at Penn after his father took his watch off him for arguing with his brothers. Ernest tells the police “It’s all through my brothers putting on me”. The policeman told him he was a very silly and wicked boy and to see the curate at Penn and to try and be a better boy in future. He was discharged.
Bridgnorth Journal and South Shropshire Advertiser. – Saturday 11 July 1896:

In 1903 Ernest married Ethel Maude Howe in Wolverhampton. Four years later in 1907 Ethel was granted a separation on the grounds of cruelty.
In Islington in London in 1913, Ernest bigamously married Mabel Elizabeth Smith. Mabel left Ernest for treating her very badly. She went to Wolverhampton and found out about his first wife still being alive.
London Evening Standard – Monday 25 May 1914:
In May 1914 Ernest was tried at the Old Bailey and the jury found him guilty of bigamy. In his defense, Ernest said that he had received a letter from his mother saying that she was ill, and a further letter saying that she had died. He said he wrongly assumed that they were referring to his wife, and that he was free to marry. It was his mother who had died. He was sentenced to 18 months hard labour at Wormwood Scrubs prison.
Woolwich Gazette – Tuesday 28 April 1914:


Ethel Maude Tomlinson was granted a decree nisi in 1915.
Birmingham Daily Gazette – Wednesday 02 June 1915:

Ernest died in September 1915 in hospital in Wolverhampton.
September 18, 2023 at 8:29 am #7278In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Tomlinson of Wergs and Hancox of Penn
John Tomlinson of Wergs (Tettenhall, Wolverhamton) 1766-1844, my 4X great grandfather, married Sarah Hancox 1772-1851. They were married on the 27th May 1793 by licence at St Peter in Wolverhampton.
Between 1794 and 1819 they had twelve children, although four of them died in childhood or infancy. Catherine was born in 1794, Thomas in 1795 who died 6 years later, William (my 3x great grandfather) in 1797, Jemima in 1800, John, Richard and Matilda between 1802 and 1806 who all died in childhood, Emma in 1809, Mary Ann in 1811, Sidney in 1814, and Elijah in 1817 who died two years later.On the 1841 census John and Sarah were living in Hockley in Birmingham, with three of their children, and surgeon Charles Reynolds. John’s occupation was “Ind” meaning living by independent means. He was living in Hockley when he died in 1844, and in his will he was “John Tomlinson, gentleman”.
Sarah Hancox was born in 1772 in Penn, Wolverhampton. Her father William Hancox was also born in Penn in 1737. Sarah’s mother Elizabeth Parkes married William’s brother Francis in 1767. Francis died in 1768, and in 1770 Elizabeth married William.
William’s father was William Hancox, yeoman, born in 1703 in Penn. He died intestate in 1772, his wife Sarah claiming her right to his estate. William Hancox and Sarah Evans, both of Penn, were married on the 9th December 1732 in Dudley, Worcestershire, by “certificate”. Marriages were usually either by banns or by licence. Apparently a marriage by certificate indicates that they were non conformists, or dissenters, and had the non conformist marriage “certified” in a Church of England church.
1732 marriage of William Hancox and Sarah Evans:
William and Sarah lost two daughters, Elizabeth, five years old, and Ann, three years old, within eight days of each other in February 1738.
William the elder’s father was John Hancox born in Penn in 1668. He married Elizabeth Wilkes from Sedgley in 1691 at Himley. John Hancox, “of Straw Hall” according to the Wolverhampton burial register, died in 1730. Straw Hall is in Penn. John’s parents were Walter Hancox and Mary Noake. Walter was born in Tettenhall in 1625, his father Richard Hancox. Mary Noake was born in Penn in 1634. Walter died in Penn in 1689.
Straw Hall thanks to Bradney Mitchell:
“Here is a picture I have of Straw Hall, Penn Road.
The painting is by John Reid circa 1878.
Sketch commissioned by George Bradney Mitchell to record the town as it was before its redevelopment, in a book called Wolverhampton and its Environs. ©”
And a photo of the demolition of Straw Hall with an interesting story:

In 1757 a child was abandoned on the porch of Straw Hall. Aris’s Birmingham Gazette 1st August 1757:

The Hancox family were living in Penn for at least 400 years. My great grandfather Charles Tomlinson built a house on Penn Common in the early 1900s, and other Tomlinson relatives have lived there. But none of the family knew of the Hancox connection to Penn. I don’t think that anyone imagined a Tomlinson ancestor would have been a gentleman, either.
Sarah Hancox’s brother William Hancox 1776-1848 had a busy year in 1804.
On 29 Aug 1804 he applied for a licence to marry Ann Grovenor of Claverley.
In August 1804 he had property up for auction in Penn. “part of Lightwoods, 3 plots, and the Coppice”
On 14 Sept 1804 their first son John was baptised in Penn. According to a later census John was born in Claverley. (before the parents got married)(Incidentally, John Hancox’s descendant married a Warren, who is a descendant of my 4x great grandfather Samuel Warren, on my mothers side, from Newhall, Derbyshire!)
On 30 Sept he married Ann in Penn.
In December he was a bankrupt pig and sheep dealer.
In July 1805 he’s in the papers under “certificates”: William Hancox the younger, sheep and pig dealer and chapman of Penn. (A certificate was issued after a bankruptcy if they fulfilled their obligations)
He was a pig dealer in Penn in 1841, a widower, living with unmarried daughter Elizabeth.Sarah’s father William Hancox died in 1816. In his will, he left his “daughter Sarah, wife of John Tomlinson of the Wergs the sum of £100 secured to me upon the tolls arising from the turnpike road leading from Wombourne to Sedgeley to and for her sole and separate use”.
The trustees of toll road would decide not to collect tolls themselves but get someone else to do it by selling the collecting of tolls for a fixed price. This was called “farming the tolls”. The Act of Parliament which set up the trust would authorise the trustees to farm out the tolls. This example is different. The Trustees of turnpikes needed to raise money to carry out work on the highway. The usual way they did this was to mortgage the tolls – they borrowed money from someone and paid the borrower interest; as security they gave the borrower the right, if they were not paid, to take over the collection of tolls and keep the proceeds until they had been paid off. In this case William Hancox has lent £100 to the turnpike and is leaving it (the right to interest and/or have the whole sum repaid) to his daughter Sarah Tomlinson. (this information on tolls from the Wolverhampton family history group.)William Hancox, Penn Wood, maltster, left a considerable amount of property to his children in 1816. All household effects he left to his wife Elizabeth, and after her decease to his son Richard Hancox: four dwelling houses in John St, Wolverhampton, in the occupation of various Pratts, Wright and William Clarke. He left £200 to his daughter Frances Gordon wife of James Gordon, and £100 to his daughter Ann Pratt widow of John Pratt. To his son William Hancox, all his various properties in Penn wood. To Elizabeth Tay wife of Thomas Tay he left £200, and to Richard Hancox various other properties in Penn Wood, and to his daughter Lucy Tay wife of Josiah Tay more property in Lower Penn. All his shops in St John Wolverhamton to his son Edward Hancox, and more properties in Lower Penn to both Francis Hancox and Edward Hancox. To his daughter Ellen York £200, and property in Montgomery and Bilston to his son John Hancox. Sons Francis and Edward were underage at the time of the will. And to his daughter Sarah, his interest in the toll mentioned above.
Sarah Tomlinson, wife of John Tomlinson of the Wergs, in William Hancox will:

-
AuthorSearch Results