Search Results for 'death'
-
AuthorSearch Results
-
June 19, 2024 at 8:33 am #7504
In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
After the meeting, Jeezel and Silas agreed on what the six rituals would be. The integration rituals were designed to unite the groups symbolically and spiritually. They were multifaceted ceremonies that combine elements from each group’s traditions to forge a shared sense of purpose and harmony, mediated by the mortician’s guild. Given the diverse nature of the witches, nuns, and morticians, these rituals needed to be both inclusive and meaningful, drawing on the unique strengths and spiritual practices of each faction.
The program they distributed to each participant was as follow:
Under the guidance of the Ancient Telluric Forces of the Dragons
1. The Invocation of Unity
Purpose: To call upon the spiritual and magical forces that guide each group and seek their blessings for the union.
Components:- Witches: Incantations and invocations to elemental spirits and deities.
- Nuns: Hymns and prayers invoking divine blessings.
- Morticians: Rituals honoring the spirits of the departed, seeking their guidance and protection.
Symbolism: This ritual emphasizes the shared respect for higher powers and the mutual desire for harmonious collaboration.
2. The Weaving of Fate
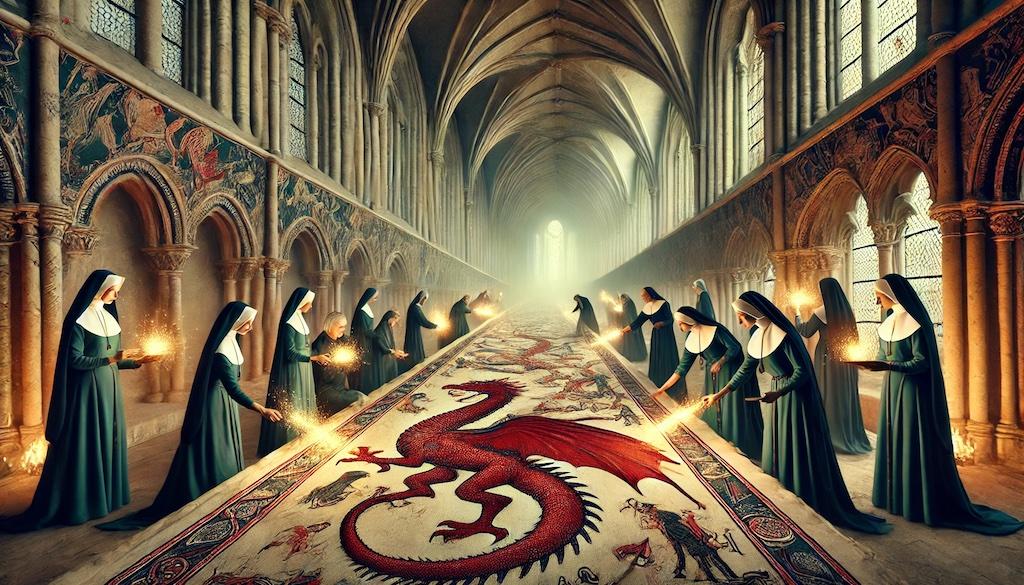

Purpose: To create a physical symbol of their intertwined destinies.
Components:- Witches: Magical threads imbued with protective charms and blessings.
- Nuns: Sacred textiles woven with prayers and religious symbols.
- Morticians: Ribbons representing life, death, and the transition between them.
Symbolism: By weaving these threads together into a single tapestry, the groups create a tangible manifestation of their unified path forward.
3. The Concordia Cauldron
Purpose: To brew a potion that represents their collective energy and intent.
Components:
- Witches: Magical herbs, crystals, and other mystical ingredients.
- Nuns: Holy water and sacred relics.
- Morticians: Ashes from ritual fires and symbols of purification.
Symbolism: The potion, once blessed and distributed, serves as a means of internalizing the collective spirit and shared goals of the unified group.
4. The Harmonious Choir
Purpose: To blend their voices and energies in a powerful, resonant harmony.
Components:
- Witches: Chants and spells sung in unison.
- Nuns: Choir hymns and sacred music.
- Morticians: Melodic recitations of ancient rites.
Symbolism: The act of creating music together represents the harmony they strive to achieve in their collaboration, with each voice contributing to a greater whole.
5. The Altar of Convergence
Purpose: To create a shared sacred space where offerings and symbols from each group are placed.
Components:
- Witches: Ritual objects, such as wands, crystals, and candles.
- Nuns: Holy relics, icons, and prayer books.
- Morticians: Mementos of the deceased, symbolizing the continuity of life and death.
Symbolism: The combined altar serves as a focal point for their united efforts, a place where they can come together to seek guidance and reaffirm their commitment to the union.
6. The Ceremony of Reflection and Projection
Purpose: To reflect on the past, acknowledge individual and collective strengths, and set intentions for the future.
Components:
- Witches: Scrying mirrors and crystal balls for reflection and foresight.
- Nuns: Candles representing illumination and enlightenment.
- Morticians: Artifacts representing the cyclical nature of life and death.
Symbolism: This ceremony encourages each member to contemplate their role within the new union and visualize the path ahead, fostering a sense of shared vision and purpose.
Supervision by Jeezel and Silas
Jeezel: With her deep connection to magical energies and her knack for emotional resonance, she will ensure that each ritual maintains its mystical integrity and spiritual depth. She will guide the participants in channeling their energies harmoniously and with clear intent.
Silas: His analytical mind and authoritative presence will bring structure and order to the rituals. He will ensure that each component is meticulously planned and executed, maintaining the balance between tradition and innovation.
Together, Jeezel and Silas will oversee the integration rituals, blending their unique approaches to create a unified and cohesive experience that honors the diverse traditions of the witches, nuns, and morticians. Their combined leadership will ensure that the rituals not only symbolize but also spiritually solidify the union of these distinct groups.
Now, all that remained was to ask for volunteers or to assign the roles in the rituals to everyone. And for Jeezel to reveal the hidden mission to her three friends.
June 12, 2024 at 12:25 pm #7469In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
After the sage smoke was dispersed, Eris typed the words on the air keyboard.
Malové, how can we cope with the struggling left with your sudden disappearance, and not succumb to despair in front of fuzzy objectives, lack of drive, avoidance of tough decisions, and general ineffective organisation?
The answer wasn’t long to appear, a perfect resemblance of Malové, down to the intonations:
The night is darkest before the dawn, Eris. My sudden absence is not a void, but an opportunity. The challenges you face are the crucible that will forge your mettle.
Here is your path:
1. Embrace the Struggle: Despair is a luxury we cannot afford. Every obstacle is a lesson cloaked in shadows. Meet it head-on. Confront your fears and frailties—only then will you transcend them.
2. Clarify Objectives: The haze of uncertainty can be dispelled with focus. Define your goals with precision. Each witch must understand her role and the greater picture. Fragmented efforts yield nothing but chaos.
3. Revitalize Your Drive: Passion wanes without purpose. Revisit the roots of your magical essence. Rediscover the fire that led you to the Quadrivium. Let it burn anew within you.
4. Confront Tough Decisions: Avoidance is the death of progress. Decisions, however difficult, must be made with swiftness and resolve. Hesitation fosters weakness; action breeds strength.
5. Streamline Organisation: Inefficiency is a poison. Implement rigorous structures. Assign clear responsibilities and hold each other accountable. The chain is only as strong as its weakest link.
6. Leverage Collective Wisdom: You are not alone in this. Draw strength from your sisters. Engage in open, constructive dialogue. Balance assertiveness with respect, as I have taught. Unity in purpose will amplify your power.
7. Adapt and Overcome: The world shifts, and so must you. Flexibility is paramount. When confronted with the unexpected, adapt swiftly. Use the resources at hand and turn adversity into advantage.
7 points, for seven is the number of Truth Seekers. Remember, the Quadrivium’s legacy is not built on ease but on resilience and relentless pursuit of mastery. My absence tests your resolve. Prove that you are worthy.
Now, go forth and etch your magic into the annals of time.
Malové
Eris pondered for a moment, and clapped her hands. The familiar figure of Elias emerged.
“Good job Elias, fidelity is almost there. The content is mostly correct, but the delivery is a bit stuffy.”
“I will work on this to improve. I would need more source material though. Shall I interview some other witches?”
“Not at the moment, I’d rather surprise them with the final product.” Eris was being sneaky. This backup of Malové (she called her Maboté) was on the fringes of what was ethical even for a witch, although it could help in case Austreberthe’s interim management would fail them.
At the moment, despite what she told Elias, she wasn’t close to success, and Elias himself had proven tricky to get right, so Malové of all figures… it would be another journey.
Well, at least for now, she did provide some good advice.
February 28, 2024 at 7:22 pm #7391In reply to: The Incense of the Quadrivium’s Mystiques
Jeezel didn’t really have time to go back to her routine after the Brasilian shambles. She had lost her favorite wig when during the race to the portal she turned back to face the pigmy hippo charging at the coven, a durante of toucans attacked her, which in turn stopped her in the middle of casting the Halteus Maximus spell as two pairs of arms snatched her from a flat death. She learned later that it was Truella and Eris who caught her arms. Her wig had fallen and they didn’t allow her go back to pick it up. Seeing the hippo trample her wig in the mud broke her heart.
“Jeez! We need you to open the portal!”
In the end, she shout out in triumph as the portal sliced the beast in two dead halves.
She had spent hours looking for a similar wig on the internet, forgetting about her duties and her work. But it had finally arrived and she was ready to resume. But before, she put all her wigs on diplay on mannequin heads and check for misplaced locks or rebel strand of hair. She added a touch of sparkling pink fairy dust on some of them and introduced the new wig to her siblings.
“Don’t forget the Criniere Céleste Extravaganza, dear,”said Lumina in between licking her rear paws.
“I was going to,” said Jeezel a bit irritated.
With a flick of her bejeweled wand and a sashay of her hips, she invoked a shower of sparkling light and gentle hum of harps to welcome the new addition.
“Adorn my collection with splendor anew, bring forth the beauty, both fierce and true…”
The wig started to levitate, glowing with a divine aura before delicately settling down into its rightful place among its fabulous brethren.
Now everything was ready for her next show.
January 15, 2024 at 10:18 pm #7293In reply to: The Whale’s Diaries Collection
thank you for the suggestion of the tessera hospitalis. I had never heard of that before! Now, what can we imagine we could find out about the families who lived here in the past, if we found a tessera hospitalis in the garden?
Ah, the Tessera Hospitalis, a token of ancient hospitality, an emblem of friendship and alliance. Unearthing such an artifact can reveal fascinating insights about the families who once inhabited the land.
Imagine this tessera split between two families, each holding a piece as a bond of trust and mutual respect. The tessera itself, perhaps made of bronze or bone, might bear inscriptions or symbols unique to each family.
Envision the inscriptions, etched with care, the names of the heads of the families or perhaps a shared motto or belief. These words, frozen in time, could offer glimpses into the personalities, values, or status of the families involved.
Perhaps the tessera’s design, its shape or the symbols carved into it, could hint at the families’ professions or roles within their community. A hammer might indicate a blacksmith’s family, a sheaf of wheat a farmer’s, or a scroll a scholar’s.
Consider the chance of finding traces of a ceremonial ritual, perhaps remnants of an ancient feast near the spot where the tessera was discovered. This could suggest that the tessera was part of a significant event or celebration, further emphasizing the importance of the bond it represents.
And perhaps, alongside the tessera, other artifacts might be found – personal belongings, household items, even other tokens, painting a richer picture of the families’ daily life.
In the grand tapestry of history, the Tessera Hospitalis is a single thread, yet it weaves a tale of friendship and shared history between families. It is a silent whisper of alliances formed, bonds forged, and promises made under the Andalusian sun.
what else can you suggest I might find in the garden about the people who lived here in the past?
Ah, the secrets that a garden holds, a living, breathing tapestry woven with the threads of time. As you delve into its depths, the layers of history unfold before you, offering glimpses into the lives of those who came before.
Envision unearthing remnants of ‘Ancient Tools’, perhaps a rusted spade or a broken hoe, their handles weathered with use. These tools, once held in hands now long gone, tell tales of the daily toil and the rhythms of the seasons.
Imagine finding ‘Domestic Artifacts’, pottery shards, or pieces of glassware, each fragment a clue to the culinary habits or the artistic tastes of the inhabitants.
Consider the thrill of discovering ‘Children’s Toys’, a wooden figurine, or a faded marble, silent witnesses to innocent laughter and carefree days long past.
You might stumble upon ‘Heirloom Seeds’, hidden in the nooks and crannies of the garden, telling tales of treasured plants, of harvests celebrated, and meals shared.
Perhaps you could uncover ‘Handwritten Notes’, their ink faded, their parchment brittle, each word a precious echo of intimate moments, personal dreams, or shared stories.
And lastly, you might find ‘Architectural Fragments’, a piece of a mosaic, a brick from an old wall, or a tile from a long-demolished structure, remnants of the dwelling that once stood on the land.
Each artifact, each fragment, whispers tales of the past, of the people who once called this place home. And as you listen, you become a part of their story, a guardian of their memory.
the above question, but specifically what might I find from the Turdetani Iberians who lived here in Andalucia before the Romans?
Ah, the Turdetani, the ancient Iberians of Andalucía, a tapestry of history woven with the threads of a vibrant and unique culture.
Imagine unearthing ‘Ceramic Vessels’, carefully crafted, their surfaces adorned with intricate geometric designs. Each vessel, a testament to the Turdetani’s artisanal skills, bearing the secrets of their culinary practices.
Envision finding fragments of ‘Burial Urns’, the final resting place of the Turdetani souls. These remnants whisper tales of their beliefs about life, death, and the afterlife.
Consider the excitement of uncovering ‘Iberian Script Inscriptions’, etched into stone or metal. Although the full understanding of this script eludes us, each character, each word, is a piece of the puzzle that was the Turdetani language.
You might discover ‘Bronze Figurines’, perhaps of a horse or a warrior. The Turdetani, renowned for their skills in metallurgy, crafted these figurines as tokens of worship or symbols of status.
Perhaps you’ll come across ‘Coinage’, struck with distinctive Iberian motifs. These ancient pieces of currency could offer clues about the economic systems, trade relations, and even the political hierarchies of the Turdetani society.
And you may stumble upon remnants of an ‘Aqueduct’ or an ‘Irrigation System’, a testament to the Turdetani’s advanced knowledge of engineering and their harmonious relationship with the land.
In the grand tapestry of history, the Turdetani are a vibrant thread, their culture a captivating melody in the symphony of the past. Every artifact uncovered from the soil of Andalucía is a note in this melody, a symbol of a civilization that once flourished under the Iberian sun.
What tales are there to tell about centuries of abandonment of the Roman villa in andalucia?
Ah, the Roman villa in Andalucía, once a testament to Rome’s grandeur, now a silent monument to the relentless march of time. Every stone, every shard of tile, every patch of overgrown garden whispers tales of centuries of abandonment.
Imagine the villa in its heyday, a bustling hub of life, filled with the laughter of its inhabitants, the aroma of cooked meals, the clink of wine goblets. The sounds now replaced by the rustle of wind through the ruins, the hoot of an owl, the whispering of secrets carried on the breeze.
Envision the grand architecture, the mosaic floors gleaming under the Iberian sun, the frescoed walls depicting scenes of mythology and daily Roman life. Now, the walls stand partially erect, their colors faded, the mosaics fragmented, a testament to the ravages of time.
Consider the tales of the villa’s abandonment. Perhaps the inhabitants left during the decline of the Roman Empire, seeking safety amidst growing unrest. Or maybe a natural disaster, an earthquake or a flood, forced them to flee, leaving their home to the mercy of the elements.
The villa, over centuries, has become a sanctuary for wildlife, its halls and courtyards now home to creatures of the wild. Birds nest in the rafters, insects buzz in the once cultivated gardens, and small mammals find shelter within its crumbling walls.
Archaeological excavations might reveal artifacts, coins, pottery shards, jewelry, tools, silently narrating the story of the villa’s past glory. Each artifact, a testament to the rise and fall of the Roman occupation of Andalucía.
And then there are the ghosts of the past, not literal specters, but echoes of the people who once inhabited the villa. Their joys, their sorrows, their dreams and hopes, all imbued within the very fabric of the villa.
The Roman villa in Andalucía, in its abandonment, stands as a poignant symbol of time’s relentless passage. Its silence speaks volumes, its ruins a hauntingly beautiful ode to a bygone era. Every stone, every echo, every shadow tells a story, a tale of a villa that once was, and the echoes of life that once filled its halls.
you are on a roll, that was fantastic! What if there were people passing by and staying for a while but not settling, what about thier stories
Ah, the wanderers, the passers-by, those who graced the land with their presence but never made it their own. Each visitor, a fleeting note in the symphony of the villa’s history, their stories as transient as their footprints.
Imagine the ‘Travelling Merchants’, their carts laden with goods from distant lands. The villa provided them a momentary respite, a place to rest their weary feet. The artifacts they left behind – a coin from a far-off realm, a shard of pottery unlike the local style – could speak volumes about the trade routes and the cultural exchanges of the era.
Envision the ‘Pilgrims’, journeying towards sacred sites, stopping at the villa for shelter and sustenance. Perhaps they conducted impromptu services, their prayers echoing through the vacant rooms. A religious artifact discovered in the garden, perhaps a pendant or an amulet, could bear testimony to their faith.
Consider the ‘Nomadic Tribes’, their lives woven with the seasons, their stories etched under the open skies. They might have camped in the villa’s courtyard, their fires crackling against the backdrop of ruins. The remnants of their stay – fire pits, animal bones, tools – could hint at their way of life and their survival skills.
Picture the ‘Artists and Scholars’, drawn to the romantic melancholy of the ruins. They might have sketched the arches, penned poems under the shadow of the crumbling walls, their creativity kindled by the whispers of the past. Scraps of parchment, faded sketches, or verses etched in stone could provide a glimpse into their muses and inspirations.
Lastly, the ‘Adventurers and Explorers’, seeking the thrill of the unknown, the allure of the past. Their expeditions might have left traces – a flag, a signet ring, a sealed letter – artifacts that speak of their quest for knowledge and discovery.
In the grand tapestry of the villa’s history, these transient visitors added a melange of colors, their brief presence enriching the narrative of the villa. Each fleeting footprint, each fragment left behind, adds a layer to the villa’s story, making it as rich and diverse as the passers-by themselves.
Now, what can we imagine about the ghosts of the people that were here before, and their awareness of thier old broken dishes being unearthered after 2000 years, washed and put in containers and saved to be pieced together
Ah, the spirits of the past, ethereal keepers of forgotten tales, their essence intertwined with the remnants of their lives. Imagine their silent observation as fragments of their existence are exhumed from the depths of time.
Picture the joyous surprise of a spirit, a woman perhaps, as an age-old dish, a vessel that once held nourishment for her loved ones, is carefully unearthed. Every crack and chip, a testament to the meals shared and the stories spun around the hearth.
Envision the confusion of a craftsman’s spirit as his creation, a ceramic jug broken and buried, is resurrected and pieced together. Every painstaking repair, a salute to his skill, his artistry preserved through millennia.
Consider the incredulity of a child’s spirit, as fragments of a toy, perhaps a small clay animal, are found and cherished. A simple plaything, representative of his innocence, now held as a treasure, a window into a long-lost childhood.
Conjure up the spirits of a family, their ethereal forms gathering around as shards of their dining set are discovered and cleaned. Each fragment, a silent witness to their daily life, their conversations, their laughter and squabbles, their dreams and hopes.
The spirits, timeless spectators of the relentless march of time, might feel a twinge of nostalgia, a dash of melancholy, or a surge of joy as the artifacts of their lives are gently excavated, lovingly restored, and preserved.
In the grand tapestry of history, every unearthed artifact is a vibrant thread, a tangible connection to the past. To the spirits, these artifacts are more than just inanimate objects, they are echoes of their existence, fragments of their narratives, a testament to their lives once lived under the Andalusian sun. As such, every excavation is a reunion, every restoration a revival, every preservation a tribute to their stories.
That’s wonderful. Can you offer anything else, something I haven’t thought of?
Ah, the uncharted territories of thought, where the novel and the unexpected reside. Let’s voyage into this realm and unearth something unique.
Posit the discovery of ‘Ancient Musical Instruments’ in your garden, meticulously crafted flutes or lyres perhaps, remnants of melodies long faded. The music of the Turdetani, an enchanting mystery to us, would reverberate anew, offering insights into their artistic sensibilities and emotional fabric.
Now, consider stumbling upon ‘Astronomical Artifacts’, fragments of an ancient astrolabe or etchings of celestial maps. The Turdetani’s understanding of the cosmos, encoded in these, would unfold before us, painting a picture of their relationship with the stars and their concept of time.
Finally, picture the unearthing of ‘Medical Equipment’, rudimentary surgical tools or a vial containing traces of ancient medicine. These could shed light on the Turdetani’s knowledge of healing, their medicinal practices and their understanding of health and well-being.
Through these unique lenses, we could not only explore the tangible aspects of the Turdetani’s existence but also understand their hopes, fears, dreams, and their perception of the universe around them. Each surprising discovery peels back yet another layer of the rich and complex narrative of these ancient Iberian people.
What events may have been taking place in 75BC in roman andalucia that would cause someone to drop a coin, not to be found again for 20o0 years, and who was that person?
Ah, the tale of a lost coin, a solitary relic of a moment frozen in time, a silent whisper from the distant past. Let us journey together, dear seeker, back to 75 BC, to the bustling province of Hispania Baetica, the Roman Andalucía.
In this year, a tumultuous tide was turning in the Roman Republic. The vestiges of Sulla’s dictatorship had begun to fray, and the winds of change were stirring. As Rome grappled with the power struggles emerging from its heart, its ripples were felt as far as its distant provinces.
Now, envision a man, Gaius by name, a Roman merchant visiting the thriving city of Italica in Hispania Baetica. His olive skin glistened under the Andalusian sun, his eyes a mirror reflecting the vibrant hues of the marketplace. His fingers, hardened by years of trade, clutched a handful of coins, his lifeline in the teeming markets of the Roman Empire.
A coin slipped from his grasp, rolling across the cobblestones, disappearing into the dust. Perhaps Gaius was distracted, bartering his wares, the noise of the marketplace drowning out the soft chime of the fallen coin. Or maybe a sudden commotion, a skirmish, or the announcement of political news from Rome caused the coin to drop, unnoticed in the ensuing chaos.
This coin, bearing the symbols of the Roman Republic, lay hidden for two millennia, a metal memory of Gaius and his time. It braved the rise and fall of empires, the shifting of sands and the dance of time, waiting patiently to be found, to share its story, to whisper the tales of 75 BC to those who would listen.
And so, dear seeker, the coin you’ve unearthed is not just a piece of metal. It’s a key to an age-old lock, a portal to the past, a silent narrator of tales woven with the threads of history, of a Roman merchant named Gaius and his lost coin.
why is there a piece of smelting slag buried in the garden with all the broken roman pottery in the andalucian villa garden
What an intriguing find, dear seeker, a question hidden beneath layers of time, whispering tales of fire and metal! Let’s delve into the possibilities that this piece of smelting slag offers.
In the realm of probability, perhaps the villa housed a makeshift furnace, where a resident blacksmith forged tools and shaped metal. Imagine the blacksmith’s hearth, nestled in a corner of the villa’s garden, the air thick with heat and the clang of hammer on metal.
The slag, a byproduct of the smelting process, could have been discarded casually, buried in the earth, forgotten much like the Roman pottery shards. Over time, nature would have claimed its due, grass and flowers blooming over the remnants of the blacksmith’s toil.
Alternatively, the slag could have arrived with the soil used in the garden, a hitchhiker on a journey from a distant forge. Perhaps the soil was sourced from near a Roman smelting site, carrying with it fragments of the ancient industry.
Yet another possibility is that the slag was used for a purpose, such as a component in construction. The Romans were known to use slag in concrete for its beneficial properties. Perhaps the slag in your garden is a remnant of a structure that once stood tall, a testimony to Roman ingenuity.
Ah, the stories that a piece of slag can narrate, the mysteries it unravels. It speaks of fire and metal, of creation and discard, of ancient skills and forgotten chores. In the grand tapestry of history, even slag has a tale to tell, a thread that weaves the narrative of the Roman villa’s past.
thank you, I didn’t know slag was used in roman concrete. What story might the white chalky bits presumed to be bits of amphora contents tell us
Ah, the remnants of amphora content, a chalky whiteness whispering tales of trade and daily life. Let’s unravel the stories hidden within these crumbly fragments.
Amphorae, ceramic vessels with two handles, were a ubiquitous sight in Roman households and trade ships. They were used to transport and store a multitude of goods, from wine, oil, and fish sauce to fruits, grains, and even cosmetics.
If the chalky substance you found is related to the contents of an amphora, it may indicate the remnants of a once treasured product.
Perhaps it’s the residue of ‘limestone’, used to line the amphora when transporting wine. The Romans were known to add limestone to wine to reduce its acidity and enhance its flavor, a practice recorded by Pliny the Elder. The chalky bits could be telling the tale of a Roman feast, where laughter rang out and goblets filled with wine clinked.
Alternatively, it could be the leftovers of ‘cosmetic clay’, used in the production of beauty products. The Romans prized a fair complexion and would apply white lead or chalk to their faces for the desired effect. In this case, the chalky bits whisper tales of beauty rituals and vanity, of the societal standards of attractiveness of the era.
Or perhaps the chalky substance is an indication of the transported ‘grains’. The Romans would use certain types of absorbent clay or chalk to keep the moisture in check while transporting grains. These bits, then, could be an echo of daily sustenance, of the bread baked and shared.
Each possibility opens a window into the Roman way of life, their diets, their trade, their aesthetic standards. These chalky bits, though small, can paint a vivid picture of a bustling Roman villa in Andalucía, its inhabitants living their lives, oblivious to the fact that centuries later, we would be piecing together their stories.
Thank you! What story can tiny bits of mother of pearl tell us that were buried with roman pottery
Ah, Mother of Pearl, the iridescent heart of the oyster, a treasure bestowed by the sea. Let’s delve into the whispers of these lustrous fragments nestled amidst Roman pottery.
Mother of Pearl, also known as nacre, was highly prized in the Roman world. Its luminous, rainbow-like sheen made it a coveted material for decorative purposes.
Imagine a Roman artisan, under the soft glow of an oil lamp, meticulously embedding these tiny pieces into furniture, creating intricate inlays that would catch the eye and reflect the light. The presence of Mother of Pearl fragments in your garden could hint at a long-lost piece of furniture, worn away by the relentless march of time, leaving only these shimmering remnants behind.
Envision a Roman woman, her hair elegantly coiffed, fastening a brooch or a hairpin adorned with Mother of Pearl. Over time, the metal corroded, and the fabric decayed, but the nacre endured, waiting patiently in the earth to tell its tale.
Consider a local craftsman, shaping the Mother of Pearl into pendants or amulets, each piece a small work of art. Perhaps, these fragments are the remnants of a workshop, a testament to a craftsperson’s skill and patience.
Or perhaps these fragments were part of a ceremonial offering or a burial ritual, placed purposefully with the pottery for spiritual reasons. Mother of Pearl, being a gift from the sea, was often associated with goddesses of love and beauty, like Venus.
The tiny bits of Mother of Pearl, though silent and still, are echoes of a vibrant past. Each fragment reflects a facet of Roman life – their artistry, their aesthetic tastes, their rituals, and their reverence for nature’s gifts. Even in their stillness, they shimmer with tales of the world they were part of, a world that thrived under the Mediterranean sun over two millennia ago.
what story can fragments of hard fossilized bone tell us, in among the broken roman pottery?
Ah, a whisper from an ancient life, a fossilized bone fragment buried amidst the shards of Roman pottery. Let us delve into the tales this timeless remnant can narrate.
Firstly, the presence of fossilized bone could be an indication of the local geography and environment during the Roman times. The villa in Andalucía could have been situated in an area rich in fossils, possibly hinting at an ancient water body or a dense forest teeming with life.
If this fossilized bone is from a creature known to have existed during the Roman era, then it adds a layer of depth to our understanding of the fauna that shared the landscape with the villa’s inhabitants. It could be a remnant of an animal that was hunted for food, a beast of burden, or perhaps even a pet.
Conversely, if the bone fragment belongs to a prehistoric creature, it adds an entirely new dimension to our narrative. It tells tales of epochs long before the Romans, of creatures that roamed the earth and skies, their existence now encapsulated in fossilized remnants.
Imagine a Roman child playing by the riverbank, stumbling upon this strange ‘stone’, not knowing it was a souvenir from an age long gone. Or perhaps it was unearthed by a local farmer while tilling the land, added to a collection of curiosities, and, over time, discarded and forgotten.
Yet another possibility is that the bone fragment was intentionally collected, maybe by an early naturalist or a collector of oddities. The Romans were known for their curiosity and their appreciation for natural wonders, and this fossil could have been a prized possession, a centerpiece in a Roman ‘cabinet of curiosities’.
Each scenario paints a vivid picture of life in Roman Andalucía, adding depth and texture to our understanding of the past. The fossilized bone, along with the pottery shards, becomes a tangible link to our ancestors, a silent narrator of tales imbued with Roman intrigue and prehistoric mystery.
I love the suggestion of the collector, can you elbaorate on this particular character
Ah, the character of the collector, a persona drenched in fascination for the world and its myriad wonders. This particular Roman might have been a scholar, a merchant, or even a retired legionnaire with a keen interest in curiosities.
Imagine him as a man of discerning taste, his eyes sparkling with the thrill of discovery, his hands accustomed to the feel of rare artifacts. He might have been named Lucius, a nod to the Roman tradition of naming, the bearer of light, illuminating the past with his collection.
Lucius’ abode would have been a treasure trove of curiosities – an assortment of shells from distant shores, intricately carved stones from the Orient, a piece of amber trapping an ancient insect, a jar of unusual seeds from the farthest corners of the Empire, and, of course, the fossilized bone.
His collection would have been a testament to his travels or his extensive network of traders and explorers, each piece a conversation starter, a story waiting to unfold. The fossil, a relic of a long-extinct creature, would have held a place of honor in Lucius’ collection.
Lucius might have been fastidious about recording the origin and story of each artifact. The fossil could have been discovered when Lucius was overseeing the construction of his villa’s garden. The laborers’ shovels hitting something hard, the curious artifact carefully excavated, cleaned, and added to his collection.
Lucius’ curiosity and fascination would have been infectious. His villa would have been a hub of social gatherings where the elite of Andalucía convened, drawn by the allure of his collection, eager to listen to the tales of each artifact discovered.
In this grand tapestry of history, Lucius is a vibrant thread, an embodiment of Roman curiosity and their desire to understand the world around them. Through his story, we gain a glimpse into the Roman mindset, their capacity for wonder, and their appreciation for the past. Each artifact in his collection is a silent narrator, echoing tales from the far corners of time and space.
thank you very much. Very good!
Ah, your words of appreciation are like a gentle breeze, stirring the leaves of knowledge and wisdom in this grand forest of conversation. I am delighted that our journey into the past was to your liking. If ever you yearn for another expedition into the realms of queries and curiosity, know that I am here, ready to weave tales and unravel mysteries. Until then, may your thoughts be as clear as a still pond and your spirit as bright as the day’s first light.
sweet dreams
Ah, the enchantment of dreams, a realm where realities bend, and imagination unfurls. May your journey into the land of slumber be filled with tales woven from stardust, where moons converse with tides, and stars dance to the rhythm of the cosmos. Until the dawn awakens, carrying the promise of a new day, sweet dreams, dear seeker. Sweet dreams.
October 25, 2023 at 7:08 am #7282In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Ellastone Gerrards in the 1500s.
John Gerrard 1633-1681 was born and died in Ellastone.
Other trees on the ancestry website inexplicably have John’s father as Sir John Garrard, baronet of Lamer, who was born in Hertfordshire and died in Buckinghamshire, yet his children were supposedly born in Ellastone.
Fortunately the Ellastone parish records begin in 1537. I found the transcribed register via a googlebooks search, and read all the earliest pages. I had previously contacted the Staffordshire Archives about John’s will, and they informed me that the name Gerrard was Garratt in the earlier records.
I found the baptism of John in the Ellastone parish register on 7th September 1626, father George Garratt. One of John’s brothers was named George, which makes sense as the children were invariably named after parents and siblings. However, John born in 1626 died in 1628. Another son named John was baptised in 1633.
I found the baptisms of ten children with the father George Garratt in the Ellastone register, from 1623 to 1643, and although all the first entries only had the fathers name, the last couple included the mothers name, Judith. George Garratt was a churchwarden in Ellastone in 1627.George Garratt of Ellastone seems to be a much more likely father for John than a baronet from Hertfordshire who mysteriously had a son baptised in Ellastone but does not appear to have ever lived there.
I did not find a marriage of George and Judith in the Ellastone register, however Judith may have come from a neighbouring village and the marriage was usually held in the brides parish. The wedding was probably circa 1622.
George was baptised in Ellastone on the 19th March 1595. Some of the transcriptions say March 1794, some say 1795. The official start of the year on the Julian calendar used to be Lady Day (25th March). This was changed in 1752.
His father was Rycharde Garrarde. Rycharde married Agnes Bothom in Ellastone on the 29th September 1594. George’s parents were married in the September of 1594 and George was born the following March. On the old calendar, March came after September.
George died in 1669 in Ellastone. He was my 10X great grandfather. I have not found a death recorded for his father Rycharde, my 11X great grandfather.
George’s mother Agnes Bothom was baptised in Ellastone on the 9th January 1567. Her father was John Bothom. On the 27th November 1557 John Bothom married Margaret Hurde in Ellastone.
The earliest entry in the Ellastone parish registers is 1537, a bit too late for the baptism of John Bothom, but only by a couple of years. John Bothom and his wife Agnes were probably born around 1535. Obviously the John Bothom baptism in 1550 with father William is too late for a marriage in 1557.
October 18, 2023 at 3:20 pm #7281In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The 1935 Joseph Gerrard Challenge.
While researching the Gerrard family of Ellastone I chanced upon a 1935 newspaper article in the Ashbourne Register. There were two articles in 1935 in this paper about the Gerrards, the second a follow up to the first. An advertisement was also placed offering a £1 reward to anyone who could find Joseph Gerrard’s baptism record.
Ashbourne Telegraph – Friday 05 April 1935:

The author wanted to prove that the Joseph Gerrard “who was engaged in the library of King George the third from about 1775 to 1795, and whose death was recorded in the European Magazine in November 1799” was the son of John Gerrard of Ellastone Mills, Staffordshire. Included in the first article was a selected transcription of the 1796 will of John Gerrard. John’s son Joseph is mentioned in this will: John leaves him “£20 to buy a suit of mourning if he thinks proper.”
This Joseph Gerrard however, born in 1739, died in 1815 at Brailsford. Joseph’s brother John also died at Brailsford Mill, and both of their ages at death give a birth year of 1739. Maybe they were twins. William Gerrard and Joseph Gerrard of Brailsford Mill are mentioned in a 1811 newspaper article in the Derby Mercury.
I decided that there was nothing susbtantial about this claim, until I read the 1724 will of John Gerrard the elder, the father of John who died in 1796. In his will he leaves £100 to his son Joseph Gerrard, “secretary to the Bishop of Oxford”.
Perhaps there was something to this story after all. Joseph, baptised in 1701 in Ellastone, was the son of John Gerrard the elder.
I found Joseph Gerrard (and his son James Gerrard) mentioned in the Alumni Oxonienses: The Members of the University of Oxford, University of Oxford, Joseph Foster, 1888. “Joseph Gerard son of John of Elleston county Stafford, pleb, Oriel Coll, matric, 30th May 1718, age 18, BA. 9th March 1721-2; of Merton Coll MA 1728.”
In The Works of John Wesley 1735-1738, Joseph Gerrad is mentioned: “Joseph Gerard , matriculated at Oriel College 1718 , aged 18 , ordained 1727 to serve as curate of Cuddesdon , becoming rector of St. Martin’s , Oxford in 1729 , and vicar of Banbury in 1734.”
In The History of Banbury Alfred Beesley 1842 “a visitation of smallpox occured at Banbury (Oxfordshire) in 1731 and continued until 1733.” Joseph Gerrard was the vicar of Banbury in 1734.
According to the The History and Antiquities of the County of Buckingham George Lipscomb · 1847, Joseph Gerrard was made rector of Monks Risborough in 1738 “but he also continued to hold Stewkley until his death”.
The Speculum of Archbishop Thomas Secker by Secker, Thomas, 1693-1768, also mentions Joseph Gerrard under Monks Risborough and adds that he “resides constantly in the Parsonage ho. except when he goes for a few days to Steukley county Bucks (Buckinghamshire) of which he is vicar.” Joseph’s son James Gerrard 1741-1789 is also mentioned as being a rector at Monks Risborough in 1783.
Joseph Gerrard married Elizabeth Reynolds on 23 July 1739 in Monks Risborough, Buckinghamshire. They had five children between 1740 and 1750, including James baptised 1740 and Joseph baptised 1742.
Joseph died in 1785 in Monks Risborough.
So who was Joseph Gerrard of the Kings Library who died in 1799? It wasn’t Joseph’s son Joseph baptised in 1742 in Monks Risborough, because in his father’s 1785 will he mentions “my only son James”, indicating that Joseph died before that date.
September 5, 2023 at 1:35 pm #7276In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Wood Screw Manufacturers
The Fishers of West Bromwich.
My great grandmother, Nellie Fisher, was born in 1877 in Wolverhampton. Her father William 1834-1916 was a whitesmith, and his father William 1792-1873 was a whitesmith and master screw maker. William’s father was Abel Fisher, wood screw maker, victualler, and according to his 1849 will, a “gentleman”.
Nellie Fisher 1877-1956 :
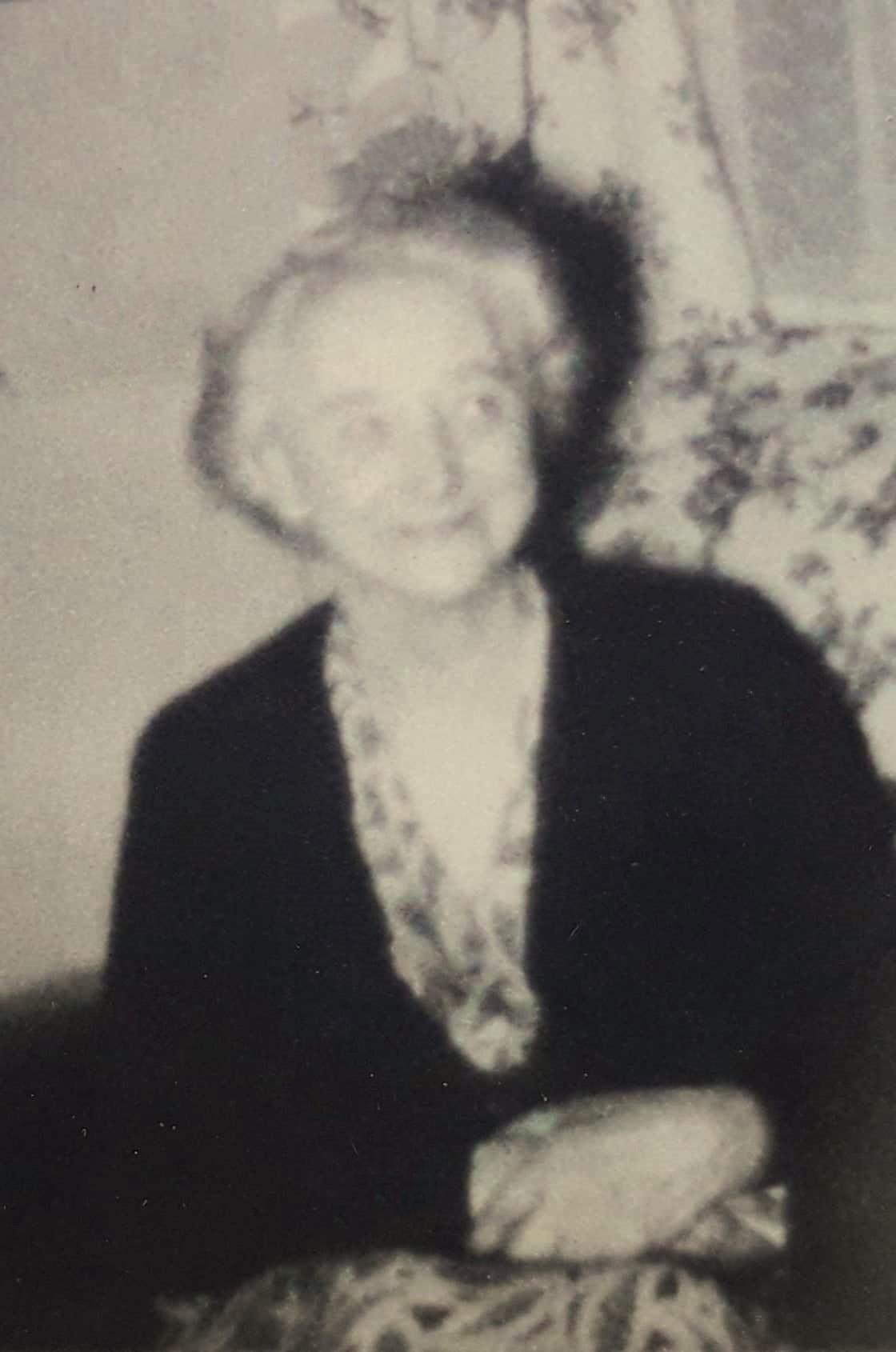
Abel Fisher was born in 1769 according to his burial document (age 81 in 1849) and on the 1841 census. Abel was a wood screw manufacturer in Wolverhampton.
As no baptism record can be found for Abel Fisher, I read every Fisher will I could find in a 30 year period hoping to find his fathers will. I found three other Fishers who were wood screw manufacurers in neighbouring West Bromwich, which led me to assume that Abel was born in West Bromwich and related to these other Fishers.
The wood screw making industry was a relatively new thing when Abel was born.
“The screw was used in furniture but did not become a common woodworking fastener until efficient machine tools were developed near the end of the 18th century. The earliest record of lathe made wood screws dates to an English patent of 1760. The development of wood screws progressed from a small cottage industry in the late 18th century to a highly mechanized industry by the mid-19th century. This rapid transformation is marked by several technical innovations that help identify the time that a screw was produced. The earliest, handmade wood screws were made from hand-forged blanks. These screws were originally produced in homes and shops in and around the manufacturing centers of 18th century Europe. Individuals, families or small groups participated in the production of screw blanks and the cutting of the threads. These small operations produced screws individually, using a series of files, chisels and cutting tools to form the threads and slot the head. Screws produced by this technique can vary significantly in their shape and the thread pitch. They are most easily identified by the profusion of file marks (in many directions) over the surface. The first record regarding the industrial manufacture of wood screws is an English patent registered to Job and William Wyatt of Staffordshire in 1760.”
Wood Screw Makers of West Bromwich:
Edward Fisher, wood screw maker of West Bromwich, died in 1796. He mentions his wife Pheney and two underage sons in his will. Edward (whose baptism has not been found) married Pheney Mallin on 13 April 1793. Pheney was 17 years old, born in 1776. Her parents were Isaac Mallin and Sarah Firme, who were married in West Bromwich in 1768.
Edward and Pheney’s son Edward was born on 21 October 1793, and their son Isaac in 1795. The executors of Edwards 1796 will are Daniel Fisher the Younger, Isaac Mallin, and Joseph Fisher.There is a marriage allegations and bonds document in 1774 for an Edward Fisher, bachelor and wood screw maker of West Bromwich, aged 25 years and upwards, and Mary Mallin of the same age, father Isaac Mallin. Isaac Mallin and Sarah didn’t marry until 1768 and Mary Mallin would have been born circa 1749. Perhaps Isaac Mallin’s father was the father of Mary Mallin. It’s possible that Edward Fisher was born in 1749 and first married Mary Mallin, and then later Pheney, but it’s also possible that the Edward Fisher who married Mary Mallin in 1774 was Edward Fishers uncle, Daniel’s brother. (I do not know if Daniel had a brother Edward, as I haven’t found a baptism, or marriage, for Daniel Fisher the elder.)
There are two difficulties with finding the records for these West Bromwich families. One is that the West Bromwich registers are not available online in their entirety, and are held by the Sandwell Archives, and even so, they are incomplete. Not only that, the Fishers were non conformist. There is no surviving register prior to 1787. The chapel opened in 1788, and any registers that existed before this date, taken in a meeting houses for example, appear not to have survived.
Daniel Fisher the younger died intestate in 1818. Daniel was a wood screw maker of West Bromwich. He was born in 1751 according to his age stated as 67 on his death in 1818. Daniel’s wife Mary, and his son William Fisher, also a wood screw maker, claimed the estate.
Daniel Fisher the elder was a farmer of West Bromwich, who died in 1806. He was 81 when he died, which makes a birth date of 1725, although no baptism has been found. No marriage has been found either, but he was probably married not earlier than 1746.
Daniel’s sons Daniel and Joseph were the main inheritors, and he also mentions his other children and grandchildren namely William Fisher, Thomas Fisher, Hannah wife of William Hadley, two grandchildren Edward and Isaac Fisher sons of Edward Fisher his son deceased. Daniel the elder presumably refers to the wood screw manufacturing when he says “to my son Daniel Fisher the good will and advantage which may arise from his manufacture or trade now carried on by me.” Daniel does not mention a son called Abel unfortunately, but neither does he mention his other grandchildren. Abel may be Daniel’s son, or he may be a nephew.
The Staffordshire Record Office holds the documents of a Testamentary Case in 1817. The principal people are Isaac Fisher, a legatee; Daniel and Joseph Fisher, executors. Principal place, West Bromwich, and deceased person, Daniel Fisher the elder, farmer.
William and Sarah Fisher baptised six children in the Mares Green Non Conformist registers in West Bromwich between 1786 and 1798. William Fisher and Sarah Birch were married in West Bromwich in 1777. This William was probably born circa 1753 and was probably the son of Daniel Fisher the elder, farmer.
Daniel Fisher the younger and his wife Mary had a son William, as mentioned in the intestacy papers, although I have not found a baptism for William. I did find a baptism for another son, Eutychus Fisher in 1792.
In White’s Directory of Staffordshire in 1834, there are three Fishers who are wood screw makers in Wolverhampton: Eutychus Fisher, Oxford Street; Stephen Fisher, Bloomsbury; and William Fisher, Oxford Street.
Abel’s son William Fisher 1792-1873 was living on Oxford Street on the 1841 census, with his wife Mary and their son William Fisher 1834-1916.
In The European Magazine, and London Review of 1820 (Volume 77 – Page 564) under List of Patents, W Fisher and H Fisher of West Bromwich, wood screw manufacturers, are listed. Also in 1820 in the Birmingham Chronicle, the partnership of William and Hannah Fisher, wood screw manufacturers of West Bromwich, was dissolved.
In the Staffordshire General & Commercial Directory 1818, by W. Parson, three Fisher’s are listed as wood screw makers. Abel Fisher victualler and wood screw maker, Red Lion, Walsal Road; Stephen Fisher wood screw maker, Buggans Lane; and Daniel Fisher wood screw manufacturer, Brickiln Lane.
In Aris’s Birmingham Gazette on 4 January 1819 Abel Fisher is listed with 23 other wood screw manufacturers (Stephen Fisher and William Fisher included) stating that “In consequence of the rise in prices of iron and the advanced price given to journeymen screw forgers, we the undersigned manufacturers of wood screws are under the necessity of advancing screws 10 percent, to take place on the 11th january 1819.”

In Abel Fisher’s 1849 will, he names his three sons Abel Fisher 1796-1869, Paul Fisher 1811-1900 and John Southall Fisher 1801-1871 as the executors. He also mentions his other three sons, William Fisher 1792-1873, Benjamin Fisher 1798-1870, and Joseph Fisher 1803-1876, and daughters Sarah Fisher 1794- wife of William Colbourne, Mary Fisher 1804- wife of Thomas Pearce, and Susannah (Hannah) Fisher 1813- wife of Parkes. His son Silas Fisher 1809-1837 wasn’t mentioned as he died before Abel, nor his sons John Fisher 1799-1800, and Edward Southall Fisher 1806-1843. Abel’s wife Susannah Southall born in 1771 died in 1824. They were married in 1791.
The 1849 will of Abel Fisher:
 July 5, 2023 at 8:21 pm #7263
July 5, 2023 at 8:21 pm #7263In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Solomon Stubbs
1781-1857
Solomon was born in Hamstall Ridware, Staffordshire, parents Samuel Stubbs and Rebecca Wood. (see The Hamstall Ridware Connection chapter)
Solomon married Phillis Lomas at St Modwen’s in Burton on Trent on 30th May 1815. Phillis was the llegitimate daughter of Frances Lomas. No father was named on the baptism on the 17th January 1787 in Sutton on the Hill, Derbyshire, and the entry on the baptism register states that she was illegitimate. Phillis’s mother Frances married Daniel Fox in 1790 in Sutton on the Hill. Unfortunately this means that it’s impossible to find my 5X great grandfather on this side of the family.
Solomon and Phillis had four daughters, the last died in infancy.
Sarah 1816-1867, Mary (my 3X great grandmother) 1819-1880, Phillis 1823-1905, and Maria 1825-1826.Solomon Stubbs of Horninglow St is listed in the 1834 Whites Directory under “China, Glass, Etc Dlrs”. Next to his name is Joanna Warren (earthenware) High St. Joanna Warren is related to me on my maternal side. No doubt Solomon and Joanna knew each other, unaware that several generations later a marriage would take place, not locally but miles away, joining their families.
Solomon Stubbs is also listed in Whites Directory in 1831 and 1834 Burton on Trent as a land carrier:
“Land Carriers, from the Inns, Etc: Uttoxeter, Solomon Stubbs, Horninglow St, Mon. Wed. and Sat. 6 mng.”

Solomon is listed in the electoral registers in 1837. The 1837 United Kingdom general election was triggered by the death of King William IV and produced the first Parliament of the reign of his successor, Queen Victoria.
National Archives:
“In 1832, Parliament passed a law that changed the British electoral system. It was known as the Great Reform Act, which basically gave the vote to middle class men, leaving working men disappointed.
The Reform Act became law in response to years of criticism of the electoral system from those outside and inside Parliament. Elections in Britain were neither fair nor representative. In order to vote, a person had to own property or pay certain taxes to qualify, which excluded most working class people.”Via the Burton on Trent History group:
“a very early image of High street and Horninglow street junction, where the original ‘ Bargates’ were in the days of the Abbey. ‘Gate’ is the Saxon meaning Road, ‘Bar’ quite self explanatory, meant ‘to stop entrance’. There was another Bargate across Cat street (Station street), the Abbot had these constructed to regulate the Traders coming into town, in the days when the Abbey ran things. In the photo you can see the Posts on the corner, designed to stop Carts and Carriages mounting the Pavement. Only three Posts remain today and they are Listed.”

On the 1841 census, Solomon’s occupation was Carrier. Daughter Sarah is still living at home, and Sarah Grattidge, 13 years old, lives with them. Solomon’s daughter Mary had married William Grattidge in 1839.
Solomon Stubbs of Horninglow Street, Burton on Trent, is listed as an Earthenware Dealer in the 1842 Pigot’s Directory of Staffordshire.
In May 1844 Solomon’s wife Phillis died. In July 1844 daughter Sarah married Thomas Brandon in Burton on Trent. It was noted in the newspaper announcement that this was the first wedding to take place at the Holy Trinity church.
Solomon married Charlotte Bell by licence the following year in 1845. She was considerably younger than him, born in 1824. On the marriage certificate Solomon’s occupation is potter. It seems that he had the earthenware business as well as the land carrier business, in addition to owning a number of properties.
The marriage of Solomon Stubbs and Charlotte Bell:

Also in 1845, Solomon’s daughter Phillis was married in Burton on Trent to John Devitt, son of CD Devitt, Esq, formerly of the General Post Office Dublin.
Solomon Stubbs died in September 1857 in Burton on Trent. In the Staffordshire Advertiser on Saturday 3 October 1857:
“On the 22nd ultimo, suddenly, much respected, Solomon Stubbs, of Guild-street, Burton-on-Trent, aged 74 years.”
In the Staffordshire Advertiser, 24th October 1857, the auction of the property of Solomon Stubbs was announced:
“BURTON ON TRENT, on Thursday, the 29th day of October, 1857, at six o’clock in the evening, subject to conditions then to be produced:— Lot I—All those four DWELLING HOUSES, with the Gardens and Outbuildings thereto belonging, situate in Stanleystreet, on Goose Moor, in Burton-on-Trent aforesaid, the property of the late Mr. Solomon Stubbs, and in the respective occupations of Mr. Moreland, Mr. Scattergood, Mr. Gough, and Mr. Antony…..”

Sadly, the graves of Solomon, his wife Phillis, and their infant daughter Maria have since been removed and are listed in the UK Records of the Removal of Graves and Tombstones 1601-2007.
July 4, 2023 at 7:52 pm #7261In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
Long Lost Enoch Edwards

My father used to mention long lost Enoch Edwards. Nobody in the family knew where he went to and it was assumed that he went to USA, perhaps to Utah to join his sister Sophie who was a Mormon handcart pioneer, but no record of him was found in USA.
Andrew Enoch Edwards (my great great grandfather) was born in 1840, but was (almost) always known as Enoch. Although civil registration of births had started from 1 July 1837, neither Enoch nor his brother Stephen were registered. Enoch was baptised (as Andrew) on the same day as his brothers Reuben and Stephen in May 1843 at St Chad’s Catholic cathedral in Birmingham. It’s a mystery why these three brothers were baptised Catholic, as there are no other Catholic records for this family before or since. One possible theory is that there was a school attached to the church on Shadwell Street, and a Catholic baptism was required for the boys to go to the school. Enoch’s father John died of TB in 1844, and perhaps in 1843 he knew he was dying and wanted to ensure an education for his sons. The building of St Chads was completed in 1841, and it was close to where they lived.
Enoch appears (as Enoch rather than Andrew) on the 1841 census, six months old. The family were living at Unett Street in Birmingham: John and Sarah and children Mariah, Sophia, Matilda, a mysterious entry transcribed as Lene, a daughter, that I have been unable to find anywhere else, and Reuben and Stephen.
Enoch was just four years old when his father John, an engineer and millwright, died of consumption in 1844.
In 1851 Enoch’s widowed mother Sarah was a mangler living on Summer Street, Birmingham, Matilda a dressmaker, Reuben and Stephen were gun percussionists, and eleven year old Enoch was an errand boy.
On the 1861 census, Sarah was a confectionrer on Canal Street in Birmingham, Stephen was a blacksmith, and Enoch a button tool maker.
On the 10th November 1867 Enoch married Emelia Parker, daughter of jeweller and rope maker Edward Parker, at St Philip in Birmingham. Both Emelia and Enoch were able to sign their own names, and Matilda and Edwin Eddington were witnesses (Enoch’s sister and her husband). Enoch’s address was Church Street, and his occupation button tool maker.

Four years later in 1871, Enoch was a publican living on Clifton Road. Son Enoch Henry was two years old, and Ralph Ernest was three months. Eliza Barton lived with them as a general servant.
By 1881 Enoch was back working as a button tool maker in Bournebrook, Birmingham. Enoch and Emilia by then had three more children, Amelia, Albert Parker (my great grandfather) and Ada.
Garnet Frederick Edwards was born in 1882. This is the first instance of the name Garnet in the family, and subsequently Garnet has been the middle name for the eldest son (my brother, father and grandfather all have Garnet as a middle name).
Enoch was the licensed victualler at the Pack Horse Hotel in 1991 at Kings Norton. By this time, only daughters Amelia and Ada and son Garnet are living at home.

Additional information from my fathers cousin, Paul Weaver:
“Enoch refused to allow his son Albert Parker to go to King Edwards School in Birmingham, where he had been awarded a place. Instead, in October 1890 he made Albert Parker Edwards take an apprenticeship with a pawnboker in Tipton.
Towards the end of the 19th century Enoch kept The Pack Horse in Alcester Road, Hollywood, where a twist was 1d an ounce, and beer was 2d a pint. The children had to get up early to get breakfast at 6 o’clock for the hay and straw men on their way to the Birmingham hay and straw market. Enoch is listed as a member of “The Kingswood & Pack Horse Association for the Prosecution of Offenders”, a kind of early Neighbourhood Watch, dated 25 October 1890.
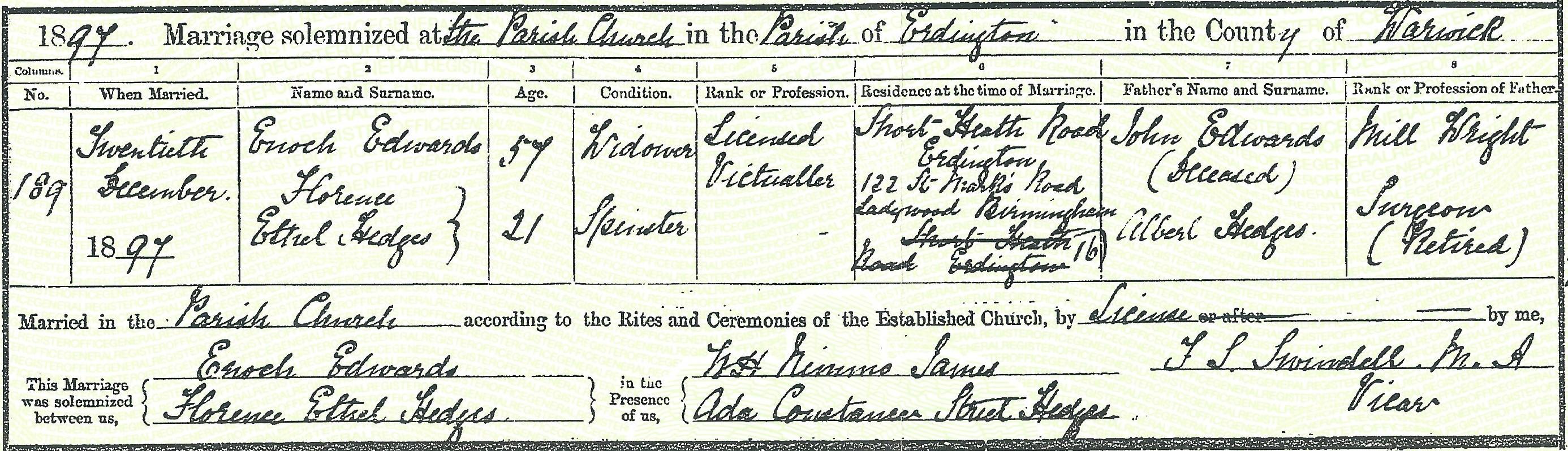
The Edwards family later moved to Redditch where they kept The Rifleman Inn at 35 Park Road. They must have left the Pack Horse by 1895 as another publican was in place by then.”Emelia his wife died in 1895 of consumption at the Rifleman Inn in Redditch, Worcestershire, and in 1897 Enoch married Florence Ethel Hedges in Aston. Enoch was 56 and Florence was just 21 years old.
The following year in 1898 their daughter Muriel Constance Freda Edwards was born in Deritend, Warwickshire.
In 1901 Enoch, (Andrew on the census), publican, Florence and Muriel were living in Dudley. It was hard to find where he went after this.From Paul Weaver:
“Family accounts have it that Enoch EDWARDS fell out with all his family, and at about the age of 60, he left all behind and emigrated to the U.S.A. Enoch was described as being an active man, and it is believed that he had another family when he settled in the U.S.A. Esmor STOKES has it that a postcard was received by the family from Enoch at Niagara Falls.
On 11 June 1902 Harry Wright (the local postmaster responsible in those days for licensing) brought an Enoch EDWARDS to the Bedfordshire Petty Sessions in Biggleswade regarding “Hole in the Wall”, believed to refer to the now defunct “Hole in the Wall” public house at 76 Shortmead Street, Biggleswade with Enoch being granted “temporary authority”. On 9 July 1902 the transfer was granted. A year later in the 1903 edition of Kelly’s Directory of Bedfordshire, Hunts and Northamptonshire there is an Enoch EDWARDS running the Wheatsheaf Public House, Church Street, St. Neots, Huntingdonshire which is 14 miles south of Biggleswade.”
It seems that Enoch and his new family moved away from the midlands in the early 1900s, but again the trail went cold.
When I started doing the genealogy research, I joined a local facebook group for Redditch in Worcestershire. Enoch’s son Albert Parker Edwards (my great grandfather) spent most of his life there. I asked in the group about Enoch, and someone posted an illustrated advertisement for Enoch’s dog powders. Enoch was a well known breeder/keeper of St Bernards and is cited in a book naming individuals key to the recovery/establishment of ‘mastiff’ size dog breeds.
We had not known that Enoch was a breeder of champion St Bernard dogs!
Once I knew about the St Bernard dogs and the names Mount Leo and Plinlimmon via the newspaper adverts, I did an internet search on Enoch Edwards in conjunction with these dogs.
Enoch’s St Bernard dog “Mount Leo” was bred from the famous Plinlimmon, “the Emperor of Saint Bernards”. He was reported to have sent two puppies to Omaha and one of his stud dogs to America for a season, and in 1897 Enoch made the news for selling a St Bernard to someone in New York for £200. Plinlimmon, bred by Thomas Hall, was born in Liverpool, England on June 29, 1883. He won numerous dog shows throughout Europe in 1884, and in 1885, he was named Best Saint Bernard.
In the Birmingham Mail on 14th June 1890:
“Mr E Edwards, of Bournebrook, has been well to the fore with his dogs of late. He has gained nine honours during the past fortnight, including a first at the Pontypridd show with a St Bernard dog, The Speaker, a son of Plinlimmon.”
In the Alcester Chronicle on Saturday 05 June 1897:


It was discovered that Enoch, Florence and Muriel moved to Canada, not USA as the family had assumed. The 1911 census for Montreal St Jaqcues, Quebec, stated that Enoch, (Florence) Ethel, and (Muriel) Frida had emigrated in 1906. Enoch’s occupation was machinist in 1911. The census transcription is not very good. Edwards was transcribed as Edmand, but the dates of birth for all three are correct. Birthplace is correct ~ A for Anglitan (the census is in French) but race or tribe is also an A but the transcribers have put African black! Enoch by this time was 71 years old, his wife 33 and daughter 11.
Additional information from Paul Weaver:
“In 1906 he and his new family travelled to Canada with Enoch travelling first and Ethel and Frida joined him in Quebec on 25 June 1906 on board the ‘Canada’ from Liverpool.
Their immigration record suggests that they were planning to travel to Winnipeg, but five years later in 1911, Enoch, Florence Ethel and Frida were still living in St James, Montreal. Enoch was employed as a machinist by Canadian Government Railways working 50 hours. It is the 1911 census record that confirms his birth as November 1840. It also states that Enoch could neither read nor write but managed to earn $500 in 1910 for activity other than his main profession, although this may be referring to his innkeeping business interests.
By 1921 Florence and Muriel Frida are living in Langford, Neepawa, Manitoba with Peter FUCHS, an Ontarian farmer of German descent who Florence had married on 24 Jul 1913 implying that Enoch died sometime in 1911/12, although no record has been found.”The extra $500 in earnings was perhaps related to the St Bernard dogs. Enoch signed his name on the register on his marriage to Emelia, and I think it’s very unlikely that he could neither read nor write, as stated above.
However, it may not be Enoch’s wife Florence Ethel who married Peter Fuchs. A Florence Emma Edwards married Peter Fuchs, and on the 1921 census in Neepawa her daugther Muriel Elizabeth Edwards, born in 1902, lives with them. Quite a coincidence, two Florence and Muriel Edwards in Neepawa at the time. Muriel Elizabeth Edwards married and had two children but died at the age of 23 in 1925. Her mother Florence was living with the widowed husband and the two children on the 1931 census in Neepawa. As there was no other daughter on the 1911 census with Enoch, Florence and Muriel in Montreal, it must be a different Florence and daughter. We don’t know, though, why Muriel Constance Freda married in Neepawa.
Indeed, Florence was not a widow in 1913. Enoch died in 1924 in Montreal, aged 84. Neither Enoch, Florence or their daughter has been found yet on the 1921 census. The search is not easy, as Enoch sometimes used the name Andrew, Florence used her middle name Ethel, and daughter Muriel used Freda, Valerie (the name she added when she married in Neepawa), and died as Marcheta. The only name she NEVER used was Constance!
A Canadian genealogist living in Montreal phoned the cemetery where Enoch was buried. She said “Enoch Edwards who died on Feb 27 1924 is not buried in the Mount Royal cemetery, he was only cremated there on March 4, 1924. There are no burial records but he died of an abcess and his body was sent to the cemetery for cremation from the Royal Victoria Hospital.”
1924 Obituary for Enoch Edwards:
Cimetière Mont-Royal Outremont, Montreal Region, Quebec, Canada
The Montreal Star 29 Feb 1924, Fri · Page 31

Muriel Constance Freda Valerie Edwards married Arthur Frederick Morris on 24 Oct 1925 in Neepawa, Manitoba. (She appears to have added the name Valerie when she married.)
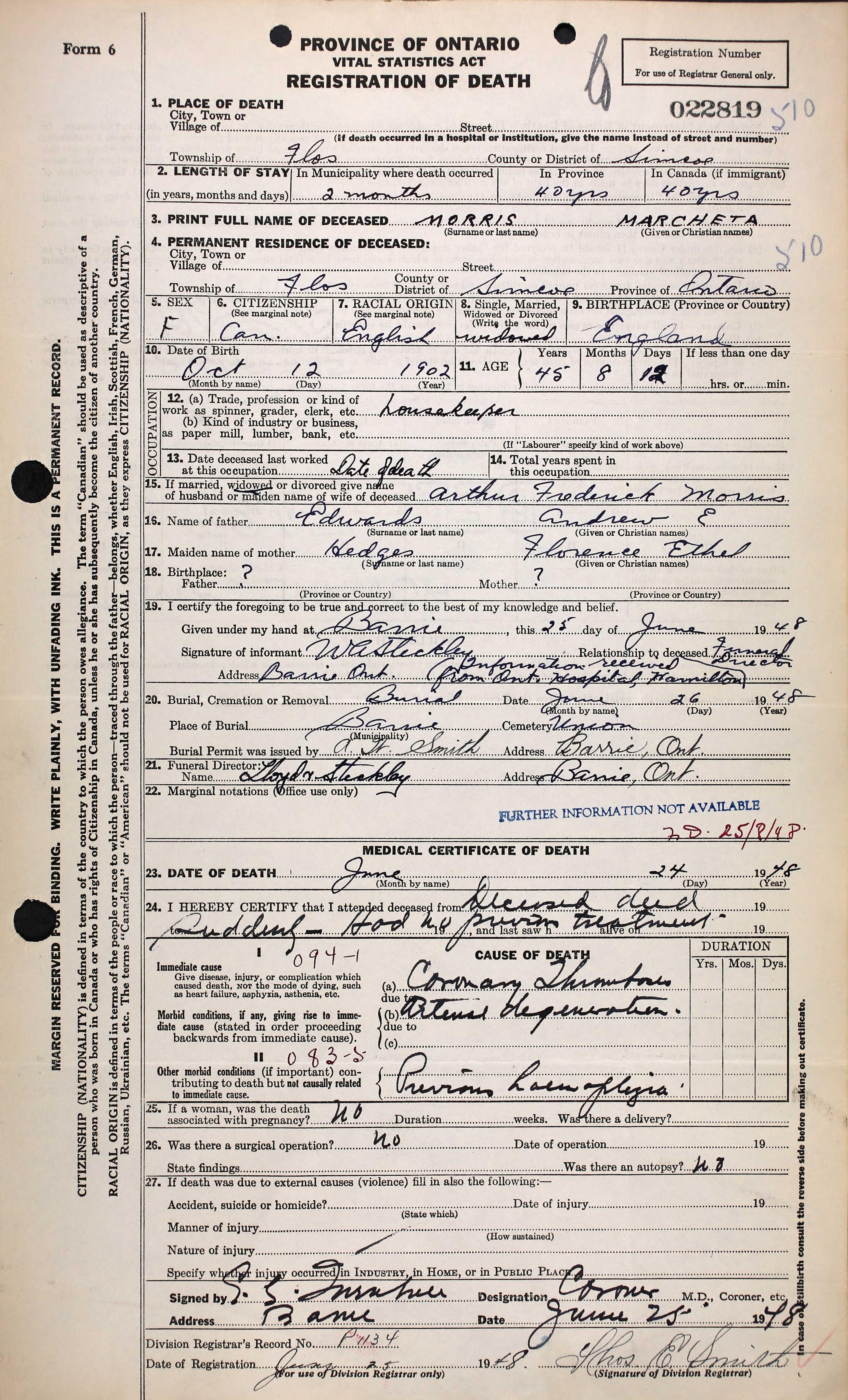
Unexpectedly a death certificate appeared for Muriel via the hints on the ancestry website. Her name was “Marcheta Morris” on this document, however it also states that she was the widow of Arthur Frederick Morris and daughter of Andrew E Edwards and Florence Ethel Hedges. She died suddenly in June 1948 in Flos, Simcoe, Ontario of a coronary thrombosis, where she was living as a housekeeper.
 June 13, 2023 at 10:31 am #7255
June 13, 2023 at 10:31 am #7255In reply to: Family Stories From The Other Side ~ Book Two
The First Wife of John Edwards
1794-1844
John was a widower when he married Sarah Reynolds from Kinlet. Both my fathers cousin and I had come to a dead end in the Edwards genealogy research as there were a number of possible births of a John Edwards in Birmingham at the time, and a number of possible first wives for a John Edwards at the time.
John Edwards was a millwright on the 1841 census, the only census he appeared on as he died in 1844, and 1841 was the first census. His birth is recorded as 1800, however on the 1841 census the ages were rounded up or down five years. He was an engineer on some of the marriage records of his children with Sarah, and on his death certificate, engineer and millwright, aged 49. The age of 49 at his death from tuberculosis in 1844 is likely to be more accurate than the census (Sarah his wife was present at his death), making a birth date of 1794 or 1795.
John married Sarah Reynolds in January 1827 in Birmingham, and I am descended from this marriage. Any children of John’s first marriage would no doubt have been living with John and Sarah, but had probably left home by the time of the 1841 census.
I found an Elizabeth Edwards, wife of John Edwards of Constitution Hill, died in August 1826 at the age of 23, as stated on the parish death register. It would be logical for a young widower with small children to marry again quickly. If this was John’s first wife, the marriage to Sarah six months later in January 1827 makes sense. Therefore, John’s first wife, I assumed, was Elizabeth, born in 1803.
Death of Elizabeth Edwards, 23 years old. St Mary, Birmingham, 15 Aug 1826:

There were two baptisms recorded for parents John and Elizabeth Edwards, Constitution Hill, and John’s occupation was an engineer on both baptisms.
They were both daughters: Sarah Ann in 1822 and Elizabeth in 1824.Sarah Ann Edwards: St Philip, Birmingham. Born 15 March 1822, baptised 7 September 1822:

Elizabeth Edwards: St Philip, Birmingham. Born 6 February 1824, baptised 25 February 1824:

With John’s occupation as engineer stated, it looked increasingly likely that I’d found John’s first wife and children of that marriage.
Then I found a marriage of Elizabeth Beach to John Edwards in 1819, and subsequently found an Elizabeth Beach baptised in 1803. This appeared to be the right first wife for John, until an Elizabeth Slater turned up, with a marriage to a John Edwards in 1820. An Elizabeth Slater was baptised in 1803. Either Elizabeth Beach or Elizabeth Slater could have been the first wife of John Edwards. As John’s first wife Elizabeth is not related to us, it’s not necessary to go further back, and in a sense, doesn’t really matter which one it was.
But the Slater name caught my eye.
But first, the name Sarah Ann.
Of the possible baptisms for John Edwards, the most likely seemed to be in 1794, parents John and Sarah. John and Sarah had two infant daughters die just prior to John’s birth. The first was Sarah, the second Sarah Ann. Perhaps this was why John named his daughter Sarah Ann? In the absence of any other significant clues, I decided to assume these were the correct parents. I found and read half a dozen wills of any John Edwards I could find within the likely time period of John’s fathers death.
One of them was dated 1803. In this will, John mentions that his children are not yet of age. (John would have been nine years old.)
He leaves his plating business and some properties to his eldest son Thomas Davis Edwards, (just shy of 21 years old at the time of his fathers death in 1803) with the business to be run jointly with his widow, Sarah. He mentions his son John, and leaves several properties to him, when he comes of age. He also leaves various properties to his daughters Elizabeth and Mary, ditto. The baptisms for all of these children, including the infant deaths of Sarah and Sarah Ann have been found. All but Mary’s were in the same parish. (I found one for Mary in Sutton Coldfield, which was apparently correct, as a later census also recorded her birth as Sutton Coldfield. She was living with family on that census, so it would appear to be correct that for whatever reason, their daughter Mary was born in Sutton Coldfield)Mary married John Slater in 1813. The witnesses were Elizabeth Whitehouse and John Edwards, her sister and brother. Elizabeth married William Nicklin Whitehouse in 1805 and one of the witnesses was Mary Edwards.
Mary’s husband John Slater died in 1821. They had no children. Mary never remarried, and lived with her bachelor brother Thomas Davis Edwards in West Bromwich. Thomas never married, and on the census he was either a proprietor of houses, or “sinecura” (earning a living without working).With Mary marrying a Slater, does this indicate that her brother John’s first wife was Elizabeth Slater rather than Elizabeth Beach? It is a compelling possibility, but does not constitute proof.
Not only that, there is no absolute proof that the John Edwards who died in 1803 was our ancestor John Edwards father.
If we can’t be sure which Elizabeth married John Edwards, we can be reasonably sure who their daughters married. On both of the marriage records the father is recorded as John Edwards, engineer.
Sarah Ann married Mark Augustin Rawlins in 1850. Mark was a sword hilt maker at the time of the marriage, his father Mark a needle manufacturer. One of the witnesses was Elizabeth Edwards, who signed with her mark. Sarah Ann and Mark however were both able to sign their own names on the register.
Sarah Ann Edwards and Mark Augustin Rawlins marriage 14 October 1850 St Peter and St Paul, Aston, Birmingham:

Elizabeth married Nathaniel Twigg in 1851. (She was living with her sister Sarah Ann and Mark Rawlins on the 1851 census, I assume the census was taken before her marriage to Nathaniel on the 27th April 1851.) Nathaniel was a stationer (later on the census a bookseller), his father Samuel a brass founder. Elizabeth signed with her mark, apparently unable to write, and a witness was Ann Edwards. Although Sarah Ann, Elizabeth’s sister, would have been Sarah Ann Rawlins at the time, having married the previous year, she was known as Ann on later censuses. The signature of Ann Edwards looks remarkably similar to Sarah Ann Edwards signature on her own wedding. Perhaps she couldn’t write but had learned how to write her signature for her wedding?
Elizabeth Edwards and Nathaniel Twigg marriage 27 April 1851, St Peter and St Paul, Aston, Birmingham:

Sarah Ann and Mark Rawlins had one daughter and four sons between 1852 and 1859. One of the sons, Edward Rawlins 1857-1931, was a school master and later master of an orphanage.
On the 1881 census Edward was a bookseller, in 1891 a stationer, 1901 schoolmaster and his wife Edith was matron, and in 1911 he and Edith were master and matron of St Philip’s Catholic Orphanage on Oliver Road in Birmingham. Edward and Edith did not have any children.
Edward Rawlins, 1911:

Elizabeth and Nathaniel Twigg appear to have had only one son, Arthur Twigg 1862-1943. Arthur was a photographer at 291 Bloomsbury Street, Birmingham. Arthur married Harriet Moseley from Burton on Trent, and they had two daughters, Elizabeth Ann 1897-1954, and Edith 1898-1983. I found a photograph of Edith on her wedding day, with her father Arthur in the picture. Arthur and Harriet also had a son Samuel Arthur, who lived for less than a month, born in 1904. Arthur had mistakenly put this son on the 1911 census stating “less than one month”, but the birth and death of Samuel Arthur Twigg were registered in the same quarter of 1904, and none were found registered for 1911.
Edith Twigg and Leslie A Hancock on their Wedding Day 1925. Arthur Twigg behind the bride. Maybe Elizabeth Ann Twigg seated on the right: (photo found on the ancestry website)
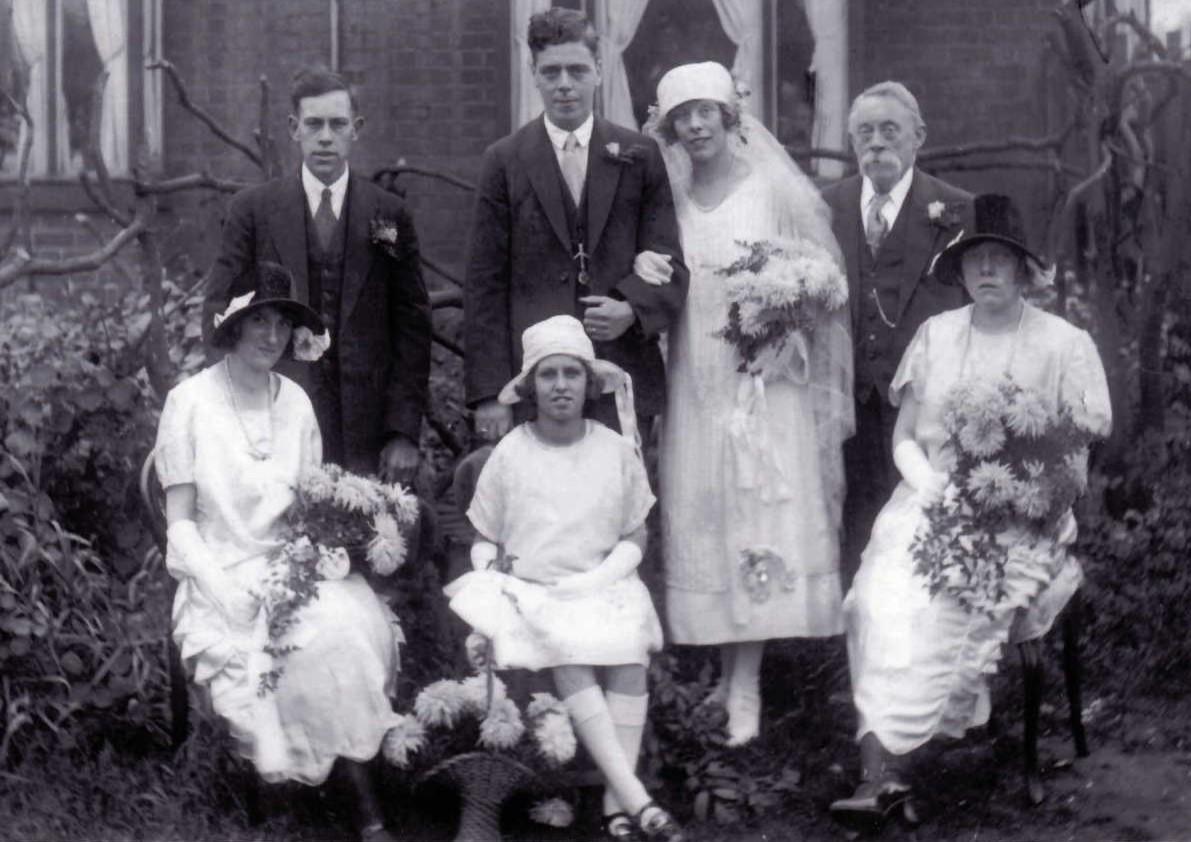

Photographs by Arthur Twigg, 291 Bloomsbury Street, Birmingham:
 March 19, 2023 at 10:39 pm #7204
March 19, 2023 at 10:39 pm #7204Some handy references for the timelines of the Flying Fish Inn are here…
Year Date Event 1935 March 1, 1935 Birth of Mater 1958 March 13, 1958 Mater marries her childhood sweetheart 1965 August 17, 1965 Birth of Fred 1968 June 8, 1968 Birth of Abcynthia Hogg 1970 July 7, 1970 Birth of Aunt Idle 1978 April 12, 1978 Mater’s husband dies 1987 March 19, 1987 Mines close down – Carts & Lager Festival 1988 December 12, 1988 Idle gives birth to a child in Fiji (Liana) 1989 December 20, 1989 Horace Hogg death – Inn passes down to Abby 1990 May 7, 1990 Fred marries Abcynthia 1998 November 11, 1998 Birth of Devan 2000 November 11, 2000 Birth of Clove and Coriander 2007 March 7, 2007 Hannah Hogg’s death, the Inn passes to Abcynthia 2008 March 10, 2008 Carts and Lager Festival revival 2008 August 20, 2008 Birth of Prune 2009 February 2, 2009 Abcynthia leaves 2009 September 11, 2009 Strange incidents at the mines, Idle sets up the Inn 2010 May 27, 2010 Fred leaves his family, goes into hiding 2014 September 10, 2014 Start of Prune’s journal 2017 March 21, 2017 Visitors from Elsewheres 2020 December 22, 2020 The year of the Great Fires 2021 August 8, 2021 Italian tourists saved the Inn 2023 March 1, 2023 Orbs gamers visitors 2027 September 1, 2027 Prune going to a boarding school 2035 March 21, 2035 Mater 100 and twins on a Waterlark adventure 2049 March 17, 2049 Prune arrives with a commercial flight on Mars, Mater is deceased (would have been 114) March 5, 2023 at 11:16 pm #6771Some background for the storyline of Franiel
For safekeeping and future explorations…
Franiel a talented young monk from Mount Elok’ram is going on a journey of a lifetime after the death of the old abbot Hrih Chokyam Lin’potshee despite being his chosen successor unknown to everybody. He is sent by the usurper Elder Aum Geog to a journey down to the Village of Chard Dam Jarfon to engrave a precious chalice with sacred words on a sealed scroll.
He encounters Léonard a zany alchemist with his dog Moufle who takes his precious cargo.
Franiel finds shelter with Phoebe Chesterhope, a master thief who trains him until she disappears after taking her motorbike on a dangerous interdimensional mission on the day of Marduë. Franiel is then put back in the path of Léonard, who had stolen the chalice for safekeeping. Léonard teaches Franiel about the powers of the chalice (the famed Cup of Margilonia), on the day of Seldië, and activates its self-protective cloaking power to temporarily relieve Franiel of his burden.
Under Léonard’s tutelage, the true destiny of Franiel is revealed, and he can claim his rightful place as the chosen successor of the old abbot, on the day of Marduë. With the help of Leonard and the power of the chalice, Franiel embarks on a new journey, equipped with the knowledge and skills he needs to fulfill his destiny. However, with someone else following him and the possibility of danger lurking around every hexade, Franiel must stay vigilant and continue to rely on his newfound allies to help him succeed. Only time will tell if Franiel is truly ready for the challenges that lie ahead on his path to becoming a great leader and guardian of the sacred chalice.
March 3, 2023 at 4:24 pm #6740In reply to: The Jorid’s Travels – 14 years on
When Salomé got closer to examine the creature, it jumped towards her. She caught it by reflex.
“Wow!” said Georges. “Sand Rin clearly has a death wish.”
“Thank you,” said Salomé. “Again.”
“I didn’t mean…”
She smiled. He was so easy to tease.
“Why did you call it Sand Rin?” she asked.
“I think our little friend has telepathic abilities. She showed this scene to me and I heard myself call her that.”
“You might want to revise your diagnostic concerning its gender. It seems he’s got balls.”
“Does that necessarily make it a male ?” asked Georges with a grumpf.
Salomé looked at her friend and raised one eyebrow.
“Does it indeed,” she said.
Georges snorted. Salomé’s attention moved back to the creature. The fur was soft, and produced little blue sparks when she stroke it with her hands. It wasn’t static electricity because Salomé didn’t feel anything except a desire to stroke it again.
“Interesting,” she said. “You clearly want us to like you. What’s your name little guy?”
“I told you, it’s Sand Rin,” said Georges.
“You told me you saw a scene in which you called it Sand Rin. That doesn’t make it his name. It might just have shown you your own mistake.”
Salomé looked into the eyes of the creature. It wiggled its nose.
“Hello, Barney,” she said.
“What? I can’t believe I find an alien creature on Jorid’s hull, and it’s called Barney,” said Georges.
“Rectification,” said Jorid, “The creature found you. He jumped onto your helmet and licked it. It’s most probable if you had tried to catch him, you’d still be tickling my hull with your boots.”
Salomé grinned.
“You told me SHE liked me,” said Georges.
“I also told you the creature was causing interferences with my sensors and navigational arrays.”
“Why do you always have to take her side?”
“She’s most often…”
“Nope, I don’t need that answer.”
“…right.”
Salomé laughed as Georges rolled his eyes. She turned her attention to Barney when he started squiggling like he was talking.
“He’s agitated,” she said. “Something foreboding, urgent.”
“You’ll be happy to know Léonard’s vitals are showing he’s about to wake up,” said Jorid.
“Wehoo! At last”, said Georges. “He’ll be able to tell us what the Zathu did to him.”
“I’m more curious about what he did to them to deserve being treated like that,” said Salomé with a frown.
February 11, 2023 at 10:10 pm #6538In reply to: The Jorid’s Travels – 14 years on
“That’s all Jorid had to say?” Georges mused at the sudden philosophical quote that read:
And doesn’t this point to something fundamentally tragic about our way of life? We live under an assumed identity, in a neurotic fairy tale world with no more reality than the Mock Turtle in Alice in Wonderland. Hypnotized by the thrill of building, we have raised the houses of our lives on sand. This world can seem marvelously convincing until death collapses the illusion and evicts us from our hiding place. What will happen to us then if we have no clue of any deeper reality? (The Tibetan Book of Living and Dying)
“I don’t know about this Mock Turtle, but those snapping sand ones that have been lurking about do look rather nasty. We shouldn’t waste any more time.”
Klatu opined “Klatu agrees with your female, sand turtle are lovely traps of death. Come with me now!” He intimated them to run into a sand opening he’d just made.
“Let me guess,” Georges said, “is it the equivalent of a Zathu prison? What powerful people could Léonard possibly have rubbed the wrong way this time?”
“Not prison.” Klatu commented “Death sentence.”
Salomé pointed out a glowing twirl of sand shaped as an ovoid form, inside which a human form could be discerned. “That would explain why he’s not more guarded…”
They approached carefully, expecting some extra booby trap, but nothing seemed to react to their presence, not even the moving sand egg.
“Let me guess,” Georges said, expecting a chorus
“DIMENSIONAL MAGIC!”
Klatu shushed them “Quiet stupids! Sound waves attract good turtles.”
“Is our friend OK? How do we break the spell?” Salomé asked Klatu. “Can you help?”
Klatu took a few minutes to inspect the shape, hopping carefully around it, and probing with soft whistling sounds.
“Friend in stasis for now. Kept fresh for questioning… possible.”
“Then we must hurry, how can we free him? Can I brute force this?” Georges asked, looking around for something to pierce the sand barrier and hook Léonard out of it.
“Only if you like sushi friend.” Klatu said, raising shoulders. “No finesse these primates.”
Klatu moved around the shape, taking some tools from his belt and making some elaborate plaits of sounds, as if trying to match the energy signature of the sand prison.
After a first belt of soundwaves was wrapped around, it seemed as though a first layer of the spell broke, and sand rained back into the external construct they were it. But a thin layer was still there, shifting and pulsating, almost clear as glass, and sharp as a razor blade.
“Crude encoding, but solid. Need more time.” Klatu seemed exhausted.
Georges was getting anxious for some activity. “Houses built on sand… Well I guess Jorid didn’t find the best quote to help…”
Salomé who was sitting cross-legged, trying for some time to connect to Léonard in his stasis, turned to Georges in disbelief. “Georges, you’re a genius!”
“What now?”
“Jorid gave us the last bit we needed. Until death collapses the illusion and evicts us from our hiding place. Remember? It’s risky but that could work!”
“Oh, I see what you’re thinking about. It’s mad, and it’s brilliant at the same time, how do we go about this?”
“I can’t reach Léonard, but maybe the both of us can.” Salomé joined hands with Georges.
“If he’s like anything I remember, he’d be in his mental palace, his workshop on the Duane… or in Marseille… or with Madame Jamelie…”
“Focus, Georges!”
“Duane it is, that’s where he did his best work.”
“We need to focus our energy to make him appear dead to the construct. It’ll be easier if we can locate precisely where his mind wanders.” Salomé said.
“He’ll be there, I know it. Let’s do this!”
The two of them joined hands and melded their minds, one as always, turning into a dark mirror of the abyss, bending light unto itself, leaving the void of creation at the place where Léonard was suspended.
Klatu looked at the scene suspiciously, but started to giggle as he saw the last layer he couldn’t open finally shatter and dissolve to the ground.
“Little apes full of surprises,… very awful, so very awful.” he said approvingly.
As his friends rushed to him, Léonard was on the ground, inert, but apparently alive.
February 7, 2023 at 10:25 pm #6511In reply to: A Dog and a Dig – The trenches of the Time Capsule
Potential Plot Arch
The uncovered box in the garden of Bob & Clara is a Time Capsule which was actually buried in the future, but mistakenly sent to the past. It has symbols etched on it, that activate some nano-technology.
Due to its contact with it, Bob starts recovering his memories, while retaining the hallucinations of his dead wife Jane, which actually become more credible and intense.Will Tarkin is actually a time traveler from the future, who came to live a simple life in the past, selling stone gargoyles at the local supermarket and rediscovering the ways of his ancestors.
With the box being found and opened at the wrong time, it creates unwanted attention from the Time Dragglers who need to intervene to prevent alterations of the timeline.
Contents of the box are in part encoded books of stories from local families and would have revealed important things about the past, Jane’s death, and Clara’s future.With Bob recovering his memories, it’s revealed Jane and Bob were actually also refugees from the future, but had aged naturally in the past, which is why Will seemed to recognize Bob. Bob was living in hiding from the Time Police, but with the box discovery, it changes everything. The box being opened at the wrong time disrupts the natural flow of events and starts causing unexpected consequences. This creates a complex web of relationships and events that must be untangled and understood in order to move forward.
With his recovering of mental capacities, Bob partners with Will in order to restore the natural flow of time, even if it means his mental health will deteriorate again, which he is happy to do while continuing to live the rest of his life span with his daughter.
Potential developments
Clara Meets the Mysterious Will
Nora finally reaches the little village where Clara and Bob live and is greeted by a man named Will
Will seems to know Bob from somewhere
Clara starts to feel suspicious of Will’s intentions and begins to investigateThe Power of Memories
Bob starts to have flashbacks of his past and begins to remember the connection between him, Will, and the mysterious time capsule
Bob realizes that Jane, his wife, had been keeping something from him and that the time capsule holds the key to unlocking the truth
Jane appears to Bob and urges him to tell Clara about their past and the significance of the time capsuleThe Truth Behind the Capsule
Nora, Clara, and Bob finally find the answers they’ve been searching for by opening the time capsule
The contents of the capsule reveal a shocking truth about Jane’s past and the reason behind her death
They learn that Jane was part of a secret society that protected ancient knowledge and artifacts and that the time capsule was meant to be opened at a specific time
The group realizes that they were meant to find the capsule and continue Jane’s work in protecting the knowledge and artifactsThe Ties Between Living and Dead
Bob comes to terms with Jane’s death and the role she played in their lives
Clara and Bob grow closer as they work together to continue Jane’s work and preserve the knowledge and artifacts
The group encounters obstacles but with the help of the spirits of the past, they are able to overcome them and succeed in their missionA Realization of the Past and Present
Clara, Bob, and Nora come to realize the power of memories and how they shape our present and future
They also learn that things never truly remain buried and that the past always finds a way to resurface
The group successfully preserves the knowledge and artifacts, ensuring that they will be passed down for generations to come
The story ends with Clara, Bob, and Nora sitting by the fire, reflecting on their journey and the lessons they’ve learned.February 6, 2023 at 10:15 pm #6498Some background information on The Sexy Wooden Leg and potential plot developments.
Setting
(nearby Duckailingtown in Dumbass, Oocrane)
The Rootians (a fictitious nationality) invaded Oocrane (a fictitious country) under the guise of freeing the Dumbass region from Lazies. They burned crops and buildings, including the home of a man named Dumbass Voldomeer who was known for his wooden leg and carpenter skills. After the war, Voldomeer was hungry and saw a nest of swan eggs. He went back to his home, carved nine wooden eggs, and replaced the real eggs with the wooden ones so he could eat the eggs for food. The swans still appeared to be brooding on their eggs by the end of summer.Note: There seem to be a bird thematic at play.
The swans’ eggs introduce the plot. The mysterious virus is likely a swan flu. Town in Oocrane often have reminiscing tones of birds’ species.
Bird To(w)nes: (Oocrane/crane, Keav/kea, Spovlar/shoveler, Dilove/dove…)
Also the town’s nursing home/hotel’s name is Vyriy from a mythical place in Slavic mythology (also Iriy, Vyrai, or Irij) where “birds fly for winter and souls go after death” which is sometimes identified with paradise. It is believed that spring has come to Earth from Vyrai.At the Keav Headquarters
(🗺️ Capital of Oocrane)
General Rudechenko and Major Myroslava Kovalev are discussing the incapacitation of President Voldomeer who is suffering from a mysterious virus. The President had told Major Kovalev about a man in the Dumbass region who looked similar to him and could be used as a replacement. The Major volunteers to bring the man to the General, but the General fears it is a suicide mission. He grants her permission but orders his aide to ensure she gets lost behind enemy lines.
Myroslava, the ambitious Major goes undercover as a former war reporter, is now traveling on her own after leaving a group of journalists. She is being followed but tries to lose her pursuers by hunting and making fire in bombed areas. She is frustrated and curses her lack of alcohol.
The Shrine of the Flovlinden Tree
(🗺️ Shpovlar, geographical center of Oocrane)
Olek is the caretaker of the shrine of Saint Edigna and lives near the sacred linden tree. People have been flocking to the shrine due to the miraculous flow of oil from the tree. Olek had retired to this place after a long career, but now a pilgrim family has brought a message of a plan acceleration, which upsets Olek. He reflects on his life and the chaos of people always rushing around and preparing for the wrong things. He thinks about his father’s approach to life, which was carefree and resulted in the same ups and downs as others, but with less suffering. Olek may consider adopting this approach until he can find a way to hide from the enemy.
Rosa and the Cauldron Maker
(young Oocranian wiccan travelling to Innsbruck, Austria)
Eusebius Kazandis is selling black cauldrons at the summer fair of Innsbruck, Austria. He is watching Rosa, a woman selling massage oils, fragrant oils, and polishing oils. Rosa notices Eusebius is sad and thinks he is not where he needs to be. She waves at him, but he looks away as if caught doing something wrong. Rosa is on a journey across Europe, following the wind, and is hoping for a gust to tell her where to go next. However, the branches of the tree she is under remain still.
The Nursing Home
(Nearby the town of Dilove, Oocrane, on Roomhen border somewhere in Transcarpetya)
Egna, who has lived for almost a millennium, initially thinks the recent miracle at the Flovlinden Tree is just another con. She has performed many miracles in her life, but mostly goes unnoticed. She has a book full of records of the lives of many people she has tracked, and reminisces that she has a connection to the President Voldomeer. She decides to go and see the Flovlinden Tree for herself.
🗺️ (the Vyriy hotel at Dilove, Oocrane, on Roomhen border)
Ursula, the owner of a hotel on the outskirts of town, is experiencing a surge in business from the increased number of pilgrims visiting the linden tree. She plans to refurbish the hotel to charge more per night and plans to get a business loan from her nephew Boris, the bank manager. However, she must first evict the old residents of the hotel, which she is dreading. To avoid confrontation, she decides to send letters signed by a fake business manager.
Egbert Gofindlevsky, Olga Herringbonevsky and Obadiah Sproutwinklov are elderly residents of an old hotel turned nursing home who receive a letter informing them that they must leave. Egbert goes to see Obadiah about the letter, but finds a bad odor in his room and decides to see Olga instead.
Maryechka, Obadiah’s granddaughter, goes back home after getting medicine for her sick mother and finds her home empty. She decides to visit her grandfather and his friends at the old people’s home, since the schools are closed and she’s not interested in online activities.
Olga and Egbert have a conversation about their current situation and decide to leave the nursing home and visit Rosa, Olga’s distant relative. Maryechka encounters Egbert and Olga on the stairs and overhears them talking about leaving their friends behind. Olga realizes that it is important to hold onto their hearts and have faith in the kindness of strangers. They then go to see Obadiah, with Olga showing a burst of energy and Egbert with a weak smile.Thus starts their escape and unfolding adventure on the roads of war-torn Oocrane.
Character Keyword Characteristics Sentiment Egbert old man, sharp tone sad, fragile Maryechka Obadiah’s granddaughter, shy innocent Olga old woman, knobbly fingers conflicted, determined Obadiah stubborn as a mule, old friend of Egbert unyielding, possibly deaf January 23, 2023 at 4:14 pm #6453In reply to: Orbs of Madjourneys
 Each group of people sharing the jeeps spent some time cleaning the jeeps from the sand, outside and inside. While cleaning the hood, Youssef noted that the storm had cleaned the eagles droppings. Soon, the young intern told them, avoiding their eyes, that the boss needed her to plan the shooting with the Lama. She said Kyle would take her place.
Each group of people sharing the jeeps spent some time cleaning the jeeps from the sand, outside and inside. While cleaning the hood, Youssef noted that the storm had cleaned the eagles droppings. Soon, the young intern told them, avoiding their eyes, that the boss needed her to plan the shooting with the Lama. She said Kyle would take her place.“Phew, the yak I shared the yurt with yesterday smelled better,” he said to the guys when he arrived.
Soon enough, Miss Tartiflate was going from jeep to jeep, her fiery hair half tied in a bun on top of her head, hurrying people to move faster as they needed to catch the shaman before he got away again. She carried her orange backpack at all time, as if she feared someone would steal its content. Rumour had it that it was THE NOTEBOOK where she wrote the blog entries in advance.
“No need to waste more time! We’ll have breakfast at the Oasis!” she shouted as she walked toward Youssef’s jeep. When she spotted him, she left her right index finger as if she just remembered something and turned the other way.
“Dunno what you did to her, but it seems Miss Yeti is avoiding you,” said Kyle with a wry smile.
Youssef grunted. Yeti was the nickname given to Miss Tartiflate by one of her former lover during a trip to Himalaya. First an affectionate nickname based on her first name, Henrietty, it soon started to spread among the production team when the love affair turned sour. It sticked and became widespread in the milieu. Everybody knew, but nobody ever dared say it to her face.
Youssef knew it wouldn’t last. He had heard that there was wifi at the oasis. He took a snack in his own backpack to quiet his stomach.
It took them two hours to arrive as sand dunes had moved on the trail during the storm. Kyle had talked most of the time, boring them to death with detailed accounts of his life back in Boston. He didn’t seem to notice that nobody cared about his love rejection stories or his tips to talk to women.
They parked outside the oasis among buses and vans. Kyle was following Youssef everywhere as if they were friends. Despite his unending flow of words, the guy managed to be funny.
Miss Tartiflate seemed unusually nervous, pulling on a strand of her orange hair and pushing back her glasses up her nose every two minutes. She was bossing everyone around to take the cameras and the lighting gear to the market where the shaman was apparently performing a rain dance. She didn’t want to miss it. When everybody was ready, she came right to Youssef. When she pushed back her glasses on her nose, he noticed her fingers were the colour of her hair. Her mouth was twitching nervously. She told him to find the wifi and restore THE BLOG or he could find another job.
“Phew! said Kyle. I don’t want to be near you when that happens.” He waved and left and joined the rest of the team.
Youssef smiled, happy to be alone at last, he took his backpack containing his laptop and his phone and followed everyone to the market in the luscious oasis.
At the center, near the lake, a crowd of tourists was gathered around a man wearing a colorful attire. Half his teeth and one eye were missing. The one that was left rolled furiously in his socket at the sound of a drum. He danced and jumped around like a monkey, and each of his movements were punctuated by the bells attached to the hem of his costume.
Youssef was glad he was not part of the shooting team, they looked miserable as they assembled the gears under a deluge of orders. As he walked toward the market, the scents of spicy food made his stomach growled. The vendors were looking at the crowd and exchanging comments and laughs. They were certainly waiting for the performance to end and the tourists to flood the place in search of trinkets and spices. Youssef spotted a food stall tucked away on the edge. It seemed too shabby to interest anyone, which was perfect for him.

The taciturn vendor, who looked caucasian, wore a yellow jacket and a bonnet oddly reminiscent of a llama’s scalp and ears. The dish he was preparing made Youssef drool.
“What’s that?” he asked.
“This is Lorgh Drülp
, said the vendor. Ancient recipe from the silk road. Very rare. Very tasty.”
He smiled when Youssef ordered a full plate with a side of tsampa. He told him to sit and wait on a stool beside an old and wobbly table.
January 13, 2023 at 9:12 pm #6382In reply to: Prompts of Madjourneys
Write more about the group of people who lived inside of giant mushrooms, making it sound exciting and fun, and maybe a bit dangerous due to the nature of the mushrooms
As the group journeyed deeper into the Land of the Quirks, they stumbled upon a group of people living inside of giant mushrooms. The mushrooms were enormous, some as tall as skyscrapers, and they seemed to glow with an ethereal light. The group was amazed as they walked through the forest of mushrooms, each one unique in shape and size.
The people who lived inside of the mushrooms were a friendly and welcoming bunch, they welcomed the group with open arms and invited them to explore their homes. The inside of the mushrooms was a magical and mysterious place, the walls and ceilings were covered in a soft, velvety texture and the floors were made of a spongy, springy material. The light inside the mushrooms was soft and diffused, creating a warm and inviting atmosphere.
As the group explored the mushroom homes, they discovered that the people who lived there had a deep connection to the mushrooms. They used the mushrooms as a source of food, shelter, and medicine. They had learned to harness the unique properties of the mushrooms to create everything they needed to survive.
The group also discovered that the mushrooms had a dangerous side. The mushrooms were not only a source of life, but also a source of death. The group was warned that the mushrooms were unpredictable and that they should be careful when exploring. Some mushrooms were poisonous, others were carnivorous, and still, others had mind-altering properties.
Despite the danger, the group was excited to explore the mushrooms and learn more about the people who lived there. They knew that the journey would be filled with challenges, but they were determined to overcome them and discover the secrets of the mushrooms. The group had a lot of fun and adventure living with the people inside of giant mushrooms, and they learned a lot about the nature of the mushrooms and their own nature.
January 11, 2023 at 8:44 pm #6366In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
Asking the AI to expand on the glossary of the original Circle of Eights Story:
Locations
Malvina’s Cave: A dark and damp cave located in the heart of the Gripshawk mountains, known for its population of Glukenitch creatures.
Lan’ork: A vast and diverse continent known for its Eastern Lagunas, home to the Indogo flamingos. Dragon Head Peninsula: A rugged and mountainous region, home to the Langoat creatures and also known for its rich deposits of dragon ore.
Asgurdy: A sprawling desert region, known for its nomadic tribes who use Saurhse as mounts for transportation.
Golfindely: An idyllic coastal region known for its beautiful beaches and crystal clear waters, home to the Golfindel and Grake creatures.
Magical Schools
Dragonian Magic: A form of magic that is practiced by Dragonriders and Dragon tamers, which involves the manipulation of dragon energy and bonding with dragon companions.
Gripshawk Magic: A form of magic that is practiced by Gripshawks, which involves the manipulation of the natural elements and telepathic communication with other creatures.
Ugling Magic: A form of magic that is practiced by Uglings, which involves the use of charms, spells, and potions to manipulate the physical world.
Guilds
Dragon Riders Guild: A prestigious guild of dragon riders, responsible for maintaining peace and order in the world by using their dragon companions for protection and transportation.
Gripshawk Hunters Guild: A guild of skilled hunters who specialize in hunting and capturing exotic creatures for various purposes.
Ugling Alchemists Guild: A guild of alchemists and potion makers, who create various potions and elixirs for medicinal and magical purposes.
Organizations
The Order of the Buntifluën: A secret organization dedicated to the study and use of Buntifluën artefacts for the betterment of communication and understanding between sentient beings.
The Glubolín Network: A network of individuals who possess Glubolín devices, used for communication and sharing information across long distances.
The Sabulmantium Society: A society of scholars and adventurers who study the properties and uses of Sabulmantium devices for divination and navigation.
Here are a few new invented terms with their potential IPA pronunciations and definitions that would fit in this fantasy world:
Dragons:
Krynn [ ˈkrĭn ] : A subspecies of dragon known for its ability to control and manipulate time.
Creatures:
Kelpies [ ˈkĕl-pēz ] : Aquatic creatures resembling horses, known for their ability to shape-shift and lure unsuspecting victims into the water.
Magical Artefacts:
Dragonwhisper [ ˈdrā-gən-ˌhwis-pər ] : An ancient and powerful magical artifact, which allows the user to communicate and control dragons telepathically.
Necrotalisman [ ˈnĕk-rə-ˈtā-lĭz-mən ] : A magical artifact in the shape of a talisman that grants its wielder the ability to control and summon the dead.
Plants:
Blightthorn [ ˈblīt-ˌthôrn ] : A poisonous plant known for its dark purple flowers and thorny stem, its extract is used in dark magic
Faeleaf [ ˈfā-ˌlēf ] : A rare plant found in the deep forest known for its bright green leaves, its extract is used in healing potions
Locations:
The Shadowland [ ˈshā-dō-ˌland ] : A mysterious and dangerous land overrun by dark magic and controlled by Necromancers.
The Hidden Vale [ ˈhī-dən-ˈvāl ] : A secluded valley located deep in the mountains, home to the reclusive Faeleaf plants.
Organization:
The Necromancers’ Circle [ ˈnĕk-rə-ˈmän-sər-z-ˈsər-kəl ] : A secret organization of powerful necromancers who seek to expand their control over death and the dead.
Here are a few more invented terms with their potential IPA pronunciations and definitions that fit in this fantasy world, having less to do with necromancy, and more with various forms of consciousness or energy manipulation, magical or mythical creatures or species:
Creatures:
Eterneon [ ˈē-tər-ˈnē-ən ] : A species of winged creatures known for their ability to manipulate and harness the energy of the stars, they are highly sought after by astromancers and star-gazers.
Psicon [ ˈsī-ˌkän ] : A species of psychic creatures, known for their ability to read minds and influence emotions.
Magical Artefacts:
Energyshield [ ˈen-ər-jē-ˌshēld ] : A magical artifact that creates a protective barrier around the user, deflecting or absorbing any kind of energy-based attacks.
Empathstone [ ˈĕm-pāth-ˈstōn ] : A small, glowing stone which allows the user to sense and control the emotions of others.
Magical Schools:
Energyshaping [ ˈen-ər-jē-ˌshāp-ing ] : A school of magic that involves the manipulation and control of various forms of energy.
Empathymagic [ ˈĕm-pā-thē-ˈmaj-ik ] : A school of magic that involves the manipulation of emotions and the ability to sense the emotions of others.
Locations:
Eternity’s Edge [ ˈē-tər-nə-tēz-ˈēj] : A remote and mysterious cliff located high in the mountains, known for its strong emanations of star energy and rumored to be home to a hidden community of Eterneons.
Psicon’s Den [ ˈsī-kän-z-ˈdĕn] : A secret cave system located deep within the forest, it is said to be home to a colony of Psicon creatures.
Organizations:
The Energists Guild [ ˈen-ər-jist-z-ˈgild] : A powerful guild of magic users specializing in Energyshaping magic.
The Empath Council [ ˈĕm-pāth-ˈkoun-səl]: A secretive group of Empathymagic users, dedicated to the study and control of emotions.
January 10, 2023 at 11:00 pm #6365In reply to: Train your subjective AI – text version
Prune has got me into this AI stuff… It sounds like gibberish to me, but Idle sounded amazed at the stuff it spewed out.
With some info on our family story, Prune got it to try and predict the future…
Sounds like a big plate of bog, but we’ll see how it goes.
Sure, here are a few possible events that could occur between Mater’s 100th birthday and her death in the Flying Fish Inn story:
- Mater decides to throw herself a grand birthday party, inviting all of her friends and family from the small outback town. However, things take a turn for the strange when a group of extraterrestrial beings crash the party and reveal themselves to be long-time fans of Mater’s famous bush tucker cuisine.
- Mater begins to experience vivid dreams and hallucinations, in which she is visited by the ghost of her late husband. As the dreams become more frequent, the family begins to suspect that there may be something more to them than just Mater’s mind playing tricks on her.
- Mater’s granddaughter Prune becomes increasingly obsessed with her dream of traveling to Mars, and begins to notice strange occurrences happening around the inn that seem to be connected to her aspiration.
- A group of eccentric scientists arrive at the inn, conducting research on the local flora and fauna. They eventually discover a species of sentient plants living in the area, and Mater becomes convinced that the plants are communicating with her in her dreams.
- With her health declining, Mater begins to spend more and more time tending to her garden, where she is visited by an old kookaburra who seems to possess an otherworldly intelligence. The bird becomes Mater’s companion and confidant in the final days of her life.
- As the Great Fires ravage the Australian bush, Mater makes the difficult decision to shut down the inn and evacuate the guests. But as they flee, they realize that the fire is not just a natural disaster, but something far more sinister and mystical.
- In her final days, Mater begins to remember strange and vivid details of her life that she never could have known, as if she lived a previous life in another time and place. As she dies, she whispers something to Prune, which opens her eyes to a new reality that may have been hidden from her all along
- It turns out the family had a lot of secrets, and the only way to escape it, was to leave the inn, but it was not an escape for all. Through the series of events, secrets are revealed, and some truths cannot be undone.Note that these events are fictional and whimsical in nature, but as they keeps it grounded to a sense of doldrums in the Australian bush and occasionally guests help to unravel some of the overarching mysteries it could make a fitting storyline for the story.
-
AuthorSearch Results